What Is OpenAI Function Calling?
The OpenAI API is great at generating the response in a systematic way. You can manage your prompts, optimize the model output, and perform, build, and language applications with few lines of code.
Even with all the good stuff, the OpenAI API was a nightmare for the developers and engineers. Why? They are accustomed to working with structured data types, and working with unstructured data like strings is hard.
To get consistent results, developers have to use regular expressions (RegEx) or prompt engineering to extract the information from the text string.
This is where OpenAI's function calling capability comes in. It allows GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models to take user-defined functions as input and generate structure output. With this, you don't need to write RegEx or perform prompt engineering.
In this tutorial, I'll explain step-by-step how OpenAI function calling can help resolve common developer problems caused by irregular model outputs.
Develop AI Applications
Using OpenAI Without Function Calling
In this section, we will generate responses using the GPT-3.5-Turbo model without function calling to see if we get consistent output or not.
Before installing the OpenAI Python API, you must obtain an API key and set it up on your local system. Follow the GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 via the OpenAI API in Python tutorial to learn how to get the API key and set it up. The tutorial also includes examples of setting up environment variables in DataLab, DataCamp's AI-enabled data notebook.
For further assistance, check out the code in OpenAI Function Calling workbook on DataLab.
Upgrade the OpenAI Python API to V1 using:
pip install --upgrade openai -qAfter that, initiate the OpenAI client using the API key.
import os
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
api_key=os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY'],
)Note: OpenAI no longer offers free credits to new users, so you have to buy them to use the API.
We will write a random student description. Either you can come up with your own text or use ChatGPT to generate one for you.
student_1_description = "David Nguyen is a sophomore majoring in computer science at Stanford University. He is Asian American and has a 3.8 GPA. David is known for his programming skills and is an active member of the university's Robotics Club. He hopes to pursue a career in artificial intelligence after graduating."In the next part, we will write a prompt to extract student information from the text and return the output as a JSON object. We will extract the name, major, school, grades, and clubs in the student description.
# A simple prompt to extract information from "student_description" in a JSON format.
prompt1 = f'''
Please extract the following information from the given text and return it as a JSON object:
name
major
school
grades
club
This is the body of text to extract the information from:
{student_1_description}
'''Add the prompt to the OpenAI API chat completion module to generate the response.
# Generating response back from gpt-3.5-turbo
openai_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model = 'gpt-3.5-turbo',
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': prompt_1}]
)
openai_response.choices[0].message.contentThe response is quite good. Let’s convert it into JSON to understand it better.
'{\n "name": "David Nguyen",\n "major": "computer science",\n "school": "Stanford University",\n "grades": "3.8 GPA",\n "club": "Robotics Club"\n}'We will use the `json` library to convert the text into a JSON object.
import json
# Loading the response as a JSON object
json_response = json.loads(openai_response.choices[0].message.content)
json_responseThe final result is pretty much perfect. So, why do we need Function Calling?
{'name': 'David Nguyen',
'major': 'computer science',
'school': 'Stanford University',
'grades': '3.8 GPA',
'club': 'Robotics Club'}
Let’s try the same prompt, but using a different student description.
student_2_description="Ravi Patel is a sophomore majoring in computer science at the University of Michigan. He is South Asian Indian American and has a 3.7 GPA. Ravi is an active member of the university's Chess Club and the South Asian Student Association. He hopes to pursue a career in software engineering after graduating."We will just change the student description text in the prompt.
prompt2 = f'''
Please extract the following information from the given text and return it as a JSON object:
name
major
school
grades
club
This is the body of text to extract the information from:
{student_2_description}
'''And, run the chat completion function using the second prompt.
# Generating response back from gpt-3.5-turbo
openai_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model = 'gpt-3.5-turbo',
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': prompt_2}]
)
# Loading the response as a JSON object
json_response = json.loads(openai_response.choices[0].message.content)
json_responseAs you can see, it is not consistent. Instead of returning one club, it has returned the list of clubs joined by Ravi. It is also different from the first student.
{'name': 'Ravi Patel',
'major': 'computer science',
'school': 'University of Michigan',
'grades': '3.7 GPA',
'club': ['Chess Club', 'South Asian Student Association']}
OpenAI Function Calling Example
To resolve this issue, we will now use a recently introduced feature called Function Calling. It is essential to create a custom function to add necessary information to a list of dictionaries so that the OpenAI API can understand its functionality.
- name: write the Python function name that you have recently created.
- description: the functionality of the function.
- parameters: within the “properties”, we will write the name of the arguments, type, and description. It will help OpenAI API to identify the world that we are looking for.
Note: Make sure you are following the correct pattern. Learn more about function calling by reading the official documentation.
student_custom_functions = [
{
'name': 'extract_student_info',
'description': 'Get the student information from the body of the input text',
'parameters': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'name': {
'type': 'string',
'description': 'Name of the person'
},
'major': {
'type': 'string',
'description': 'Major subject.'
},
'school': {
'type': 'string',
'description': 'The university name.'
},
'grades': {
'type': 'integer',
'description': 'GPA of the student.'
},
'club': {
'type': 'string',
'description': 'School club for extracurricular activities. '
}
}
}
}
]Next, we will generate responses for two student descriptions using a custom function added to the "functions" argument. After that, we will convert the text response into a JSON object and print it.
student_description = [student_1_description,student_2_description]
for i in student_description:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model = 'gpt-3.5-turbo',
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': i}],
functions = student_custom_functions,
function_call = 'auto'
)
# Loading the response as a JSON object
json_response = json.loads(response.choices[0].message.function_call.arguments)
print(json_response)As we can see, we got uniform output. We even got grades in numeric instead of string. Consistent output is essential for creating bug-free AI applications.
{'name': 'David Nguyen', 'major': 'computer science', 'school': 'Stanford University', 'grades': 3.8, 'club': 'Robotics Club'}
{'name': 'Ravi Patel', 'major': 'computer science', 'school': 'University of Michigan', 'grades': 3.7, 'club': 'Chess Club'}Multiple Custom Functions
You can add multiple custom functions to the chat completion function. In this section, we will see the magical capabilities of OpenAI API and how it automatically selects the correct function and returns the right arguments.
In the Python list of the dictionary, we will add another function called “extract_school_info,” which will help us extract university information from the text.
To achieve this, you have to add another dictionary of a function with name, description, and parameters.
custom_functions = [
{
'name': 'extract_student_info',
'description': 'Get the student information from the body of the input text',
'parameters': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'name': {
'type': 'string',
'description': 'Name of the person'
},
'major': {
'type': 'string',
'description': 'Major subject.'
},
'school': {
'type': 'string',
'description': 'The university name.'
},
'grades': {
'type': 'integer',
'description': 'GPA of the student.'
},
'club': {
'type': 'string',
'description': 'School club for extracurricular activities. '
}
}
}
},
{
'name': 'extract_school_info',
'description': 'Get the school information from the body of the input text',
'parameters': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'name': {
'type': 'string',
'description': 'Name of the school.'
},
'ranking': {
'type': 'integer',
'description': 'QS world ranking of the school.'
},
'country': {
'type': 'string',
'description': 'Country of the school.'
},
'no_of_students': {
'type': 'integer',
'description': 'Number of students enrolled in the school.'
}
}
}
}
]We will generate a “Stanford University” description using ChatGPT to test our function.
school_1_description = "Stanford University is a private research university located in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by Leland Stanford and his wife, Jane Stanford, in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr. The university is ranked #5 in the world by QS World University Rankings. It has over 17,000 students, including about 7,600 undergraduates and 9,500 graduates23. "Create the list of student and school descriptions and pass it through the OpenAI chat completion function to generate the response. Make sure you have provided the updated custom function.
description = [student_1_description, school_1_description]
for i in description:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model = 'gpt-3.5-turbo',
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': i}],
functions = custom_functions,
function_call = 'auto'
)
# Loading the response as a JSON object
json_response = json.loads(response.choices[0].message.function_call.arguments)
print(json_response)The GPT-3.5-Turbo model has automatically selected the correct function for different description types. We get perfect JSON output for the student and the school.
{'name': 'David Nguyen', 'major': 'computer science', 'school': 'Stanford University', 'grades': 3.8, 'club': 'Robotics Club'}
{'name': 'Stanford University', 'ranking': 5, 'country': 'United States', 'no_of_students': 17000}We can even look under the name that the repose is generated using the “extract_school_info” function.
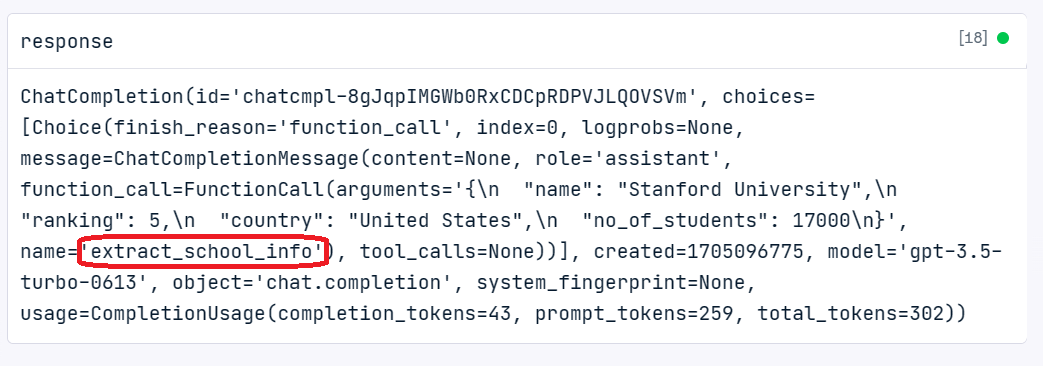
Applications of Function Calling
In this section, we will build a stable text summarizer that will summarize the school and student information in a certain way.
First, we will create two Python functions, extract_student_info and extract_school_info, that take the arguments from function calling and return a summarized string.
def extract_student_info(name, major, school, grades, club):
"""Get the student information"""
return f"{name} is majoring in {major} at {school}. He has {grades} GPA and he is an active member of the university's {club}."
def extract_school_info(name, ranking, country, no_of_students):
"""Get the school information"""
return f"{name} is located in the {country}. The university is ranked #{ranking} in the world with {no_of_students} students."- Create the Python list, which consists of student one description, random prompt, and school one description. The random prompt is added to validate the automatic function calling mechanic.
- We will generate the response using each text in the `descriptions` list.
- If a function call is used, we will get the name of the function and, based on it, apply the relevant arguments to the function using the response. Otherwise, return the normal response.
- Print the outputs of all three samples.
descriptions = [
student_1_description,
"Who was a Abraham Lincoln?",
school_1_description
]
for i, sample in enumerate(descriptions):
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model = 'gpt-3.5-turbo',
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': sample}],
functions = custom_functions,
function_call = 'auto'
)
response_message = response.choices[0].message
if dict(response_message).get('function_call'):
# Which function call was invoked
function_called = response_message.function_call.name
# Extracting the arguments
function_args = json.loads(response_message.function_call.arguments)
# Function names
available_functions = {
"extract_school_info": extract_school_info,
"extract_student_info": extract_student_info
}
fuction_to_call = available_functions[function_called]
response_message = fuction_to_call(*list(function_args .values()))
else:
response_message = response_message.content
print(f"\nSample#{i+1}\n")
print(response_message)- Sample#1: The GPT model has selected “extract_student_info,” and we got a short summary about the student.
- Sample#2: The GPT model has not selected any function and treated the prompt as a regular question, and as a result, we got the biography of Abraham Lincoln.
- Sample#3: The GPT model has selected “extract_school_info,” and we got a short summary about Stanford University.
Sample#1
David Nguyen is majoring in computer science at Stanford University. He has 3.8 GPA and he is an active member of the university's Robotics Club.
Sample#2
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States. He served as president from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. Lincoln led the country through its greatest internal crisis, the American Civil War, and his Emancipation Proclamation declared slaves in Confederate territory to be free. He is known for his leadership, his commitment to preserving the Union, and his efforts to abolish slavery. Lincoln's presidency is widely regarded as one of the most transformative in American history.
Sample#3
Stanford University is located in the United States. The university is ranked #5 in the world with 17000 students.Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned about OpenAI's function calling. We also learned how to use it to generate consistent outputs, create multiple functions, and build a reliable text summarizer.
If you want to learn more about the OpenAI API, consider taking the Working with OpenAI API course and using the OpenAI API in Python cheat sheet to create your first AI-powered project.
FAQs
How does OpenAI function calling handle complex nested JSON outputs?
OpenAI function calling allows you to define nested JSON structures in the function schema. By specifying the hierarchical relationships within the parameters property, you can ensure the model generates properly nested and structured JSON outputs for complex data requirements.
Can OpenAI function calling be used with external APIs or databases?
Yes, OpenAI function calling can be integrated with external APIs or databases by creating custom functions that execute API calls or database queries based on the arguments passed from the model. This enables dynamic interactions with external systems while maintaining consistent and structured responses.
What happens if the model’s function call doesn’t match any defined functions?
If the model’s function call doesn’t match a defined function or the provided schema, the function call is not triggered, and the model treats the input as a standard text-based prompt, returning a typical text-based response instead. This ensures flexibility in handling varied input types.
Earn a Top AI Certification

As a certified data scientist, I am passionate about leveraging cutting-edge technology to create innovative machine learning applications. With a strong background in speech recognition, data analysis and reporting, MLOps, conversational AI, and NLP, I have honed my skills in developing intelligent systems that can make a real impact. In addition to my technical expertise, I am also a skilled communicator with a talent for distilling complex concepts into clear and concise language. As a result, I have become a sought-after blogger on data science, sharing my insights and experiences with a growing community of fellow data professionals. Currently, I am focusing on content creation and editing, working with large language models to develop powerful and engaging content that can help businesses and individuals alike make the most of their data.



