Generative AI (Artificial Intelligence) is a topic that has been making a ton of headlines in recent years. What once was limited to research labs and universities is now making its way into domain-specific industries like finance, healthcare, education, eCommerce, and many more. Generative AI refers to a type of artificial intelligence that involves the use of algorithms to generate new data or content.
Tech-savvy businesses, new and old, can gain an advantage over their competitors by learning how to use this innovative technology. As we have all seen in the recent media, we are very much at the forefront of an arms race among companies to integrate artificial intelligence into their platforms. You can learn more about how to bridge this generative AI talent gap in our separate webinar.
Elevate Your Organization's AI Skills
Transform your business by empowering your teams with advanced AI skills through DataCamp for Business. Achieve better insights and efficiency.

Uses of Generative AI
Generative AI is used in a variety of applications. We’ve explored some of the creative uses of generative AI and projects you can build with generative AI models in separate posts. However, here are some of the notable use cases we’re seeing at the moment:
Images
Generative AI can create new images based on existing ones, such as creating a new portrait based on a person’s face or a new landscape based on existing scenery.
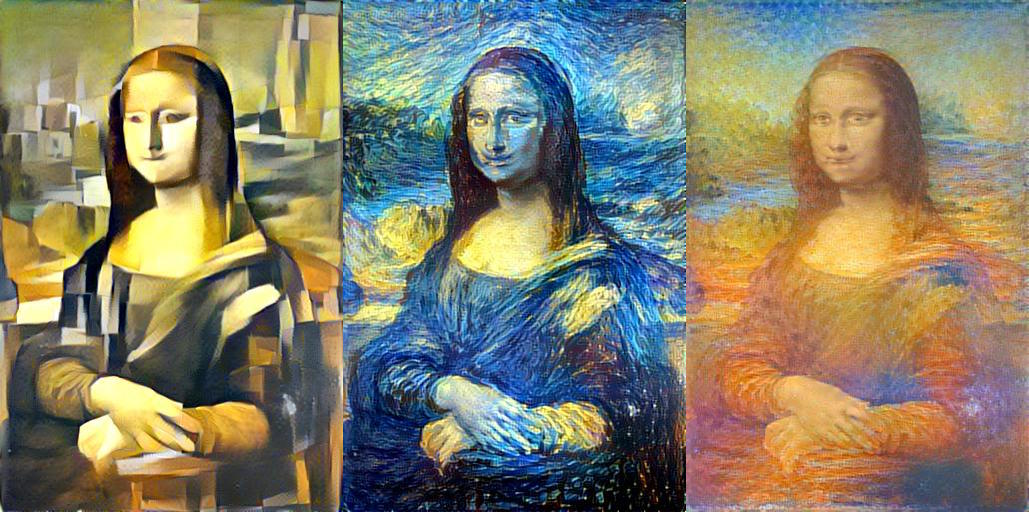

The Mona Lisa in the styles of Picasso, Van Gogh, and Monet
Text
You can use tools like ChatGPT and Google Bard to write news articles, blog posts, poetry, and even scripts.
Audio
You can use it to generate music, sound effects, and even voice acting. Custom audio content for various purposes can be created, from background scores for videos to unique tunes for branding purposes.
Natural language interfaces
It can be used to create interactive and intuitive communication tools, enhancing digital interactions across various platforms.
Image synthesis
Generative AI can create detailed virtual models, enhancing visualization in diverse industries such as retail, real estate, and more.
Space synthesis
This technology can assist in designing virtual environments, proving useful in sectors such as virtual reality, gaming, and online retail.
Product design and object synthesis
Novel designs can be generated based on existing data, opening possibilities in industries like fashion, home decor, and automotive.
Pharmaceuticals
Generative AI can help create virtual models and predict potential pharmaceutical research outcomes, aiding in drug discovery and treatment personalization.
Personalized marketing
Tailored ads or marketing content can be created, boosting the effectiveness of marketing campaigns across platforms.
AI in the workplace
For me, AI is having a massive positive impact on how I work. As an enablement lead at Specsavers, I regularly use AI to troubleshoot, support other users, and generate informative content.
Sure, I was doing all this before our AI friends arrived, but my speed in delivery has dramatically increased, allowing me to support more projects/users & it has become a tool I recommend to all.
In eCommerce, generative AI has become increasingly important as businesses seek ways to personalize the customer experience and improve their operations.
The Basics of Generative AI
It all started with a prompt! Generative AI starts with a prompt that could be in the form of text, an image, a video, a design, musical notes, or any input that the AI system can process. This prompt can be manually input by the user (for example, using GPT-3 to generate text based on the user input) or automated (for example, StyleGAN is a generative adversarial network (GAN) that can generate high-quality images based on a dataset of images.)
There are several types of generative models that are commonly used in machine learning, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Transformer-based models. Here's a brief overview of each type:
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs are a type of neural network that consists of two parts: a generator and a discriminator. The generator handles generating new data, while the discriminator is responsible for deciding whether the data is real or fake. The two parts are trained together in a process known as adversarial training, where the generator tries to produce data that the discriminator cannot distinguish from real data.
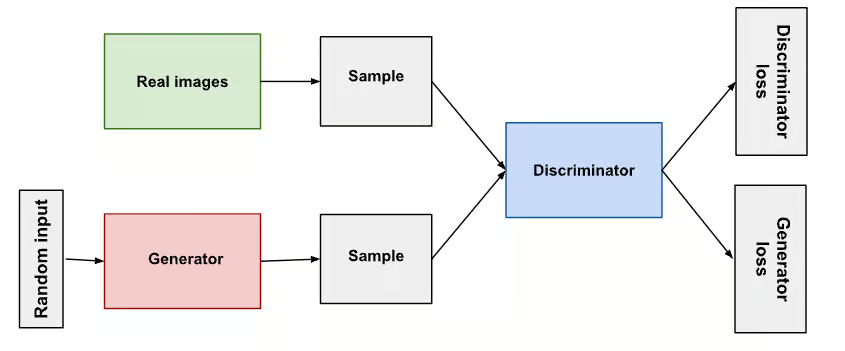
An overview of GAN structure - source
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
VAEs are another type of neural network used for generative modeling. They work by encoding input data into a lower-dimensional space and then decoding it back into the original space. The encoder and decoder are trained together to minimize the difference between the original data and the reconstructed data. You
Transformer-based models
Transformer-based models are commonly used for natural language processing tasks. They work by processing sequences of input data and generating sequences of output data. Transformer-based models are particularly useful for generating text, such as product descriptions or customer reviews.
Training the models
All of these models learn from data to generate new instances. During the training process, the models are fed a large dataset of examples and learn to find patterns and relationships within the data. Once the model has been trained, it can be used to generate new instances by sampling from the learned distribution.
For example, a GAN might be trained on a dataset of images and learn to generate new images similar to the ones in the dataset.
A VAE might be trained on a dataset of faces and learn to generate new faces that are similar to the ones in the dataset.
And a transformer-based model might be trained on a dataset of product descriptions and learn to generate new descriptions that are similar in style and content to the ones in the dataset.
Overall, these generative models are powerful tools for generating new content and data, and they are widely used in a variety of applications.
Generative AI in eCommerce
Generative AI has many applications in eCommerce, and businesses are using it to personalize the customer experience, improve their operations, and increase sales. Here are some of the areas in which eCommerce organizations are using generative AI:
Product recommendations
One of the most common applications of generative AI in eCommerce is product recommendations. Businesses can use generative models to analyze customer data and generate personalized recommendations for each customer. For example, Amazon uses generative AI to generate personalized product recommendations for its customers based on their browsing and purchase history.
Personalization
Generative AI can also be used to personalize the customer experience in other ways, such as by generating personalized content or customizing the user interface. For example, a business might use generative AI to generate personalized product descriptions or to customize the layout of its website based on each customer's preferences.
Customer engagement
Customer engagement can also be improved by creating virtual assistants and chatbots that can provide personalized support and recommendations. For example, a business might use generative AI to create a chatbot that can answer common business-related questions like requesting access to a system or requesting annual leave.
Content generation
AI can be used to generate a wide range of content for eCommerce businesses, including product descriptions, reviews, and ads. Check out the DataCamp article on how to use ChatGPT for sales to learn more about using generative AI for content generation.
Generative AI in eCommerce Case Studies
Several eCommerce businesses have successfully implemented generative AI to improve their operations.
Some quick-fire examples include:
- Amazon uses Generative AI to personalize content for its customers.
- Shopify recently launched Shopify Magic to help sellers save time, sell more, and get products in front of even more shoppers.
- eBay is using Generative AI to power its Smart Store, which helps sellers create a personalised shopping experience for their users.
- Etsy is using Generative AI to unlock the future of B2B Commerce in Emerging Markets.
Let’s look at a couple in more detail:
Amazon
First on the list, and I'm sure no surprise to anyone reading, Amazon is getting involved with generative AI. Amazon uses generative AI to generate personalized product recommendations for its customers visiting the site. On top of this, rather than release chatbots like its nearest rivals at Microsoft (ChatGPT) and Google (bard), they have taken a different angle by utilizing its dominance in the cloud space via AWS (Amazon Web Services) to release two new AI language models on its platform, Bedrock.
Bedrock will allow customers to use Amazon's machine learning models without their data being leaked back into the wider pool of information used to train those systems. This should address one key concern for organizations that want to build their own generative AI products.
Alibaba Group
The Alibaba Group has recently unveiled its generative AI model named Tongyi Qianwen, truth from a thousand questions, which will be integrated into all of the company’s apps in the near future.
The model can be used to summarise meeting notes, write emails and draft business proposals. It will also be added to Tmall Genie, Alibaba’s voice assistant.
The technology “will bring about big changes to the way we produce, the way we work and the way we live our lives,” according to CEO Daniel Zhang. The aim is to open the model up to clients so they can build their own customized large language models, and they have already begun registering users.
Limitations and Ethical Considerations
The first question for many data leaders when considering generative AI in the workplace is something like, ‘what are generative AI tools doing with all this data?’ And this raises the question, ‘can we just ask AI any question?’ And the short answer, for now anyway, is a firm no.
We have already seen multiple data leaks from AI being used in the workplace (see the Samsung ban of ChatGPT among employees after a sensitive code leak), and many businesses putting their own internal rules and regulations around how AI can be used at work into place, with some banning the use entirely.
Generative AI limitations and challenges
- Data quality and quantity. To learn from and produce realistic and relevant content, Generative AI models require a lot of high-quality data. However, finding, collecting, cleaning, and labeling such data can be time-consuming, costly, and prone to errors or biases. Businesses may not currently have the skills or knowledge to do this at scale.
- Evaluation and feedback. It can be challenging to evaluate and improve these models as there is no clear or objective way to measure the quality, accuracy, originality, or usefulness of the generated content. Although human feedback is essential, it can also be subjective, inconsistent, or scarce. Again, without dedicated resource, this can be difficult.
- Scalability and reliability. The computational resources and power required to train and run Generative AI models can limit their scalability and reliability. Additionally, they can generate unexpected or undesirable outputs that can harm the reputation or trust of the eCommerce business or its customers.
Ethical considerations of generative AI
- Privacy and security. Sensitive or personal data of the eCommerce business or its customers, such as their preferences, behaviors, identities, or financial information, can potentially be accessed, used, or leaked by Generative AI models. This can raise privacy and security concerns and risks.
- Fairness and accountability. The biases or prejudices of the data Generative AI models are trained on, or the humans they interact with, can potentially be reflected or amplified. This can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes or decisions that can affect the eCommerce business or its customers. There should be mechanisms to ensure fairness and accountability for the generative AI models and their outputs.
- Transparency and trust. Generative AI models can potentially generate content that is indistinguishable from human-made content. This can create confusion or deception among the eCommerce business or its customers. There should be ways to disclose or verify the source and nature of the generative AI content and to ensure its quality and relevance.
Future Prospects
Generative AI has many applications in various domains, but one of the most promising and exciting ones is eCommerce, with many future prospects on the horizon.
Augmented reality and virtual reality
AI can be paired with VR & AR to provide customers with more immersive shopping experiences. For example, a generative AI-powered AR app could help customers visualize furniture in their own homes before making a purchase.
Product discovery
Generative AI can help customers find the products they want or need more easily and efficiently. For example, generative AI can create realistic and diverse product images based on textual descriptions or sketches, allowing customers to visualize their desired products better.
The technology can also generate personalized product recommendations based on customer preferences, behavior, and feedback, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Customer engagement
Businesses can use AI to communicate with their customers more effectively and creatively. For example, using tools like stable diffusion, you can create engaging and relevant content for social media platforms, blogs, newsletters, or ads, attracting more traffic and conversions.
Generative AI can also generate natural and human-like responses for chatbots or voice assistants, providing better customer service and support.
Fraud prevention
AI can help businesses detect and prevent fraudulent activities or attacks on their eCommerce platforms more effectively and accurately. For example, AI tools can create synthetic identities or faces for verification purposes, making it harder for impostors or bots to access the platform.
You can also use Generative AI to generate realistic and diverse data for training or testing purposes, improving the performance and robustness of fraud detection models. Learn more about Fraud Detection in Python with DataCamp’s online course.
Conclusion
Generative AI is a powerful technology that can create new and engaging content for eCommerce businesses. It can help them attract more customers, personalize their experiences, and increase their loyalty. It will also help businesses optimize their operations, such as inventory management, pricing, and marketing. The effective utilization of Generative AI and AI, in general, will be a significant differential feature when choosing between multiple platforms for a customer/user.
Generative AI is a game-changer for eCommerce and a valuable asset for any business that wants to thrive in the digital age. Learn about the generative AI concepts in DataCamp’s course.
Training 2 or more people?

Data Enablement Lead with over 10 years of experience in the world of data and analytics. I am passionate about helping businesses unlock the value of their data and have experience working with cross-functional teams to drive data initiatives. My expertise includes data governance, data quality management, data architecture, and analytics.



