Course
Businesses are rushing to automate customer support, lead qualification, and internal workflows with AI agents. The technology finally works well enough to be useful, but building chatbots from scratch means assembling frameworks like LangChain and debugging API integrations. It works and has its plus side, but the development cycle is going to be slow.
Platforms like Botpress offer a different workflow. You get visual tools for designing conversation flows. The underlying AI models can be the same, but the infrastructure for building, testing, and deploying is already there.
In this article, I'll walk you through building AI agents with Botpress. You'll learn the platform architecture, build your first bot, connect it to real services, and deploy it to production. I'll also share some techniques and best practices I've picked up from working with the platform, so you can save time.
What Is Botpress?
Botpress is a platform for building AI agents that carry on conversations with users, trigger actions based on what's said, and connect to tools like Shopify, Google Sheets, or your own REST APIs. Competitors include Dialogflow, Rasa, Microsoft Bot Framework, and Amazon Lex.
Platform overview
Botpress provides both a visual development environment (Botpress Studio) and programmatic control through APIs. The visual interface lets non-technical team members design conversation flows, while developers can write code. Some platforms like Rasa are code-first, which can be more straightforward if you're a solo developer comfortable writing YAML and Python.
With Botpress, you define what your bot should do (instructions and workflows), what it knows (knowledge bases and tables), and what actions it can take (integrations and custom code). The platform handles the infrastructure: hosting, scaling, and orchestration.
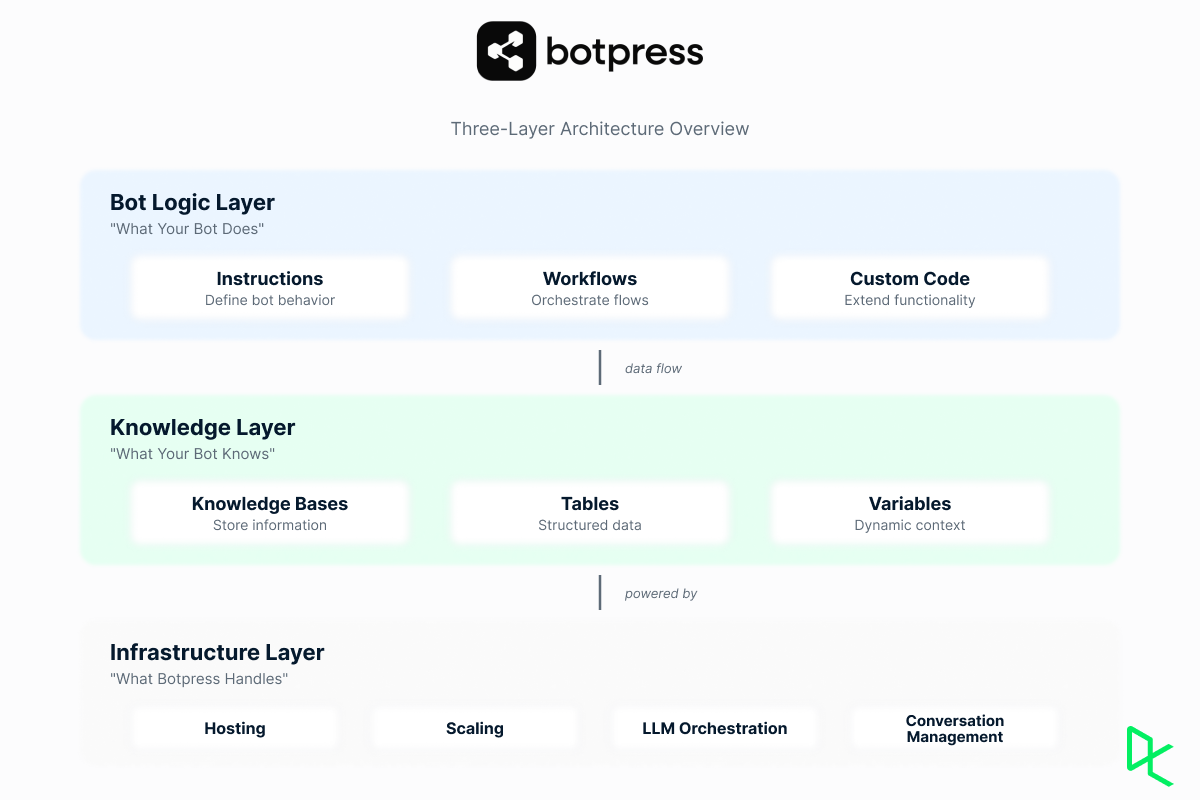
The Botpress architecture and layers. Image by Author
Compared to building from scratch with frameworks like LangChain, Botpress gives you production-ready components. Compared to pure no-code platforms, it gives you the option to write actual code when the pre-built visual tools can't do what you need
Who uses Botpress?
The platform serves everyone from solo developers building their first chatbot to enterprises deploying agents across multiple channels. Common use cases include customer support automation, lead qualification, appointment scheduling, and internal help desk systems.
According to a Botpress customer story, Ruby Labs reported a 98% resolution rate after adopting their solution. These figures come from vendor case studies and should be interpreted in context.
Setting Up Botpress
Let me now show you how to set up Botpress, by which I mean how to configure the Botpress CLI and SDK for a "bot-as-code" workflow.
Installation
To get started, you would need:
-
Node.js version 18 or higher (LTS recommended)
-
Package manager:
npm,pnpm, oryarn -
A code editor. VS Code or Cursor is highly recommended for TypeScript support
To install, follow these steps:
-
Open your terminal or command prompt
-
Install the Botpress CLI globally using
npm:
npm install -g @botpress/cli3. Verify the installation by checking the version:
bp --versionI recommend running Node.js and the Botpress CLI inside WSL2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux) to avoid common Windows pathing and permission issues.
If you receive an error running bp in PowerShell, you may need to adjust your execution policy. Run PowerShell as Administrator and execute: Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned.
Local development
Local development lets you use GitHub for version control, TypeScript for type safety, and tools like GitHub Copilot to auto-generate code. This approach treats your chatbot like any other software project.
Initial configuration
Once the CLI is installed, you need to connect your local environment to your Botpress Cloud account.
1. Authenticate
Log in to your account to link your CLI key.
bp loginThis will open a browser window to authorize the CLI.
2. Initialize a project
Create a new directory for your bot and initialize the structure.
mkdir my-first-bot
cd my-first-bot
bp initFollow the prompts to select a TypeScript template.
3. Set up environment variables
Create a .env file in your project root to store sensitive keys (like database credentials or third-party API keys). Never commit this file to Git.
4. Deploy to test
Push your local bot to the cloud to test it in the Studio.
bp deployGetting Started with Botpress Studio
Botpress Studio is where you actually build your bots.
Visual development environment
The Studio opens with a canvas showing your bot's conversation flow. Nodes represent steps in the conversation, and connections between nodes show how users move through your bot. Right-click anywhere on the canvas to create a new node.
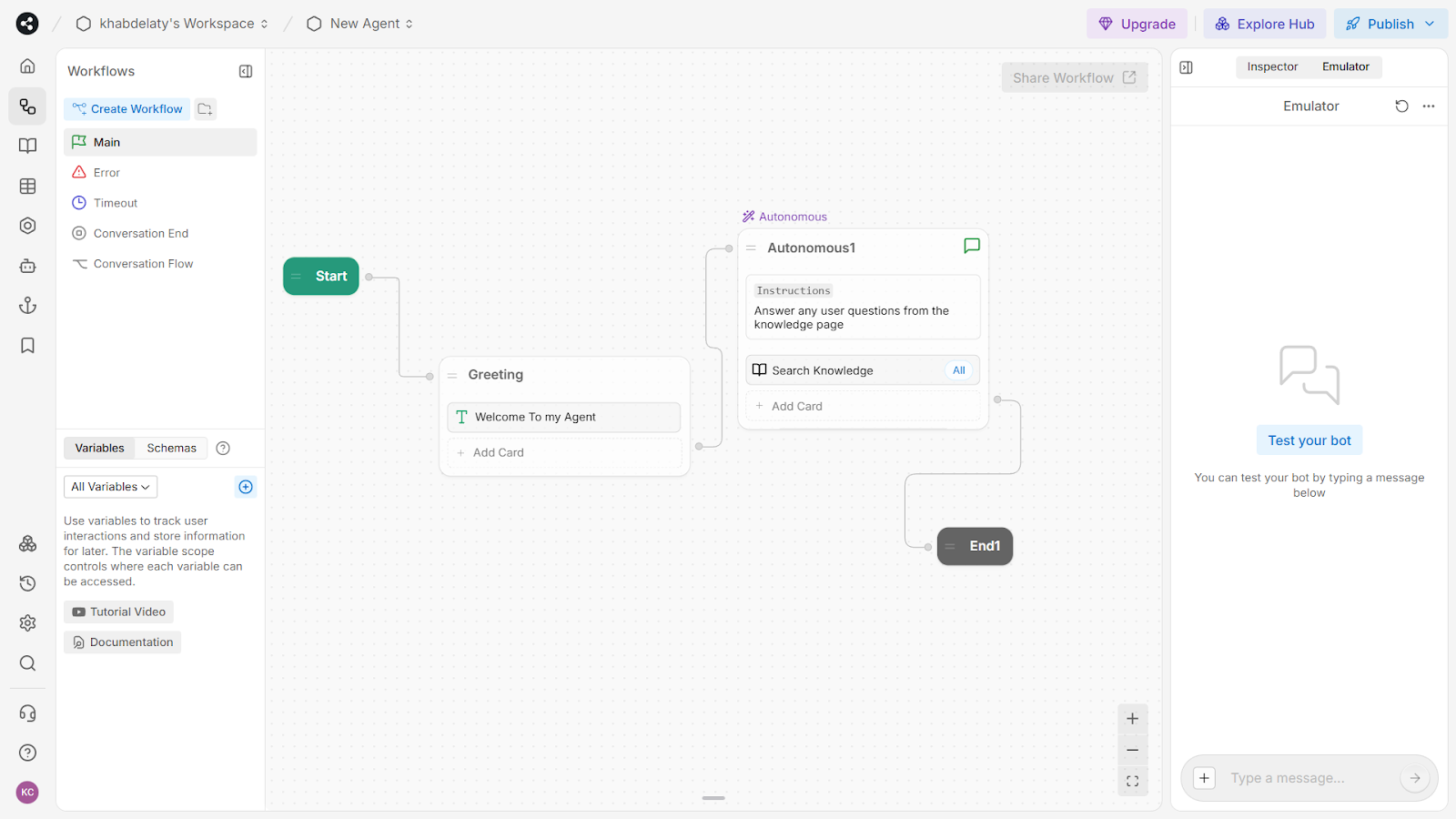
The left sidebar shows workflows, system flows, variables, and schemas. The right sidebar displays the inspector for the selected node, where you can configure instructions and attached actions. Use the emulator at the bottom to test the bot in real time.
Botpress templates
The Botpress Hub contains production-ready templates for customer support, appointment scheduling, lead qualification, and more. The Kitchen Sink template demonstrates advanced concepts like user data loading, workflow routing, and live agent handoff. Customize the instructions, swap in your knowledge base, and deploy.
Creating your first bot
Let's build a simple customer support bot. Create a new bot and name it "support-bot". Skip the wizard and go straight to the Studio.
In the Home tab (if it's not visible, connect your start node to a new autonomous node), add instructions:
You are a helpful customer support agent. Answer questions about our products and services using the knowledge base. Be friendly, concise, and professional. If you can't answer a question, offer to connect the user with a human agent.Now add a knowledge base. Click Knowledge Bases in the left sidebar, then Create Knowledge Base. Choose Website as the source type and enter your company website URL. Botpress will crawl the site and extract information.
Back in the Home tab, scroll to Knowledge Bases and toggle on the knowledge base you just created. This gives your autonomous node access to that information.
Test it in the emulator. Ask "What are your business hours?" or "How do I return a product?" The bot searches your knowledge base and responds with relevant info.
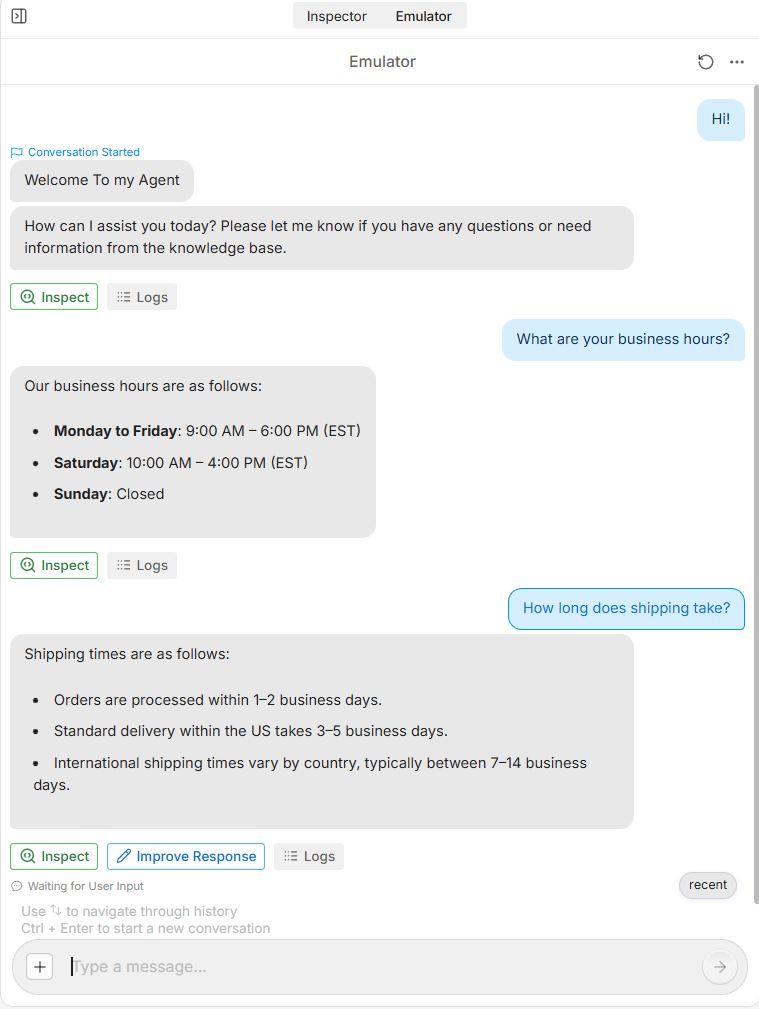
Testing a customer support bot in the Botpress emulator with real-time responses
This basic bot already handles a surprising amount of customer support. It answers questions from your website, maintains conversation context, and responds naturally. You built it in about five minutes.
Natural Language Understanding
If you've built chatbots before 2023, you might have noticed something different about what you just did: You didn't train any intent classifiers or write entity extraction rules, like with an NLU system (pre-LLM). (And if you're new to all of this, just know that older platforms require a lot of upfront training work that Botpress skips entirely.)
Here is what is happening: Botpress uses large language models for natural language understanding. You write instructions explaining what your bot should do, and the LLM handles intent recognition, entity extraction, and contextual understanding at runtime.
This changes what you actually configure. Common entities like dates, times, and contact information work immediately because the LLM conveniently already understands these patterns. Domain-specific entities require different treatment: you describe what you need in your instructions, and optionally define schemas. The LLM interprets these requirements the same way it interprets everything else.
Building Advanced Conversation Logic
Simple bots answer questions. Advanced bots make decisions and integrate with external systems. Botpress provides the tools to build both, though I'd argue most teams overcomplicate things early. You often don't need workflow logic until you've proven the basic Q&A actually works.
Workflow architecture
Workflows organize your bot's logic into manageable segments. The main workflow handles the primary conversation flow. Sub-workflows handle specific tasks. This could be things like scheduling appointments or processing returns.
Nodes within workflows represent distinct steps. A standard node executes a sequence of actions from top to bottom. An autonomous node uses the LLM to decide which actions to take and in what order. Entry and exit nodes mark where users enter and leave sub-workflows.
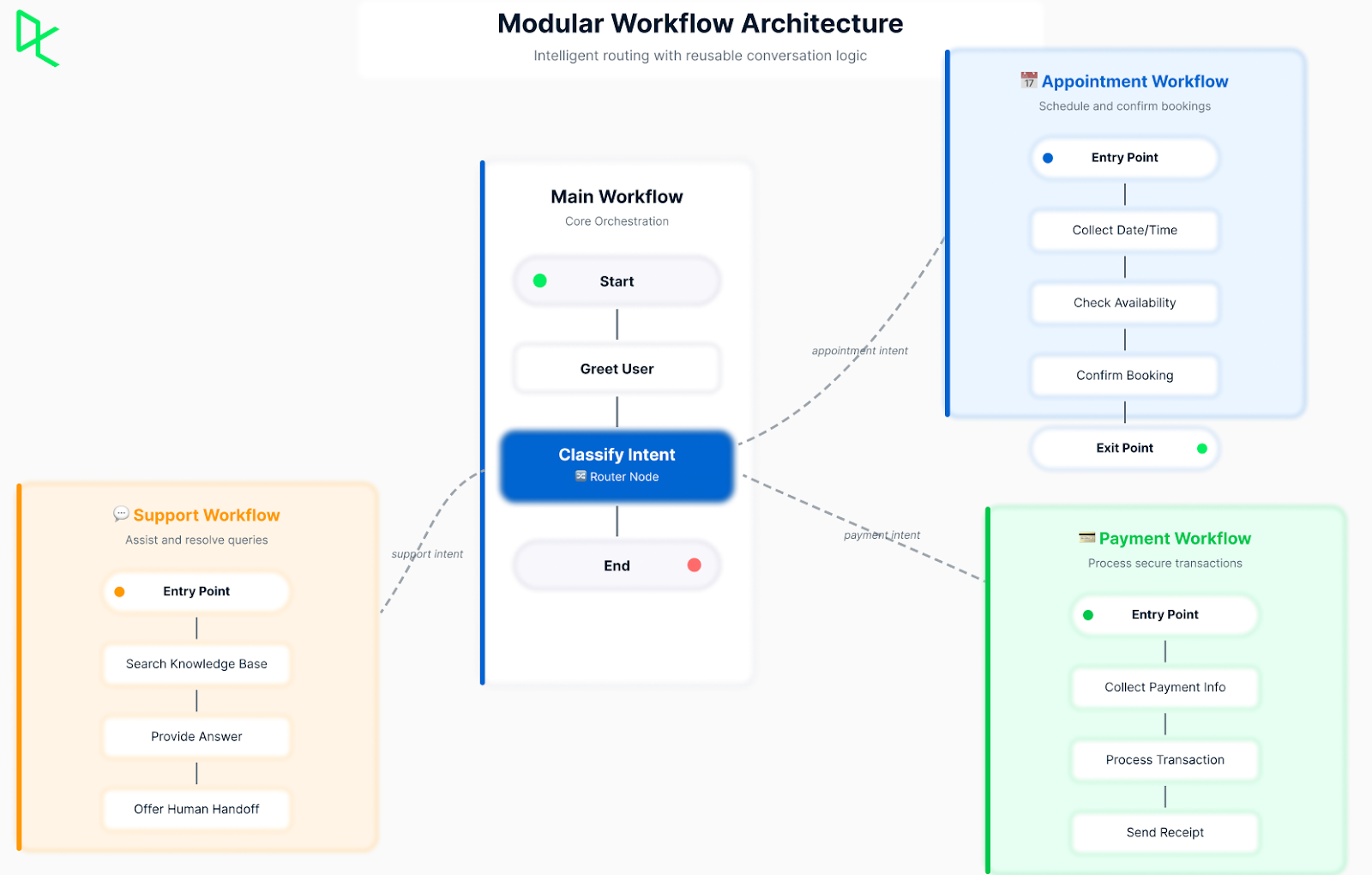
Botpress modular workflow architecture. Image by Author
Modular conversation logic means breaking complex tasks into smaller, reusable pieces. Build a workflow for collecting payment information once, then reuse it in checkout, subscription, and donation flows. This reduces duplication and makes maintenance easier.
The router pattern directs users to appropriate workflows based on their needs. After an initial greeting, classify the user's intent and route them to the right sub-workflow. This keeps each workflow focused on a single task.
Conversation design best practices
The breakthrough in language understanding is real, but it won't fix a poorly structured bot. You still need clear conversation flows and intentional design. The real difference is that you're designing at a higher level by defining what the bot should do rather than training it to recognize specific phrases.
Start with a clear greeting that sets expectations. Design for the happy path first, then add error handling. Keep autonomous nodes focused on one conceptual task. Use confirmation steps for important actions like payments. Map the user journey before building workflows to identify decision points and required info.
I’ve also read that too many "are you sure?"-type prompts condition users to click through without processing what they’re reading. “When every action requires confirmation, none of the confirmations are effective,” is probably a good heuristic. Save your confirmation requirements for genuinely irreversible operations: payments, account deletions, data loss.
Workflow automation
Beyond the basics covered here, Botpress supports hooks for lifecycle automation (running code when conversations start, messages are sent, etc.) and scheduled workflows for recurring tasks like appointment reminders. These are powerful tools, but they're also where things get complex quickly.
Integrations and Plugin Ecosystem
Botpress bots become powerful when they connect to external services. The Botpress Hub provides pre-built integrations for common tools, and you can build custom integrations for proprietary systems.
Pre-built integrations
The Hub includes integrations for messaging platforms (WhatsApp, Slack, Microsoft Teams, Telegram), CRMs (HubSpot, Salesforce), productivity tools (Google Calendar, Google Drive, SharePoint), and payment processors (Stripe). If you need to connect to a popular service, there's likely already an integration available.
Installing an integration adds new cards to your card tray. For example, a CRM integration provides cards for creating contacts, updating deals, and searching records. Drag these cards into your workflows to connect your bot.
Configuration happens in the integration settings. You provide API credentials, select which data to access, and map bot variables to external fields. The integration handles authentication, rate limiting, and error recovery.
Custom integrations
For proprietary systems or unique requirements, build custom integrations using the integration SDK. Define the integration interface, implement connection logic, and handle authentication. The SDK provides helpers for OAuth flows and webhook handling. Test locally with included utilities before deploying. Store credentials in configuration variables, validate all inputs, and implement proper error handling.
Pricing Models and Deployment Options
Botpress pricing is structured around AI usage rather than per-message or per-conversation fees. Whether that's expensive depends on your volume and use case. The simple customer support bot we built earlier—answering questions from a knowledge base—makes one or two LLM calls per user message and costs very little, which isn’t surprising since we built it fast and it’s just an example.
A more complex bot that also searches your CRM, checks inventory, and calculates shipping costs makes additional LLM calls to process that data, which increases AI costs proportionally. The platform passes through AI costs at provider rates without markup, so your actual spend depends on how many LLM calls each conversation requires and which model you choose.
Pricing structure
Botpress offers multiple subscription plans with different features and use cases:
|
Plan |
Price |
Best For |
Key Features |
|
Pay-as-you-go |
$0/month + AI spend |
Solo developers, learning, testing |
Community support, Visual Studio, $5 monthly AI credit, $100 AI spend cap |
|
Plus |
$89/month + AI spend |
Small teams, growing projects |
Technical support, human handoff, watermark removal, conversation insights |
|
Team |
$495/month + AI spend |
Established teams |
Advanced support, role-based access, real-time collaboration, custom analytics |
|
Managed |
$1,495/month (AI included) |
Businesses wanting hands-off management |
Priority support, custom development, ongoing maintenance, monthly strategy calls |
|
Enterprise |
Custom pricing |
Large organizations |
Dedicated support manager, white glove onboarding, custom workspace limits, SLA guarantees |
The restaurant bot I built earlier used the free tier. The pay-as-you-go model lets you experiment without any monthly commitment, and you only start paying when your bot actually handles conversations.
Deployment and scaling
Botpress scales automatically as traffic grows, handling 10 or 10,000 conversations consistently. Add-ons extend functionality with additional storage, increased limits, and premium integrations. Enterprise features include SSO, audit logs, role-based access control, and dedicated support.
Community and Support
The official documentation includes code examples, video tutorials, and reference material.
The Botpress Discord server has over 30,000 members who ask questions, share bots, and learn from other developers. The Botpress team actively participates. GitHub discussions provide space for feature requests and bug reports. You'll also find community-built templates that cover common use cases, so you don't always have to start from scratch.
Conclusion
The restaurant bot we built is simple, but the same approach works for more complex projects. The visual workflow editor and integration system scale well whether you're building a basic FAQ bot or something more sophisticated.
The key is starting small. Build a bot that does one thing well, deploy it, learn from real usage, and expand from there. Don't try to automate everything at once. Focus on the task that will deliver the most value with the least complexity.
To build your AI and chatbot skills, check out our Building Chatbots in Python course and our ChatGPT Fundamentals track. For prompt engineering techniques that improve your bot's responses, see Understanding Prompt Engineering. For workflow automation and AI agents beyond chatbots, explore our n8n: A Guide With Practical Examples tutorial and Building Your First AI Agent with n8n code-along.
I’m a data engineer and community builder who works across data pipelines, cloud, and AI tooling while writing practical, high-impact tutorials for DataCamp and emerging developers.
Botpress FAQs
Do I need coding experience to use Botpress?
No. The visual interface lets you build bots by dragging and connecting nodes. Coding helps for advanced features, but it's not required for basic bots.
How much does Botpress cost for a production bot?
The free tier works for testing. Production bots on pay-as-you-go typically cost $20-50/month for 1,000 conversations, depending on usage. Paid plans start at $89/month.
Can Botpress integrate with my existing systems?
Yes. There are 190+ pre-built integrations for tools like HubSpot, Salesforce, and Stripe. For custom systems, you can build integrations using the SDK or make API calls.
How do I handle conversations the bot can't resolve?
Build a handoff workflow that transfers to a human agent. The bot collects context, creates a ticket, and the agent sees the full conversation history before taking over.
What's the difference between knowledge bases and tables?
Knowledge bases store unstructured content like docs and FAQs that the bot searches. Tables store structured data like customer records that the bot queries and updates.
Is Botpress secure and compliant with regulations?
Yes. Data is encrypted, code runs in sandboxes, and the platform supports GDPR compliance. Enterprise plans add SSO, audit logs, and custom security features.


