Kurs
The Python pass statement is a null operation that does nothing when executed. The pass statement is usually used as a placeholder in Python code where code is needed, but no action is required.
Before we get started, I recommend taking DataCamp’s Introduction to Python course to learn the basics of Python programming language. The Python Cheat Sheet for Beginners will also help refresh your skills and guide you during the learning.
Quick Answer: How to Use the pass Statement in Python
The simplest way to use the pass statement in Python is to place it in any code block that you want to leave empty. For example, you can place the pass statement in a function to avoid errors that would otherwise occur when you leave it empty.
def my_function():
passWhat is the pass Statement?
The Python pass statement serves as a placeholder in situations where a statement is syntactically necessary, but no actual code is needed. The pass statement is a null operation that returns nothing when executed in a code block. The pass statement has different use cases, including function and class definitions, loops, conditional statements, and exception handling. In the following sections, we will examine the above uses in detail.
Why Use the pass Statement?
The pass statement is important in Python programming when writing code. Below are some of the different scenarios when the pass statement is useful.
Placeholder for future code
The pass statement is used as a placeholder when code is to be included in the future. This approach allows the pass statement to maintain the code structure for improved readability. In the example below, the pass statement has been used where the function body will be written.
# Include pass as placeholder to be implemented later
def calculate_sum(a, b):
pass Avoiding errors
The pass statement is also used to avoid errors in empty loops, functions, and classes. This use case ensures you can define the functions, classes, or loops and then include the body later when required. The examples below show the code error in an empty loop and successful code execution using the pass statement.
# An empty function will return an error
def some_function():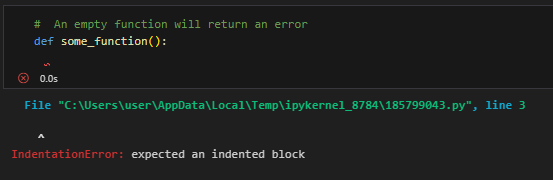
Python output showing function with pass statement. Image by Author.
# Placeholder to avoid syntax error
def some_function():
passMaintaining syntactic structure
The pass statement can be used to maintain the code syntax without implementing the logic. This use case is usually implemented during code building to give the flow of the code structure.
In the example below, the pass statement is used to maintain the syntactic structure of the function and will be implemented later when building the code.
# Define a function named 'complex_function'
def complex_function():
# Loop through numbers from 0 to 9 (10 iterations)
for i in range(10):
# Check if the current number 'i' is even
if i % 2 == 0:
pass # Placeholder for future logic to handle even numbers
else:
print(i)Using pass in Control Flow Constructs
The pass statement is also useful in control flow constructs, including conditional statements and loops.
Conditional statements
The pass statement can be used in the if, elif, and else logical functions to maintain the code syntax. The pass statement can be used as a placeholder in these conditional statements before future code implementation.
condition = True
if condition:
pass # Placeholder for future implementationx = 10
if x > 10:
pass # To be filled with logic for x > 10
elif x == 10:
pass # To be filled with logic for x == 10
else:
pass # To be filled with logic for x < 10Loops
The pass statement can also be included in the loop structure when you haven't decided what to include in the loop iteration. The examples below show the pass statement in the for and while loops.
for i in range(5):
pass # Placeholder for loop bodycondition = True
while condition:
pass # Placeholder for loop bodyUsing pass in Function and Class Definitions
The pass statement is useful as a placeholder in function and class definitions. For context, see the following examples.
Functions
The pass statement can be used in functions to avoid syntax errors when executing the code. In this case, the pass statement is used as a placeholder to maintain the function structure for future code implementation.
def my_function():
pass # Placeholder for future implementation
def add_numbers(a, b):
pass # Placeholder for addition logic
def process_data(data):
pass # Placeholder for data processing logicClasses
The pass statement can also be used in classes as a placeholder. This method helps maintain the class syntax, allowing one to add the methods and definitions later.
class MyClass:
pass # Placeholder for future attributes and methods
class DataProcessor:
pass # Placeholder for data processing class
class User:
pass # Placeholder for user-related attributes and methodsReal-World Use Cases
Since the pass statement in Python is used for null operations, it has different use cases in code development. They include the following:
-
Temporary Code Blocks: The
passstatement is used as a placeholder in Python code to create temporary code blocks in functions, classes, or loops. These techniques allow developers to write well-structured and syntactically correct code for later implementation. -
Prototyping: The
passstatement is also used to create a prototype of Python code during its initial development. It allows for the creation of a structure to follow when developing the code. -
Debugging: The
passstatement can be used to debug Python code by isolating the focused code block from the rest. The example below shows code isolation when debugging.
def complex_function():
# Initial implementation
part_one()
pass # Temporarily bypass part_two for debugging
part_three()You can also use the pass statement to temporarily block a code chunk from executing while debugging.
try:
risky_operation()
except ValueError:
pass # Ignore ValueError for now while testing other partsI recommend taking DataCamp’s Python Developer course to learn more about developing packages and programs. In this course, you will learn practical examples of the pass statement during code development.
Alternatives to the pass Statement
There are different alternatives to the pass statement that function as a placeholder in Python code. The following are the common examples you will encounter during your learning.
Comments
Comments are usually used to leave notes and describe code functions. They may also be appropriate for placeholders since you can comment out a code to prevent its execution and later remove the comment to implement the code. However, careful consideration should be taken when adding comments as placeholders since they do not maintain the code syntax. This approach might result in errors when not implemented appropriately.
# def future_function():
# Implementation goes hereEllipsis (...)
Python’s built-in function, the ellipsis (...), performs null operations like the pass statement. The ellipsis is the best alternative to the pass statement as it helps maintain the code syntax.
# Include ellipsis as placeholder to be implemented later
def calculate_sum(a, b):
...NotImplementedError
You can use the NotImplementedError to indicate a function has not been implemented. Raising the NotImplementedError is useful when you define methods that would be overridden in the subclass.
# Raising NotImplementedError as a placeholder
def future_function():
raise NotImplementedError("This function is not implemented yet.")Summary comparison
| Method | Maintains Syntactic Structure | Execution Impact | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| pass | Yes | None | Placeholder, maintaining code syntax |
| comments | No | None | Notes and explanations |
| Ellipsis (...) | Yes | None | Placeholder, maintaining code syntax |
| NotImplementedError | Yes | Raises exception | Ensuring later code implementation |
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
Although the pass statement is simple to use in Python, there are some mistakes you should look out for and ensure best practices for improved readability.
Pitfalls
The common mistakes you might encounter include the following:
-
Leaving the
passstatement in the production code leads to incomplete execution. -
Using the
passstatement where alternatives such as comments orNotImplementedErrormight be appropriate. -
Overusing the
passstatement in longer code blocks makes code readability and logical flow hard.
Best practices
I recommend the following best practices to ensure you use the pass statement appropriately in your code.
-
Only use the
passstatement in prototyping and initial development of your code. Always review your code to ensure it is not included in your production code to avoid errors. -
When you use the
passstatement, include additional comments to indicate what will be implemented in the placeholder. -
Use the
NotImplementedErrorin abstract methods to override and implement the subclasses as needed.
Conclusion and Further Learning
In this article, we learned to use a pass statement as a null operator and placeholder in Python code. The pass statement is important during code development as it helps avoid errors by maintaining the code syntax. It is important you understand the different use cases of the pass statements to write clean and maintainable code. I highly encourage you to practice using the pass statement in your learning to improve code readability and syntax.
I recommend taking DataCamp’s Python Fundamentals and Python Python Programming courses to further improve your understanding of Python programming. These courses will help you learn how to write improved and optimized code using the techniques covered in this tutorial. Finally, you should consider taking our Data Analyst with Python to kickstart your career as a data analyst.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the pass statement in Python?
The pass statement is a null operation in Python that does nothing when executed in a code block.
When should I use the pass statement?
When you do not want to implement the code yet, you should use the pass statement as a placeholder.
What is the advantage of using the pass statement?
The pass statement helps maintain code syntax for improved readability and logic flow.
What are the alternatives of the pass statement?
The pass statement alternatives include comments, ellipsis (...), and raising the NotImplementedError.
Does the pass statement have performance issues?
There are no performance issues related to the pass statement since it does nothing during code execution.
