Becoming a Data Engineer: DataCamp Certification Journey
Table of Contents
- 📖 Background (Invalid URL)
- 🎓 Certification Achievement (Invalid URL)
- 📝 Understanding Data Models (Invalid URL)
- ⭐ Star Schema (Invalid URL)
📖 Background
Hello everyone! As someone on the path to becoming a Data Engineer, I’ve taken a big step forward with DataCamp’s certification. This program isn't just about learning; it's about proving to myself—and to future employers—that I have the essential skills in data management, especially with SQL.
This journey through DataCamp has been eye-opening. It’s shown me how important and powerful SQL skills are as a foundation for any data engineering role. And now, I’m not just learning these skills; I’m mastering them to build a career that’s all about making data work smarter.
For anyone thinking about a career in data, or if you're just starting to explore data engineering, getting certified is a brilliant move. It shows you’re serious about your professional growth and ready to tackle the challenges of big data.
🎓 Certification Achievement
I am proud to share my Data Engineer Associate Certification from DataCamp, marking a significant milestone in my journey towards becoming an expert in data engineering. This certification validates my proficiency in essential data management skills, especially SQL, and lays a strong foundation for my career.
You can view my certification here.
The image below showcases my certification, reflecting my dedication to advancing my skills and expertise in data engineering.
📝 Understanding Data Models
Choosing the right data model is essential for organizing and using data effectively. Each model serves a different purpose and audience. Below is a brief overview of the main types of data models and their key characteristics.
Data Models Overview:
| Data Model | Purpose | Components | Audience | Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conceptual | High-level overview | Major entities and their relationships | Business stakeholders and planners | What data is needed |
| Logical | Detailed structure | Entities, attributes, and relationships | Data planners and designers | Ensures data organization and consistency |
| Physical | Data storage implementation | Database tables, columns, data types | Database administrators and developers | Efficient data storage and access |
⭐ Star Schema
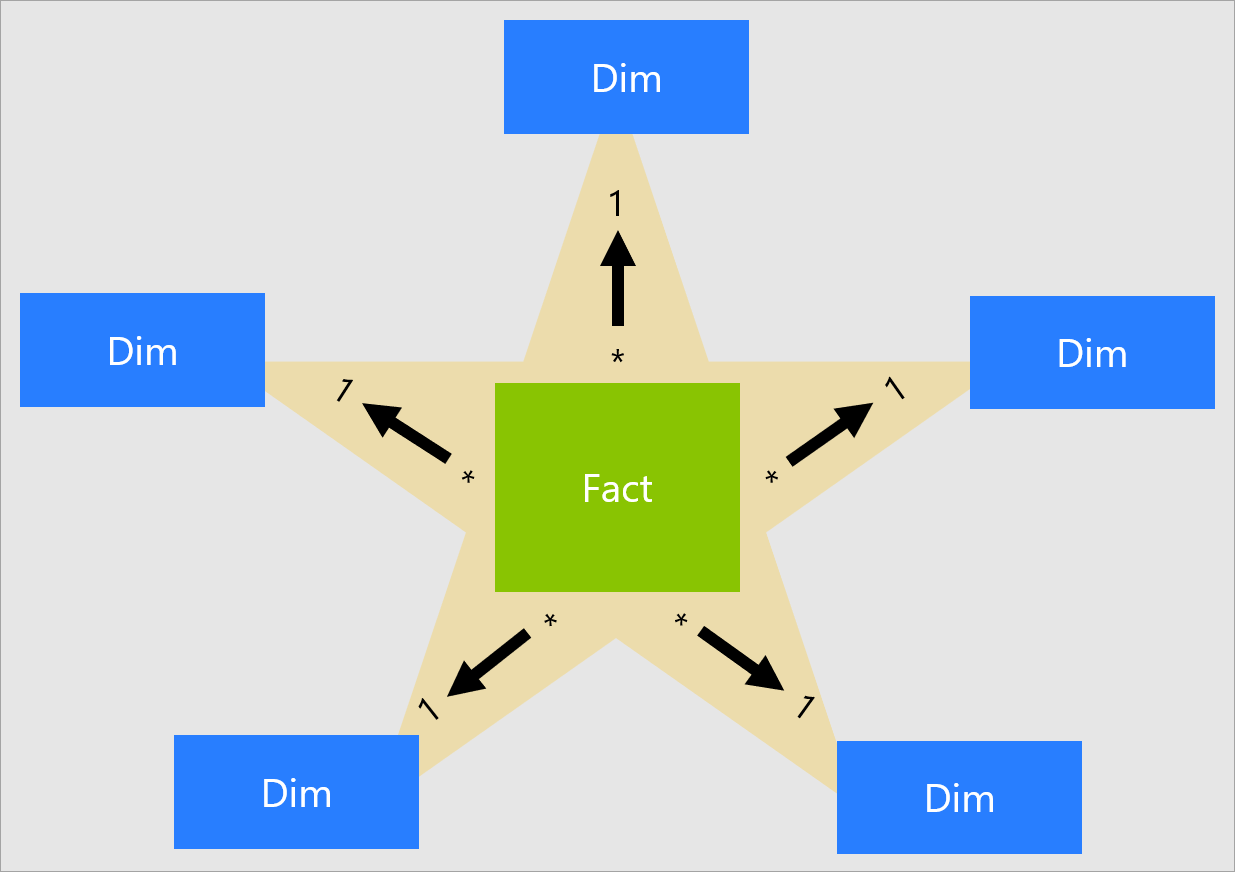
A star schema is a type of physical data model used in data warehousing and business intelligence. Imagine it like a star, with a central fact table surrounded by dimension tables.
-
Fact Table: The main table that stores key numbers and metrics, such as sales amounts. It contains:
- Quantitative Data: The actual numbers, like the total sales.
- Foreign Keys: References to other tables that provide more context and details.
-
Dimension Tables: Smaller tables that describe the data in the fact table. They contain:
- Descriptive Attributes: Information like dates, product descriptions, and customer details.
- Denormalized Data: Repeated data to make searching and reporting faster and easier.
Properties and Benefits:
- Simplicity: Easy to understand and use.
- Denormalization: Reduces complex joins, speeds up queries.
- Optimized for Performance: Efficient for read-heavy operations.
- Ideal for Reporting: Facilitates quick and easy data analysis.