Have this cheat sheet at your fingertips
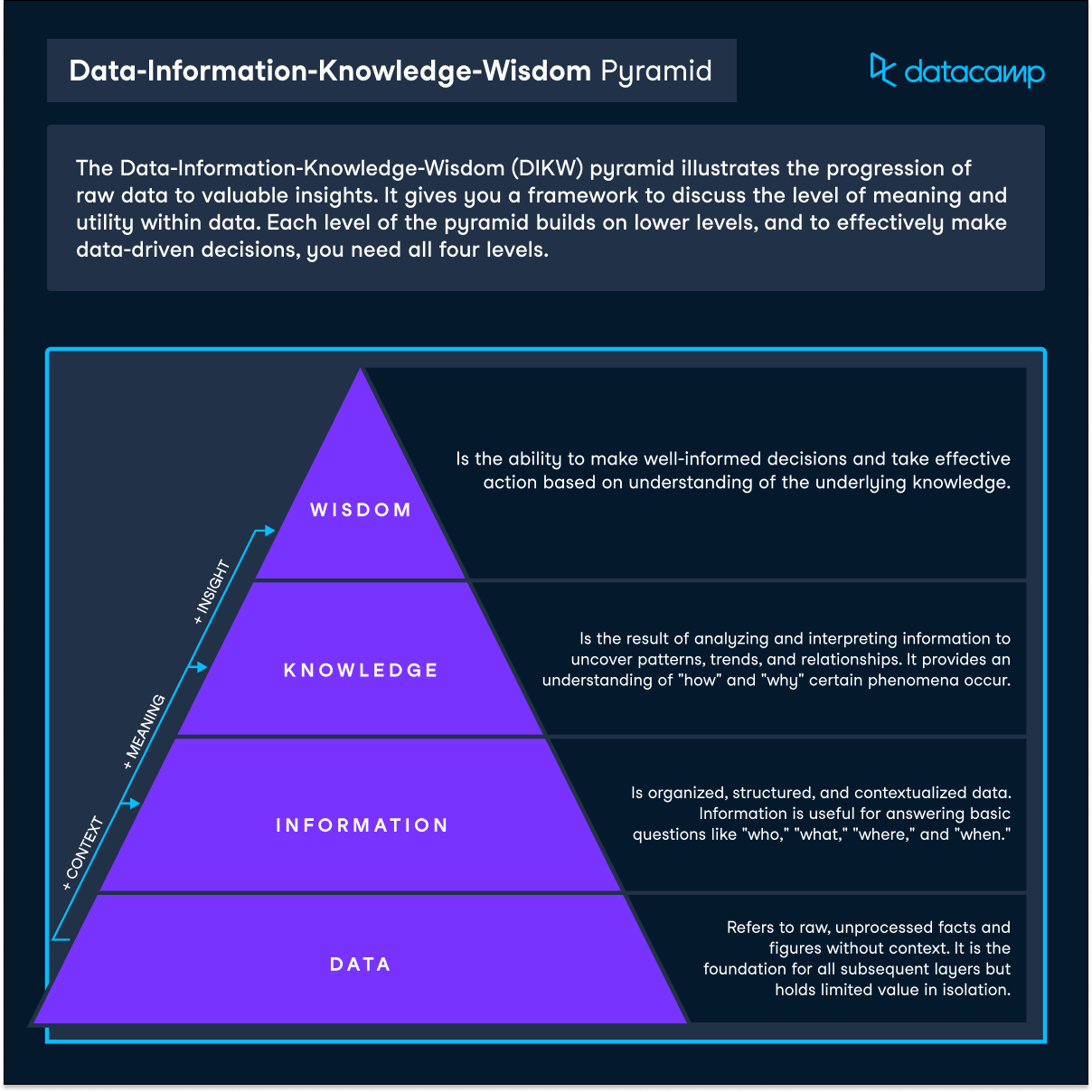
Download PDFThe Data-Information-Knowledge-Wisdom (DIKW) pyramid illustrates the progression of raw data to valuable insights. It gives you a framework to discuss the level of meaning and utility within data. Each level of the pyramid builds on lower levels, and to effectively make data-driven decisions, you need all four levels.
Wisdom is the ability to make well-informed decisions and take effective action based on understanding of the underlying knowledge.
Knowledge is the result of analyzing and interpreting information to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships. It provides an understanding of "how" and "why" certain phenomena occur.
Information is organized, structured, and contextualized data. Information is useful for answering basic questions like "who," "what," "where," and "when."
Data refers to raw, unprocessed facts and figures without context. It is the foundation for all subsequent layers but holds limited value in isolation.
Everyday Life Example: Fitness tracking
Fitness tracking devices collect your health and activity data, but your end goal is to use that to make decisions about how to train or how to manage your health.
Wisdom: Understanding these patterns lets you make informed decisions about adjusting your exercise routine, sleep habits, and other lifestyle factors to improve your health and fitness.
⇧
Knowledge: Analyzing and interpreting the information may reveal patterns, such as increased step count leading to improved sleep quality or a correlation between heart rate and workout intensity.
⇧
Information: The smartwatch app organizes and structures the data, displaying it in a comprehensible format, such as daily step count, average heart rate, and hours of sleep per night.
⇧
Data: The smartwatch collects raw data such as the number of steps taken, heart rate, and sleep duration.
Marketing Example: A Digital Marketing Campaign
Website tracking tools collect view and click data, but the marketing team's end goal is to make decisions about how to optimize the return on investment of an advertising campaign.
Wisdom: Understanding customer preferences and market trends lets the marketing team make informed decisions about targeting specific audience segments, tailoring messaging, and allocating resources to maximize the campaign's return on investment (ROI).
⇧
Knowledge: Analyzing and interpreting information from this campaign, and comparing it to past campaigns, uncovers patterns such as the most effective ad formats, optimal posting times, and key attributes of high-converting customers.
⇧
Information: The data is organized and structured, providing metrics like click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, impressions, and cost per acquisition (CPA) across each marketing channel.
⇧
Data: The raw data for the campaign consists of individual user interactions with marketing materials, such as clicks, views, likes, shares, and purchases.
Sales Example: Customer Relationship Management
CRM software records interactions with customers, but the sales team's end goal is to make decisions about how to optimize revenue from prospects.
Wisdom: Understanding customer behavior and sales patterns lets the sales team make informed decisions to prioritize high-value leads, tailor their sales approach, and efficiently allocate resources to maximize revenue and customer satisfaction.
⇧
Knowledge: Analyzing and interpreting information from the CRM uncovers patterns such as the most effective sales techniques, optimal follow-up timing, and key attributes of high-value customers.
⇧
Information: Data from the CRM is organized and structured, providing metrics like lead conversion rates, average deal size, sales cycle duration, and customer lifetime value (CLV) across industries and customer segments.
⇧
Data: The raw CRM data consists of individual customer interactions with the sales team, such as phone calls, emails, meetings, proposals, and closed deals.
Product Example: Mobile App Development
Mobile apps collect user data, and you can get additional feedback data from users, but the product manager's end goal is to make decisions to improve the app.
Wisdom: Understanding user needs, preferences, and pain points lets the product manager make informed decisions to prioritize feature development, enhance user experience, and allocate resources effectively to maximize user satisfaction and retention.
⇧
Knowledge: Analyzing and interpreting information from app usage and user feedback uncovers patterns such as frequently requested features, causes of user frustration, and key factors driving user engagement and loyalty.
⇧
Information: App usage and user feedback data is organized and structured, providing metrics like average session duration, feature usage frequency, user retention rates, and common feedback themes across user segments.
⇧
Data: The raw data consists of individual user interactions with the app, such as button clicks, screen views, and time spent in the app, as well as user-submitted feedback through reviews, surveys, and support tickets.
Finance Example: Financial Planning
Every business records financial transactions, but the Chief Financial Officer's end goal is to make decisions to maximize profitability and growth.
Wisdom: Understanding the company's financial health and market conditions lets the CFO make informed decisions to prioritize investments, manage expenses, and allocate resources effectively to maximize profitability and growth.
⇧
Knowledge: Analyzing and interpreting financial information uncovers patterns such as the most profitable product lines, cost drivers, and key factors impacting revenue and expenses.
⇧
Information: Financial data is organized and structured into financial statements and reports, providing insights into metrics like revenue, net income, cash flow, gross margin, and return on investment (ROI) across business units and time periods.
⇧
Data: The raw data consists of individual financial transactions and records, such as sales invoices, expense receipts, payroll records, and asset valuations.
Get certified in data literacy and land your dream role
Our certification programs help you stand out and prove your skills are job-ready to potential employers.