Course
Data professionals work with data from various sources, such as websites or marketing campaigns, that likely contain inconsistencies. Identifying and correcting these inconsistencies is usually the first step toward analyzing a dataset.
This is where implementing master data management (MDM) can help. MDM is a unique approach that offers a comprehensive and precise view of your data, regardless of its multiple sources.
It organizes all the data points by entities (e.g., customers, locations, products, suppliers, etc.) with a unique identifier called a master record. This helps data professionals find the information they need quickly and confidently. You can learn more about Building Trust in Data Within Your Organization in a separate webinar.
In this article, we will explore the master data management concept in detail to help you effectively harness and manage your data.
Strengthen Your Data Privacy & Governance
Ensure compliance and protect your business with DataCamp for Business. Specialized courses and centralized tracking to safeguard your data.

What is Master Data Management?
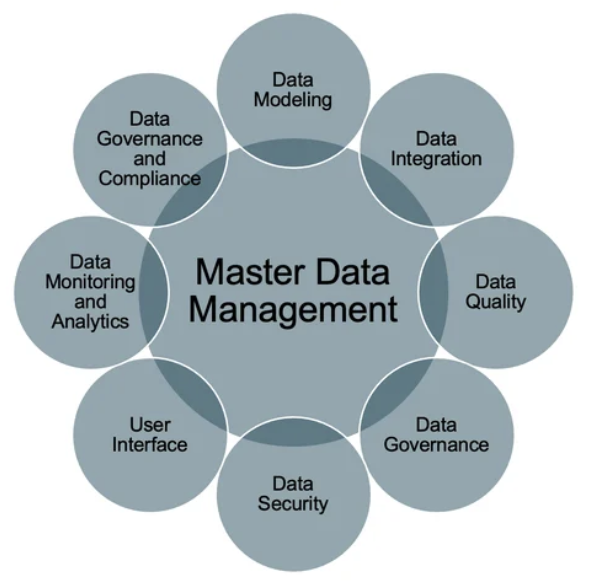
Components of master data management. Source: STIBO Systems
Master data management refers to the process of creating a single record for each business entity, such as customer, store, or product, from different internal and external data sources and applications. This gives an accurate view of the organization’s data from the master record.
Suppose you work at a company where you have to analyze customer data. You observe a specific customer's data - say, Joseph - lies across various sources and systems. However, there are a few problems and inconsistencies with this data:
- Inconsistent Naming Conventions: Different systems and departments have recorded the same customer with variations in his name (Josef, Joe, Joey).
- Multiple Identifiers: Joseph has used multiple email addresses to make purchases, which can lead to fragmented and duplicated records.
- Data Discrepancies: Slight differences in product IDs across systems can make it difficult to accurately track customer transactions and behavior.
Due to these discrepancies, duplicate entries could exist, making it difficult to form a clear picture of Joseph.
But let’s say your organization adheres to master data management best practices. In that case, you observe that all the critical data about Joseph would be linked to a single source of truth or common point of reference, which we call the master record. This helps you quickly identify this particular customer in your dataset.
What Are the Key Components of Master Data Management?
Common key components of MDM include semantic consistency, synchronization, data stewardship, data quality, and more. Let’s take a look at each.
1. Semantic consistency
Semantic consistency sets and enforces a consistent data format and interpretation standard for seamless data processing and analysis. For example, you work for an XYZ retail company with a master data management system.
When you look at sales data from the e-commerce store, you see the term “customer discount,” which indicates a percentage reduction in price at checkout.
But there is a twist.
When you look at the loyalty program data, the term “customer discount” indicates reward points earned from past purchases that can be redeemed in the future.
One method to achieve semantic consistency is to identify homonyms (same word, different meaning) and establish business rules for the term "customer data" in each specific context.
2. Data synchronization
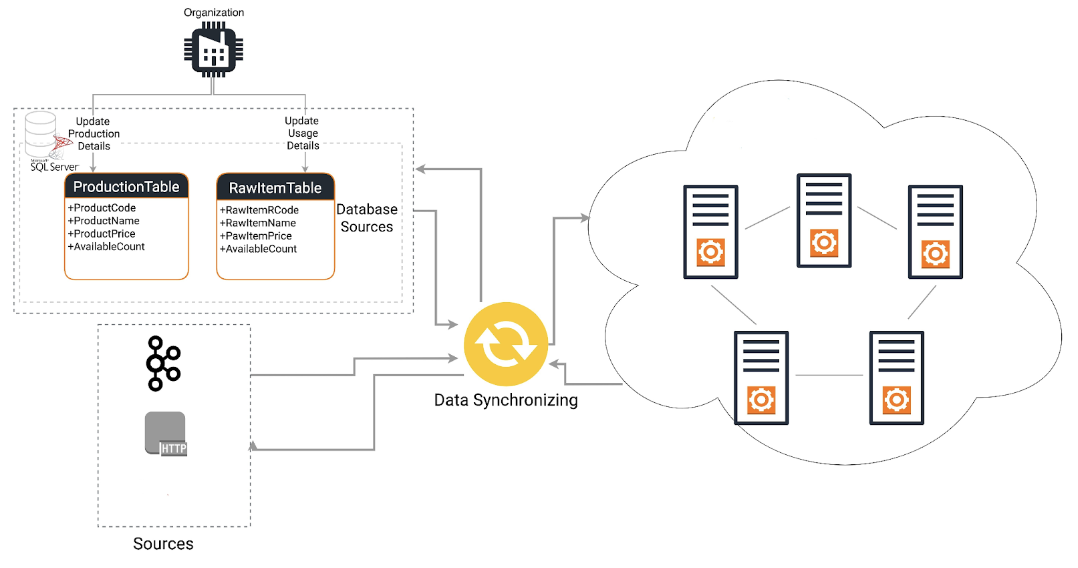 Data synchronization across different systems. Source
Data synchronization across different systems. Source
Data synchronization keeps all data up to date and ensures any changes are accurately reflected throughout the master data repository.
For example, when new customers sign up for a subscription service, they fill in their details in the online signup process. Once this is done, master data synchronization will do the following:
- Identification of New Customer Record: Recognizing that a new customer has signed up and a new record has been created.
- Data Transformation: Converting the new customer data into a standardized format and structure that matches the requirements of the billing system. This step is crucial for maintaining consistency across different systems.
- Data Delivery: Sending the transformed customer data to all relevant connected systems, such as the billing system and customer portal.
- Data Integration: Each connected system then integrates the received customer data into its respective database, ensuring all systems have the latest and consistent information.
3. Data stewardship
Data stewardship refers to the responsibility and ownership assigned to departments or individuals for specific data domains in the master data repository.
Suppose you, as a data scientist, are asked to clean customer data in the MDM system. In this case, the marketing team would be the data steward, who can guide you about data quality standards, such as valid email formats.
This collaboration will improve data quality and ensure your cleaning efforts align with data governance fundamentals. If you want to master data governance fundamentals, you can grab the cheat sheet here.
4. Data quality
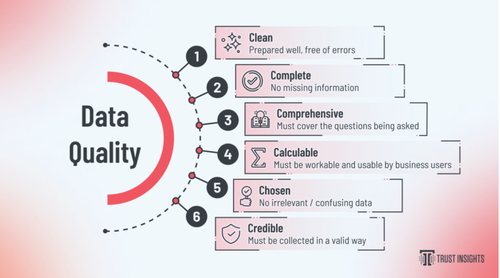
Qualitative characteristics of high-quality data. Source
Data quality ensures that master data in the MDM system is valid, complete, and consistent. This implies that all important data elements for a master record should be available. For example, email addresses or any other details about the customer shouldn’t be missing from the customer records.
MDM also uses data cleaning and profiling techniques to maintain data quality. These techniques clean up duplicate master records and correct errors and invalid formatting.
5. Master data repository
A master data repository is where all the critical data about your business entities is stored and managed in a well-organized and standardized manner. It stores all data records for entities such as products, suppliers, customers, employees, and locations.
Here, each entity has a single master record with complete information. In addition, the repository contains all data elements, data points, and other attributes and details about these entities.
6. Data security
Master data management deploys different security measures to protect data from unauthorized access and modification. These measures include:
- Granular Access Control: This restricts who can view and edit data within the master data repository, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information.
- Data Encryption and Audit Trails: Encryption protects data at rest and in transit, while audit trails log user activities to monitor and track any changes made within the master data repository. This helps in detecting and preventing unauthorized access and modifications.
- Compliance Enforcement: MDM systems enforce compliance with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, by implementing pre-defined controls to protect sensitive data and define user rights. This ensures that the organization adheres to legal and regulatory requirements.
7. Data mapping
Data mapping is another invaluable component of master data management. It integrates data from multiple sources into a consistent and complete view within the master data repository.
It connects data elements across domains and systems with their corresponding fields within the repository. This ensures that all data values align with the format and structure defined in the MDR.
What Are the Benefits of Master Data Management?
Master data management can improve your organization's overall data management practices. Let’s look at its key benefits:
Improved data quality
MDM maintains consistency and accuracy across all connected systems within an organization. This means you will have cleaner and more reliable data for analysis and making the right decisions.
Efficiency
MDM rationalizes data management and maintains single centralized sources of truth for critical data elements. So, the time and effort required to reconcile data, perform data entry, and perform data maintenance are substantially reduced across multiple systems and departments.
Regulatory compliance
Most industries are subject to strict data privacy, security, and governance regulations. MDM helps ensure an organization complies by maintaining complete and accurate data regarding confidentiality rules.
It also helps organizations establish consistent data management practices to ensure regulatory compliance. Ensuring customer records are consistent and accurate across CRM, billing, and marketing systems helps comply with regulations that require accurate record-keeping.
Streamlined operations
MDM simplifies complex data context by bringing together in one view all the previously disparate types, formats, and overall structures of data. This single view of the data model helps seamlessly augment cross-functional collaboration, better coordination of departments, and smooth support of business processes.
Fewer extra costs
MDM cuts unnecessary data management costs by optimizing data quality. Such costs could be those associated with manual data entry, errors and inconsistencies in data, the cost of reconciliation efforts, regulatory fines, and inefficiency because of data silos.
In effect, MDM allows organizations to allocate resources correctly and achieve the intended return on data investment.
What are Master Data Management Strategies and Best Practices?
When implementing a master data management system in your organization, you must plan strategically to enhance its functions and maximize its potential.
Define clear objectives and scope
First, you need to define what objectives you want to achieve with master data management. There could be some specific challenges you want to address. You must also pen down the master data entities that are specific and critical for your business (e.g., customers, products, locations).
This will help you prioritize resources and ensure that the master data management system focuses on the data with the biggest impact.
Invest in the right technology
There are many master data management platforms, and investing in the right one requires assessing it based on a few important features. Ask yourself questions regarding its strengths – whether it focuses on deep data cleansing and standardization or its main focus is data governance.
Moreover, check its integration capabilities. It should connect well with your existing ERP, CMS, or other data warehouse systems to give you a complete picture of your data.
Establish a data governance framework
A data governance framework sets rules for who can access the data and what data quality standards will be followed across your organization.
The master data management service you choose will follow this data governance framework to enforce a consistent data format. So it’s important to establish the right data governance framework because doing so will promote uniformity across departments. To learn more about building trust in data with data governance, you can listen to our Building Trust in Data with Data Governance podcast episode.
Implement data standardization
Your organization must have clear data standards for all master data entities. This includes defining data formats, such as how a customer’s address should be stored in the MDR.
There would be some common terminologies. There could also be a standard coding scheme unique to your organization that you want to maintain across all departments.
All of this comes under data standardization, which ensures that all the organization’s data in the MDR is stored according to the same data definitions.
Continuously monitor and improve
Once you implement MDM in your organization, you need to regularly monitor user adoption rates (the number of people actively using MDM and its functionalities), data quality metrics, and system performance.
This way, you can identify areas for improvement and adjust your master data management strategy based on your business needs and data management practices.
Upskill your teams
The effective implementation of master data management requires not only the right tools but also the right skills. Businesses are facing an ever-growing demand for data accuracy, governance, and integration, so ensuring your team is equipped with the knowledge to manage and optimize data is essential.
DataCamp for Business offers comprehensive learning paths designed to upskill your workforce in data management, governance, and analysis. With courses that cover key concepts like data quality, integration, and security, your team will be prepared to manage master data efficiently and confidently.
Request a demo today and empower your organization to harness the full potential of MDM by investing in training that supports both personal growth and business objectives.
What Are Some of the Challenges of Master Data Management?
There are a few challenges regarding master data management, which can be addressed by preparing and knowing how to counter them.
Scalability and flexibility
MDM systems that are not scalable can’t accommodate an increase in data as business needs evolve. For long-term success, you must choose an MDM system that can adapt to increasing data volumes and integrate with new applications.
User adoption and change management
Getting employees on board and adapting to master data management could be challenging if they are averse to change. To encourage them to use MDM within the organization, you must conduct comprehensive training, give them confidence, and resolve any concerns.
You can also address these challenges by carefully planning and carrying out counter activities to ensure the trouble-free implementation of master data management within your organization.
What Are Some Master Data Management Jobs?
MDM has created many jobs in the market and offers a range of career opportunities for professionals with data management skills. Here are some common MDM jobs and roles:
Junior-level jobs
- Master Data Management Specialist/Analyst
- Data Steward
- Data Quality Analyst
- Data Integration Specialist
- MDM System Administrator
Senior-level jobs
- Data Governance Specialist/Manager
- Data Architect/MDM Architect
- MDM Solutions Consultant
- Data Quality Manager
- Business Analyst (MDM)
- Data Security Analyst (MDM)
- Data Warehouse Analyst (MDM focus)
What Are Some Common Master Data Management Tools?
Let’s look at some of the most used master data management tools in the industry:
MDM Tool | Unique Capabilities |
Informatica MDM | The Informatica master data management software is excellent for cleansing, governance, integration, and multi-domain master data management capabilities. |
IBM InfoSphere Master Data Management | IBM InfoSphere master data management software provides data quality tools and master data synchronization across various systems. |
SAP Master Data Governance | SAP master data management software focuses on domain-specific data management, providing strong integration with SAP applications and in-built workflows. |
Oracle Master Data Management | As part of the Oracle Cloud platform, it offers data quality management, data governance, and data integration capabilities for enterprises. |
There are plenty of master data management solutions available in the market. To select the best MDM solution, assess your organization’s business needs, budget, and existing IT infrastructure.
Final Thoughts
Master Data Management enforces a reliable and consolidated view of data across the organization. This makes it easier for data scientists and stewards to work closely on complete and consistent datasets.
If you want to deepen your understanding of these and similar concepts, taking a data management concepts course can provide valuable insights into the frameworks and methodologies that underpin MDM.
Additionally, understanding data governance principles is helpful for successful MDM implementation. Enrolling in a data governance concepts course will equip you with the knowledge to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and security within your organization.
Happy learning, and keep your data organized!
Training 2 or more people? Check out our Business solutions
Get your team access to the full DataCamp library, with centralized reporting, assignments, projects and more

I'm a content strategist who loves simplifying complex topics. I’ve helped companies like Splunk, Hackernoon, and Tiiny Host create engaging and informative content for their audiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is MDM necessary for small businesses?
Small businesses can sometimes struggle with data silos and inconsistencies. MDM can help these small businesses enhance data quality to use their datasets better.
How long does it take to implement MDM?
Simple implementations might take a few months, while larger projects involving extensive data cleansing and integration could take a year or more.
What are the ongoing costs of maintaining an MDM system?
Ongoing costs include software licenses, implementation fees, maintenance fees, and human resources for data quality management.
How can I ensure data security within an MDM system?
Define user access levels, incident response protocols, and data encryption practices to implement strong data security within your MDM system.
How does MDM differ from data governance?
MDM involves managing and integrating master data. Whereas data governance refers to a framework of policies and procedures that define how to manage data within an organization. MDM operates within the boundaries specified by data governance in an organization.
