Course
The while loop is somewhat similar to an if statement, it executes the code inside, if the condition is True. However, as opposed to the if statement, the while loop continues to execute the code repeatedly as long as the condition is True.
The while Loop

The syntax of the while loop is very similar to the if statement, as you can see above. The while loop is not very common, but in some cases, it can be very useful.
Example
Suppose you are numerically calculating a model based on your data. This will typically involve taking the same steps repeatedly until the error between your model and your data is below some boundary. When you can reformulate the problem as repeating an action until a condition is met, a while loop is often the way to go.
In the below example, you initially start with an error equal to 50.0. Next, you will write a while loop, in the condition part, we write error > 1, so that the while loop executes again as long as the error is above 1. Inside the while loop, you divide the error by four and update the error variable. When we run it the first time, we receive 12.5.

Python will then go back to the condition of the while loop with the new error equal to 12.5. The condition will again be true, and the code is executed.

Python will again move back to the condition of the while loop and attempt to re-run the code. Because 3.125 is greater than 1, the code makes the calculation.

Finally, the new condition of the while loop is less than 1, so the code results in an error and won't run.

This example will come in handy because it's time to build a while loop yourself! We're going to code a while loop that implements a very basic control system for an inverted pendulum. If there's an offset from standing perfectly straight, the while loop will incrementally fix this offset.
Note that if your while loop takes too long to run, you might have made a mistake. In particular, remember to indent the contents of the loop!
Example of While Loop Error (Continuously Running)
Suppose you were to comment out or remove the error value's updates and rerun the script. The error won't be updated, and the condition will always be true. This will result in the while loop running forever.
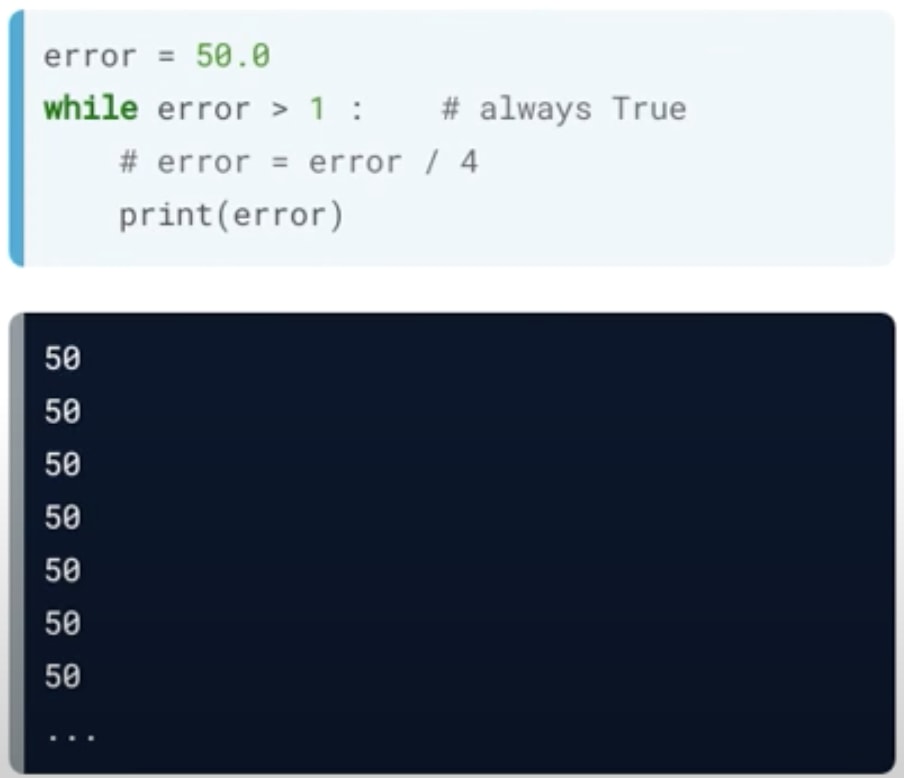
If you were to make this mistake on your system, you would have to interrupt the Python program by pressing the Control + C keys.
Example
In the below example, you will create the variable offset with an initial value of 8. Then you will write a while loop that keeps running as long as the offset is not equal to 0.
Inside the while loop:
- You will print out the sentence
"correcting...". - Next, decrease the value of
offsetby 1. You can do this withoffset = offset - 1. - Finally, within your while loop, print out
offsetso you can see how it changes.

When we run the above program, it produces the following result:
correcting...
7
correcting...
6
correcting...
5
correcting...
4
correcting...
3
correcting...
2
correcting...
1
correcting...
0
To learn more about while loops, please see this video from our course Intermediate Python.
This content is taken from DataCamp’s Intermediate Python course by Hugo Bowne-Anderson.
Check out our Python Loops tutorial as well as our Emulating a Do-While Loop in Python tutorial to keep learning about and practicing with loops in Python to become an expert.