Course
Random numbers play a key role in simulations, sampling, and many other things. If you’re working in Excel and need random numbers, the RANDARRAY() function is the first function you need to know.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to use RANDARRAY() to build dynamic arrays of random numbers and customize them for your needs, whatever they are.
What Is the RANDARRAY() Function in Excel?
The RANDARRAY() function in Excel allows users to generate an array of random numbers. This function is especially useful for simulations, sampling, or whenever you need a set of random values in your worksheet. Like, for example, if you were trying to create stratified random samples to test an experiment in your company, you might use RANDARRAY().
Key Features of Excel’s RANDARRAY()
Before diving into usage, it's important to understand the main features of RANDARRAY() in Excel:
- Generates an array of random numbers
- Allows specification of the number of rows and columns
- Supports setting minimum and maximum values
- Can generate either whole numbers or decimals
- Updates automatically when the worksheet recalculates
Syntax of RANDARRAY()
The syntax for the RANDARRAY() function in Excel is as follows:
=RANDARRAY([rows], [columns], [min], [max], [whole_number])-
[rows]: Number of rows to fill -
[columns]: Number of columns to fill -
[min]: Minimum value (optional) -
[max]: Maximum value (optional) -
[whole_number]:TRUEfor whole numbers,FALSEfor decimals (optional)
How to Use RANDARRAY() in Excel
Now that I mentioned the features and syntax, let's get to the important thing, which is how to use. Just follow these steps:
-
Select the cell where you want the random numbers to start
-
Enter the
RANDARRAY()formula with your desired parameters -
Press Enter to generate the array
For example, to generate a 3x2 array of random whole numbers between 1 and 100:
=RANDARRAY(3, 2, 1, 100, TRUE)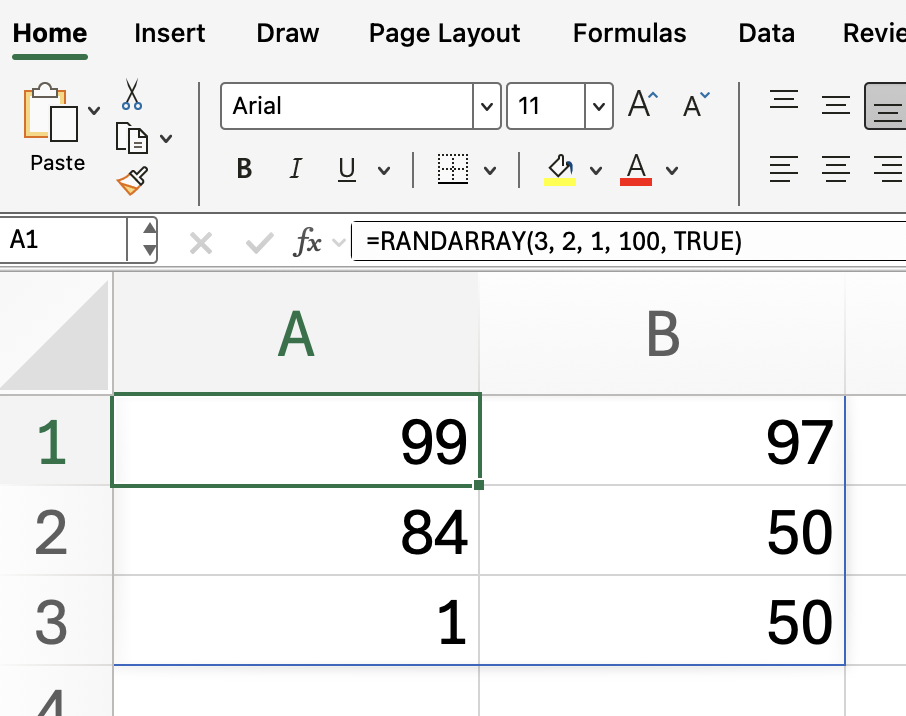
This will fill a 3-row by 2-column range with random integers from 1 to 100.
Customizing Your Random Arrays
You can customize the output of RANDARRAY() in Excel by adjusting its arguments. Here are some common scenarios.
To generate decimals between 0 and 1 in a 5x1 array:
=RANDARRAY(5, 1)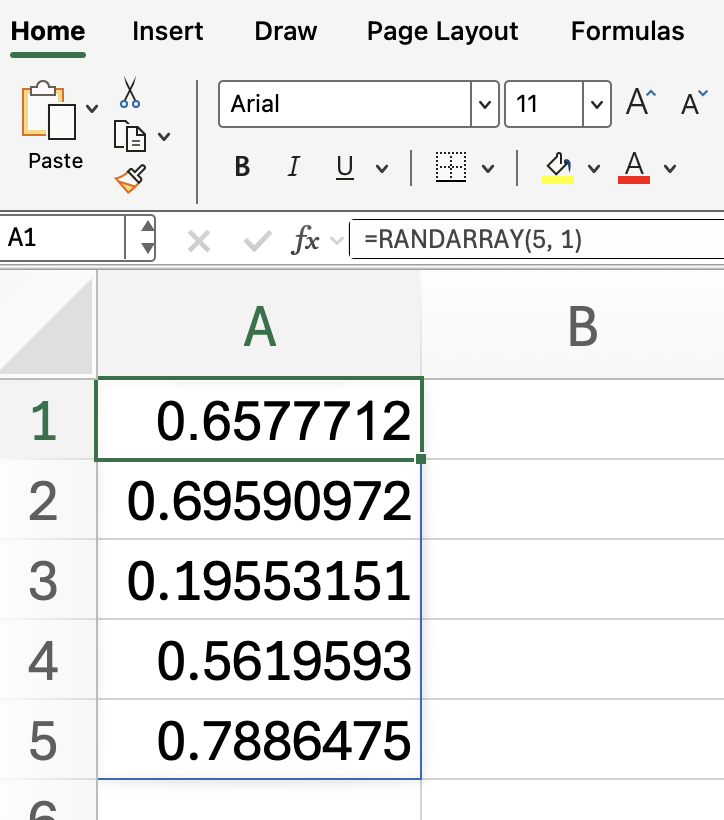
To generate whole numbers between 10 and 50 in a single column with 10 rows:
=RANDARRAY(10, 1, 10, 50, TRUE)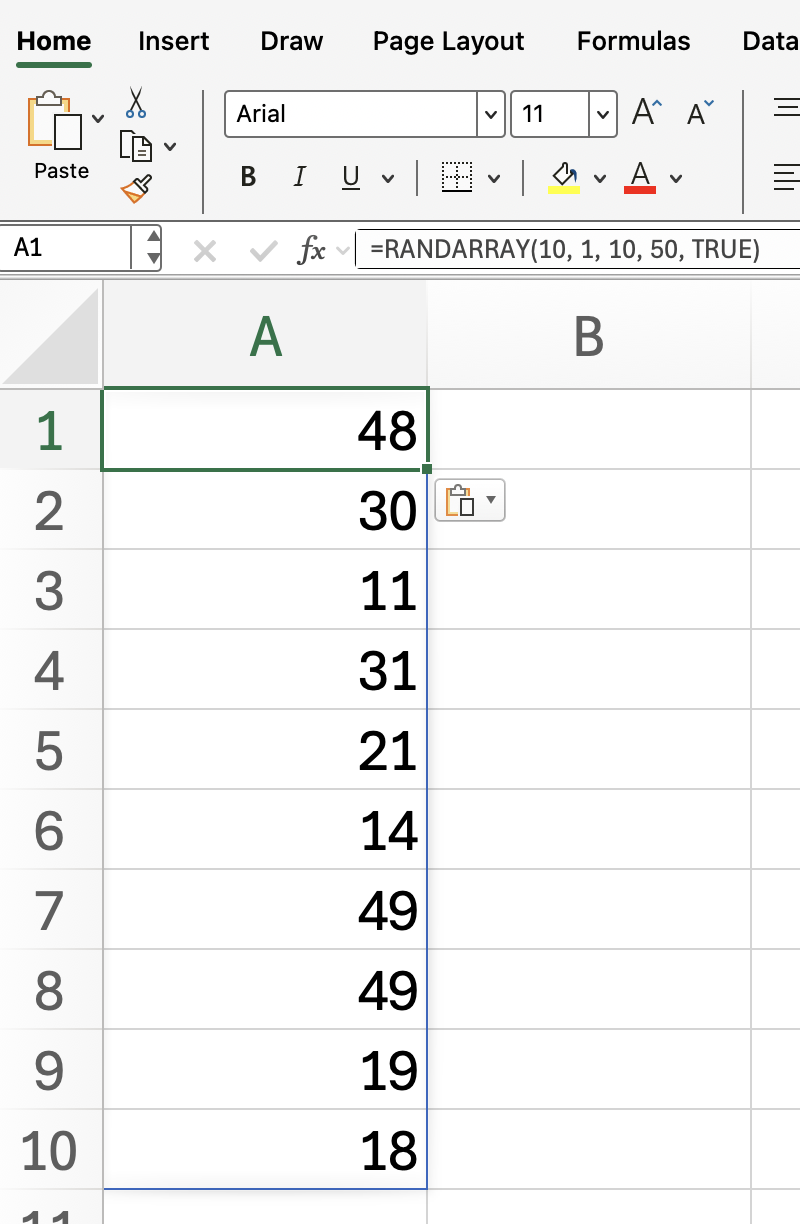
To create a 4x4 grid of random numbers between 100 and 200:
=RANDARRAY(4, 4, 100, 200)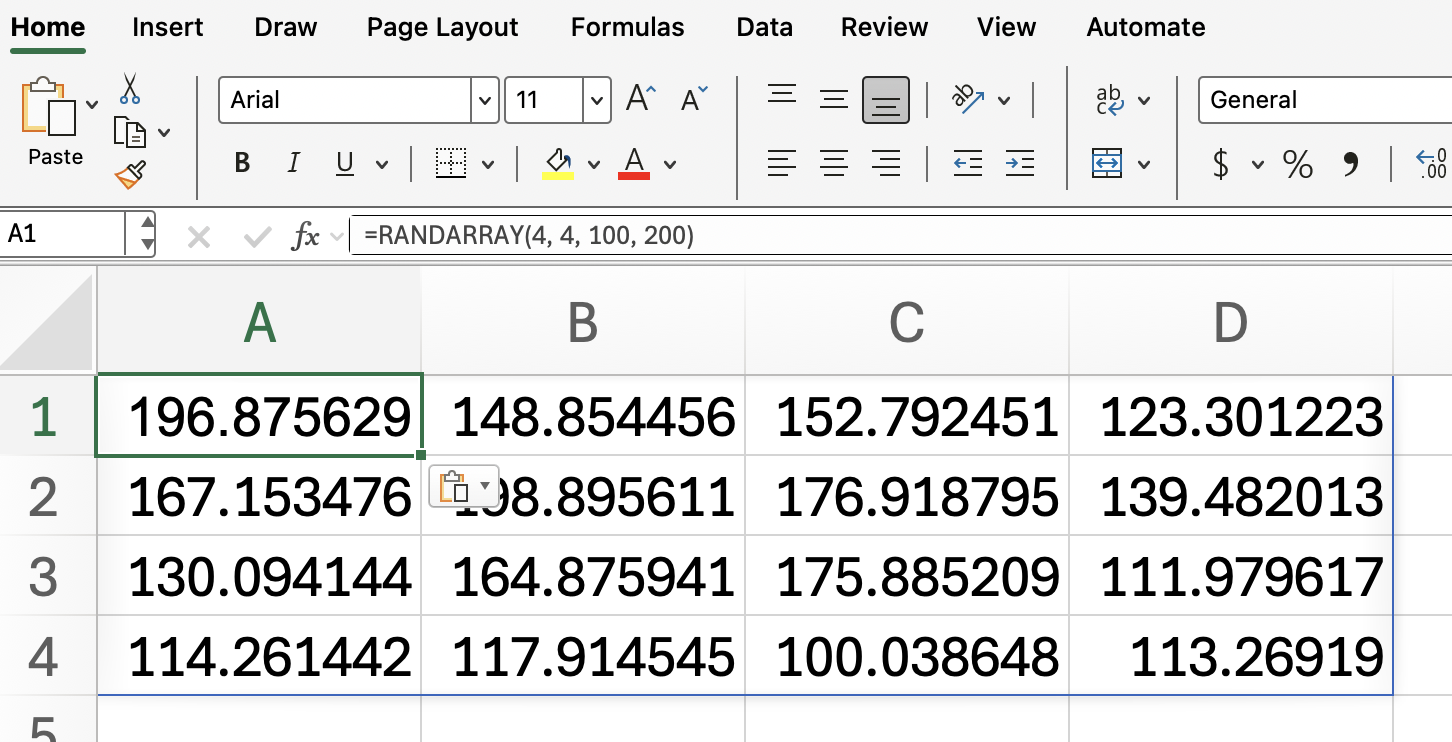
How RANDARRAY() Is Different from Other but Similar Excel Functions
Understanding the differences between RANDARRAY() and other Excel random number functions helps you choose the right tool for your needs.
-
RAND(): Generates a single random decimal between 0 and 1 -
RANDBETWEEN(): Generates a single random integer between two values -
RANDARRAY(): Generates an array of random numbers, with options for size, range, and type
This makes RANDARRAY() the most flexible option when you need multiple random numbers at once.
Tips for Using RANDARRAY() in Excel
When working with RANDARRAY() in Excel, keep these tips in mind:
-
The array updates every time the worksheet recalculates, so values will change unless you copy and paste as values
-
Combine with other functions like
SORT()orUNIQUE()for advanced randomization -
Use the optional arguments to control the type and range of numbers generated
Conclusion
The RANDARRAY() function in Excel is a powerful tool for generating random numbers in a flexible and dynamic way. By understanding its syntax and options, you can quickly create arrays of random values tailored to your needs. Whether for simulations, sampling, or data analysis, RANDARRAY() makes random number generation in Excel easier than ever.
Keep learning with us. Take our Data Analysis in Excel course to keep improving your skills as a data analyst.

I'm a data science writer and editor with contributions to research articles in scientific journals. I'm especially interested in linear algebra, statistics, R, and the like. I also play a fair amount of chess!