Course
Excel gives you a few different ways to find the average. The aptly named AVERAGE() function is your starting point, but there are also variations like AVERAGEIF(), AVERAGEIFS(), and AVERAGEA() for more specialized situations.
In this article, I’ll show you how to use the AVERAGE() function in Excel, and then I’ll help you understand the other useful average functions I named above.
How to Use AVERAGE() in Excel
The AVERAGE() function in Excel calculates the arithmetic mean of a range of numbers. To use this function, you simply pick the range of cells you want to average, and use the function like so:
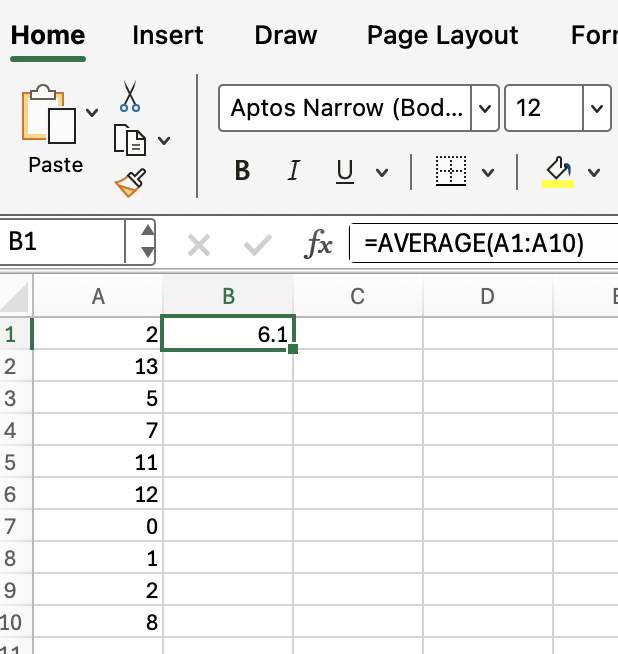
=AVERAGE(A1:A10)This formula will return the average of the values in cells A1 through A10, as you can see in this screenshot:
Other Useful Excel Average Functions
As promised, let me mention the several other functions that Excel offers, which are used for finding averages under slightly different conditions. Here are some of the most commonly used:
-
AVERAGEIF(): Calculates the average of cells that meet a single condition. -
AVERAGEIFS(): Calculates the average of cells that meet multiple conditions. -
AVERAGEA(): Includes logical values and text representations of numbers.
Now I'll show each with a quick example:
AVERAGEIF() in Excel
The AVERAGEIF() function allows you to average only those cells that meet a specific criterion. This is useful when you want to exclude certain values from your calculation.
=AVERAGEIF(B1:B10, ">50")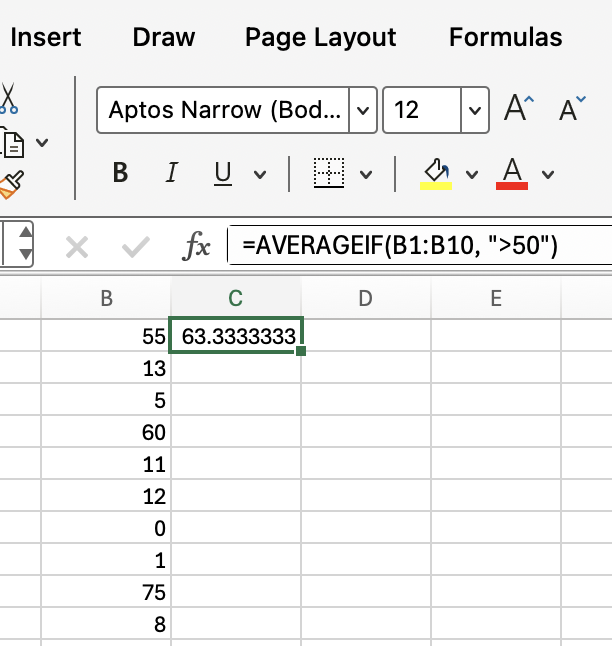
This formula averages only the values in B1:B10 that are greater than 50. So 63.3 is the approximate average of 55, 60, and 75.
AVERAGEIFS() in Excel
The AVERAGEIFS() function is similar to AVERAGEIF() but allows for multiple criteria. This is helpful when you need to apply more than one condition to your data.
=AVERAGEIFS(B1:B10, B1:B10, ">50", A1:A10, "Ford")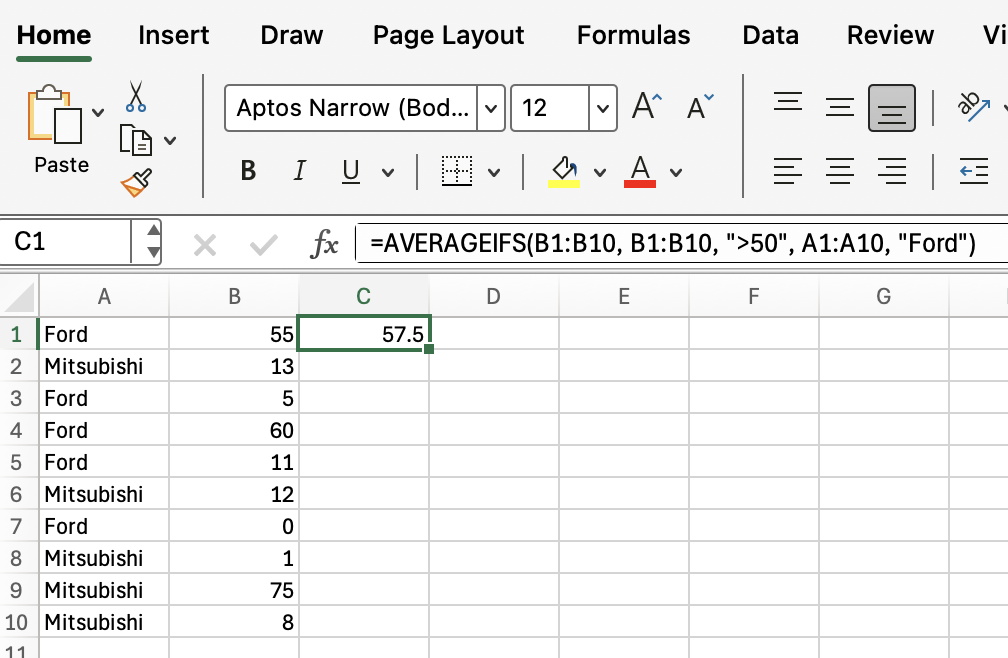
This formula averages the values in B1:B10 where the corresponding value in B1:B10 is greater than 50 and the value in A1A10 is "Ford". So if you look closely, you can see it's average two values, 55, and 60, to get a value of 57.5, because only those two values in A1:A10 meet both of those conditions.
AVERAGEA() in Excel
The AVERAGEA() function calculates the average of a range, including logical values and text representations of numbers. This can be useful when your data set includes TRUE and FALSE values or numbers stored as text. The AVERAGEA() function is something you want to know if you're going to be analyzing survey data.
=AVERAGEA(A1:A10)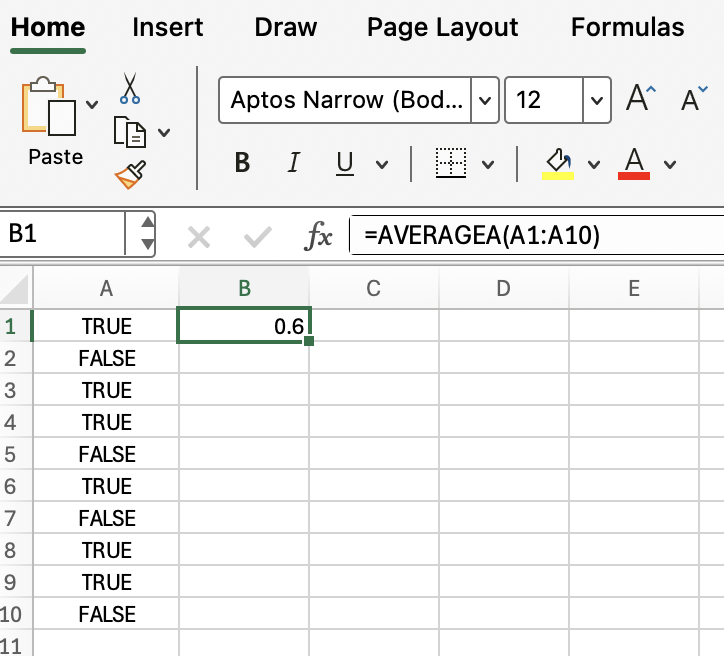
This formula averages all values in A1:A10, treating TRUE as 1, FALSE as 0.
Tips for Working with Averages in Excel
When working with averages:
-
Make sure your data range does not include unwanted blank cells or text (unless you're using
AVERAGEA(), as I showed in that last example). -
Use
AVERAGEIF()orAVERAGEIFS()to focus on specific subsets of your data -
Combine average functions with other Excel tools, such as filters or conditional formatting, for deeper analysis. Our Advanced Excel Functions course is a great resource for getting back at coming Excel functions.
Keyboard Shortcuts for Excel Average Functions
Finally, if you feel comfortable with all the above and now you want to speed up your workflow, you can use keyboard shortcuts when entering formulas:
Type your formula and press Enter to complete it
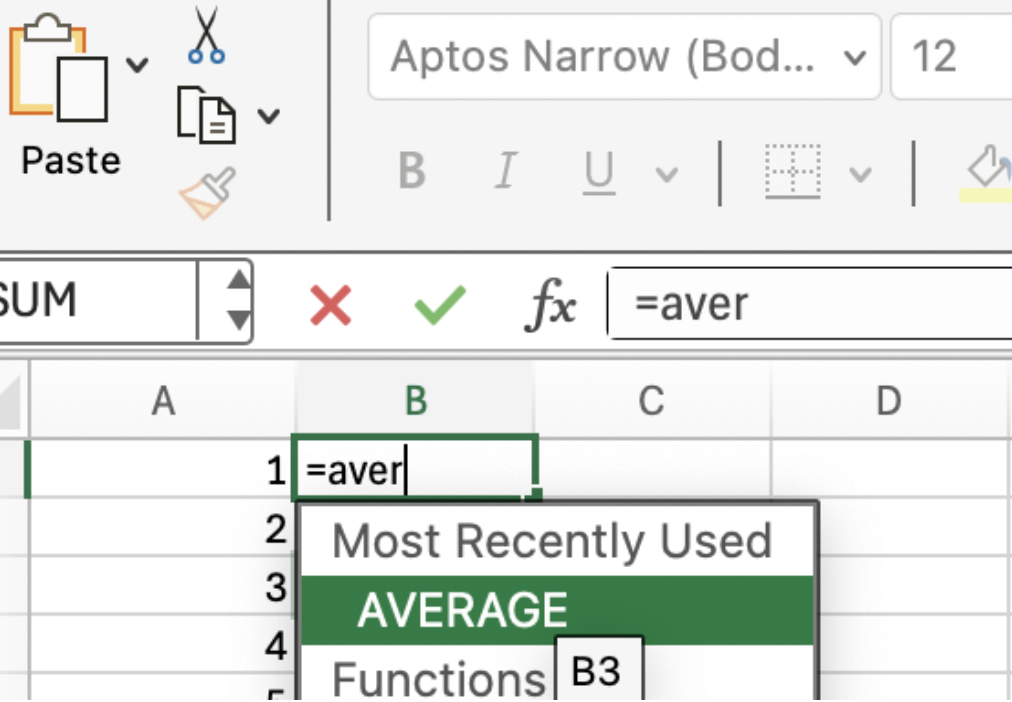
Use Tab to auto-complete function names as you type. You can see in this image how it autocompletes when you start typing:
Conclusion
AVERAGE() is something you have to work with if you are going to analyze data and extract insights. But as you started to see, there is more variation than you might expect.
Enroll in our Excel Fundamentals skill track and our Advanced Excel Functions course to keep learning.
Advance Your Career with Excel
Gain the skills to maximize Excel—no experience required.

I'm a data science writer and editor with contributions to research articles in scientific journals. I'm especially interested in linear algebra, statistics, R, and the like. I also play a fair amount of chess!