Course
Database administratos and database users face two challenges: writing complex SQL queries and securing database access. Sometimes SQL queries become more complicated due to the use of multiple joins, subqueries, and GROUP BY in a single query.
To simplify such queries, you can use some proxy over the original table. Also, sometimes from the security side, the database administrator wants to restrict direct access to the database. For example, if a table contains various columns but the user only needs three columns of data, the DBA will create a virtual table of three columns. For both purposes, you can use the view. Views can act as a proxy or virtual table. Views reduce the complexity of SQL queries and provide secure access to underlying tables.
What is a View?
Views are a special version of tables in SQL. They provide a virtual table environment for various complex operations. You can select data from multiple tables, or you can select specific data based on certain criteria in views. It does not hold the actual data; it holds only the definition of the view in the data dictionary.
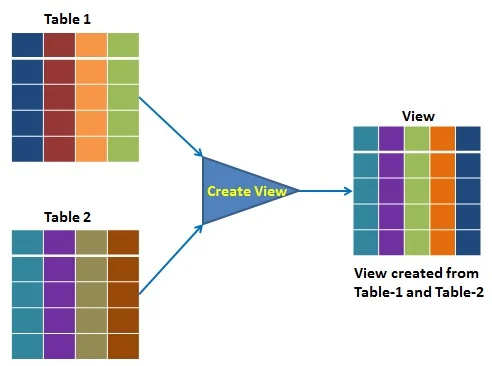
The view is a query stored in the data dictionary, on which the user can query just like they do on tables. It does not use the physical memory, only the query is stored in the data dictionary. It is computed dynamically, whenever the user performs any query on it. Changes made at any point in view are reflected in the actual base table.
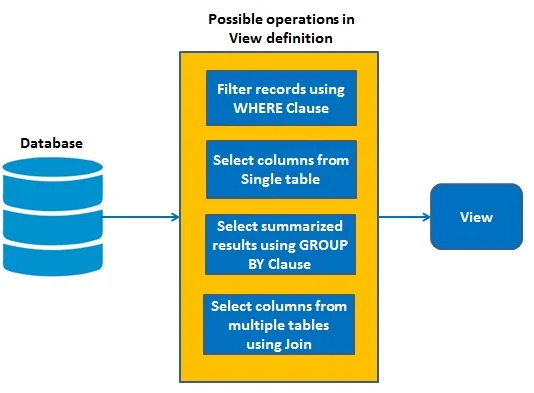
The view has primarily two purposes:
- Simplify the complex SQL queries.
- Provide restriction to users from accessing sensitive data.
Associate Data Engineer in SQL
Types of Views
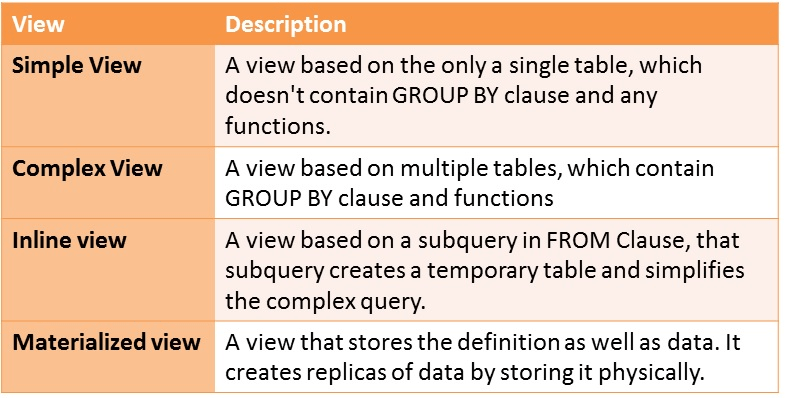
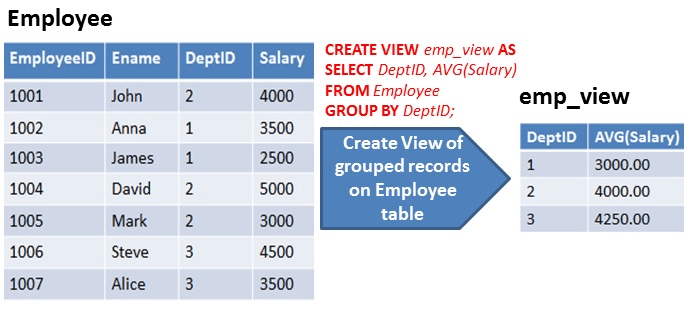
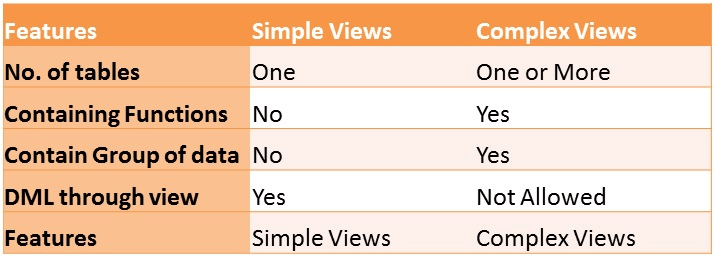
- Simple View: A view based on only a single table, which doesn't contain
GROUP BYclause and any functions. Complex View: A view based on multiple tables, which contain
GROUP BYclause and functions.Inline View: A view based on a subquery in
FROMClause, that subquery creates a temporary table and simplifies the complex query.Materialized View: A view that stores the definition as well as data. It creates replicas of data by storing it physically.
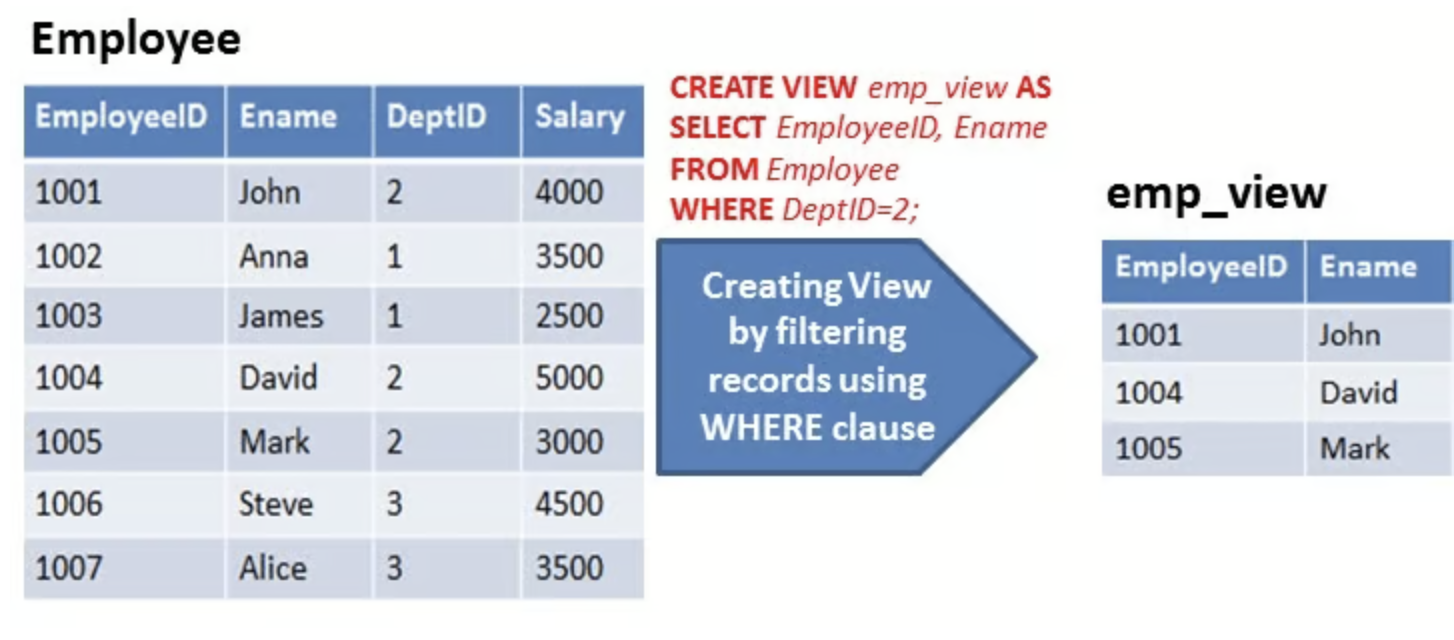
Simple View
Complex View
Inline View
An inline view is a SELECT statement in the FROM clause of another SELECT statement to create a temporary table that could be referenced by the SELECT statement. Inline views are utilized for writing complex SQL queries without join and subqueries operations. This is called a temporary table because a duplicate copy of the data returned by the stored subquery wasn't stored in the database. In Oracle and in the Postgres community, this temporary table is called an inline view. It is referred to as a subselect.

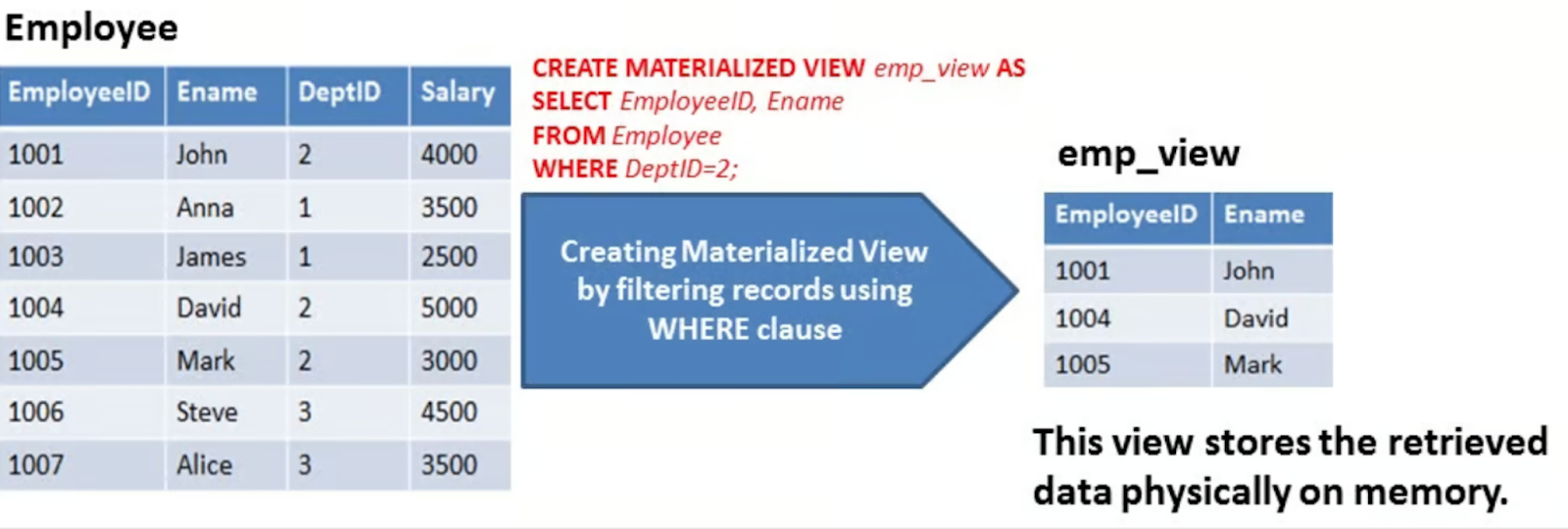
Materialized View
Materialized view replicates the retrieved data physically. This replicated data can be reused without executing the view again. This type of view is also known as "SNAPSHOTS". Materialized view reduce the processing time to regenerate the whole data. It helps remote users to replicate data locally and improve query performance. The challenging part here is to synchronize the changes in materialized views underlying tables.
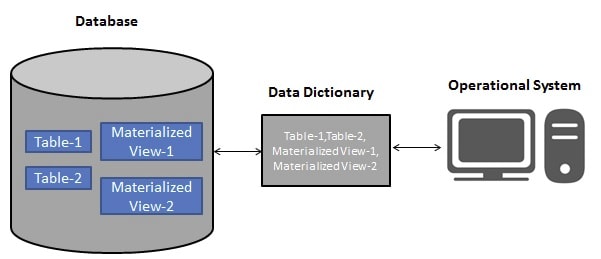
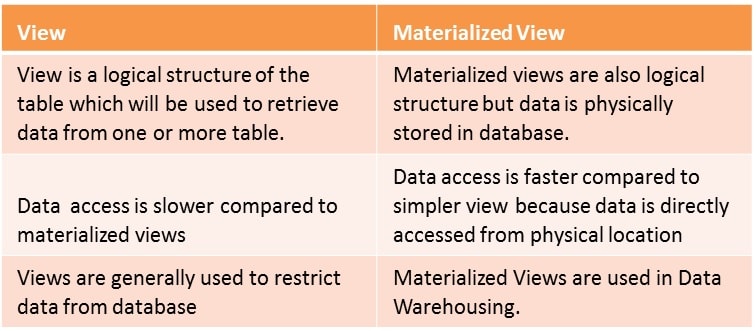
Comparison Between View and Materialized View
Creating and Dropping a view in SQL
View can be created and replaced using CREATE VIEW and REPLACE VIEW.

View can be deleted using DROP VIEW command.

Pros and Cons of Views
Views can be utilized as a subset of actual data to perform certain operations. It helps us to provide an abstraction to various users or hide the complexity for users who are accessing data from the table. For example, a user has permission to access particular columns of data rather than the whole table. It can help us to simplify complex queries into a simpler one. It also simplifies data access from multiple joined tables. It can be used as aggregated tables using group by operations. Views can be used for security purposes or can add extra value from the security point of view. It does not hold any space because it only has the definition in the data dictionary, not the copy of actual data.
Besides the lots of advantages, views also have some disadvantages such as base table structure dependency, computation time, and restrictions Views have a dependency on the table structure. If you change the table structure, then you have to change the view definition associated with it.
Conclusion
Congratulations, you have made it to the end of this tutorial!
In this tutorial, you have covered a lot of details about Views. You have learned what Views are, types of Views, Simple View, Complex View, Inline View, Materialized View, Syntax for creating and dropping views and pros and cons of Views.
Now utilize Views concept to analyze your own datasets. Thanks for reading this tutorial!
If you would like to learn more about SQL, take DataCamp's Introduction to Relational Databases in SQL course.