Course
While writing code in any language, you will have to control the flow of your program. This is generally the case when there is decision making involved - you will want to execute a certain line of codes if a condition is satisfied, and a different set of code incase it is not. In Python, you have the if, elif and the else statements for this purpose. In this tutorial, you will work with an example to learn about the simple if statement and gradually move on to if-else and then the if-elif-else statements. You will also learn about nesting and see an nested if example. Lets get started....
Simple if statement
This is the simplest example of a conditional statement. The syntax is:
if(condition):
indented Statement Block The block of lines indented the same amount after the colon (:) will be executed whenever the condition is TRUE.
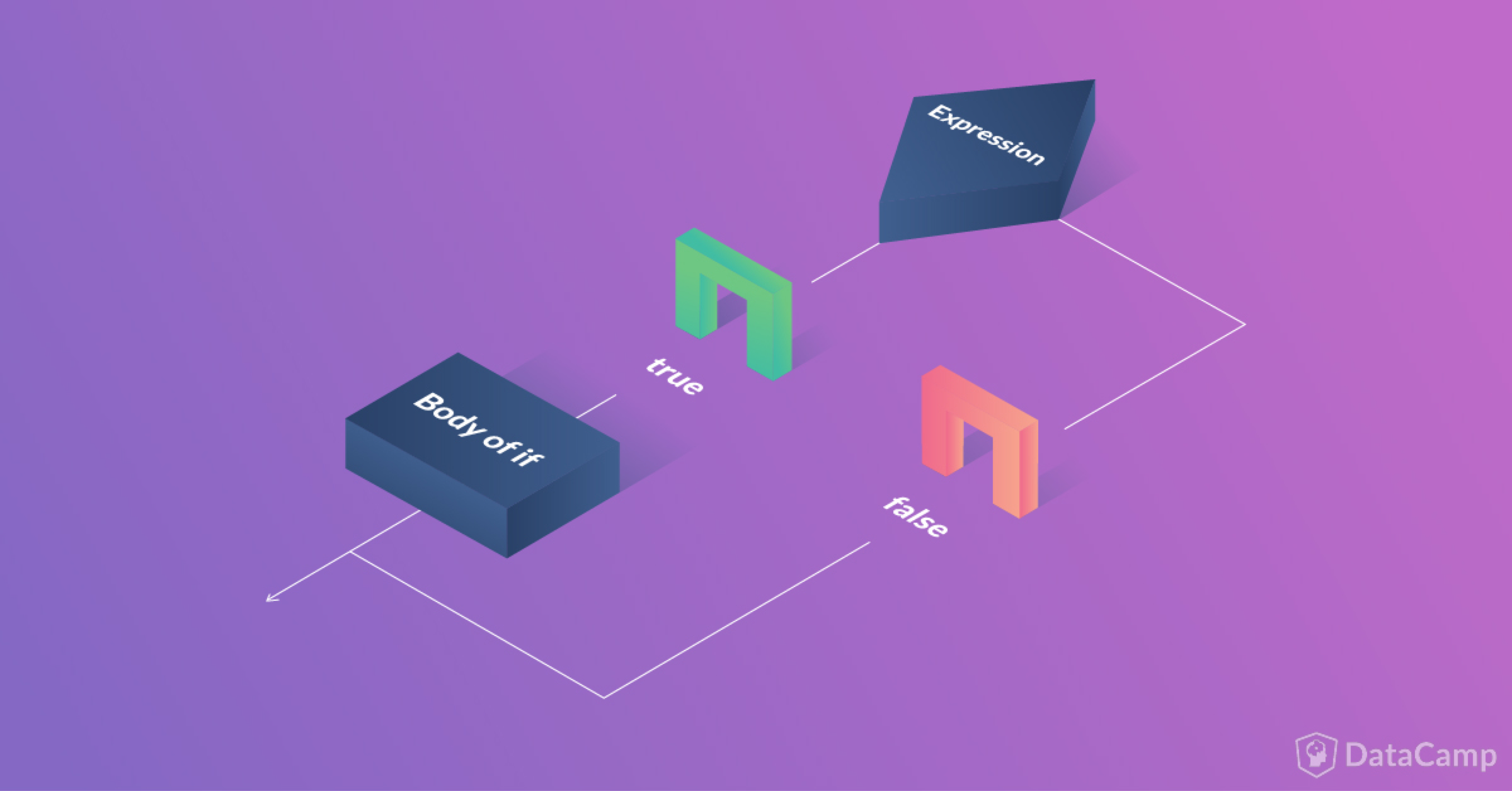
For example, lets say you are recording the score for a certain course. The total score is 100, with 50 points for the theoritical work and 50 for practical. You want to display an error message or warning if the score exceeds 100.
score_theory = 40
score_practical = 45
if(score_theory + score_practical > 100):
print("Invalid score. Please check the input.")
# no output expectedThe colon (:) is important because it separates the condition from the statements to be executed after the evaluation of the condition. This is specially important for statements where there is only a single statement and the bracket ( ) is not used. For example:
score_theory = 40
score_practical = 45
if score_theory + score_practical > 100: # End of condition
print("Invalid score. Please check the input.")
# no output expectedThe above if statement checks for the 'if' condition and determines the statement (40 + 45 = 85) > 100 to be FALSE and thus, will not print the warning. Lets make the statement TRUE and see what happens:
score_theory = 50
score_practical = 55
if(score_theory + score_practical > 100):
print("Invalid score. Please check the input.")
# Invalid score. Please check the input.Lets say you wanted to go a step further and display a statement when the total score was actually within the range, i.e. less than 100. This is when the if-else statement would help.
Single test: if-else Statement
The if-else statement is used to code the same way you would use it in the English language. The syntax for the if-else statement is:
if(condition):
Indented statement block for when condition is TRUE
else:
Indented statement block for when condition is FALSE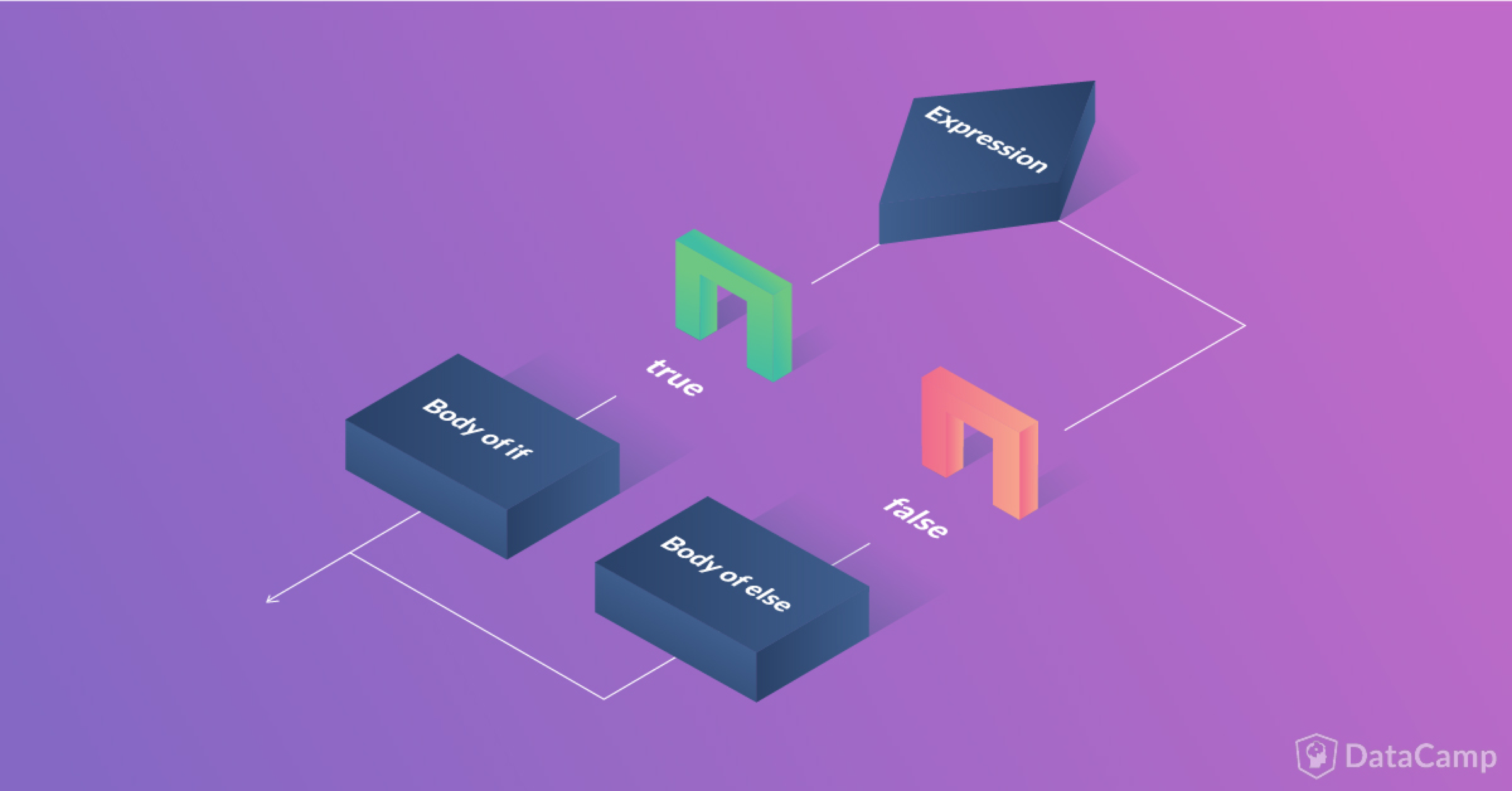
Let's try to work on the code from above and redefine the problem: When recording the score for certain coursework, you want to add together the points for the theory part and the practical part to get the total score. If the total score is less or equal than 100 - you want to display a 'Score okay' message, and if it is not, then a warning like before.
score_theory = 40
score_practical = 45
if(score_theory + score_practical > 100):
print("Please check the input. Score exceeds total possible score.")
else:
print("Score validated. Your total is: ", score_theory + score_practical)
# Score validated. Your total is: 85Tip: If you only have a line of code to be executed rather than multiple lines in the code following the condition, you can place it all in the same line. This is not a rule but just a common practise amongst coders. Rewriting the code from above in this style:
score_theory = 40
score_practical = 45
# Single statement: if(condition): Statement for when condition is true
if (score_theory + score_practical > 100): print("Please check the input. Score exceeds total possible score.")
# Single statement: if(condition): Statement for when condition is false
else: print("Score validated. Your total is: ", score_theory + score_practical)
# Score validated. Your total is: 85Now imagine a case where one of the scores exceeds 50, but the total is still less or equal than 100. What do you think would happen then?
score_theory = 60
score_practical = 40
if(score_theory + score_practical > 100):
print("Please check the input. Score exceeds total possible score.")
else:
print("Score validated. Your total is: ", score_theory + score_practical)
# Score validated. Your total is: 100This is wrong since you know that the maximum limit for individual scores for theory or practical should not exceed 50. How can you represent this in code? The answer: if-elif-else statement.
Multiple tests: Python if-elif-else Statement
Let's break down the problem we have so far and try to frame it in words before we jump into code.
-
Step 1. Input the two scores:
score_theoryandscore_practical -
Step 2. Check that neither of the scores exceeds the maximum possible score, that is, 50. This also solves the problem of the total score not excedding 100. If either one is greater than 50 - display the warning and exit.
- 2.1 Check for
score_theory - 2.2 Check for
score_practical
- 2.1 Check for
-
Step 3. If neither exceeds the score, display a 'Score okay' and exit.
# Step 1
score_theory = 60
score_practical = 20
if(score_theory > 50):
print("Please check the input score for 'Theory'.") # Step 2.1
elif(score_practical > 50):
print("Please check the input score for 'Practical'.") # Step 2.2
else:
print("Score validated. Your total is: ", score_theory + score_practical) # Step 3
# Please check the input score for 'Theory'.The syntax followed by the if-else-if statement is:
if(Condition1):
Indented statement block for Condition1
elif(Condition2):
Indented statement block for Condition2
else:
Alternate statement block if all condition checks above fails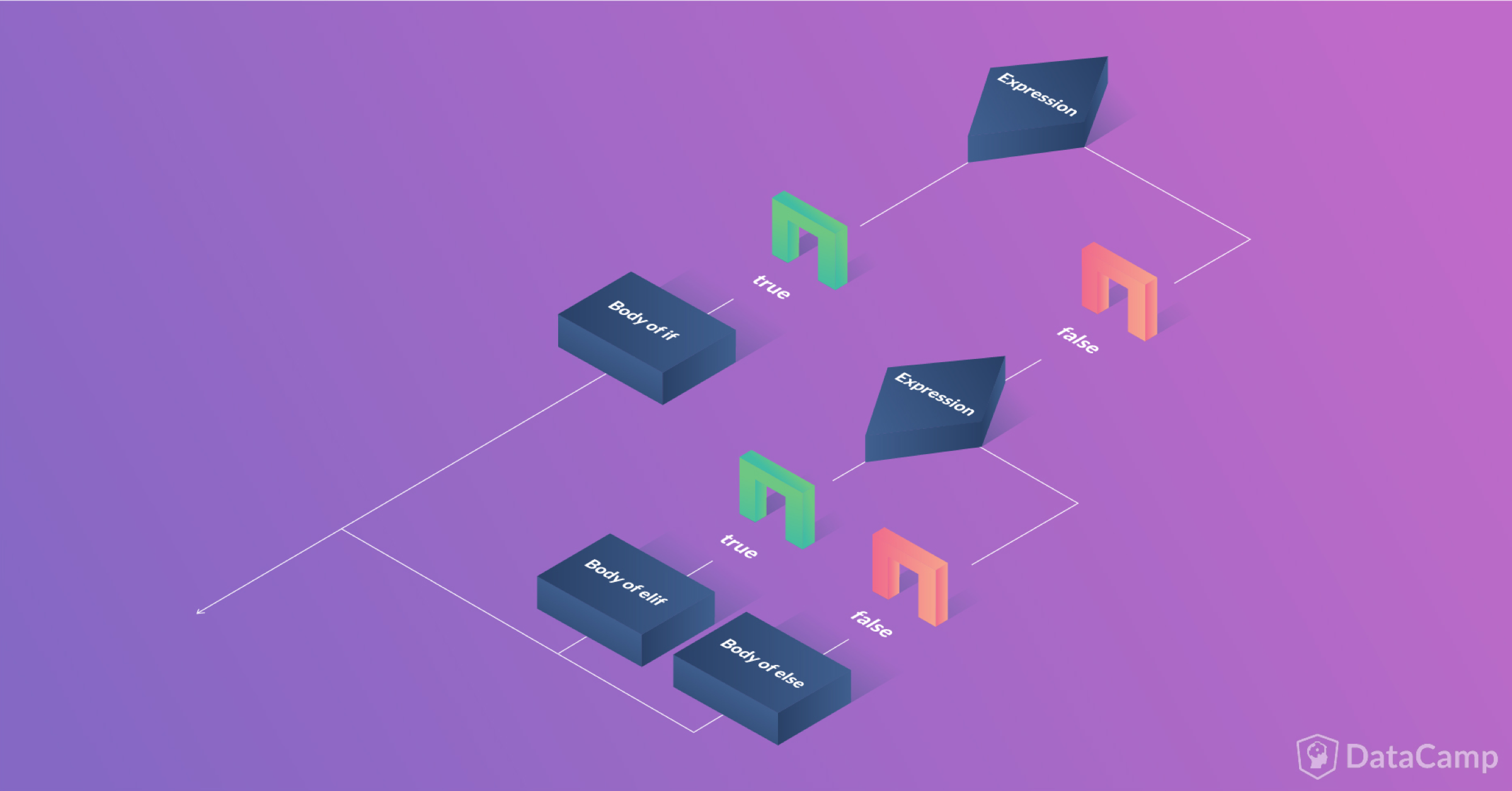
In fact, an elaborate way to see the effect of Python if-elif-else statement as just if-else statement is to write it as below:
score_theory = 60
score_practical = 20
if(score_theory > 50):
print("Please check the input score for 'Theory'.")
else:
if(score_practical > 50):
print("Please check the input score for 'Practical'.")
else:
print("Score validated. Your total is: ", score_theory + score_practical)
# Please check the input score for 'Theory'.The elif statement actually makes writing code easier. Imagine if the problem statement got more complex, then keeping track of every if-else statement within another if statement could easily become a nightmare!
Let's work some more on the same example. Now, imagine that you wanted to keep a track of multiple coursework, for example: 'Science' and 'English'. The total score for both is still the same, that is 100. However, for Science, the breakdown for theory and practical is 50-50, but for English, the breakdown is 60-40. Could you still use the formats above?
YES! And you can do this easily with the concept of Nested if Statements
Python Nested if Statements
When you have an if statement inside another if statement, this is called nesting in the programming world. It doesn't have to always be a simple if statement but you could use the concept of if, if-else, and even if-elif-else statements combined to form a more complex structure.
Let's code for the example discussed above:
coursework = "English"
score_theory = 53
score_practical = 35
if(coursework == "Science" or coursework == "science"):
if(score_theory > 50):
print("Please check the input score for 'Science: Theory'.")
elif(score_practical > 50):
print("Please check the input score for 'Science: Practical'.")
else:
print("Score validated for Science. Your total is: ", score_theory + score_practical)
elif(coursework == "English" or coursework == "english"):
if(score_theory > 60):
print("Please check the input score for 'English: Theory'.")
elif(score_practical > 40):
print("Please check the input score for 'English: Practical'.")
else:
print("Score validated for English. Your total is: ", score_theory + score_practical)
else: print("Coursework not recognised. Please enter score for either Science or English.")
# Score validated for English. Your total is: 88Notice the use of or in the code above? It is used so as to evaluate 'Science' and 'science' as the same coursework, and the same goes for 'English' and 'english'. You can make use of boolean statements such as or, and to combine multiple conditions together. But you have to be careful to understand the boolean output of such combined statements to fully realize the flow of control of your program.
We can rewrite the code above to check for the scores in the same statement, however, this does make the code hard to read and the statements hard to debug sometimes.
coursework = "English"
score_theory = 53
score_practical = 78
if(coursework == "Science" or coursework == "science"):
if(score_theory > 50 or score_practical > 50):
# Can't distinguish the error in Science: theory or Science: Practical
print("Please check the input score for Science.")
else: print("Score validated for Science. Your total is: ", score_theory + score_practical)
elif(coursework == "English" or coursework == "english"):
if(score_theory > 60 or score_practical > 40):
# Can't distinguish the error in English: theory or English: Practical
print("Please check the input score for English.")
else: print("Score validated for English. Your total is: ", score_theory + score_practical)
else: print("Coursework not recognised. Please enter score for either Science or English.")
# Please check the input score for English.Voila!
In this tutorial, you have tackled one of the major control flow mechanisms available in Python. You have worked with an example on multiple levels to see the variations of the humble if statement in action. To learn more about Python, check out DataCamp's Intro to Python for Data Science course.
Python IF, ELIF, and ELSE FAQs
What is the if statement in Python?
The if statement is used to execute a code block if a certain condition is true.
How do I use the elif statement in Python?
The elif (short for "else if") statement is used to specify additional conditions to test after the initial if statement. If the condition of the if statement is false and the condition of the elif statement is true, the block of code associated with the elif statement will be executed.
Can I have multiple elif statements in a single if block?
Yes, you can have multiple elif statements in a single if block.
What is the else statement in Python?
The else statement is used to specify a block of code that should be executed if none of the conditions in the preceding if and elif statements are true.
Can I use the else statement without any if or elif statements?
No, the else statement must be used in conjunction with an if statement. It cannot be used on its own.