Even though the data.frame object is one of the core objects to hold data in R, you'll find that it's not really efficient when you're working with time series data. You'll find yourself wanting a more flexible time series class in R that offers a variety of methods to manipulate your data.
xts or the Extensible Time Series is one of such packages that offers such a time series object. It's a powerful R package that provides an extensible time series class, enabling uniform handling of many R time series classes by extending zoo, which is the package that is the creator for an S3 class of indexed totally ordered observations which includes irregular time series.
xts has a lot to offer to make your time series analysis fast and mistake free, but it can take some time to get used to it.
This xts cheat sheet provides you not only with an overview of the xts object, how to create and inspect them, but also goes deeper into how you can manipulate time series with xts: you'll see how to replace and update values, how to select, index and subset your objects, how to handle missing values and how to perform arithmetic operations.
Click on the button below to see (and download) the xts cheat sheet:
Have this cheat sheet at your fingertips
Download PDFThis cheat sheet will help you to get yourself up to speed in no time!
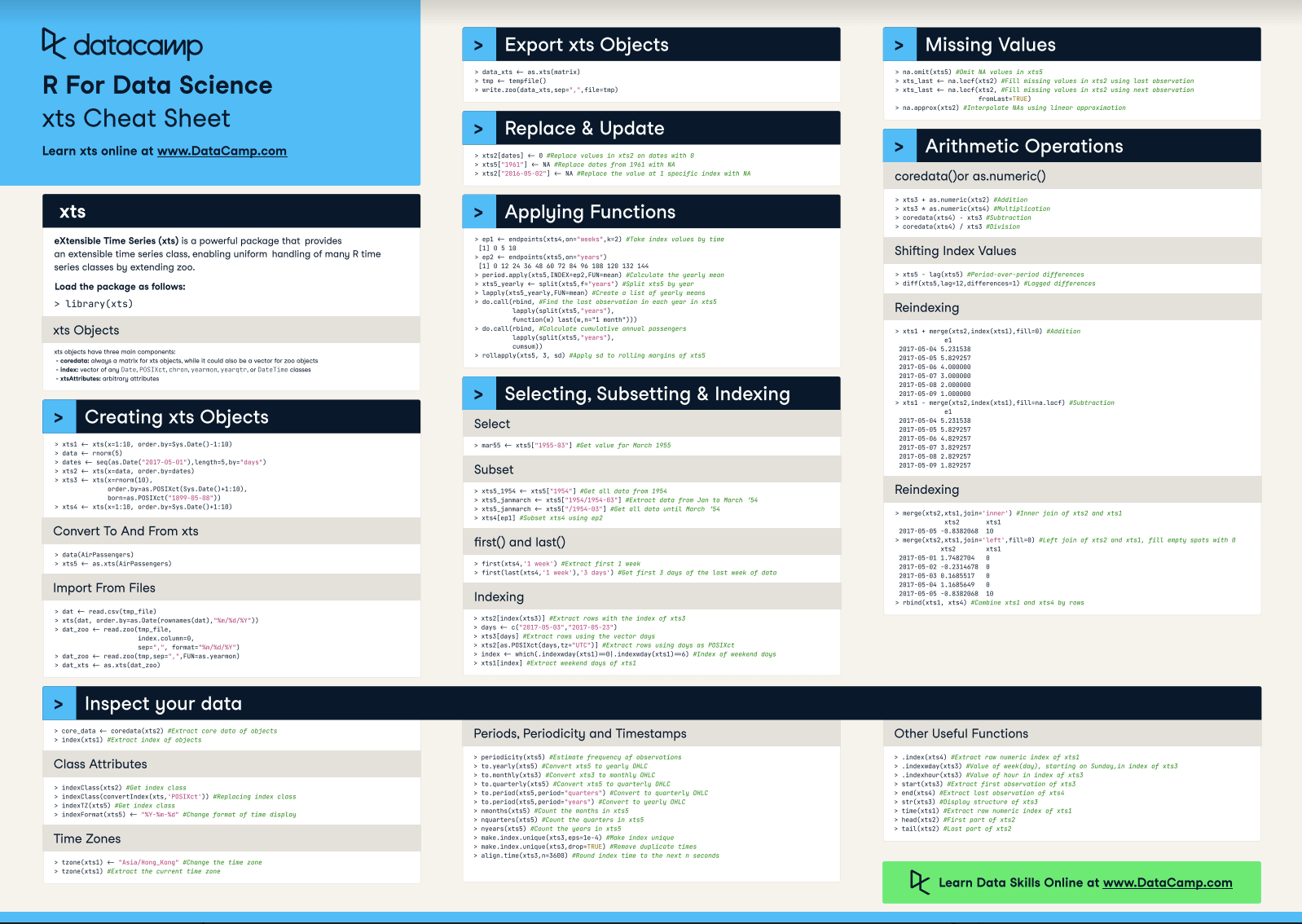
R For Data Science Cheat Sheet: xts
eXtensible Time Series (xts) is a powerful package that provides an extensible time series class, enabling uniform handling of many R time series classes by extending zoo.
Load the package as follows:
library(xts)Xts Objects
xts objects have three main components:
- coredata: always a matrix for xts objects
- index: vector of any Date, POSIXct, chron, yearmon, yearqtr, or DateTime classes
- xtsAttributes: arbitrary attributes
Creating xts Objects
xts1 <- xts(x=1:10, order.by=Sys.Date()-1:10)
data <- rnorm(5)
dates <- seq(as.Date("2017-05-01"), length=5, by="days")
xts2 <- xts(x=data, order.by=dates)
xts3 <- xts(x=rnorm(10), order.by=as.POSIXct(Sys.Date()+1:10), born=as.POSIXct("1899-05-08")
xts4 <- xts(x=1:10, order.by=Sys.Date()+1:10)Convert To And From xts
data(AirPassengers)
xts5 <- as.xts(AirPassengers)Import From Files
dat <- read.csv(tmp_file)
xts(dat, order.by=as.Date(rownames(dat),"%m/%d/%Y"))
dat_zoo <- read.zoo(tmp_file, index.column=0, sep=",", format="%m/%d/%Y")
dat_zoo <- read.zoo(tmp,sep=",",FUN=as.yearmon)
dat_xts <- as.xts(dat_zoo)Inspect Your Data
Extract core data of objects
core_data <- coredata(xts2)Extract index from objects
index(xts1)Class Attributes
Get index class
indexClass(xts2)Replacing index class
indexClass(convertIndex(xts,'POSIXct'))Get index class
indexTZ(xts5)Change format of time display
indexFormat(xts5) <- "%Y-%m-%d"Time Zones
Change the time zone
tzone(xts1) <- "Asia/Hong_Kong"Extract the current time zone
tzone(xts1)Periods, Periodicity & Timestamps
Estimate frequency of observations
periodicity(xts5)Convert xts5 to yearly OHLC
to.yearly(xts5)Convert xts3 to monthly OHLC
to.monthly(xts3)Convert xts5 to quarterly OHLC
to.quarterly(xts5)Convert to quarterly OHLC
to.period(xts5,period="quarters")Convert to yearly OHLC
to.period(xts5,period="years")Count the months in xts5
nmonths(xts5)Count the quarters in xts5
nquarters(xts5)Count the years in xts5
nyears(xts5)Make index unique
make.index.unique(xts3,eps=1e-4)Remove duplicate times
make.index.unique(xts3,drop=TRUE)Round index time to the next n seconds
align.time(xts3, n=3600)Other Useful Functions
Extract raw numeric index of xts1
.index(xts4)value of weekday in index of xts3
.indexwday(xts3)Value of hour in index of xts3
.indexhour(xts3)Extract first observation of xts3
start(xts3)Extract last observation of xts4
end(xts4)Display structure of xts3
str(xts3)Extract raw numeric index of xts1
time(xts1)First part of xts2
head(xts2)Last part of xts2
tail(xts2)Export xts Objects
data_xts <- as.xts(matrix)
tmp <- tempfile()
write.zoo(data_xts,sep=",",file=tmp)Replace & Update
Replace values in xts2 on dates with 0
xts2[dates] <- 0 Replace dates from 1961 with NA
xts5["1961"] <- NAReplace the value at 1 specific index with NA
xts2["2016-05-02"] <- NA Applying Functions
Locate endpoints by time
ep1 <- endpoints(xts4,on="weeks",k=2)
ep2 <- endpoints(xts5,on="years")Calculate the yearly mean
period.apply(xts5,INDEX=ep2,FUN=mean)Split xts5 by year
xts5_yearly <- split(xts5,f="years")Create a list of yearly means
lapply(xts5_yearly,FUN=mean) Find the last observation in each year in xts5
do.call(rbind, lapply(split(xts5,"years"), function(w) last(w,n="1 month")))Calculate cumulative annual passengers
do.call(rbind, lapply(split(xts5,"years"), cumsum))Apply standard deviation to rolling margins of xts5
rollapply(xts5, 3, sd) Selecting, Subsetting & Indexing
Select
mar55 <- xts5["1955-03"] #Get value for March 1955Subset
Get all data from 1954
xts5_1954 <- xts5["1954"] Extract data from Jan to March ‘54
xts5_janmarch <- xts5["1954/1954-03"]Get all data until March ‘54
xts5_janmarch <- xts5["/1954-03"] Subset xts4 using ep2
xts4[ep1]first() and last()
first(xts4,'1 week') #Extract first 1 week
first(last(xts4,'1 week'),'3 days') #Get first 3 days of the last week of dataIndexing
Extract rows with the index of xts3
xts2[index(xts3)] Extract rows using the vector days
days <- c("2017-05-03","2017-05-23")
xts3[days]Extract rows using days as POSIXct
xts2[as.POSIXct(days,tz="UTC")] Index of weekend days
index<-which(.indexwday(xts1)==0|.indexwday(xts1)==6) Extract weekend days of xts1
xts1[index]Missing Values
Omit NA values in xts5
na.omit(xts5)Fill missing values in xts2 using last observation
xts_last <- na.locf(xts2)Fill missing values in xts2 using next observation
xts_last <- na.locf(xts2, fromLast=TRUE)Interpolate NAs
na.approx(xts2) Arithmetic Operations
coredata() or as.numeric()
xts3 + as.numeric(xts2) #Addition
xts3 * as.numeric(xts4) #Multiplication
coredata(xts4) - xts3 #Subtraction
coredata(xts4) / xts3 #DivisionShifting Index Values
Period-over-period differences
xts5 - lag(xts5)Lagged differences
diff(xts5,lag=12,differences=1) Reindexing
xts1 + merge(xts2,index(xts1),fill=0) #Addition
xts1 - merge(xts2,index(xts1),fill=na.locf) #SubtractionMerging
merge(xts2,xts1,join='inner') # Inner join of xts2 and xts1
merge(xts2,xts1,join='left',fill=0) #Left join of xts2 and xts1,
rbind(xts1, xts4)Going Further
Want to know more about xts? Check out DataCamp's Manipulating Time Series Data in R with xts & zoo course!