Track
The ISERROR() function in Excel is a valuable tool for detecting errors in formulas or calculations. By returning TRUE if a formula results in an error and FALSE otherwise, ISERROR() helps you manage and troubleshoot your spreadsheets. It's one additional tool in your toolbox worth using. Take our Advanced Excel Functions course to discover even more.
Understanding the Excel ISERROR() Function
Here is what the ISERROR() function does: ISERROR() checks whether a value results in any error type, such as #DIV/0!, #N/A, #VALUE!, #REF!, #NUM!, #NAME?, or #NULL!.
Here’s the syntax for ISERROR():
=ISERROR(value)The value argument is the expression or cell reference you want to test for errors.
Here you can see all the different types of errors that are recognized:
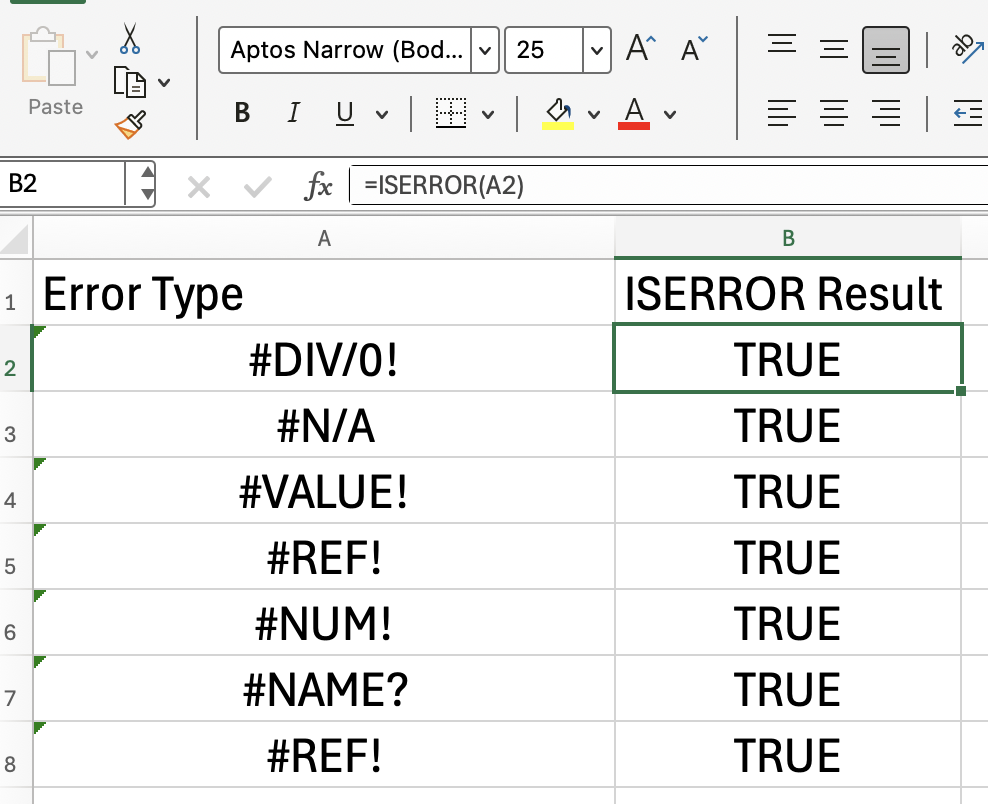
How to Use ISERROR() in Excel Formulas
Now that we see the different errors that you can find, let's see how you can use ISERROR() naturally in your work. First, here are some of the general uses:
-
Checks if a formula returns an error
-
Combines with
IF()to display custom messages or values when errors occur -
Useful in data validation to prevent error-prone entries
ISERROR() with IF()
Let’s look at an example of using ISERROR() with IF():
=IF(ISERROR(A1/A2), "Error in calculation",A1/A2)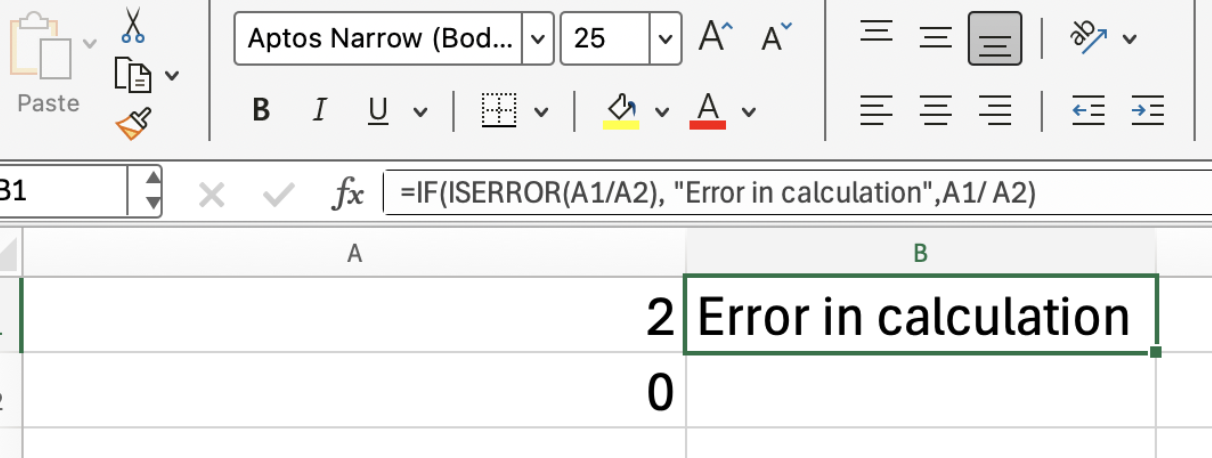
This formula checks if dividing A1 by A2 results in an error. If it does, it displays "Error in calculation"; otherwise, it shows the result.
ISERROR() with IF() and VLOOKUP()
Let's extend this example to involve a VLOOKUP(). This is another common use, since we all use lookup functions a lot and, because we are looking something up from a list, we aren't that surprised if not everything returns a result.
We already know that if a VLOOKUP() doesn’t find a match, it returns an #N/A error. Now, you can use ISERROR() to catch that error and return a friendlier and more helpful message.
=IF(ISERROR(VLOOKUP(C3,A3:B5,2,FALSE)),"The item was not found in the list",VLOOKUP(C3,A2:B4,2,FALSE))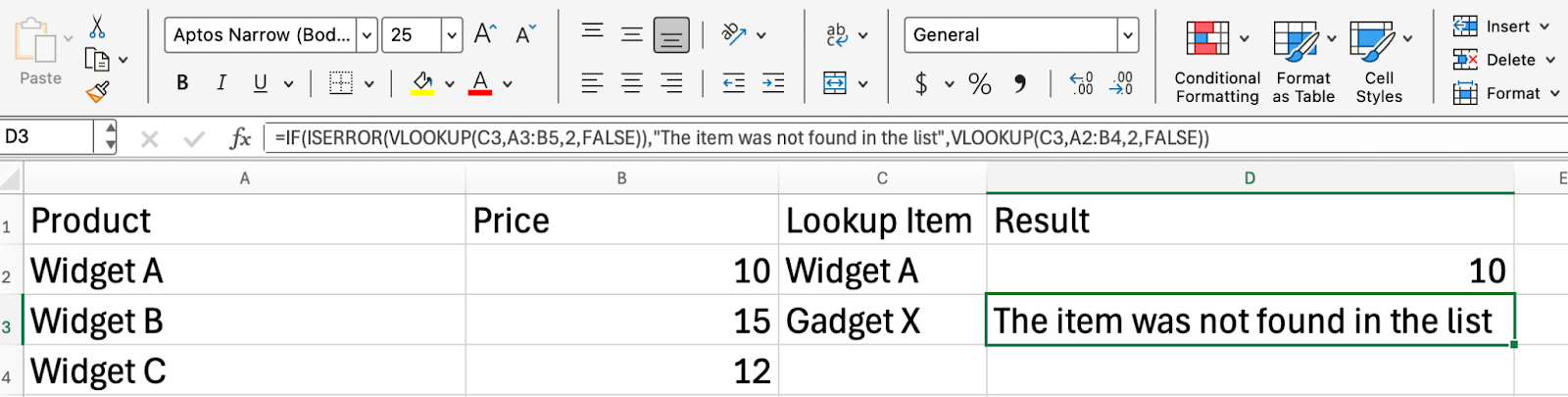
Tips for Working with Excel ISERROR()
When using ISERROR() in your spreadsheets, keep these tips in mind:
-
Use
ISERROR()to catch all error types, but considerISERR()or IFERROR() for more specific needs -
Combine with conditional formatting to visually highlight errors
-
Test your formulas with different data to make sure your error handling works as you expect
Conclusion
The ISERROR() function in Excel is a powerful way to identify and manage errors in your formulas. Incorporating it into your spreadsheets and create more reliable and user-friendly notebooks.
Next, take our Advanced Excel Functions course to keep improving your skills.
Advance Your Career with Excel
Gain the skills to maximize Excel—no experience required.

I'm a data science writer and editor with contributions to research articles in scientific journals. I'm especially interested in linear algebra, statistics, R, and the like. I also play a fair amount of chess!
