Curso
An object-oriented approach is most useful when your code involves complex interactions of many objects. In real production code, classes can have dozens of attributes and methods with complicated logic, but the underlying structure is the same as with the most simple class.
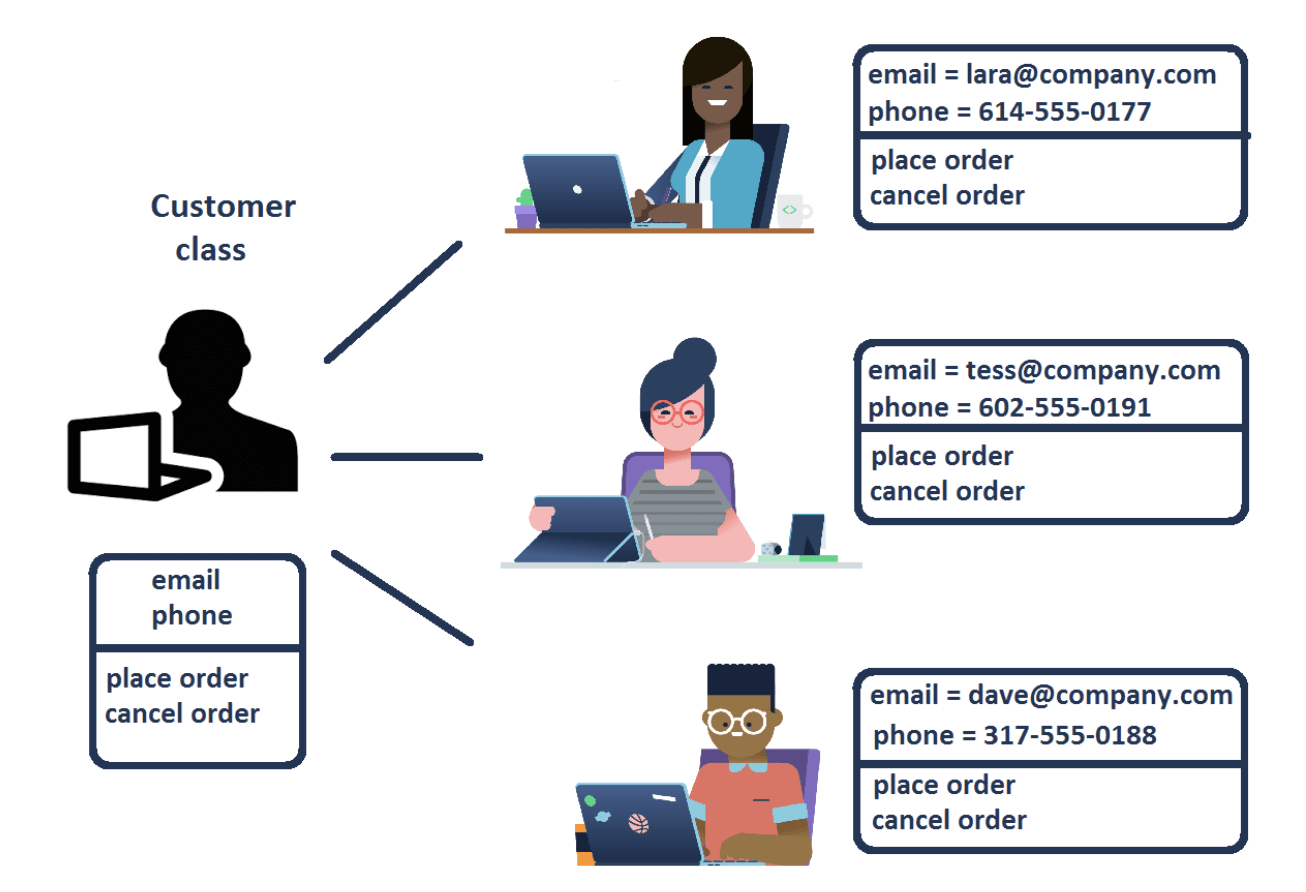
Classes are like a blueprint for objects outlining possible behaviors and states that every object of a certain type could have. For example, if you say, "every customer will have a phone number and an email, and will be able to place and cancel orders", you just defined a class! This way, you can talk about customers in a unified way. Then a specific Customer object is just a realization of this class with a particular state value.
Finding Python Classes
In Python, everything is an object. Numbers, strings, DataFrames, even functions are objects. In particular, everything you deal with in Python has a class, a blueprint associated with it under the hood. The existence of these unified interfaces is why you can use, for example, any DataFrame in the same way.
You can call type() on any Python object to find out its class. For example, the class of a numpy array is actually called ndarray (for n-dimensional array).
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2,3,4])
print(type(a))
numpy.ndarray
Classes incorporate information about state and behavior. State information in Python is contained in attributes and behavior information in methods.
Attributes and Methods
Take a numpy array: you have already been using some of its methods and attributes!
For example, every numpy array has an attribute "shape" that you can access by specifying the array's name followed by a dot and shape.
State <--> Attributes
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2,3,4])
# shape attribute
a.shape
(4,)
It also has methods like max and reshape which are also accessible via dot.
Behavior <--> Methods
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2,3,4])
# reshape method
a.reshape(2,2)
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
Creating your First Class
In this example, you will create an empty class Employee. Then you will create an object emp of the class Employee by calling Employee().
Try printing the .name attribute of emp object in the console. What happens?
# Create an empty class Employee
class Employee:
pass
# Create an object emp of class Employee
emp = Employee()
To learn more about object-oriented programming in python, please see this video from our course, Object-Oriented Programming in Python.
This content is taken from DataCamp’s Object-Oriented Programming in Python course by Aliaksandra Yarosh.
Take a look at DataCamp's Python Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Tutorial.