Track
Percentiles represent a popular concept and practical method widely used in statistics and having various real-world applications. Because of their usefulness, the great majority of modern programs and programming languages allow easy calculation of percentiles. Microsoft Excel is one such tool.
This tutorial will explore what percentiles are, what they are used for, how to calculate them in Excel, simple examples of such calculations, and possible errors to be aware of when computing percentiles in Excel.
If you need to learn or revise the basics of Excel for impactful data analysis, consider exploring DataCamp’s Introduction to Excel course and Excel Formulas Cheat Sheet.
What Percentiles Are and What They Are Used For?
A percentile, or centile, is a value of a variable of interest at or below (or strictly below) which a defined percent of values of that variable fall. In practice, we usually speak about a k-th percentile, where the value of k defines the percent of values of the variable in interest. A specific case of a k-th percentile is the median of a variable of interest, which is virtually its 50th percentile.
There are two things to note in the above definition:
- Whether we opt for "at or below" or "strictly below" determines if our percentile definition is inclusive or exclusive.
- Despite their name, percentiles are measured in the same units as the variable itself rather than in percent.
To illustrate the concept of percentiles using a simple example, if a movie rating on a movie ranking website falls within the 87th percentile, this means that the movie was ranked better than 87% of all the films on that website.
Percentiles are extensively used in statistical analysis, test score reporting, threshold identification, and ranking systems.
To refresh your knowledge of the most common descriptive analytics statistical techniques, refer to the Descriptive Statistics Cheat Sheet.
Learn Excel Fundamentals
How to Calculate Percentiles in Excel
Excel offers two main functions for calculating percentiles: PERCENTILE.INC() and PERCENTILE.EXC().
Strictly speaking, there is also the third function—PERCENTILE()—that was used in old versions of the software (Excel 2007 and earlier) and is now kept for compatibility purposes. This old function works in the same way as PERCENTILE.INC().
In this tutorial, we're going to focus on the newer functions—PERCENTILE.INC() and PERCENTILE.EXC().
PERCENTILE.INC() Excel Function
Syntax
PERCENTILE.INC(array, k)
where:
-
array—the array or range of data for which the percentile is calculated, -
k—the percentile value in the range from 0 to 1, inclusive.
Both arguments are required.
The PERCENTILE.INC() function returns the k-th percentile of values in a range, where k is in the range from 0 to 1, including the values 0 and 1. In other words, this function includes the first and last values of the array.
Algorithm
Under the hood, the PERCENTILE.INC() Excel function performs the following steps:
- Sorts the values of the provided array in ascending order.
- Determines the percentile value based on the k argument and the number N of data points in the array using the formula: k(N-1) + 1.
- If the result of the previous step isn't an integer, the algorithm interpolates between the nearest values of the array.
Example
Let's say we want to calculate the 30th percentile for an array of integers from 1 to 10 inclusive, using the PERCENTILE.INC() Excel function. Here is what our formula will look like:
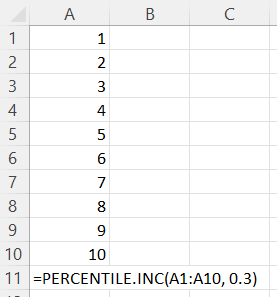
Note: While the values of the above array are sorted for illustrative purposes, we don't actually need to sort the values in advance since the algorithm will do it for us behind the scenes.
Below is the result of our calculation:
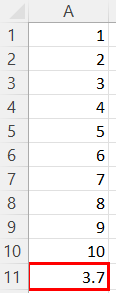
Possible Errors
-
#NUM!— when the provided array is empty, or k < 0, or k > 1. -
#VALUE!—when k is non-numeric.
PERCENTILE.EXC() Excel Function
Syntax
PERCENTILE.EXC(array, k)
where:
-
array—the array or range of data for which the percentile is calculated, -
k—the percentile value in the range from 0 to 1, exclusive.
Both arguments are required.
The PERCENTILE.EXC() function returns the k-th percentile of values in a range, where k is in the range from 0 to 1, excluding the values 0 and 1. More precisely, for an array with N data points, the value of k should satisfy both of the following conditions:
- K > 1/(N+1)
- K < N/(N+1)
Put simply, the PERCENTILE.EXC() function only defines percentiles for probabilities strictly between 0 and 1. This means it does not compute values for the absolute minimum (0th percentile) or maximum (100th percentile), though all data points are still used in interpolation.
Algorithm
Under the hood, the PERCENTILE.EXC() Excel function performs the following steps:
- Sorts the values of the provided array in ascending order.
- Determines the percentile value based on the k argument and the number N of data points in the array using the formula: k(N+1).
- If the result of the previous step isn't an integer, the algorithm interpolates between the nearest values of the array.
Example
Let's say, we want to calculate the 30th percentile for an array of integers from 1 to 10 inclusive, using the PERCENTILE.EXC() Excel function. Here is what our formula will look like:
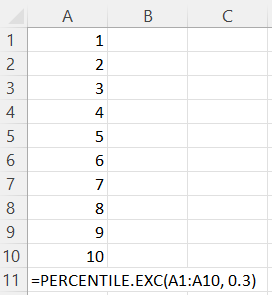
Note: While the values of the above array are sorted for illustrative purposes, we don't actually need to sort the values in advance since the algorithm will do it for us behind the scenes.
Below is the result of our calculation:
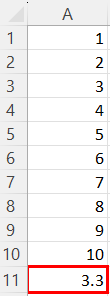
Possible Errors
-
#NUM!— when the provided array is empty, or k <= 1/(N+1), or k >= N/(N+1). -
#VALUE!—when k is non-numeric.
To learn or refresh other popular Excel functions, check out this tutorial: The 15 Basic Excel Formulas Everyone Needs to Know.
PERCENTILE.INC VS. PERCENTILE.EXC in Excel
So far, we can clearly see a lot of similarities between the PERCENTILE.INC() and PERCENTILE.EXC() Excel functions. However, there are also distinct differences between them that make them two separate functions and result in their different outcomes. Let's recap how the PERCENTILE.INC() and PERCENTILE.EXC() functions in Excel are similar and how they differ.
Similarities:
-
Function syntax.
-
Overall algorithm logic (except for the formula used to determine the percentile value).
-
Possible errors (
#NUM!when the array is empty or k is out of its possible range and#VALUE!when k is non-numeric).
Differences:
-
The possible range for the k argument:
-
PERCENTILE.INC()—from 0 to 1, inclusive. -
PERCENTILE.EXC()—from 1/(N+1) to N/(N+1), exclusive. -
Treating the values of an array:
-
PERCENTILE.INC()—includes the first and last values. -
PERCENTILE.EXC()—does not define percentiles at the first and last values (0% and 100%), but still includes all data in its interpolation. -
Formula to determine the percentile value:
-
PERCENTILE.INC()—k(N-1) + 1. -
PERCENTILE.EXC()—k(N+1).
Let's see the PERCENTILE.INC() and PERCENTILE.EXC() Excel functions in action by applying both of them on the same array of integer numbers from 1 to 10 inclusive and playing with different values of k:
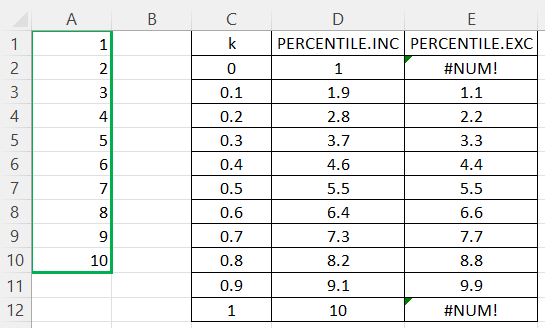
The above table shows that the PERCENTILE.EXC() function is undefined for k values at or beyond its valid range (k ≤ 1/(N+1) or k ≥ N/(N+1)). This isn’t a flaw. It reflects the mathematical definition of exclusive percentiles. The small differences between .INC() and .EXC() results near the extremes arise from how each function interpolates percentile positions.
On the other hand, we should keep in mind that in the predominant majority of cases, too low or too high values of k are of no particular value for us from the standpoint of statistics. These limitations rarely pose an issue in practice. Besides, in real life, we usually need to calculate percentiles for much larger arrays than the one from our example above, which mitigates the outcome differences.
In most cases, it makes more sense to opt for the PERCENTILE.INC() Excel function, which also matches the default formulas used to calculate percentiles in many programming languages, including Python and R.
However, if we want to avoid defining percentiles at the very edges of the dataset, the PERCENTILE.EXC() function is the appropriate choice. It won’t calculate results for the 0th or 100th percentile, but still uses all data points when interpolating between ranks.
It's important to have clean and representative data to extract valuable business insights from it. The Data Preparation in Excel course and Data Manipulation in Excel Cheat Sheet are helpful resources for learning how to efficiently prepare your data for further analysis.
Conclusion
We’ve discussed the essential statistical theory behind percentiles, their definition, the major areas of their application, and the two main functions used for calculating percentiles in Excel, including their syntax, algorithms, calculation examples, and potential errors.
We’ve also compared the two Excel functions, outlined their similarities and important differences, put both functions in action on the same data array to confront the results, and learned the best scenario for each of them.
To unlock the full power of Excel, consider taking a beginner-friendly Excel Fundamentals skill track, which will help you learn, through hands-on exercises, both basic and advanced features and formulas used for data preparation, visualization, and analysis in Excel.
Advance Your Career with Excel
Gain the skills to maximize Excel—no experience required.

IBM Certified Data Scientist (2020), previously Petroleum Geologist/Geomodeler of oil and gas fields worldwide with 12+ years of international work experience. Proficient in Python, R, and SQL. Areas of expertise: data cleaning, data manipulation, data visualization, data analysis, data modeling, statistics, storytelling, machine learning. Extensive experience in managing data science communities and writing/reviewing articles and tutorials on data science and career topics.
