Cours
L'adoption massive d'outils comme le ChatGPT et d'autres outils d'IA générative a donné lieu à un énorme débat sur les avantages et les défis de l'IA et sur la manière dont elle va remodeler notre société. Pour mieux répondre à ces questions, il est important de savoir comment fonctionnent les "grands modèles de langage" (LLM) sur lesquels reposent les outils d'IA de la prochaine génération.
Cet article propose une introduction au Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), une technique innovante qui combine des techniques d'apprentissage par renforcement et des conseils humains pour aider les LLMS comme ChatGPT à obtenir des résultats impressionnants. Nous verrons ce qu'est la RLHF, ses avantages, ses limites et sa pertinence pour le développement futur du domaine en pleine évolution de l'IA générative. Poursuivez votre lecture !
Comprendre la RLHF
Pour comprendre le rôle de la RLHF, il faut d'abord parler du processus de formation des MFR.
La technologie sous-jacente des LLM les plus populaires est un transformateur. Depuis son développement par les chercheurs de Google, les transformateurs sont devenus le modèle de pointe dans le domaine de l'IA et de l'apprentissage profond, car ils fournissent une méthode plus efficace pour traiter les données séquentielles, comme les mots d'une phrase.
Pour une introduction plus détaillée aux LLM et aux transformateurs, consultez notre cours sur les concepts des grands modèles de langage (LLM).
Les transformateurs sont pré-entraînés à l'aide d'un vaste corpus de textes recueillis sur l'internet en utilisant l'apprentissage auto-supervisé, un type d'apprentissage innovant qui ne nécessite pas d'action humaine pour étiqueter les données. Les transformateurs préformés sont capables de résoudre un large éventail de problèmes de traitement du langage naturel (NLP).
Cependant, pour qu'un outil d'IA comme ChatGPT fournisse des réponses engageantes, précises et semblables à celles des humains, l'utilisation d'un LLM pré-entraîné ne sera pas suffisante. En fin de compte, la communication humaine est un processus créatif et subjectif. Ce qui rend un texte "bon" est profondément influencé par les valeurs et les préférences humaines, ce qui le rend très difficile à mesurer ou à appréhender à l'aide d'une solution algorithmique claire.
L'idée derrière ELF est d'utiliser le feedback humain pour mesurer et améliorer la performance du modèle. Ce qui rend la méthode RLHF unique par rapport aux autres techniques d'apprentissage par renforcement, c'est l'utilisation de la participation humaine pour optimiser le modèle au lieu d'une fonction statistiquement prédéfinie pour maximiser la récompense de l'agent.
Cette stratégie permet une expérience d'apprentissage plus adaptable et personnalisée, ce qui rend les masters en droit adaptés à toutes sortes d'applications sectorielles, telles que l'assistance au codage, la recherche juridique, la rédaction d'essais et la création de poèmes.
Comment fonctionne la RLHF ?
La RLHF est un processus difficile qui implique un processus de formation à plusieurs modèles et différentes étapes de déploiement. Essentiellement, elle peut être décomposée en trois étapes différentes.
1. Sélectionnez un modèle pré-entraîné
La première étape consiste à sélectionner un LLM pré-entraîné qui sera ensuite affiné à l'aide de RLHF.
Vous pouvez également former votre LLM en partant de zéro, mais il s'agit d'un processus coûteux et fastidieux. C'est pourquoi nous vous recommandons vivement de choisir l'un des nombreux LLM pré-entraînés disponibles pour le public.
Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur la manière de former un LLM, notre tutoriel Comment former un LLM avec PyTorch fournit un exemple illustratif.
Notez que, pour répondre aux besoins spécifiques de votre modèle, avant d'entamer la phase d'affinage à l'aide du retour d'information humain, vous pourriez affiner votre modèle sur des textes ou des conditions supplémentaires.
Par exemple, si vous souhaitez développer un assistant juridique IA, vous pourriez affiner votre modèle avec un corpus de textes juridiques afin de rendre votre LLM particulièrement familier avec la formulation et les concepts juridiques.
2. Retour d'information sur l'homme
Au lieu d'utiliser un modèle de récompense statistiquement prédéfini (qui serait très restrictif pour calibrer les préférences humaines), RLHF utilise le feedback humain pour aider le modèle à développer un modèle de récompense plus subtil. Le processus se déroule comme suit :
- Tout d'abord, le modèle pré-entraîné crée un ensemble d'entraînement de paires entrée-prompts/textes générés en échantillonnant un ensemble de messages-guides.
- Ensuite, des testeurs humains classent les textes générés en suivant certaines lignes directrices afin d'aligner le modèle sur les valeurs et les préférences humaines et d'en assurer la sécurité. Ces rangs peuvent ensuite être transformés en scores à l'aide de différentes techniques, telles que les systèmes d'évaluation Elo.
- Enfin, le système utilise le retour d'information humain accumulé pour évaluer ses performances et développer un modèle de récompense.
L'image suivante illustre l'ensemble du processus :
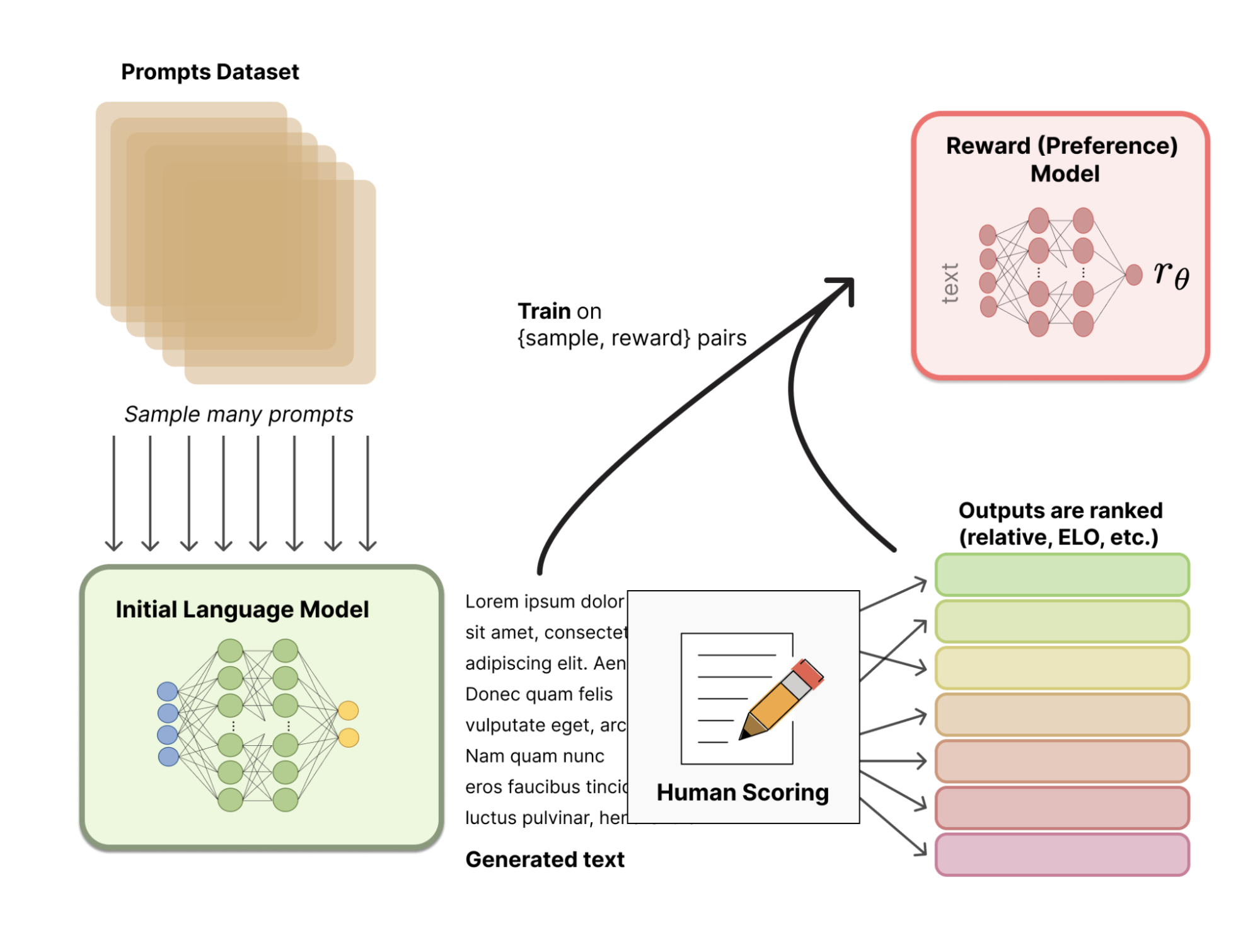
Source : Hugging Face
3. Réglage fin grâce à l'apprentissage par renforcement
Dans la dernière étape, le LLM produit de nouveaux textes et utilise son modèle de récompense basé sur le feedback humain pour produire un score de qualité. Le score est ensuite utilisé par le modèle pour améliorer ses performances sur les invites suivantes.
Le retour d'information humain et le réglage fin à l'aide de techniques d'apprentissage par renforcement sont donc combinés dans un processus itératif qui se poursuit jusqu'à ce qu'un certain degré de précision soit atteint.
Applications de l'apprentissage par renforcement à partir du feedback humain
RLHF est une technique de pointe pour affiner les LLM, tels que ChatGPT. Cependant, la RLHF est un sujet populaire, avec une littérature croissante explorant d'autres possibilités au-delà des problèmes de NLP. Vous trouverez ci-dessous une liste d'autres domaines où la RLHF a été appliquée avec succès :
- Chatbots. Le chatGPT est l'exemple le plus frappant des possibilités offertes par la RLHF. Pour en savoir plus sur l'utilisation de la RLHF par ChatGPT, consultez l' article " Qu'est-ce que ChatGPT ? " dans lequel nous avons demandé directement à ChatGPT comment elle fonctionnait.
- Robotics. La robotique est l'un des principaux domaines où la RLHF donne des résultats prometteurs. L'utilisation du feedback humain peut aider un robot à effectuer des tâches et des mouvements qu'il peut être difficile de spécifier dans une fonction de récompense. Les chercheurs de l'OpenAI ont réussi à apprendre à un robot à faire un saut périlleux arrière - une tâche assez difficile à modéliser - en utilisant la RLHF.
- Jeux. Les techniques d'apprentissage par renforcement ont été utilisées pour développer des robots de jeux vidéo. Cependant, la RLHF peut être utilisée pour former des robots sur la base des préférences humaines, ce qui leur permet de ressembler davantage à des joueurs humains plutôt qu'à de simples machines maximisant la récompense. Par exemple, OpenAI et DeepMind ont entraîné des robots à jouer à des jeux Atari avec RLHF.
Les avantages de la RLHF
La RLHF est une technique puissante et prometteuse sans laquelle les outils d'IA de la prochaine génération ne seraient pas possibles. Voici quelques-uns des avantages de la RLHF :
- Performances accrues. Le feedback humain est la clé pour que les LLM comme le ChatGPT "pensent" et sonnent comme des humains. La HLHF permet aux machines de s'attaquer à des tâches complexes, telles que les problèmes de NLP, qui impliquent des valeurs ou des préférences humaines.
- Adaptabilité. Étant donné que les LLM sont affinés à l'aide du retour d'information humain dans toutes sortes d'invites, la RLHF permet aux machines d'effectuer une série de tâches multiples et de s'adapter aux situations attendues. Les LLM nous rapprochent donc du seuil de l'IA polyvalente.
- Amélioration continue. Le RLHF est un processus itératif, ce qui signifie que le système est amélioré en permanence au fur et à mesure que sa fonction d'apprentissage s'actualise en fonction des nouveaux retours d'information de la part de l'homme.
- Sécurité accrue. En recevant un retour d'information de la part de l'homme, le système n'apprend pas seulement comment faire les choses, il apprend aussi ce qu'il ne faut pas faire, ce qui garantit des systèmes efficaces, plus sûrs et plus fiables.
Limites de la RLHF
Cependant, la RLHF n'est pas à l'épreuve des balles. Cette technique présente également certains risques et certaines limites. Vous trouverez ci-dessous quelques-unes des plus pertinentes :
- Un retour d'information humain limité et coûteux. La RLHF dépend de la qualité et de la disponibilité du retour d'information humain. Cependant, la réalisation de ce travail peut être lente, laborieuse et coûteuse, en particulier si le travail en question nécessite un grand nombre de retours d'information.
- Biais dans la rétroaction humaine. Malgré l'utilisation de lignes directrices normalisées pour fournir un retour d'information, la notation ou le classement sont en fin de compte influencés par les préférences et les valeurs humaines. Si les tâches de classement ne sont pas bien définies ou si la qualité du retour d'information humain est médiocre, le modèle peut être biaisé ou renforcer des résultats indésirables.
- Généralisation à de nouveaux contextes. Même si les mécanismes d'apprentissage tout au long de la vie sont affinés grâce à un important retour d'information de la part de l'homme, des contextes inattendus peuvent toujours survenir. Dans ce cas, le défi consiste à rendre l'agent robuste dans des situations où le retour d'information est limité.
- Hallucinations. Lorsque le retour d'information de la part de l'homme est limité ou faible, les agents peuvent être victimes d'hallucinations, c'est-à-dire d'un comportement indésirable, faux ou absurde.
Tendances et développements futurs dans le domaine de la RLHF
La RLHF est l'un des piliers des outils modernes d'IA générative, tels que ChatGPT et GPT-4. Malgré ses résultats impressionnants, la RLHF est une technique relativement nouvelle et il existe encore une grande marge d'amélioration. La recherche future sur les techniques RLHF est essentielle pour rendre les MFR plus efficaces, réduire leur empreinte environnementale et traiter certains des risques et des limites des MFR.
Pour vous tenir au courant des derniers développements en matière d'IA générative, d'apprentissage automatique et de LLM, nous vous recommandons vivement de consulter nos supports d'apprentissage :
- Introduction à l'apprentissage par renforcement - Ce tutoriel couvre les concepts de base et la terminologie de l'apprentissage par renforcement.
- Deep Learning in Python - Ce cursus aide les apprenants à élargir leurs connaissances en matière de deep learning et à faire passer leurs compétences en apprentissage automatique au niveau supérieur.
- Tutoriel sur l'apprentissage profond - Ce tutoriel donne un aperçu de l'apprentissage profond et de l'apprentissage par renforcement.
- Comment utiliser l'apprentissage automatique de manière éthique pour prendre des décisions - Cet article de blog traite de l'importance des considérations éthiques lors de l'utilisation de modèles d'apprentissage automatique.

Je suis analyste de données indépendant et je collabore avec des entreprises et des organisations du monde entier dans le cadre de projets de science des données. Je suis également formateur en science des données avec plus de 2 ans d'expérience. Je rédige régulièrement des articles sur les sciences des données en anglais et en espagnol, dont certains ont été publiés sur des sites web réputés tels que DataCamp, Towards Data Science et Analytics Vidhya En tant que scientifique des données ayant une formation en sciences politiques et en droit, mon objectif est de travailler à l'interaction des politiques publiques, du droit et de la technologie, en tirant parti du pouvoir des idées pour faire avancer des solutions et des récits innovants qui peuvent nous aider à relever des défis urgents, à savoir la crise climatique. Je me considère comme un autodidacte, un apprenant permanent et un fervent partisan de la pluridisciplinarité. Il n'est jamais trop tard pour apprendre de nouvelles choses.