Track
Text data forms a significant portion of modern data analysis tasks, spanning from customer reviews to corporate documents. The ability to extract, summarize, translate, and analyze textual information is crucial for making data-driven decisions. Snowflake Cortex AI simplifies text processing by providing a low-to-no-code environment for using AI. This article will cover the fundamental functions of Cortex AI and then provide some practical tips for implementation.
Snowflake Cortex AI itself is a powerful suite of AI and machine learning tools embedded within the Snowflake Data Cloud. It has built-in support for Large Language Model (LLM) functions such as Meta Llama 3 and Mistral Large models.
Snowflake Cortex AI is an excellent way for data practitioners of all levels to get started with AI, as it provides prebuilt AI functions in SQL, does not require an external API, and scales with the Snowflake data infrastructure.
If you are new to Snowflake, I recommend taking the Introduction to Snowflake SQL course.
Understanding Snowflake Cortex AI's Text Processing Functions
Snowflake Cortex AI provides a suite of built-in tools designed to make text processing more efficient. From summarization and translation to sentiment analysis and document parsing, these functions enable users to extract insights from large volumes of text directly within Snowflake. Let’s explore these capabilities and how they can be applied in real-world scenarios.
Large Language Model (LLM) functions
Snowflake Cortex AI provides Large Language Model (LLM) functions to perform various text-related tasks efficiently.
For instance, the COMPLETE function allows users to provide a prompt to a particular model (such as Llama3 or Mistral) and get a response back, similar to how you might use ChatGPT on the web.
You can also use particular functions such as SUMMARIZE and TRANSLATE for a quick and easy way to do specific tasks. These functions make it very easy to quickly perform summarization, translation, and sentiment analysis. If you want to learn more about LLMs in general, check out the LLMs Concepts course.
Document AI
Document AI is Snowflake’s proprietary artificial intelligence feature designed to extract and structure information from unstructured documents. At its core, it leverages Arctic-TILT, Snowflake’s specialized AI model, to analyze text from various document formats and convert it into structured, query-ready data.
With Document AI, users can:
- Upload documents (e.g., PDFs, scanned reports, invoices).
- Ask AI-driven queries to extract relevant information.
- Automate data extraction pipelines to streamline workflows.
While this tool is highly powerful, it currently has some limitations regarding supported file types, document sizes, and processing length. However, for organizations dealing with large volumes of unstructured text—such as legal documents, customer contracts, or financial statements—Document AI offers an efficient way to convert raw text into structured Snowflake databases, making downstream analysis significantly easier.
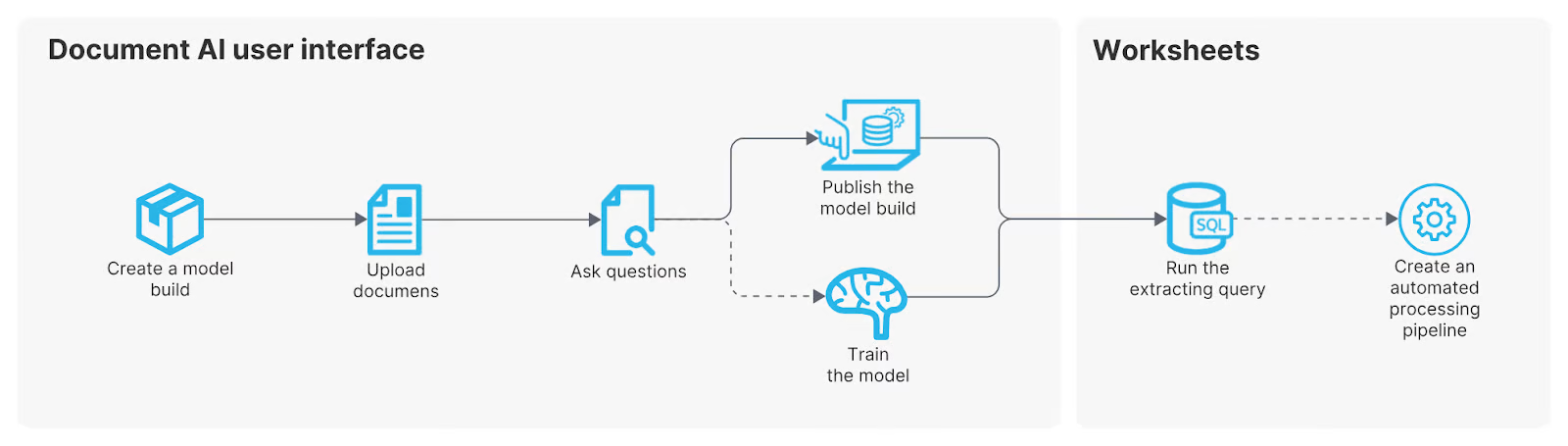
From Snowflake Document AI documentation
Key Text Processing Features in Snowflake Cortex AI
Let’s briefly look at the key features of Snowflake Cortex AI and what they can do. The next section will give a few (simple) steps for using these features.
Text summarization
Text summarization is accomplished using the SUMMARIZE function. In short, it takes a given set of text and quickly provides a summary. For instance, if you were to give it a lengthy article or report, it will provide the salient information for that text.
Text translation
The TRANSLATE function enables seamless language translation. It can take customer feedback or support tickets that were submitted in a foreign language and translate them to English. It supports a multitude of target languages such as English, French, Dutch, German, Japanese, Chinese, and more.
Sentiment analysis
Sentiment analysis discerns the overall emotion or tone of a text. It provides context on whether something is positive, negative, or neutral. Snowflake’s SENTIMENT function returns a numerical value between -1 and 1, with -1 being negative, 1 being positive, and 0 being generally neutral.
Document parsing
Document parsing may be the most complex of the functionality here. It takes a document file that is stored somewhere and extracts information from that document. We can use the PARSE_DOCUMENT function for this.
Implementing Text Processing with Snowflake Cortex AI
Now that we’ve explored Cortex AI’s text processing capabilities, let’s walk through how to put them into action, starting with setting up your environment.
Setting up your environment
There are a few steps to get ready to use Snowflake Cortex AI. Make sure you have the following complete:
- You will need the SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX_USER database user role.
- Your data must be stored in Snowflake-compatible formats.
- You must enable Cortex AI functions in your Snowflake instance.
If you do not have the necessary permissions, make sure you speak with your database administrator (or if you are the administrator, provide yourself with these roles) to get access. Also note that due to your organization’s particular settings, some models may not be available to you.
Practical examples
Let's go over some examples of the key functions of summarization, translation, and sentiment analysis. We will use various sample table names and columns. Assume that the table we are pulling from is any table in your Snowflake database, and the column contains your text information. You will quickly see how easy it can be to run these functions in Snowflake.
Summarizing Text Data
Let's start with a very common task of summarizing a variety of news articles.
-- Assume that the data is in the table ‘articles’
--We want to summarize all the text from all the articles we have in our database
SELECT SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.SUMMARIZE(article_text) AS summary
FROM articles;Translating support tickets
Another common task is translating support tickets that may not all come in your local language. SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.TRANSLATE(text, ‘source language’,’target language’) is the general syntax where the ’source language’ and ’target language’ will be written in a two-letter language code.
If that source language is an empty string ’’ then the language is automatically detected.
/* We select from the table support_tickets
The column ticket_description has all the ticket text
We are going from ‘fr’ to ‘en’ */
SELECT SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.TRANSLATE(ticket_description, 'fr', 'en') FROM support_tickets;
--If we leave the source language as just an empty string ‘’, it will automatically detect the language
SELECT SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.TRANSLATE(ticket_description, '', 'en') FROM support_tickets;Conducting sentiment analysis on customer comments
Lastly, let’s look at our customer sentiment from social media using SENTIMENT.
--Select from the social_media_comments table
--provide the text to the SENTIMENT function.
SELECT SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.SENTIMENT(comment_text) FROM social_media_comments;Best practices and considerations
As with anything AI-related, we must ensure we have a set of best practices and guidelines. Making sure we follow data privacy laws and optimizing our queries will give us the best experience using Snowflake Cortex AI.
Data privacy and security
Data privacy is one of the most critical components, especially when it comes to AI. Thankfully, Snowflake embeds it into your environment. You can utilize Snowflake’s access control framework to help ensure you are following access best practices and regulatory compliance.
- Ensure compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations when processing user data.
- Use role-based access controls (RBAC) to restrict sensitive text processing.
Performance optimization
Unstructured data can be massive. Being smart about how we process the data will minimize both run time and costs. Try these best practices for performance optimization:
- Batch processing: Process text in bulk instead of one row at a time.
- Efficient storage: Store large documents in optimized Snowflake tables.
- Indexing and caching: Use indexing for frequently accessed text data.
Conclusion
Snowflake Cortex AI simplifies text processing by offering built-in AI-powered text functions directly within Snowflake SQL. With its robust capabilities for summarization, translation, sentiment analysis, and document parsing, data practitioners of all levels can extract meaningful insights from text effortlessly.
By leveraging prebuilt AI tools, businesses can unlock valuable information and drive data-driven decisions with ease. If you are curious about learning more about Snowflake and its tooling, try these resources:
Snowflake Cortex AI Text Processing FAQs
Do I need prior AI or machine learning knowledge to use Cortex AI’s text processing functions?
No! Snowflake Cortex AI is designed for users of all skill levels, including those with little to no AI experience.
How accurate are Snowflake Cortex AI’s translation and sentiment analysis functions?
Cortex AI leverages large language models (LLMs) for translation and sentiment analysis, providing high accuracy. However, results may vary based on context, language complexity, and industry-specific jargon. It’s recommended to validate outputs for critical business applications.
Can I integrate Snowflake Cortex AI with other AI services or external tools?
Yes! You can combine Cortex AI functions with Snowpark to build advanced ML workflows or integrate it into Tableau or PowerBI for visualization of the insights.
What are some best practices for using Snowflake Cortex AI efficiently?
- Optimize queries by selecting only necessary text fields.
- Preprocess text data to remove noise before applying AI functions.
- Use caching and indexing for frequently accessed text summaries.
- Monitor query costs to avoid unnecessary compute usage.
I am a data scientist with experience in spatial analysis, machine learning, and data pipelines. I have worked with GCP, Hadoop, Hive, Snowflake, Airflow, and other data science/engineering processes.