Track
A common need in data analysis is finding the absolute value of a set of numbers quickly. Python offers an easy, built-in function for performing this task, the abs(). The absolute value function allows Python programmers to obtain the magnitude of a number, regardless of its sign, essentially making the number positive.
Understanding Absolute Value
The absolute value function in Python returns the positive distance between that number and zero on a number line. For positive real numbers, the absolute value remains the same. For negative real numbers, it becomes positive.
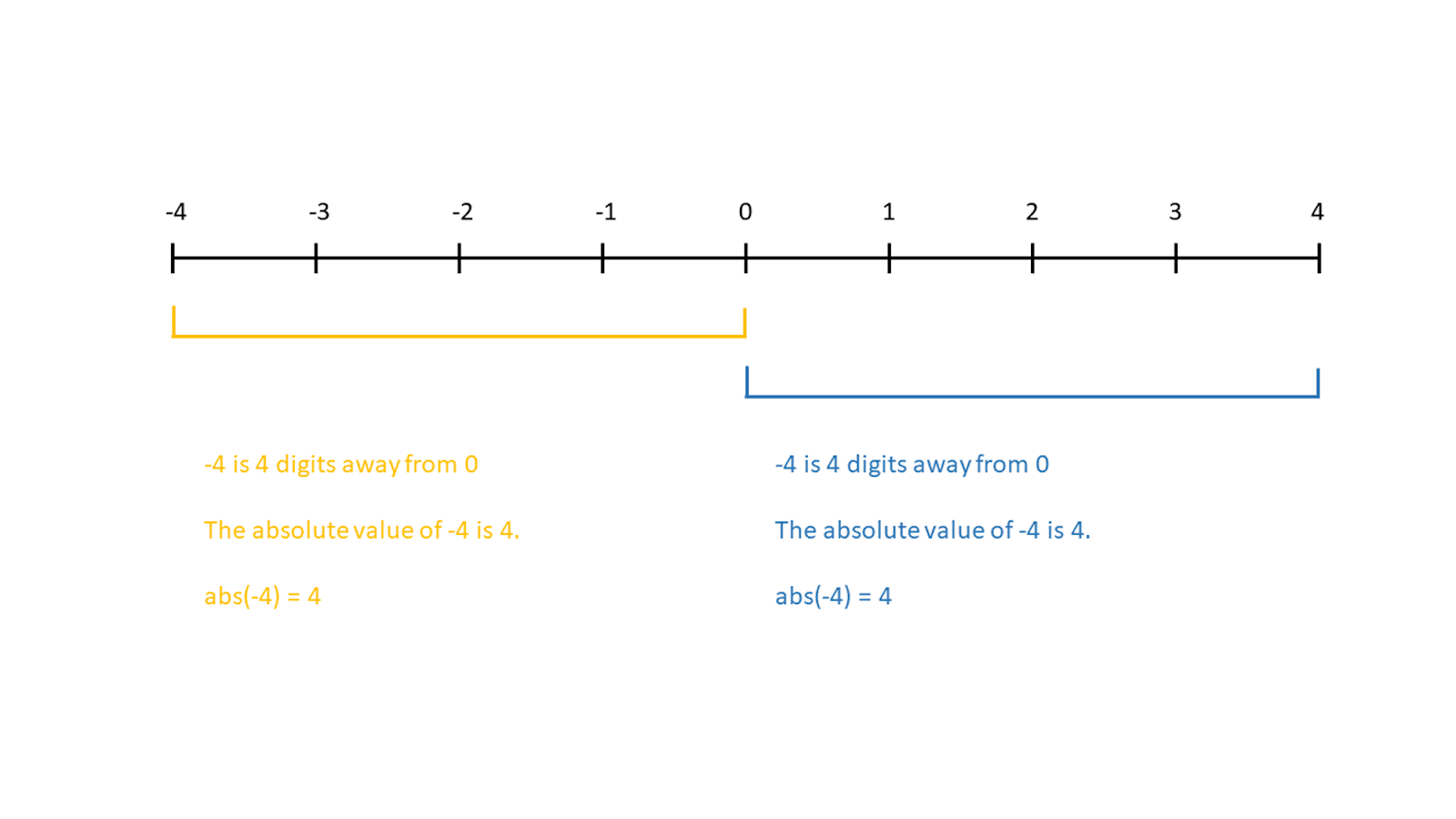
This is an easy concept to understand with integers or floats, but it gets a little tricky when working with complex numbers.
For complex numbers, the absolute value, or magnitude, is calculated using a rearrangement of the Pythagorean theorem. Check out this complex number video for a more complete explanation of why.
Put simply, if you take the absolute value of a complex number in the format of a+bi, the result will be calculated using the following equation: √ a2+b2.
Key Takeaway: The absolute value function in Python returns the magnitude of a number, regardless of its sign or complexity.
How to Use the Absolute Value Function in Python
To use the absolute value function in Python, simply pass the number as an argument.
Here's a basic example:
num = -10
absolute_value = abs(num)
print("The absolute value of", num, "is:", absolute_value)Output:
The absolute value of -10 is: 10An alternative in math.fabs()
There is an alternative method for finding an absolute method in Python: the fabs() method from the math module. This method is designed to offer more precision when working with floats, though it can also accept integers as inputs. This method does not work for complex numbers, however.
The syntax for math.fabs() is the same as for abs(), except you must import the math module before using it.
Key Takeaway: To use the abs() function, simply provide the number as an argument, and it will return its absolute value. For greater precision with floats, use the math.fabs() function.
Practical Applications
There are many situations where a negative number doesn’t make sense or would cause problems. In other cases, a data scientist may be interested in the magnitude of an effect, but not its direction. In these situations, using the abs() function is often useful.
Distance Calculation: Absolute value is used when only the magnitude of a quantity matters, such as when determining the distance between two points on a coordinate plane.
Comparisons: Sometimes, you want to compare the magnitude without losing the sign information. For example, I once had a pressure sensor that gave me values for the positive and negative pressure exerted in a space. In some contexts, this directionality information was helpful, but sometimes I just needed to compare the magnitude of two different pressure events. I used a version of the code below to make this comparison without changing the raw values.
if abs(pressure1) >= abs(pressure2):
return "Successful"
else:
return "Unsuccessful"Error Handling: Absolute value is handy in error handling scenarios where negative values might lead to unexpected behavior. Taking the absolute value ensures that only positive values are considered.
Common Issues
Non-numeric types
One common mistake when using the abs() function in Python is applying it to non-numeric types. Be sure that your input is formatted as a number, and not as a string or something else.
Information loss
Another common mistake is losing important sign information. Consider the pressure example above. If I blindly took the absolute value, I would have lost important directional information. By only using the abs() function where needed, and not changing the raw value, I retained that information for future use. It is also important to keep this in mind when drawing conclusions.
Unexpected complex numbers
Mistakes can also occur if you have an unexpected complex number in your inputs. Since the absolute value of a complex number is determined differently than other numbers, an unexpected complex number may result in odd behavior in your code downstream. Or, if you are using math.fabs(), an unexpected complex number may result in an error.
Conclusion
The absolute value function in Python is a versatile tool for obtaining the magnitude of a number, regardless of its sign. Understanding how to leverage the absolute value function is essential for Python programmers.
For more advanced mathematical concepts, consider exploring the math module in Python or this article demystifying mathematical concepts. I highly recommend taking an introductory statistics course or a statistics in Python course. Learn more about when the absolute value can be helpful in a nonmathematical situation in this article on how to learn Python like an expert and this Python programming track from DataCamp.

I am a PhD with 13 years of experience working with data in a biological research environment. I create software in several programming languages including Python, MATLAB, and R. I am passionate about sharing my love of learning with the world.
