Course
Pesky blank cells that can throw off your calculations or reporting. It's a common problem, so there's a solution. Enter,COUNTBLANK().
COUNTBLANK() allows you to count the number of empty cells in any given range, making the data cleanup process much easier.
Below, I'll walk through how COUNTBLANK() works, show the common uses, and share some tips from experience.
What Does Excel COUNTBLANK() Do?
Let's see exactly how COUNTBLANK() identifies empty cells.
COUNTBLANK() counts the number of empty cells within a specified range. It focuses solely on cells that are truly blank. If there's nothing in the cell (nothing at all), then it gets counted.
Important: The function ignores cells that appear empty but actually contain invisible characters (such as spaces) or formulas that return an empty string, like this: "".
Here's the syntax you'll use:
=COUNTBLANK(range) Where range is the group of cells you want to check.
For example, if you want to count empty cells in A1 through A10, you'd use:
=COUNTBLANK(A1:A10)Excel will return the number of truly empty cells in that range. This is a really helpful way to really quickly assess the extent of missing data.
Common Uses for Excel COUNTBLANK()
You might be wondering how COUNTBLANK() can make the biggest impact in your day-to-day
You'll find COUNTBLANK() especially useful when you need to:
- Identify missing entries in surveys or forms
- Audit spreadsheets for incomplete records
- Prepare data by flagging gaps
- Track progress in checklists
But really, the uses are too common to fully document.
What We Mean By "Blanks"
Let's spend more time so we really understand exactly what Excel considers "blank." To make use of the function and to make sure we don't enduce mistakes, we have to be careful to differentiate in our own thinking the difference between truly empty cells from those that only look empty.
COUNTBLANK() only counts cells that are completely empty. That means no spaces, no formulas - nothing at all. It's a strict definition that could surprise you.
Here are a few quick examples to illustrate:
-
A cell with a formula like
=""(which returns an empty string) is counted as blank. -
A cell with just a space (
" ") or other invisible characters isn't counted as blank. -
A cell with a formula that returns a visible value (even
0) isn't blank.
If you find that COUNTBLANK() isn't picking up certain cells you think are empty, double-check for hidden characters or underlying formulas that may be creating an illusion.
Two Excel COUNTBLANK() Examples
To put this knowledge into practice, let's walk through two examples.
Counting blanks in a range
Here, I'm using COUNTBLANK() to count blanks in a range.
Suppose you have this data in column B:
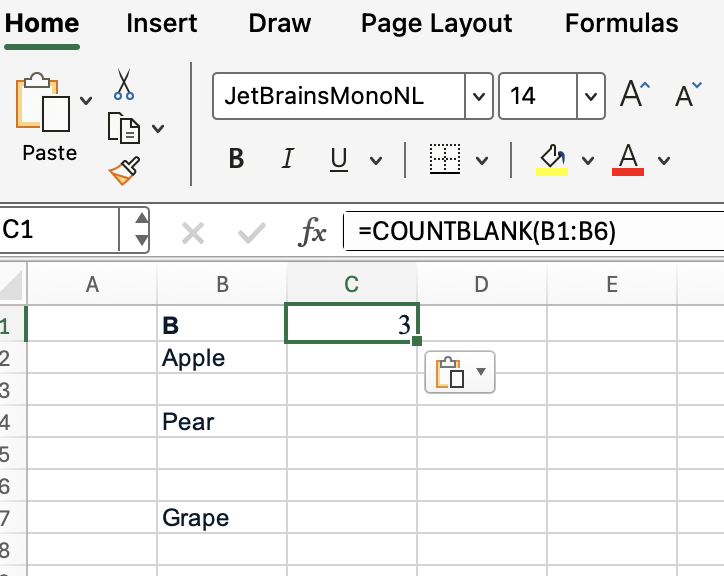
To count the number of truly blank cells in B1:B6, use:
=COUNTBLANK(B1:B6) Excel will return 3, as you can see, since B3, B5, and B6 are completely empty.
Calculating completion rate
For our second example, let's look at tracking task completion.
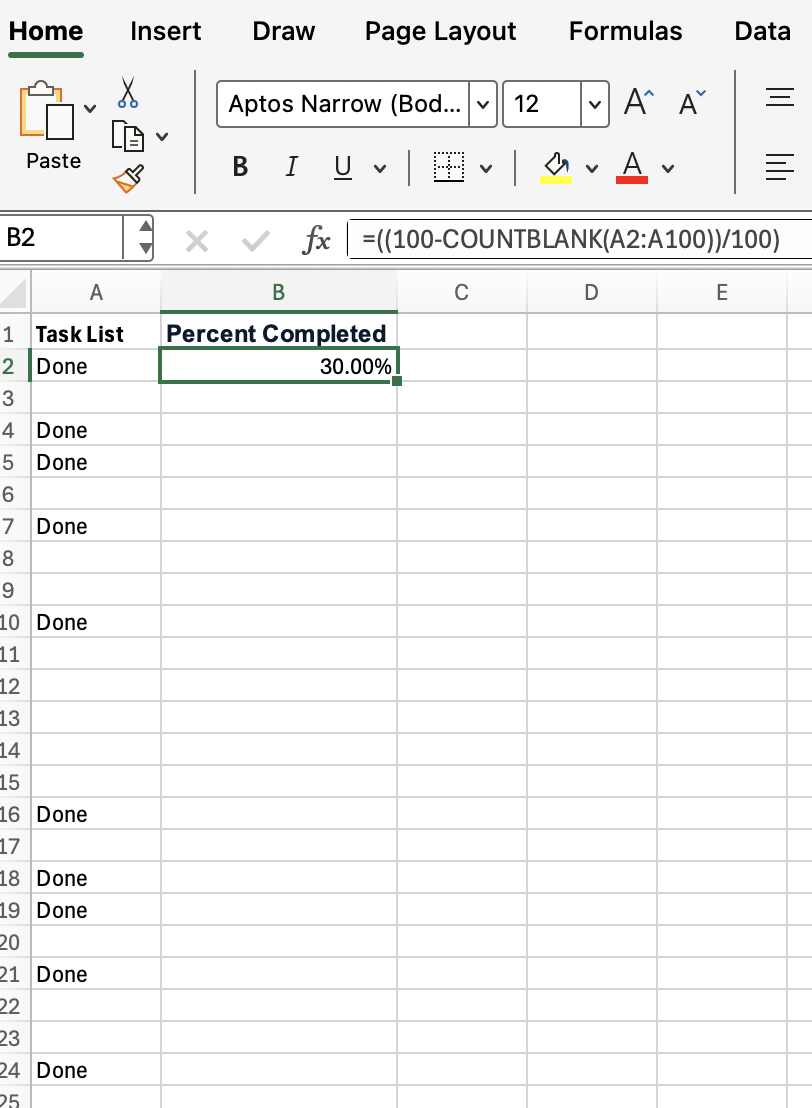
Let’s say you have a list of 100 tasks in column C, with blanks indicating incomplete tasks. To calculate the completion rate, try this approach:
=((100-COUNTBLANK(A2:A100))/100)This formula will give you the percentage of completed tasks so you can monitor progress at a glance.
Excel COUNTBLANK() vs. COUNTA() and COUNTIF()
Let’s see how COUNTBLANK() stacks up against similar functions like COUNTA() and COUNTIF().
-
COUNTA()counts all non-empty cells, including those with numbers, text, or even formulas that return an empty string. -
COUNTIF()can count based on specific criteria, including blanks (using""as the criteria). -
COUNTBLANK()(the subject of our article) is focused only on totally empty cells.
For example, if you want to count cells in range A1:A10 that are not empty, you'd use:
=COUNTA(A1:A10) Or, if you're looking to count cells with a specific value (like "Pending"), you'd use:
=COUNTIF(A1:A10,"Pending") But when your goal is to zero in on blank cells, use COUNTBLANK().
Some Helpful Tips
COUNTBLANK() is supposed to save you time, not waste it. So, here are some tips so you don't have unforeseen trouble:
-
Select a range:
COUNTBLANK()works with any rectangular range, whether that's A1:D10 or just a single row. -
Combine with other functions: To find out how many cells are filled, simply subtract
COUNTBLANK()from the total number of cells in your range. Also, because cells that look blank but contain spaces or formulas might not be counted as empty, you can address this usingTRIM()orCLEAN()to remove unwanted characters. -
Detect gaps in large data sets: Pair
COUNTBLANK()with conditional formatting to visually highlight missing entries and make patterns easier to spot.
Combine these strategies so you can quickly audit your data without trouble.
Limitations and Quirks
While COUNTBLANK() is reliable and straightforward, it does have a few funny behaviors:
-
COUNTBLANK()only works with ranges, not arrays or criteria likeCOUNTIF(). -
COUNTBLANK()can't natively check non-contiguous ranges (like A1:A10, C1:C10 in one formula). In such cases, sum multipleCOUNTBLANK()calls.
Related Excel Functions Worth Knowing
Finally, it's helpful to know about related functions that complement COUNTBLANK(). It's always good to expand your Excel toolkit.
-
ISBLANK(): Checks if a single cell is empty (returnsTRUEorFALSE). Especially handy inIF()statements. -
COUNTIF(): Counts cells based on specific criteria, including blanks or partial matches. -
COUNTA(): Counts all non-empty cells. TRIM()andCLEAN(): Can be used to make sure cells are empty soCOUNTBLANK()works as expected.
Conclusion
I'm sure that in your own work, you will find uses for COUNTBLANK() I didn't think to add as examples. It's a versatile and useful function with lots of uses, and it deserves a spot in your Excel toolkit.
There is a lot more to learn. Take our Advanced Excel Functions course to learn about other interesting things, like referencing and database functions.

I'm a data science writer and editor with contributions to research articles in scientific journals. I'm especially interested in linear algebra, statistics, R, and the like. I also play a fair amount of chess!