Data is a commodity in the modern world. Businesses are trying to collect vast amounts of information, while individuals seek to improve their data literacy. As such, the term ‘data culture’ is becoming increasingly relevant. But what is data culture? How can organizations and individuals work to build a data-driven culture?
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of data culture, its importance, its benefits, and the opportunities and challenges involved in establishing one. Whether you're a business leader looking to foster a data culture in your organization or a beginner in the field of data science, this article aims to equip you with the fundamental knowledge of data culture.
To learn more about this subject, check out our Unlocking Data Cultures: Empowering People Through Data Literacy Programs Webinar.
Training 2 or more people? Check out our Business solutions
Get your team access to the full DataCamp library, with centralized reporting, assignments, projects and more

What is Data Culture?
Before we delve into the intricacies of data culture, let's first establish a clear understanding of what it means in the context of a business environment.
Defining data culture
Data culture refers to an organizational environment where data is not only valued but is also readily accessible and used consistently to drive decision-making processes. It's a culture where data literacy is widespread, and data-driven insights are the norm rather than the exception.
It is a concept that encapsulates behaviors, attitudes, and practices, fostering an environment where data is readily available, trusted, and used consistently to drive actions.
In a data culture, data isn't confined to a specific department or a group of data scientists; instead, it permeates the entire organization, influencing how decisions are made at all levels.
Such a data culture might manifest in various ways.
For instance, a marketing team might rely on data from customer interactions to tailor their campaigns, while the HR department might use data to analyze employee performance and job satisfaction. These data-driven approaches are not isolated incidents but are part of the organization's modus operandi.
The Pillars of Data Culture
It's important to understand that a data-driven culture isn't built overnight or through a one-off initiative. Rather, it's a gradual process that involves cultivating certain key elements or 'pillars' within the organization.
These pillars serve as the foundation upon which a strong data culture is built. They are interrelated and mutually reinforcing, each contributing to creating an environment where data is not just valued but is integral to how the organization operates.
Let's explore these pillars in more detail.
Data literacy
This refers to the ability to read, understand, create, and communicate data. In a data culture, data literacy is not limited to data professionals; everyone in the organization has some understanding of data and feels comfortable using it to inform their work. We explore the state of data literacy in our comprehensive report.
Download the State of Data & AI Literacy Report 2024
Uncover what 550+ leaders in the US & UK believe about the state of their teams’ data & AI skills.
Data-driven decision-making
This is the practice of basing decisions and strategies on data analysis rather than intuition or observation alone. In a data culture, data-driven decision-making is the norm, with data serving as the foundation for strategy and planning. A great example of this pillar in action comes from Allianz, who, through their data upskilling program, were able to measure a 1.9-hour average of time saved per week for each employee upskilled.
Data democratization
For a data culture to thrive, data must be accessible to all relevant parties within the organization. This means that data is shared freely, with appropriate safeguards for privacy and security, and employees at all levels are encouraged to use data in their roles.
Data democratization involves breaking down barriers that prevent people from accessing, analyzing, and utilizing data effectively. It’s a concept that aims to empower people to make informed decisions and take action based on data insights.
Data trust
This pillar involves confidence in the quality and integrity of the data. In a data culture, there are systems and processes in place to ensure data is accurate, reliable, and up-to-date, fostering trust among those who use it. Learn more about building trust in data with our DataFramed Podcast episode.
Leadership commitment
A strong data culture requires leaders who champion the use of data and set a good example for their teams. They promote data literacy, encourage data-driven decision-making, and ensure that data is accessible and trusted.
These pillars work together to create an environment where data is valued and effectively used to drive organizational success.
Why is a Data-Driven Culture Important?
Understanding the concept of data culture is just the first step. The real question is, why should businesses invest time and resources into cultivating a data culture?
The importance of a robust data culture in today's businesses cannot be overstated.
As organizations increasingly rely on data to innovate, improve customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge, fostering a data culture has become a strategic imperative.
A strong data culture can empower businesses to make more informed decisions, drive operational efficiency, and ultimately, enhance business performance.
Let's delve into the importance of data culture and how it can be a game-changer for businesses.
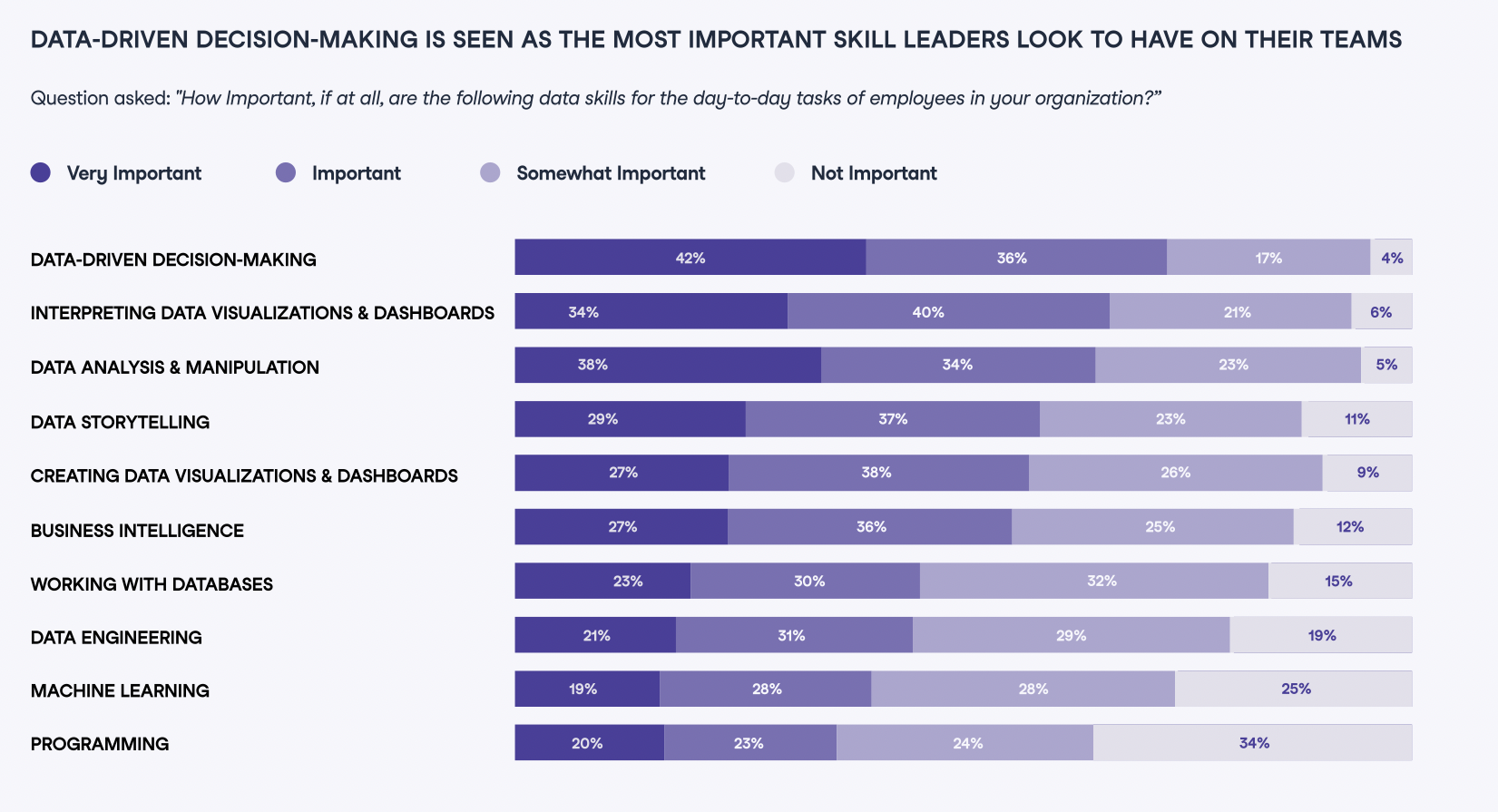
Data from The State of Data Literacy Report 2024
The role of data culture in business success
In today's data-driven world, cultivating a strong data culture is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses aiming for success and growth. Nearly three-quarters of respondents to The State of Literacy Report 2024 agreed or strongly agreed that those with data literacy skills outperformed those with inadequate data skills.
Having a robust data culture supports business objectives in several ways.
Firstly, it enables more informed decision-making. With a data culture in place, decisions at all levels of the organization are based on data-driven insights rather than intuition or guesswork. This leads to more effective strategies and better outcomes.
Secondly, a data culture fosters innovation. By encouraging the use of data, businesses can identify trends, spot opportunities, and innovate more effectively. This can lead to the development of new products, services, or processes that give the company a competitive edge.
For instance, Netflix, a company well-known for its strong data culture, uses data to make decisions about which shows to produce and how to personalize recommendations for its users. This data-driven approach has been a key factor in Netflix's success in the highly competitive streaming market.
We’re also sseeingthis need for data reflected in the global markets. For example, the global big data market is forecasted to grow to 103 billion U.S. dollars by 2027, more than double its expected market size in 2018. Organizations of all sizes are investing in collecting and processing data, and those who aren’t upskilling across their business are at risk of being left behind.
Data culture is not just an option, it is mission critical.
Sudaman Thoppan Mohanchandralal, Founder of NautilusPrinciple, and Former Chief Data Officer at Allianz Benelux
The impact of data culture on employee engagement and decision-making
A strong data culture doesn't just benefit the organization as a whole; it also has a significant impact on individual employees. When data is readily available, and its use is encouraged, employees are empowered to make decisions that are more informed and effective. This can lead to increased job satisfaction and higher levels of engagement.
Moreover, a data culture promotes transparency. When data is shared openly, employees have a better understanding of the organization's goals and their role in achieving them. This can foster a sense of ownership and commitment, further boosting engagement.
In addition, a data culture can help to break down silos within an organization. When data is shared freely, collaboration is encouraged, leading to more cohesive teams and better overall performance.
Finally, as we saw in the State of Data Literacy Report, employers are willing to pay a premium for those skilled in data literacy. Around 65% of leaders stated that they would be willing to pay a higher salary to a candidate with good data literacy skills over a candidate without them, with 77% of those who said yes claiming they would pay at least 10% to 15% extra.
A strong data culture is a powerful tool for driving business success, fostering innovation, and boosting employee engagement. By making data a central part of the organizational culture, businesses can unlock the full potential of their data and pave the way for sustained success.
Everyone should become data literate. Everyone should teach kids how to be data literate and ask important questions about the data and the world around them.
Anjali Samani, Director of Data Science & Decision Intelligence at Salesforce
How to Foster a Data Culture That Will Stick
Building a data culture is a journey that requires strategic planning, commitment, and continuous effort. It's not about implementing a set of tools or technologies but about changing mindsets and behaviors. Here's how you can cultivate a data culture in your organization:
Steps to cultivate a data culture
1. Start with leadership commitment
A data-driven culture often needs to start from the top down. Gaining buy-in from leadership is the first step towards ensuring that best practices permeate across the organization.
Chief Information Officers are concerned with data access for the rest of the organization, Chief Marketing Officers are vested in accelerating customer insights for better decision-making, and Chief Technical Officers would like product and engineering teams to use data when making product decisions.
However, it is usually the Chief Data Officer who is the best leader for promoting the data literacy agenda. It is here that you should start the process of expanding a culture based on data insights.
We’re already seeing this trend emerge. As one study suggests, in the past ten years alone, the number of Chief Data Officers within organizations has increased sevenfold, going from 12% in 2012, to 82.6% in 2023.
This ownership is essential in driving a data-driven culture. As Cindi Howson, Chief Data Strategy Officer at ThoughtSpot, highlights,
Ideally, the Chief Data Officer should own the data literacy agenda, but that is also largely dependent on where CDO sits within the broader organization. The Chief Learning or People Officer is also integral, as they help assess the organization’s current skill set and can contextualize data literacy within the overall future of work conversation.
Cindi Howson, Chief Data Strategy Officer at ThoughtSpot
2. Identify current challenges
In many organizations, the quest for comprehensive data literacy across the board will often encounter challenges. As outlined in our Data Literacy report, some of the key issues are lack of budget, inadequate training resources, lack of executive support, lack of ownership of the training program, and employee resistance.
By understanding the challenges that your organization faces, you can start to address them head-on and start working towards building a data-savvy workforce. We have a separate article on overcoming challenges in data upskilling, which explores the issue in more detail.
3. Promote data literacy
Invest in training and development to enhance data literacy across the organization. This includes understanding data, interpreting statistical analyses, and making data-driven decisions.
Starting small is often a good plan. By launching a pilot learning program targeting a small fraction of your organization, you can then iterate and improve as you expand.
For example, one of our DataCamp for Business clients, Allianz, started with 100 people using DataCamp courses and resources to upskill in certain areas. The learnings from this small-scale upskilling were then used to upskill more than 6,000 people on data.
4. Ensure data accessibility
Make data easily accessible to all employees while ensuring proper data governance and security measures are in place. This could involve implementing self-service analytics tools that allow employees to access and analyze data independently.
To encourage everyone to adopt a data-driven mindset, it’s vital to set goals for those who are upskilling. Setting transformational outcomes tied to business objectives can help in this regard. An example of such a goal could be “reducing tickets sent to the data team by enabling supply chain analysts to do simple analysis with Tableau or Power BI dashboards.”
These goals are measurable and can help specific teams or areas of the organization to work towards their targets, increasing buy-in from all involved.
According to Vijay Yadav, Director of Quantitative Sciences & Head of Data Science at the Center for Mathematical Sciences at Merck, successful data strategies mean prioritizing culture and skills transformation initiatives. Vijay explains:
Data culture and skills are a big part of a successful data strategy. Ultimately, what leaders need to understand is whether everybody in the company sees data as an asset and, if so, how do they see it? For example, somebody who’s worked on the shop floor all their life may not know how data can deliver value for them. So I think the upskilling and data literacy program is definitely something that you want to do early as part of your data strategy, to be able to deliver value down the line.
Vijay Yadav, Director of Quantitative Sciences & Head of Data Science at the Center for Mathematical Sciences at Merck
5. Encourage data-driven decision making
Foster an environment where decisions are made based on data, not intuition. This should be encouraged at all levels of the organization, from strategic decisions made by the leadership team to operational decisions made by frontline employees.
Building a data-driven culture includes reducing the fear associated with working with math and numbers. Data leaders must assuage data fear by communicating at a level that their audience is comfortable with.
Setting clear expectations can also help with making data human. Outlining how different teams and departments can benefit from being data literate and setting clear milestones for how they can achieve this plays a vital role in gaining buy-in from across an organization.
6. Create data personas
Data upskilling is not a one-size-fits-all approach. In reality, data skills are largely dependent on the needs of the individual and the relationship they’ll have with data in their day-to-day work.
As such, a crucial part of creating a data culture is identifying the data personas throughout your organization. Having such archetypes can help you understand the different needs when it comes to understanding and working with data.
In the full State of Data Literacy 2023 report, you can find our data competency framework, which can help you understand the entire spectrum of data skills that may exist within your organization. You’ll also fund an editable framework that you can tailor to your organization.
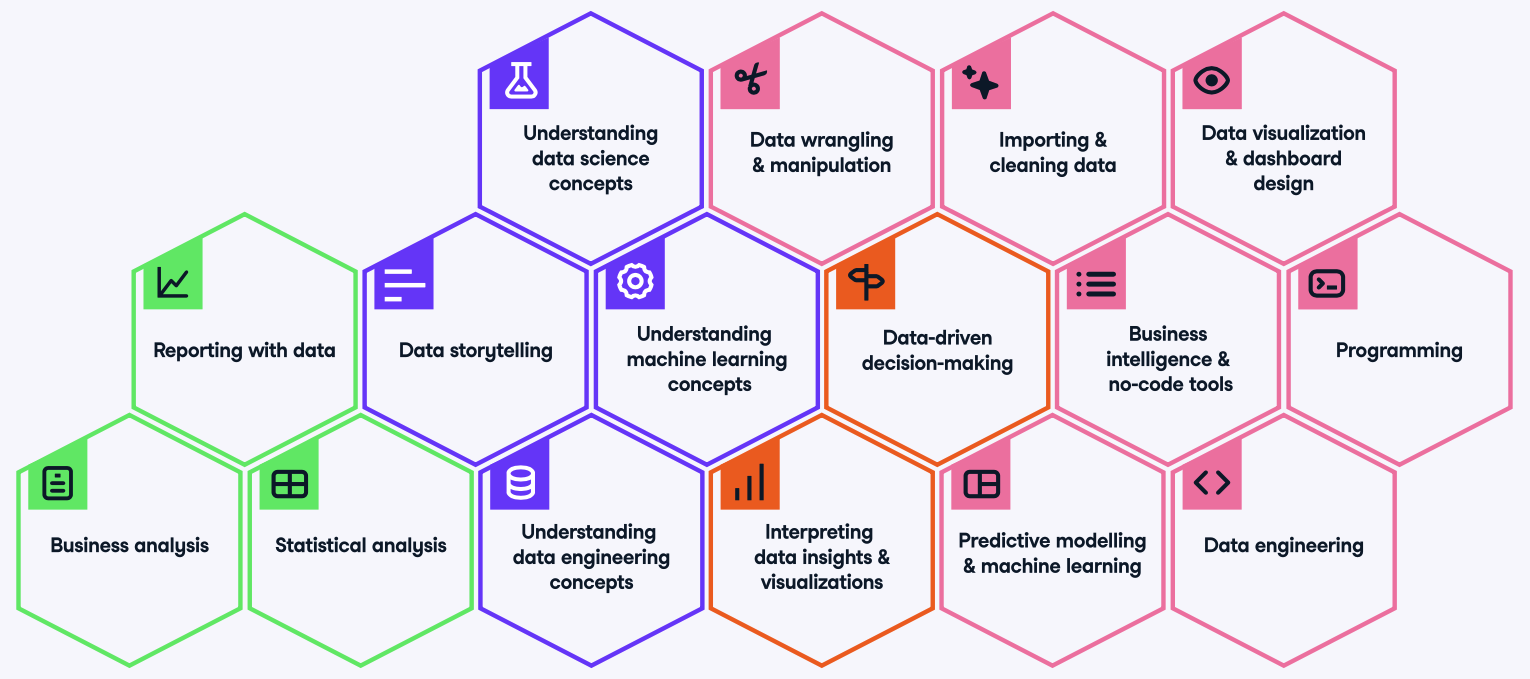
Data competency framework
7. Celebrate success
Recognize and reward the use of data in decision-making. This could be through formal recognition programs or by celebrating success stories in company meetings and communications.
Overcoming challenges in establishing a data culture
While the benefits of a data culture are clear, establishing it can come with its own set of challenges. Here are some common obstacles and strategies to overcome them.
Resistance to change
Like any cultural shift, moving to a data culture can be met with resistance. Overcome this by communicating the benefits of a data culture, providing training, and involving employees in the change process. We cover how to boost learner engagement in more detail in a separate article, which discusses how to overcome cultural and employee resistance.
The article covers various strategies you can implement, including regular promotion of the program, internal communications, learner testimonials, a learner-of-the-month program, and lunch-and-learn sessions. It’s also important to address common misconceptions about data, such as the fear of obsolescence and job automation.
Data quality issues
Poor data quality can significantly undermine trust in data and hinder the establishment of a data culture. Inaccurate, inconsistent, or outdated data can lead to misguided decisions and missed opportunities.
Therefore, it's crucial to implement robust data governance practices to ensure data is accurate, consistent, and reliable.
This process involves setting up methods for data cleaning, validation, and standardization. Regular audits should also be conducted to identify and rectify any data quality issues. By ensuring high data quality, you can build trust in data and lay a strong foundation for a data culture.
Check out our handy data quality dimensions cheat sheet, which can help you to ensure that your data is fit for purpose.
Lack of data literacy
Not everyone is comfortable with data. Many employees may lack the skills to interpret data correctly, leading to confusion or misinterpretation. This is why investing in training and support to enhance data literacy across the organization is crucial.
Training programs should be designed to cater to different skill levels - from basic data awareness for beginners to advanced analytics for more experienced users.
Regular workshops, webinars, and hands-on sessions can also be organized to help employees become more comfortable with using data. By enhancing data literacy, you can empower your employees to make better, data-driven decisions.
Data privacy concerns
Balancing data accessibility with privacy and security can be a significant challenge. In the era of stringent data protection regulations, ensuring the privacy and security of data is paramount.
Therefore, while making data accessible, it's crucial to have strong data governance and security measures in place.
This process includes setting up access controls, encrypting sensitive data, and regularly monitoring data usage to detect any anomalies. It's also important to communicate these measures clearly to employees to allay any concerns they may have about data privacy. By doing so, you can foster a data culture where data is not only accessible but also secure and trusted.
Our Introduction to Data Privacy course focuses on providing a solid foundation of privacy principles and relating them with other critical concepts within the interconnected data landscape.
Remember, fostering a data culture is a journey, not a destination. It requires ongoing effort and commitment, but the benefits it can bring to your organization make it well worth the investment.
Final Thoughts
In the era of digital transformation, data has emerged as a critical asset for businesses. As we've explored in this article, cultivating a data culture - an environment where data is valued, accessible, and used consistently to drive decision-making - is key to leveraging this asset effectively.
We've defined what a data culture is and discussed its importance in driving business success and employee engagement. We've also delved into the key pillars that constitute a data culture, including data literacy, data-driven decision-making, data accessibility, data trust, and leadership commitment.
Moreover, we've provided a step-by-step guide on how to foster a data culture in your organization, from securing leadership commitment to promoting data literacy and ensuring data accessibility. We've also addressed some of the challenges you might encounter in this journey and offered strategies to overcome them.
In conclusion, fostering a data culture is not a one-off initiative but a continuous journey that requires strategic planning, commitment, and effort. However, the benefits - informed decision-making, innovation, and increased employee engagement, to name a few - make it a worthwhile endeavor. As we move further into the data-driven era, businesses that succeed in cultivating a strong data culture will be better equipped to leverage data for sustained success.
Training 2 or more people? Check out our Business solutions
Get your team access to the full DataCamp library, with centralized reporting, assignments, projects and more
