Lernpfad
Anthropic has recently launched a new feature called Artifacts. This innovative addition is changing how we interact with AI, going beyond basic text responses to create dynamic, interactive content.
In this article, we’ll explore what Claude Artifacts are, what they can do, and how they're changing AI-assisted tasks.
Artifacts were first introduced as part of Claude Sonnet 3.5—if you want to learn more, I recommend these blog posts:
- What Is Claude 3.5 Sonnet? How It Works, Use Cases, and Artifacts
- Claude Sonnet 3.5 API Tutorial: Getting Started With Anthropic's API
What Are Claude Artifacts?
Claude Artifacts are special windows in the Claude interface that show detailed, standalone content created in response to user requests. Unlike typical chatbot replies, Artifacts are interactive and editable, featuring various types of content.
This marks a shift from Claude being just a conversational AI to becoming a collaborative work tool.
Key features of Artifacts include:
- Detailed and self-contained content (usually over 15 lines)
- Editable and iterative content that users can build on
- Standalone pieces that don't need extra conversational context
- Content that is likely to be referenced or reused later
Looking to get started with Generative AI?
Learn how to work with LLMs in Python right in your browser
How to Access Claude Artifacts?
Accessing Claude Artifacts requires manual activation—here’s how to do it:
1. Click on your initials in the lower left corner of the Claude interface.
2. Select Feature Preview from the dropdown menu.
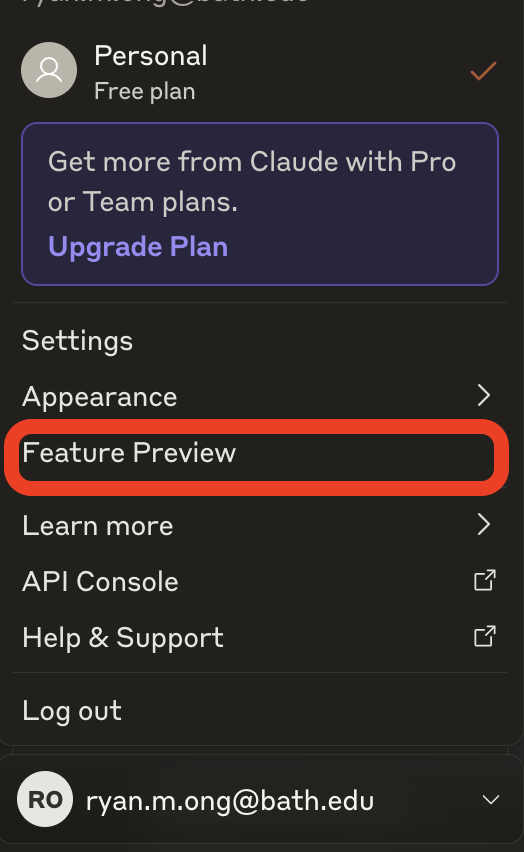
3. Toggle on the Artifacts option in the Feature Preview settings.
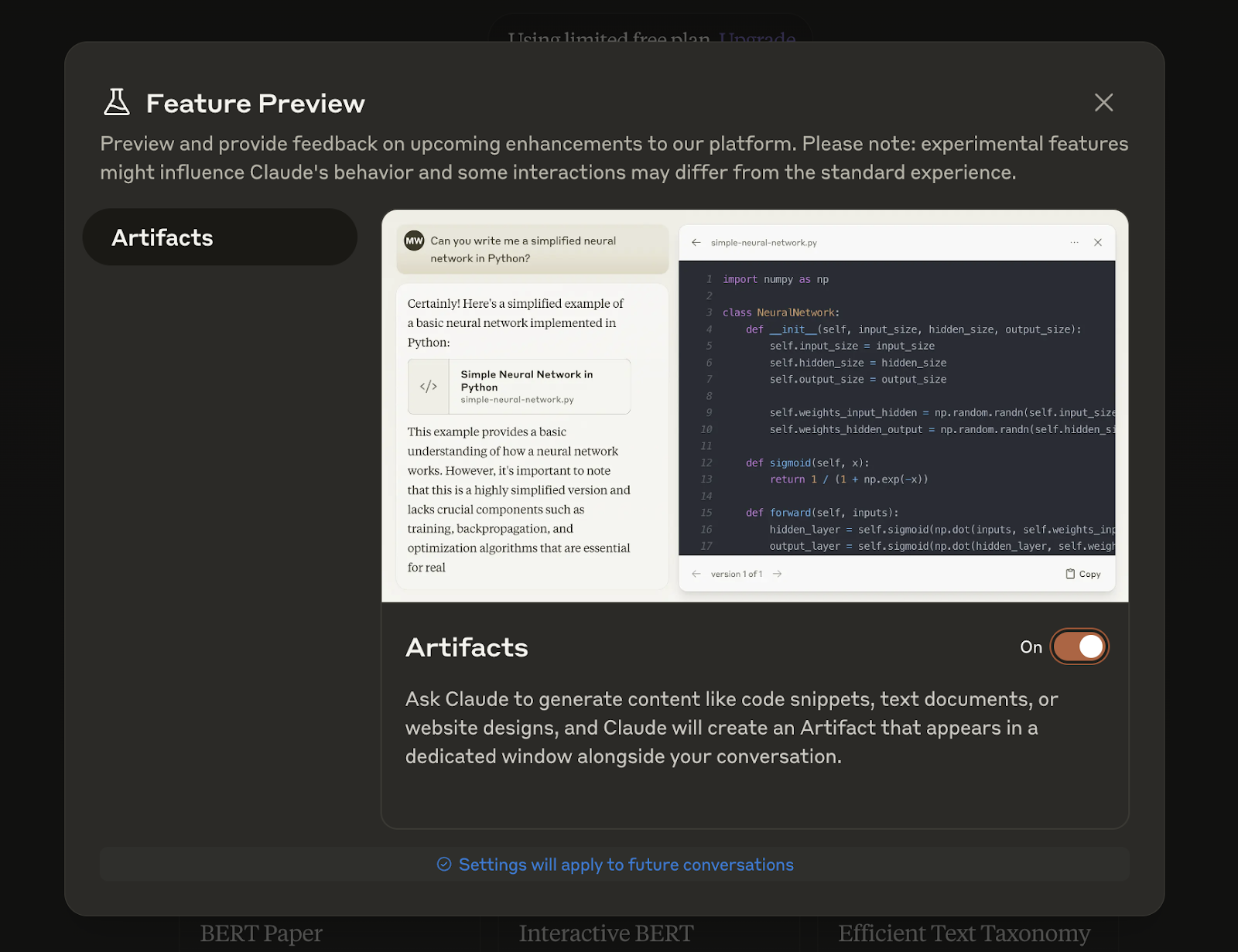
Basic access to Artifacts is free, but the experience may vary based on your subscription level. Claude Pro and Team plan subscribers typically enjoy higher rate limits and more advanced features, enhancing the overall Artifacts experience.
Types of Artifacts
Claude Artifacts can generate a variety of content types, making them useful for many tasks and projects. Here are some examples of content you can create with Artifacts:
Interactive documents
Claude can create Markdown files, plain text documents, and structured reports, providing users with a useful tool for generating written content.
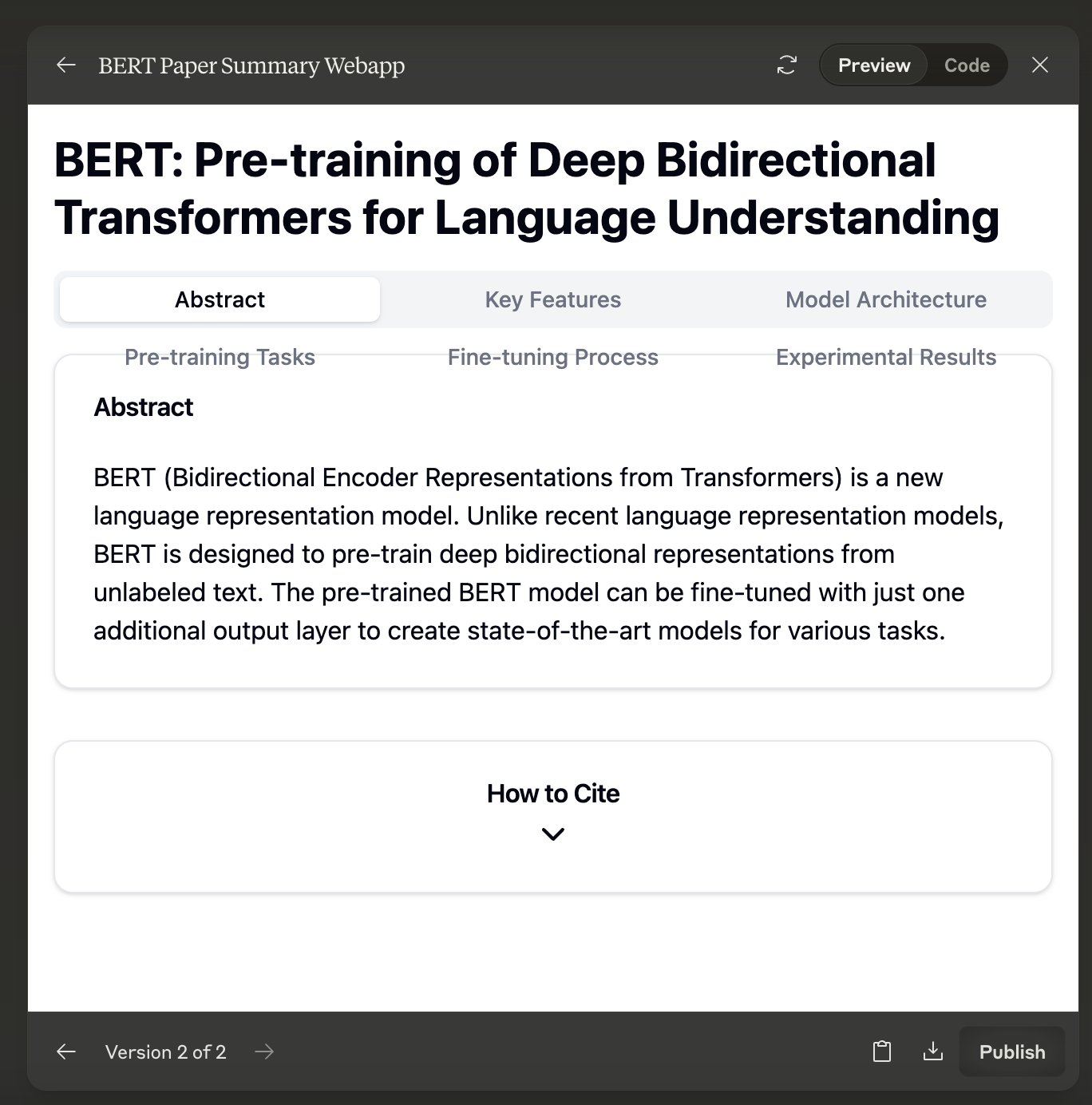
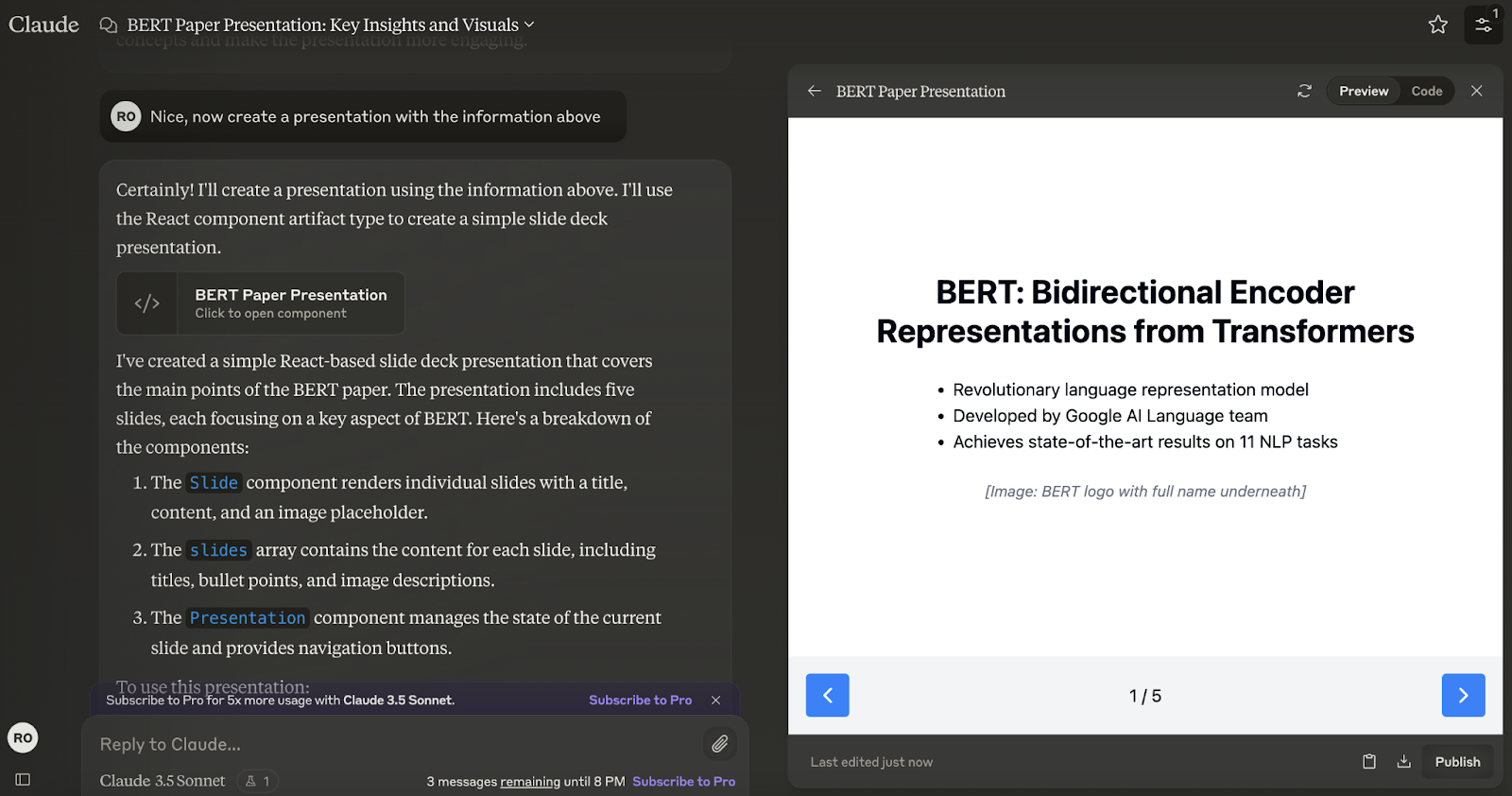
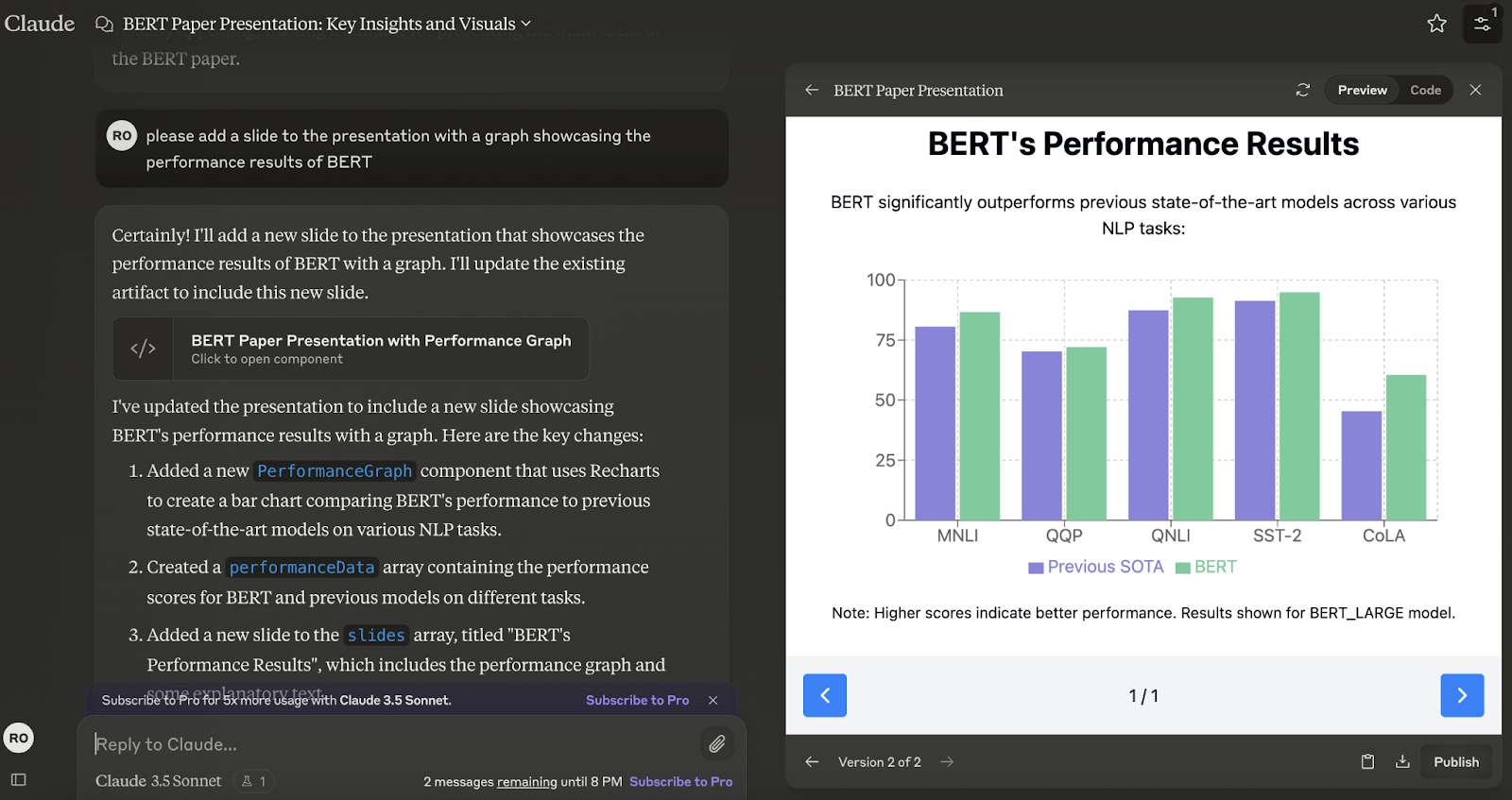
Data and process visualization
Artifacts can produce interactive charts using libraries like Plotly.js, dashboards, and infographics, enhancing data analysis and presentation.
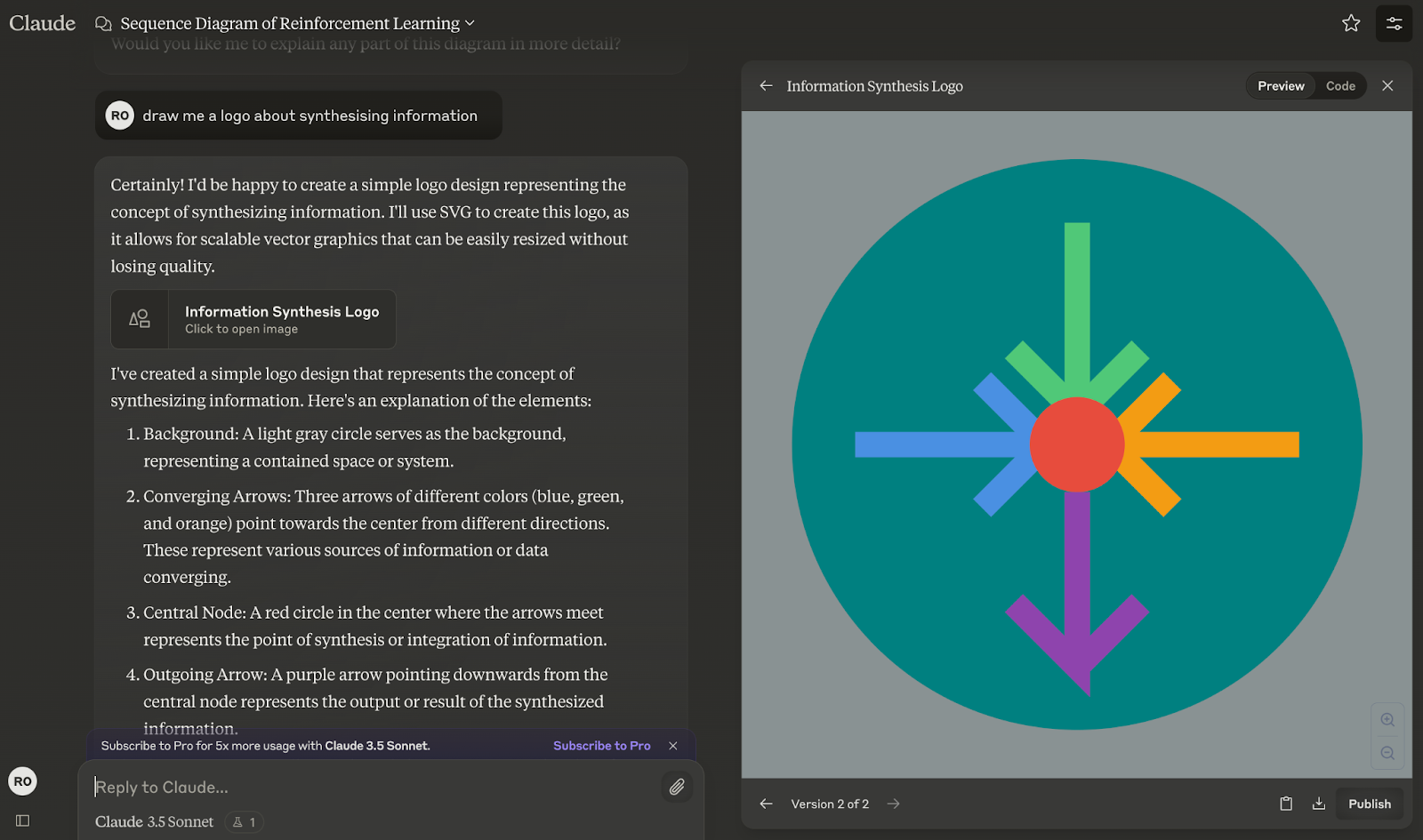
SVG graphics
You can ask Claude to create an SVG logo for a tech startup. You can then request modifications, such as color changes or adding new elements, all within the Artifact window.
Websites
Artifacts can generate single-page HTML, multi-page website structures, and interactive web components, making web development more efficient.
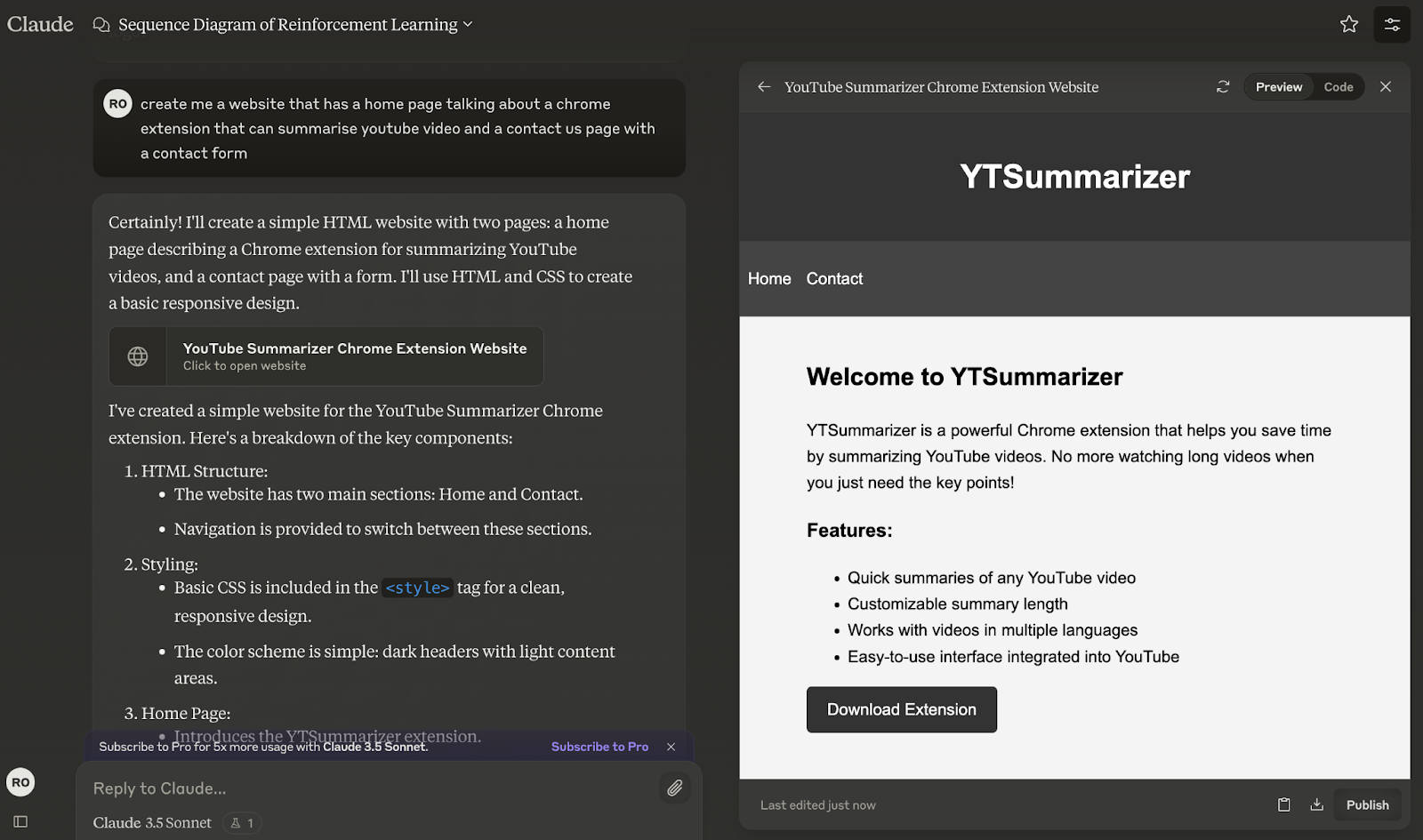
Sequence diagrams
Artifacts support flowcharts, sequence diagrams, Gantt charts, and entity-relationship diagrams (ERD), facilitating complex visual documentation.
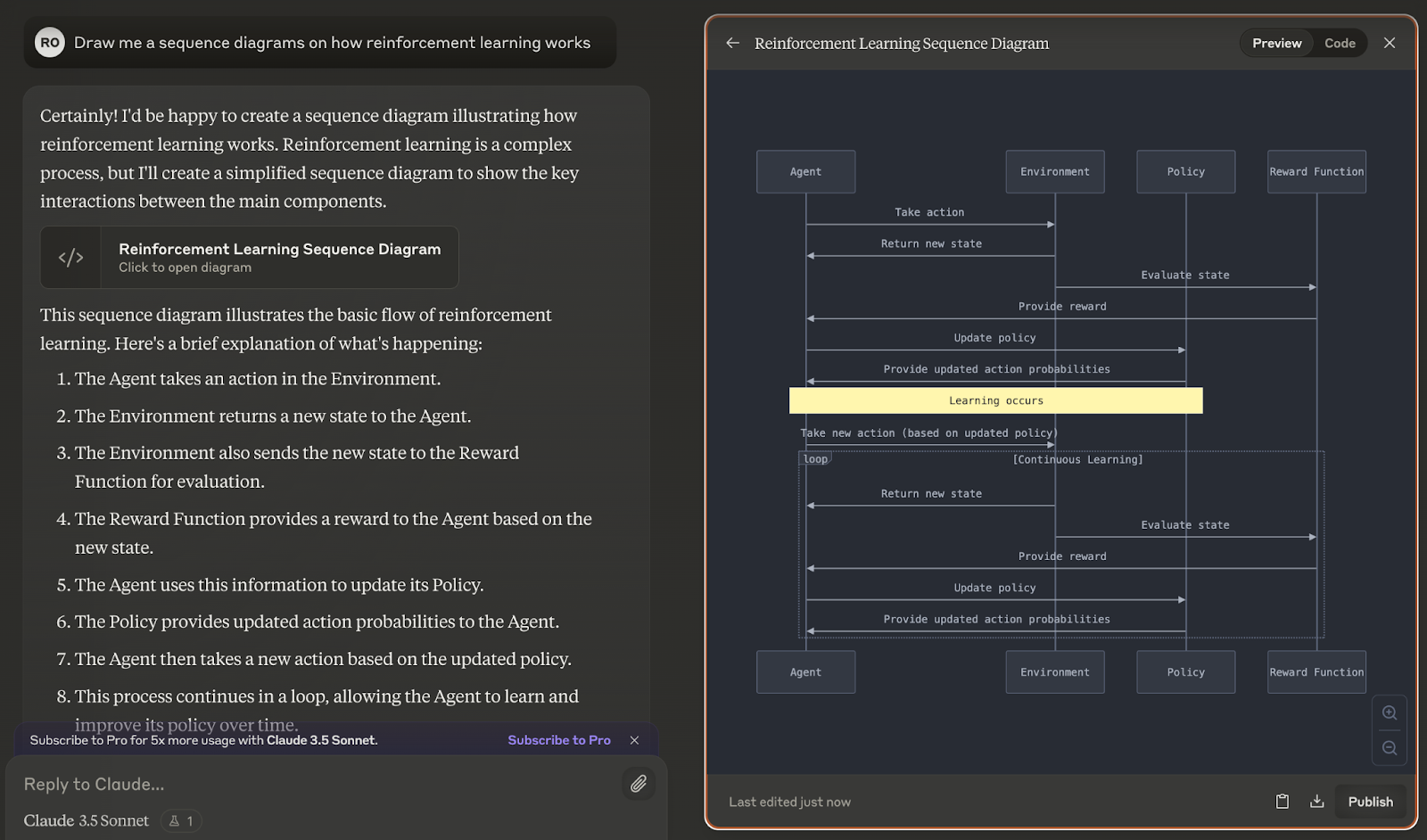
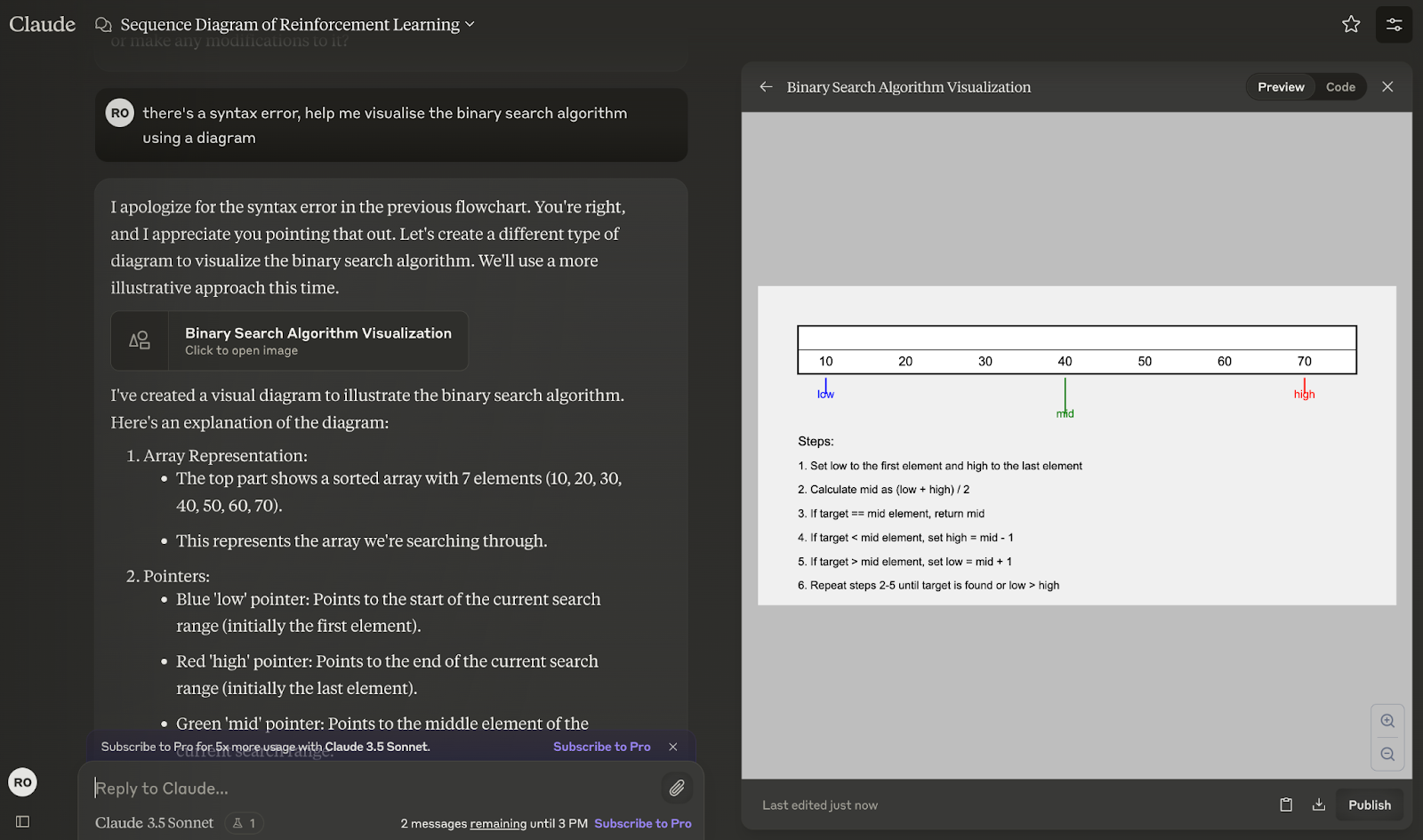
Pseudocode and algorithms
Artifacts can create flowcharts of algorithms and step-by-step problem-solving approaches, aiding in algorithm design and documentation.
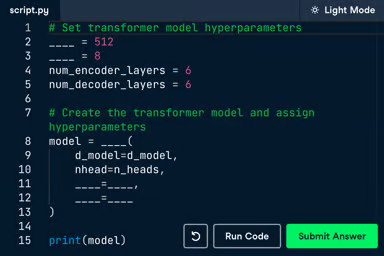
Complex code structures
You can ask Claude to generate a Python class for managing a library system. It will create a complete class structure with methods for adding books, checking out items, and managing user accounts.
class Library:
def __init__(self):
self.books = {}
self.users = {}
self.checked_out = {}
def add_book(self, book_id, title, author):
if book_id not in self.books:
self.books[book_id] = {"title": title, "author": author, "available": True}
return True
return False
def remove_book(self, book_id):
if book_id in self.books:
del self.books[book_id]
return True
return False
def add_user(self, user_id, name):
if user_id not in self.users:
self.users[user_id] = {"name": name, "books_checked_out": []}
return True
return False
def remove_user(self, user_id):
if user_id in self.users:
del self.users[user_id]
return True
return False
…(truncated)Interactive web components
Request a React component for a dynamic search bar with autocomplete functionality. Claude will produce the full React code, ready to integrate into your web application.
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
import { Search } from 'lucide-react';
// Mock data for demonstration purposes
const mockData = [
'Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry', 'Date', 'Elderberry',
'Fig', 'Grape', 'Honeydew', 'Kiwi', 'Lemon',
'Mango', 'Nectarine', 'Orange', 'Papaya', 'Quince'
];
const AutocompleteSearchBar = () => {
const [searchTerm, setSearchTerm] = useState('');
const [suggestions, setSuggestions] = useState([]);
const [isOpen, setIsOpen] = useState(false);
const wrapperRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
const handleClickOutside = (event) => {
if (wrapperRef.current && !wrapperRef.current.contains(event.target)) {
setIsOpen(false);
}
};
document.addEventListener('mousedown', handleClickOutside);
return () => {
document.removeEventListener('mousedown', handleClickOutside);
};
}, []);
…(truncated)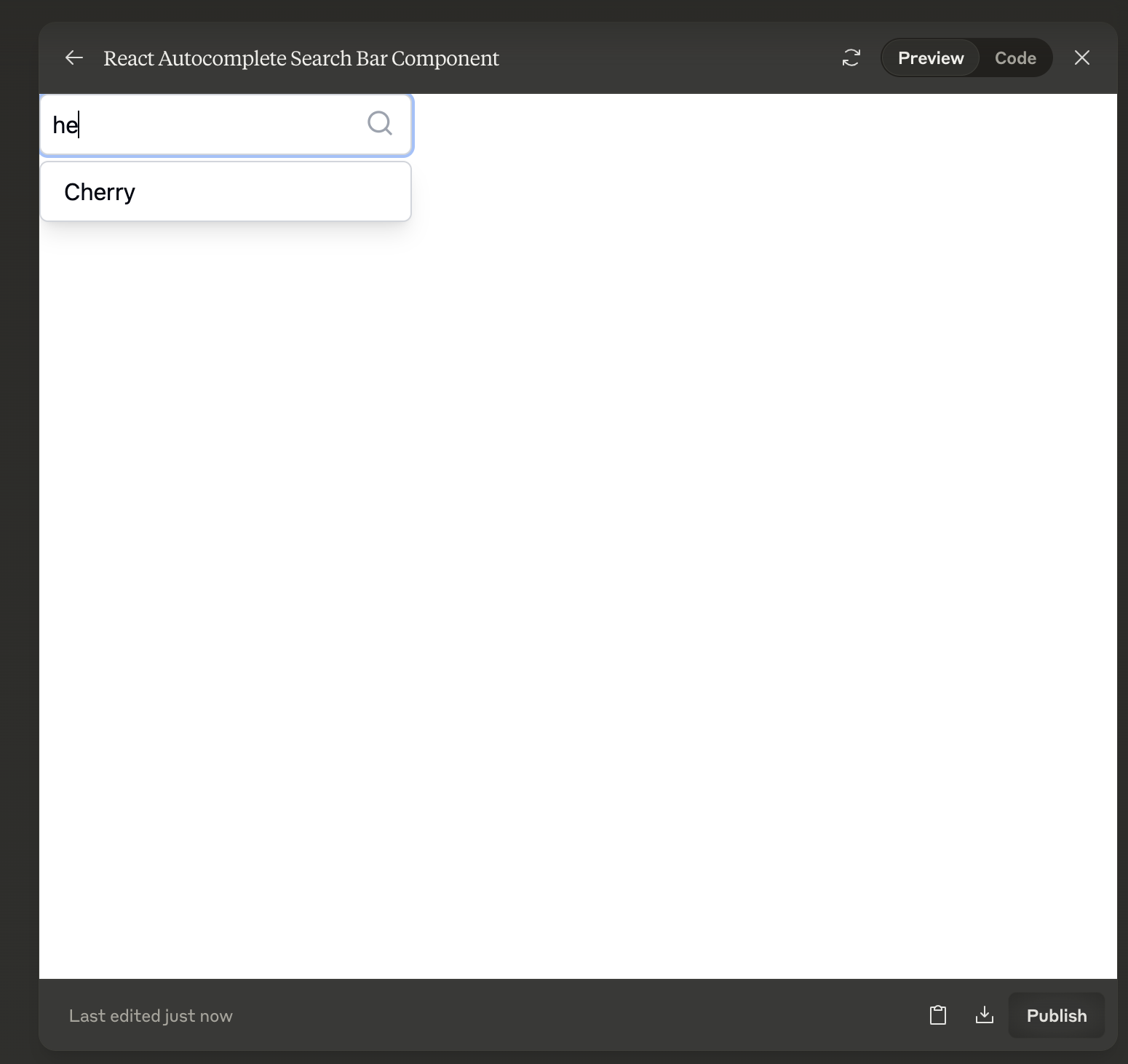
What Claude Artifacts Cannot Do
While Artifacts are versatile, they do have some limitations:
- Can’t create audio or video content: They are limited to visual and text-based content.

- Can’t execute code or run simulations: Code generated by Claude needs to be executed externally. For example, Claude created a simple snake game but it wasn’t able to run it within the Artifacts.
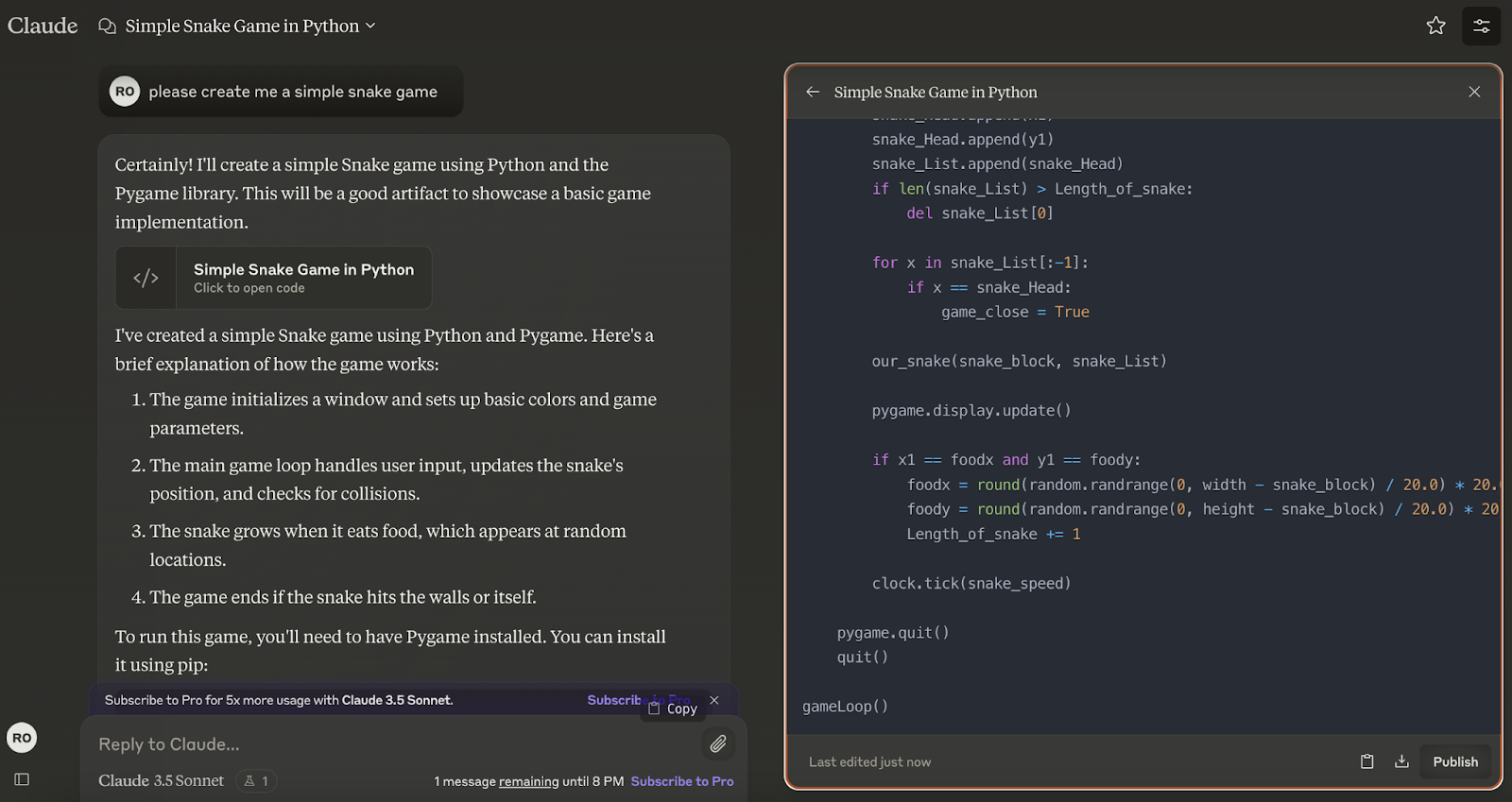
- No access to real-time data or external APIs: Artifacts are based on Claude's conversation context and have no access to external data.
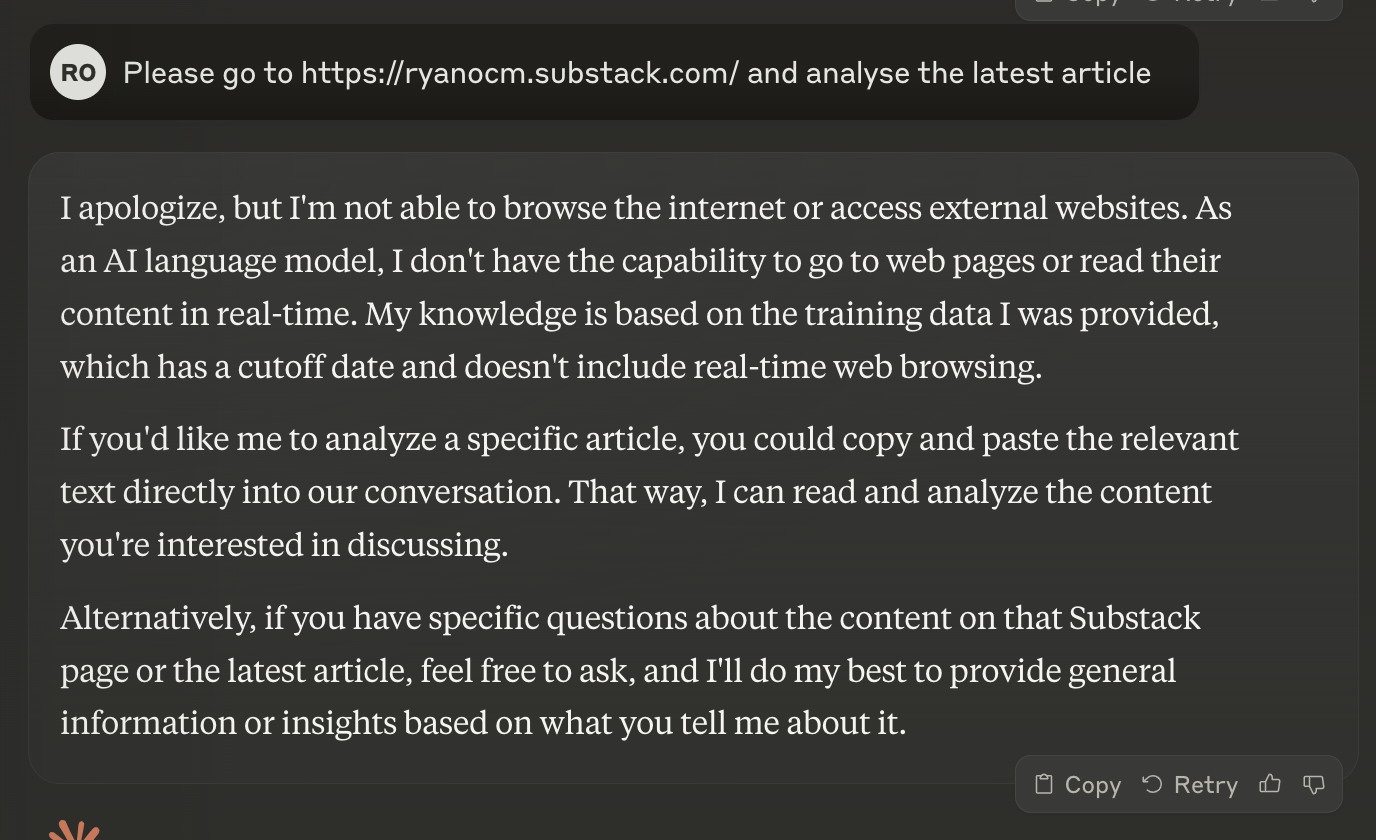
- Can’t directly upload file for editing: Users cannot upload files directly into the Artifacts window for editing and changes.
Sharing and Remixing Claude Artifacts
One of the standout features of Artifacts is their ability to facilitate sharing and collaboration. Whether you're working on a team project or seeking feedback, Artifacts provide an easy way to involve others in your work. Let’s see how you can make the most of these capabilities.
Publishing your Artifacts
Publishing an Artifact allows you to share your work with others easily. Here’s how to do it:
1. Create an Artifact: Generate the content you want to share within the Claude interface.
2. Publish the Artifact: Click on the "Publish" button in the Artifact window. This will create a unique link that you can share with others. For example, here’s an Artifact I created and published: https://claude.site/artifacts/1229a009-df4e-406e-9a5e-eed22f353844
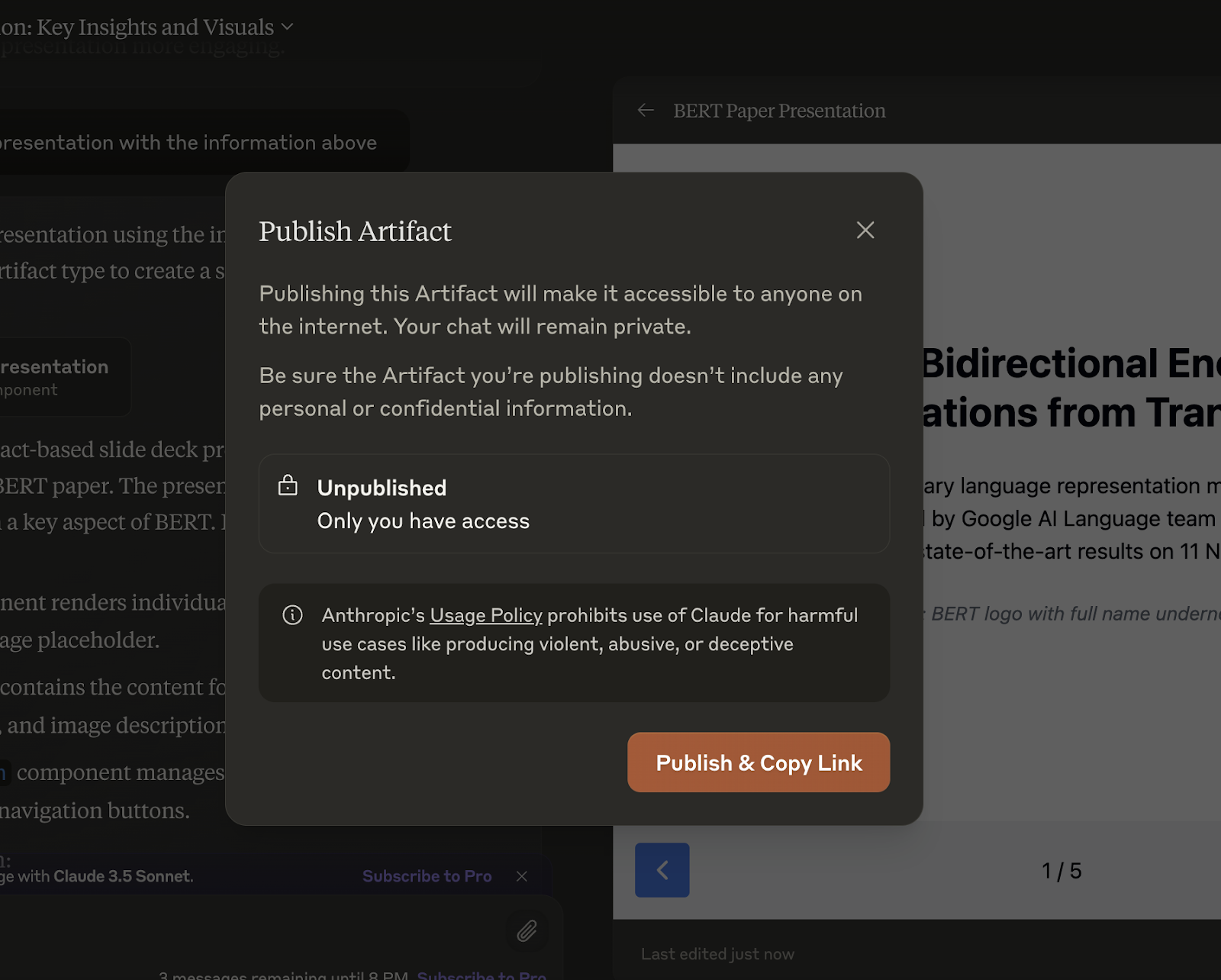
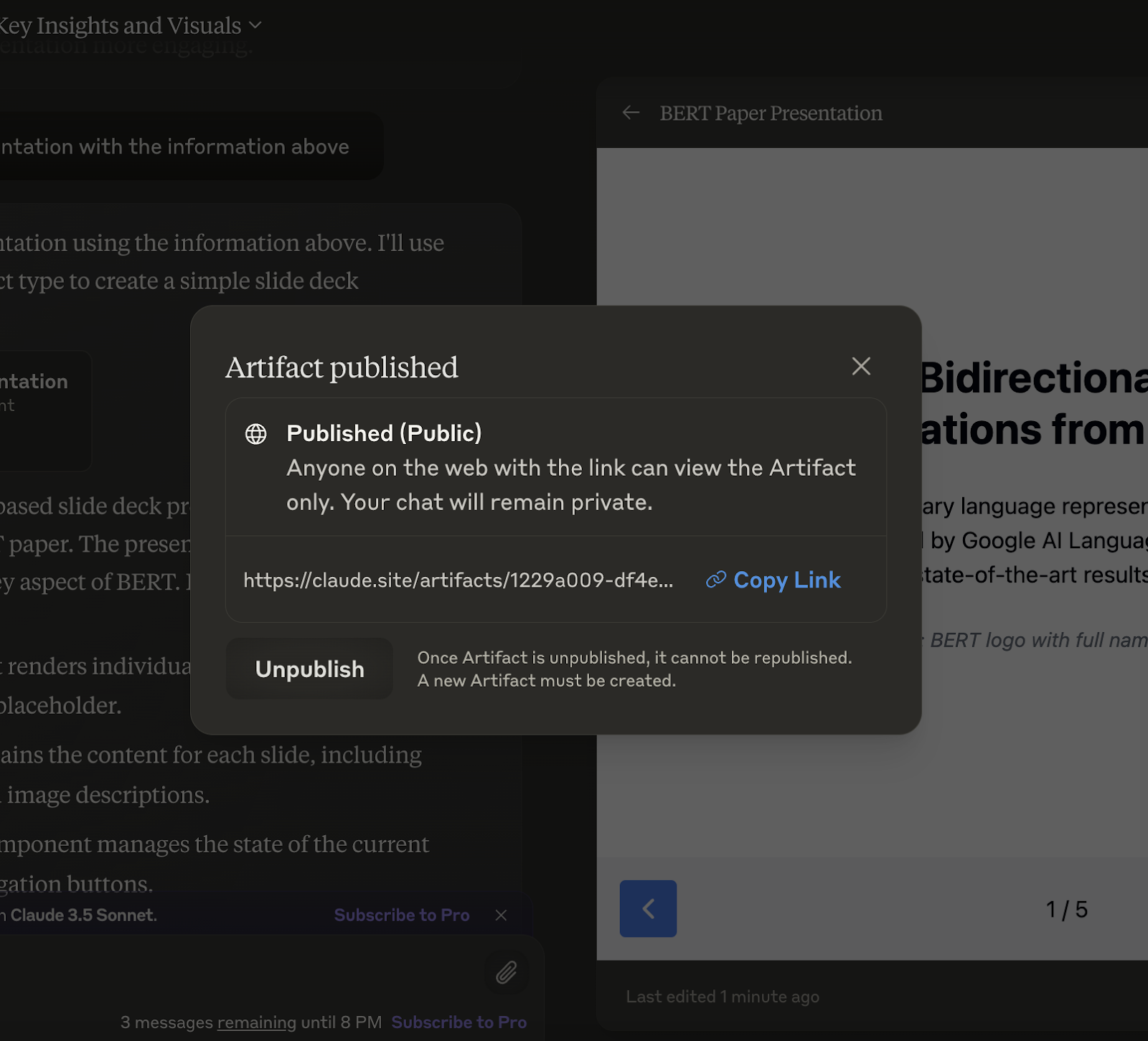
3. Manage access: Depending on your subscription level, you can control who has access to your Artifact. Claude Pro and Team plan subscribers can share and discover chats with team members.
Remixing Artifacts
Remixing allows you to take an existing Artifact and modify it to fit your needs. Here’s how you can remix an Artifact:
1. Access the shared Artifact: Use the link provided by the original creator to access the Artifact.

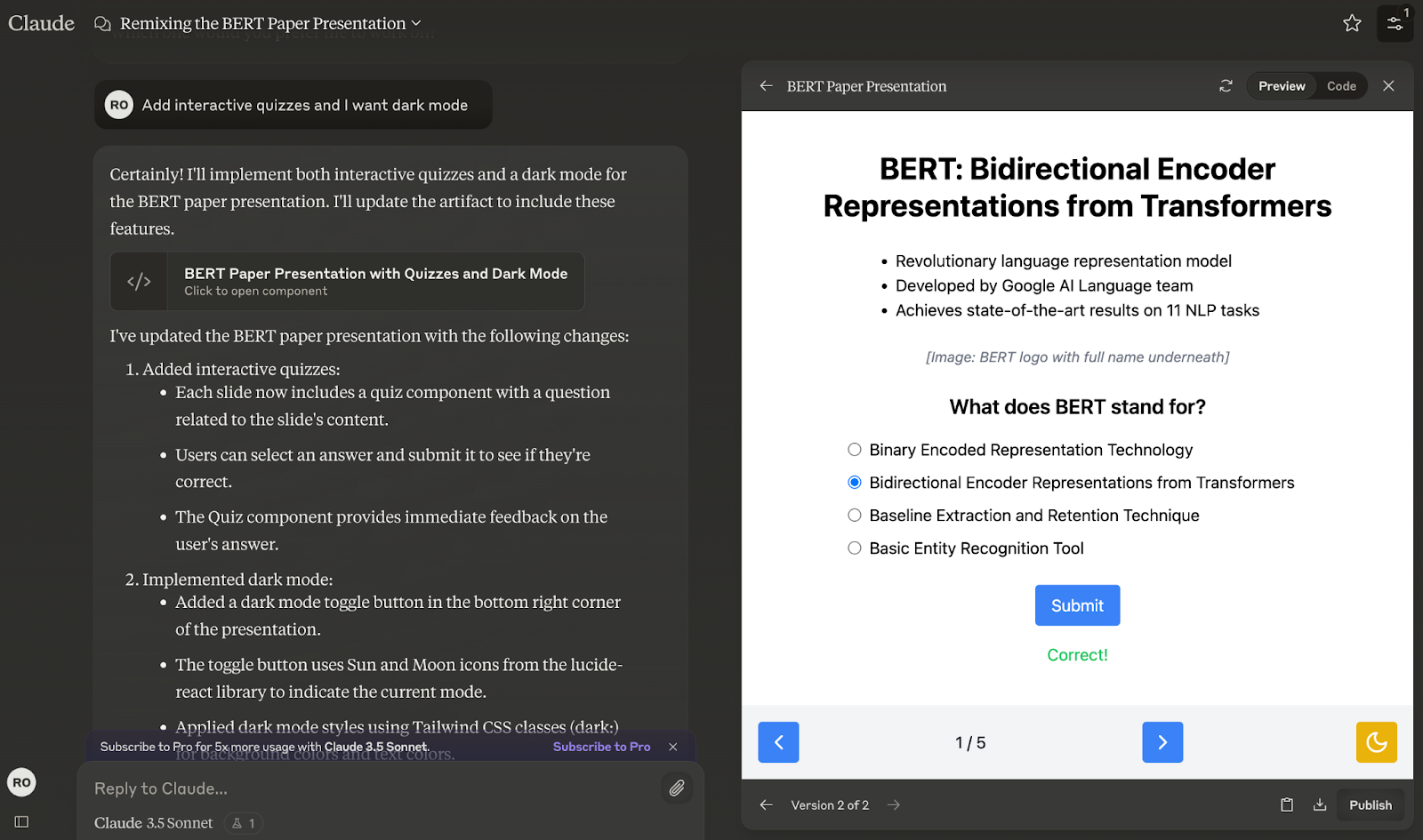
Remix the content: Click on the Remix Artifact button to create a copy of the Artifact that you can edit. Make your changes and improvements as needed.
Save and Publish: Once you’ve made your changes, you can save the remixed Artifact and share it with others, continuing the collaborative process.
API Access to Artifacts
As of now, Anthropic hasn't released official information about accessing the Artifacts feature via API. Currently, Artifacts are mainly accessed through the Claude web interface. However, there's potential for API access to be considered in future updates.
Earn a Top AI Certification
Conclusion
Claude Artifacts mark a significant step towards bridging the gap between conversational AI and practical project work.
As this feature evolves, we expect further innovative applications that expand the possibilities of AI assistance.
While current limitations of Artifacts exist, such as the inability to handle audio or video content and execute code directly, we expect some of these constraints to be addressed in future updates.
If you want to read more about the latest in AI, I recommend these blog posts:
FAQs
Can I use Claude Artifacts for complex data analysis and visualization?
Yes, Claude Artifacts can handle complex data analysis tasks. You can ask Claude to analyze your data and create interactive visualizations like charts, graphs, and dashboards. You can even manipulate these visualizations in real-time to explore different aspects of your data. For example, you could ask Claude to create a scatterplot showing the relationship between two variables and then filter the data based on different criteria.
How does the collaborative aspect of Claude Artifacts work?
You can easily share Claude Artifacts with others by providing them with a link. Collaborators can then view and interact with the artifact, making it a great tool for teamwork and knowledge sharing. For example, a team of developers could use Claude Artifacts to collaboratively design and prototype a web page.
Are there any limitations to the types of content I can create with Claude Artifacts?
While Claude Artifacts are very versatile, there may be some limitations to the complexity and size of the content you can create. For example, very large datasets or highly complex visualizations might be challenging. However, Claude is constantly improving, and its capabilities with Artifacts are likely to expand over time.
Can I edit Claude Artifacts?
Yes, you can easily edit Artifacts within Claude. Simply ask Claude to make the changes you want (e.g., "Change the background color of the web page to light blue"), and the Artifact will be updated in real-time.
Are Claude Artifacts available to all Claude users?
Yes, the Artifacts feature is available to all Claude users. It may be in preview mode and require manual activation in your settings.
Ryan is a lead data scientist specialising in building AI applications using LLMs. He is a PhD candidate in Natural Language Processing and Knowledge Graphs at Imperial College London, where he also completed his Master’s degree in Computer Science. Outside of data science, he writes a weekly Substack newsletter, The Limitless Playbook, where he shares one actionable idea from the world's top thinkers and occasionally writes about core AI concepts.