Track
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers many logging tools designed to help organizations monitor, manage, and secure their cloud infrastructure. There are tools that focus on auditing compliance (CloudTrail), resource metrics (CloudWatch), network logging (VPC Flow), and application logs (X-Ray).
These services give users insight into different portions of their AWS ecosystem and allow users to make informed decisions on managing their services. Of these, AWS CloudTrail and AWS CloudWatch have some of the more “critical” features like compliance and resource monitoring.
These two systems look at different essential needs: CloudTrail focuses on governance, auditing, and compliance, whereas CloudWatch is dedicated to performance monitoring and operational efficiency.
In this article, we’ll delve into the specifics of CloudTrail vs CloudWatch services, explore their use cases, and clarify their key differences to help you understand how to leverage them effectively. For information on some of the other AWS logging and management mechanisms, check out our cheat sheet comparing cloud service components.
Cloud Courses
What is AWS CloudWatch?
AWS CloudWatch is a monitoring service designed to collect and track metrics about resources and applications run on AWS. CloudWatch ensures visibility into system performance and even has alerting features that can notify users of issues. It offers both basic (free) and detailed (paid) monitoring, depending on the AWS service.
AWS CloudWatch Key Features
CloudWatch’s key features include dashboards, metric collection, log monitoring, and alarms. All of these are built around a set of monitoring systems which look at different components of the AWS ecosystem.
1. Metrics collection and tracking
- Monitors metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, disk I/O, and network activity across AWS resources like EC2, RDS, and Lambda.
- Metrics are typically stored in an Amazon EC2 bucket and serve as a metrics repository.
2. Monitoring systems
- A variety of monitoring systems, such as application, network, and infrastructure monitoring.
- Application monitoring focuses on application health, such as latency, availability, and faults.
- Network Monitoring has Internet Monitor and Network Monitor to track both global (Internet) traffic and hybrid (on-prem with cloud) latency and packet loss.
- Infrastructure monitoring can include insights into your containers (Amazon Elastic and Kubernetes) for resource usage such as CPU, memory, and so on. It can also track your AWS Lambda applications for the same metrics.
3. Real-time dashboards
- Provides customizable dashboards for visualizing system performance and trends in real time.
- Can showcase custom applications and metrics of choice
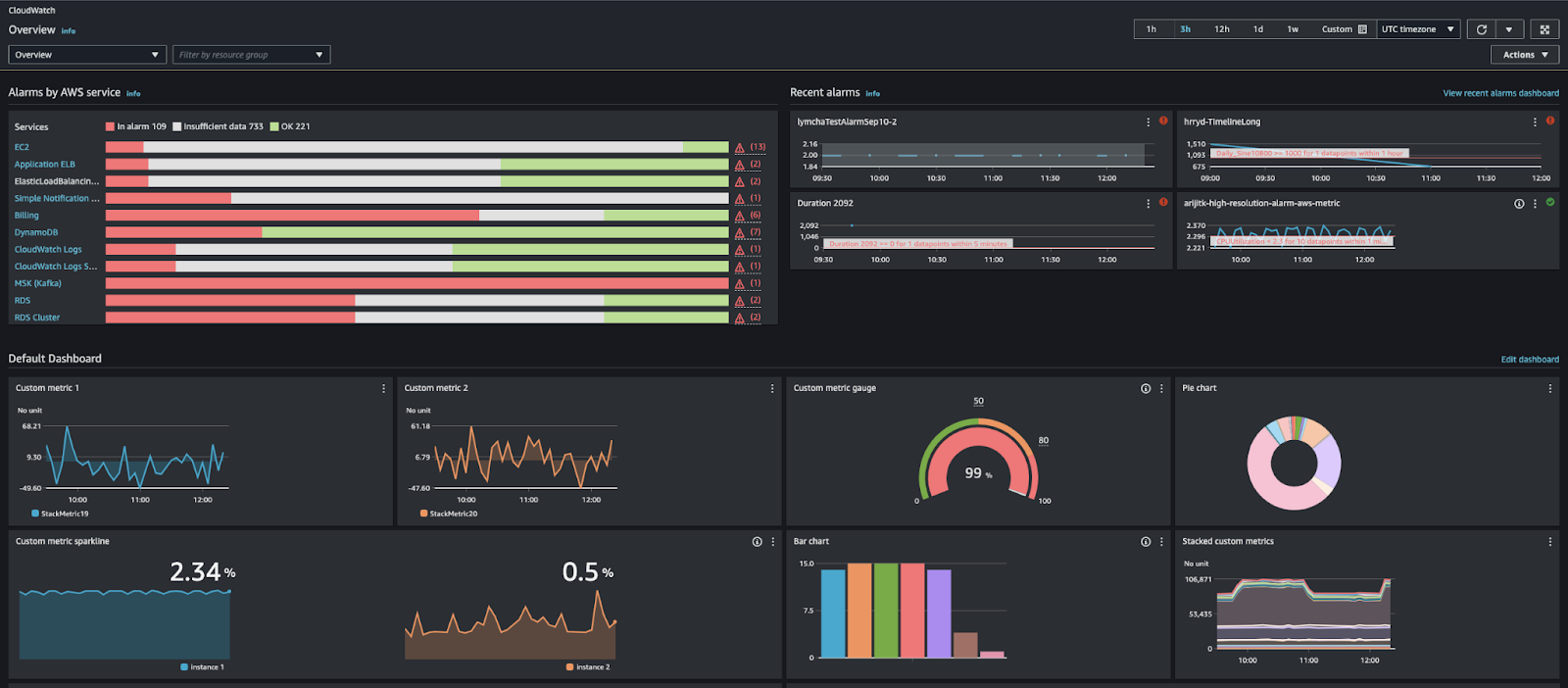
CloudWatch Dashboard: Amazon Documentation
4. Alarms and thresholds
- Sets alarms to detect and respond to anomalies in performance, automatically triggering actions or sending alerts.
- Some actions, including launching more instances or stopping under-used instances.
AWS CloudWatch Use Cases
Let’s look at a few specific use cases for AWS CloudWatch.
Performance optimization
AWS CloudWatch helps identify bottlenecks and optimize resource usage. For instance, Internet Monitor can detect latency issues on a global cloud gaming platform and recommend deploying servers in more optimal regions to reduce lag.
Automated alert
Set up alarms based on predefined thresholds for resource scaling or error detection. For example, when Service Level Objectives (SLOs) for an application are not met, CloudWatch can send alerts and offer actionable recommendations to enhance performance metrics.
Continuous visibility
Use dashboards to maintain real-time insights into system health. Dashboards are particularly useful for tracking the performance of data streams from services like AWS Kinesis and AWS Lambda. A great way to understand this process is this course on Streaming Data with AWS Kinesis and Lambda which has you ultimately build dashboards with AWS CloudWatch.
AWS Cloud Practitioner
What is AWS CloudTrail?
AWS CloudTrail is a logging service designed to track all API activity in your AWS account, ensuring accountability. It records user actions, resource changes, and service interactions, providing an immutable audit trail for governance and compliance purposes. This is particularly useful for security compliance and auditing user behavior. If you want to learn more, check out this course on AWS Security and Cost Management.
AWS CloudTrail Key Features
The key CloudTrail features revolve around monitoring user activity. Since the goal of CloudTrail is to maintain accountability and auditing ability, it makes sense that all actions will be monitored and stored.
1. Action tracking
CloudTrail logs all user actions, and this comprehensive tracking is critical for understanding the "who, what, and when" of your AWS environment.
2. Compliance support
Helps organizations meet regulatory requirements like PCI DSS and HIPAA by maintaining event history records.
In the event of violations, it can be used to track the exact timing and user account involved in the violation.
4. Integration with AWS services
CloudTrail can send logs to S3 for long-term storage or to Amazon Athena for querying and analysis. These integrations make it easier to analyze trends or investigate anomalies.
Example of CloudTrail Logs: AWS CloudTrail Blog
AWS CloudTrail Use Cases
There are a few key use cases for AWS CloudTrail that circle around audits and compliance tracking.
Security audits
CloudTrail enables detailed auditing to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and internal policies. In the event of a security incident, CloudTrail logs provide the details needed to identify the root cause and assess the impact.
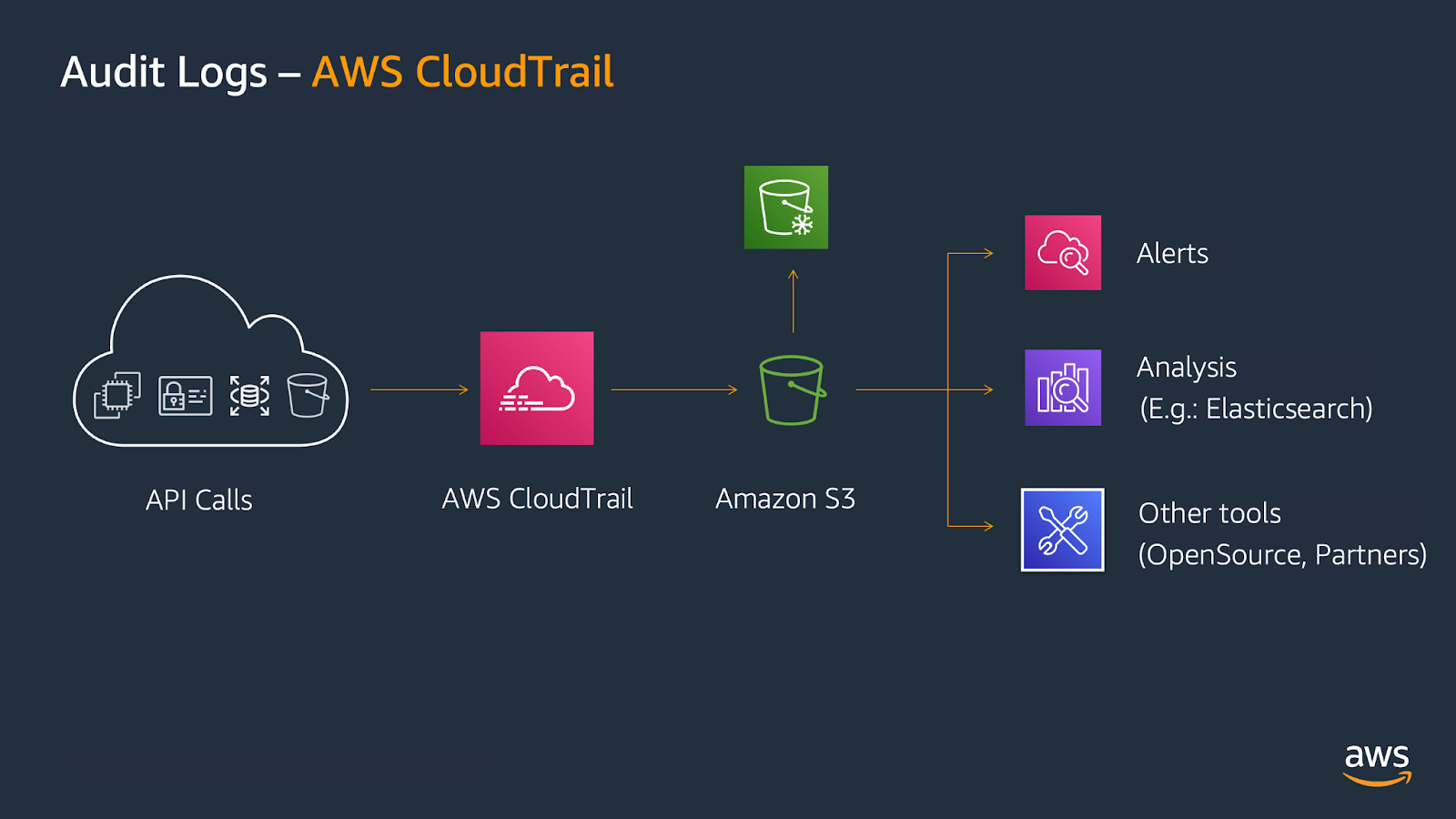
CloudTrail Audit Logs: AWS Security Maturity Model
Change troubleshooting
By reviewing logs, teams can trace changes to resources that might have caused unexpected behavior. This allows for a more straightforward way to solve any future downstream issues.
CloudTrail vs. CloudWatch: Key Differences
As stated previously, both CloudTrail and CloudWatch are fundamental logging tools in the AWS environment. However, both of these look at different components of the AWS environment and this section will cover those key differences from focus to cost.
Focus
CloudWatch and CloudTrail focus on different parts of the AWS environment.
- CloudWatch: Monitors resource performance and operational health. The goal here is to understand how AWS components are running and whether or not there are issues with latency, customer interaction, or resource limitations.
- CloudTrail: Tracks API activity for governance and compliance. The goal here is to maintain a clear “paper trail” for accountability.
Data Latency
CloudWatch has nearly zero latency, whereas CloudTrail has some latency.
- CloudWatch: Provides near real-time insights, with metrics updated as frequently as every minute. It is critical to have real-time insights as CloudWatch needs to be able to provide instantaneous alerting or make changes to resources as needed.
- CloudTrail: Logs API activity with a delay of a few minutes, focusing on historical analysis. Since the logs are generally used to look at historical actions, a lag of a few minutes is acceptable.
Integration
Both integrate seamlessly with AWS services like Lambda, S3, and SNS.
- CloudWatch: Best for operational monitoring and automated responses to performance metrics. It can also integrate with containers like Kubernetes, EC2 storage, and other applications for more detailed logging for particular use cases.
- CloudTrail: Ideal for security auditing and tracking user activities. It will integrate with EC2 storage for logging storage.
Cost
Both have a cost-free basic logging but offer advanced logging at a cost.
- CloudWatch: Basic logging of resource usage, faults, and issues is generally free. More detailed logging has costs based on the volume of metrics collected, alarms set, and complexity of data stored. Different applications have varying levels of logging detail.
- CloudTrail: Management event logging is free, but logging data events and advanced analysis incurs additional charges.
Logging Data
How logs are collected and stored differs between the two tools based on their unique use cases.
- CloudWatch: Data is provided in real-time, but can be aggregated based on timeframes. Since exact detail may not be necessary, the data provided is generally summarized at the timescale it was collected.
- CloudTrail: With the goal of providing accurate and detailed audit trails, it does not aggregate activity. Instead, it provides information on every action that was taken to create a clear outline of actions.
Key Difference Summary
Here is a table summarizing the key differences.
|
Feature |
AWS CloudWatch |
AWS CloudTrail |
|
Primary Purpose |
Monitor resource performance and operational health. |
Track API activity for governance and auditing. |
|
Focus |
Performance and metrics monitoring. |
Security, compliance, and user activity logging. |
|
Data Latency |
Near real-time (updates every minute). |
Delayed (logs recorded every few minutes). |
|
Log Types |
Real-time application and system logs, aggregated |
Historical API activity logs, not aggregated |
|
Integrations |
SNS, Lambda, Auto Scaling for operational actions. |
S3, Athena, and third-party tools for log analysis. |
|
Use Cases |
Performance optimization, automated alerts, dashboards. |
Security audits, forensic analysis, compliance. |
|
Cost |
Charges based on metrics, alarms, and log storage. |
Free for management events, additional charges for data events. |
CloudTrail vs. CloudWatch vs. AWS Config
While CloudTrail and CloudWatch handle logging and monitoring, AWS Config focuses on tracking configuration changes to AWS resources. This makes it useful for understanding how the current configuration is impacting your AWS resources. AWS Config itself is not a logging tool, but rather helps you understand how changes have impacted your AWS resource management.
- CloudTrail: Logs API activity for security and auditing to meet compliance standards
- CloudWatch: Monitors the performance of AWS resources and can be used for alarms
- AWS Config: Ensures configuration changes stay within bounds and can showcase how changes impacted resources.
Conclusion: When to Use CloudTrail and CloudWatch
For AWS users, the choice between CloudTrail and CloudWatch boils down to their goal. Use CloudWatch if you need to monitor system performance, track operational metrics, and automate responses to anomalies. Use CloudTrail if your focus is on security, compliance, or auditing user activities.
Understanding which tool to use is critical for comprehensive monitoring, logging, and maintaining AWS infrastructure. If you want to learn more about AWS and how these tools work, check out some resources:
CloudTrail vs CloudWatch FAQs
Can AWS CloudTrail and AWS CloudWatch be used together?
Yes. For example, you can configure CloudTrail logs to trigger alarms in CloudWatch when specific events occur, such as unauthorized API calls or changes to critical resources. This integration helps bridge the gap between performance monitoring and security auditing.
Does CloudWatch automatically collect metrics for all AWS services?
CloudWatch collects basic metrics for many AWS services by default, such as EC2 instance CPU usage or Lambda invocation counts. However, for detailed metrics, you may need to enable advanced monitoring features, which may incur additional costs.
How long are CloudTrail logs retained, and can they be stored for longer periods?
By default, CloudTrail retains logs for 90 days in the event history. However, you can configure CloudTrail to deliver logs to an Amazon S3 bucket for long-term storage. This is useful for compliance and forensic investigations.
How can I reduce costs associated with CloudWatch logs?
To minimize CloudWatch log costs, you can use log filters to only retain necessary logs, set up log retention policies to delete old logs automatically, and compress and export logs to Amazon S3 for long-term storage.
Is there a way to analyze CloudWatch metrics or CloudTrail logs without downloading them?
CloudWatch: Metrics can be analyzed directly in the CloudWatch console using dashboards, alarms, and metric math. Logs can be queried using CloudWatch Logs Insights.
CloudTrail: Logs can be analyzed using Amazon Athena without needing to download them. By storing CloudTrail logs in an S3 bucket, you can use SQL queries in Athena to extract insights quickly.
I am a data scientist with experience in spatial analysis, machine learning, and data pipelines. I have worked with GCP, Hadoop, Hive, Snowflake, Airflow, and other data science/engineering processes.


