Track
When working in Excel, numbers can sometimes be stored as text. This commonly happens when importing data from web pages, databases, PDFs, or text files. You can recognize this when you see numbers aligning to the left of a cell, formulas not calculating correctly, or small green triangles appearing in the corner of cells.
If left uncorrected, text-stored numbers can lead to issues, such as errors in SUM() formulas, inaccurate PivotTables, and broken charts. These problems can compromise the accuracy of reports and slow down data processing. If you need to refresh your Excel skills, I recommend taking our Data Preparation in Excel to learn how to clean and prepare data from different sources.
How to Identify Numbers Stored as Text
I mentioned how you might identify when the ‘numbers stored as text’ issue is happening. Here are a few easy ways to confirm if Excel is behaving weirdly:
- Numbers stored as text often appear left-aligned in their cells ( true numbers default to right alignment), and may display a small green triangle error indicator.
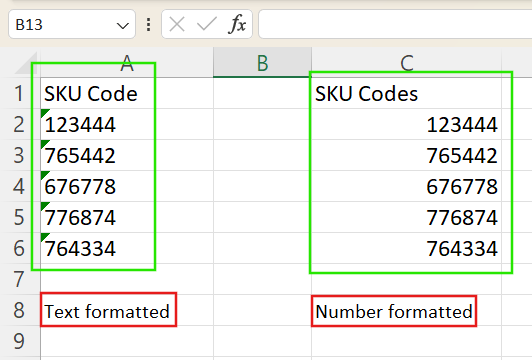
Text-formatted numbers align left in Excel. Image by Author.
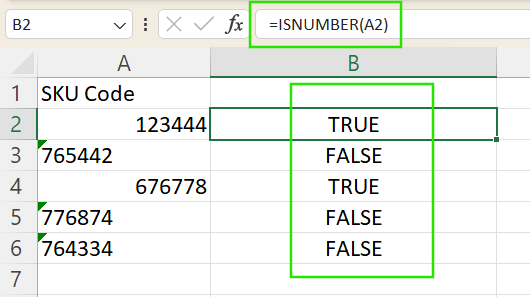
- You can use the
ISNUMBER()formula to verify. For example, entering=ISNUMBER(A2)will returnTRUEif the value inA2is indeed a number andFALSEif it’s text.
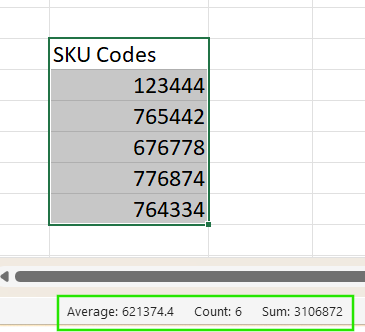
- The Excel Status Bar provides more clues: When selecting a range of true numbers, you’ll usually see
SUM,AVERAGE, andCOUNTdisplayed automatically. If the selection includes numbers stored as text, onlyCOUNTmay appear, which is a sure sign that there’s a data issue.
I recommend checking out our tutorial on How to Clean Data in Excel to learn different data cleaning techniques in Excel, including removing duplicates, handling missing values, and maintaining consistent formatting.
Methods to Convert Text to Numbers in Excel
Now that you can see the problem, let’s find a solution. Excel offers several methods to convert text-formatted numbers into true numeric values. Choosing the right approach depends on how your data is structured and the specific issue you’re facing. Below are the common techniques, each with step-by-step instructions and practical tips.
Use the Convert to Number error checking feature
If Excel detects numbers stored as text, a small green triangle appears in the corner of the cell. To fix it:
- Select the cell or range of cells.
- Click the yellow exclamation point icon that appears.
- Choose Convert to Number from the dropdown menu.
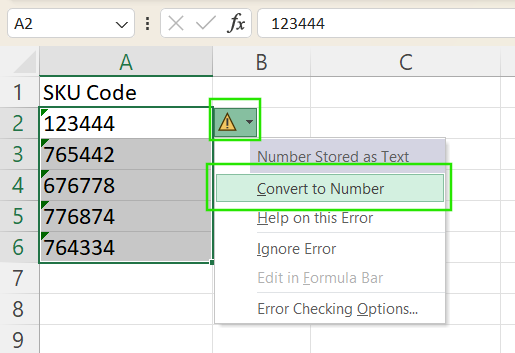
This method is fast but only works when Excel recognizes the problem automatically.
Change the cell format to General or Number
You can manually change the cell format to convert text to numbers by using these steps:
- Select the cells you want to convert.
- Go to the Home tab.
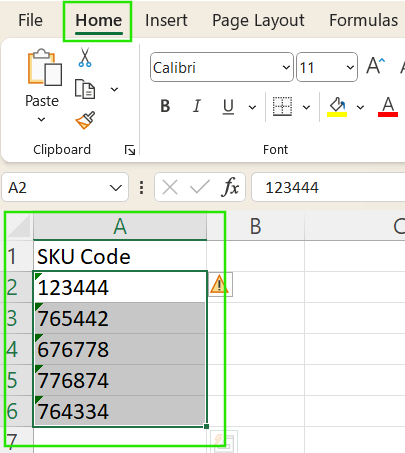
- In the Number group, open the dropdown and select General or Number.
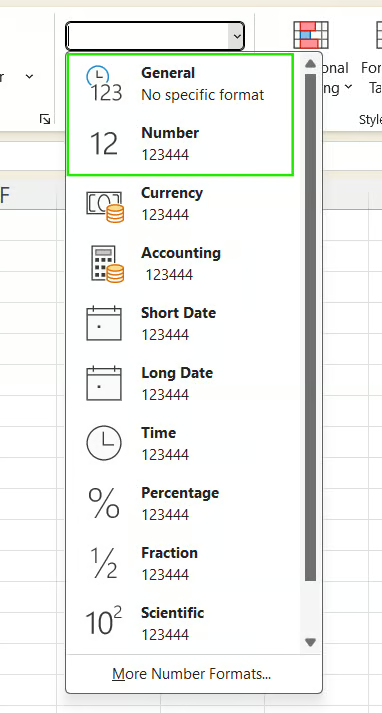
This method works best before entering data. If the numbers are already stored as text, simply changing the format may not convert them, and you may need to use an additional method to force the change.
Use Paste Special and multiply by 1
The Paste Special method reliably forces Excel to treat text as numbers. To apply this method:
- Type
1into any empty cell. - Copy that cell (Ctrl + C).
- Select the range of cells containing numbers formatted as text.
- Right-click → Paste Special → Choose Multiply → Click OK.
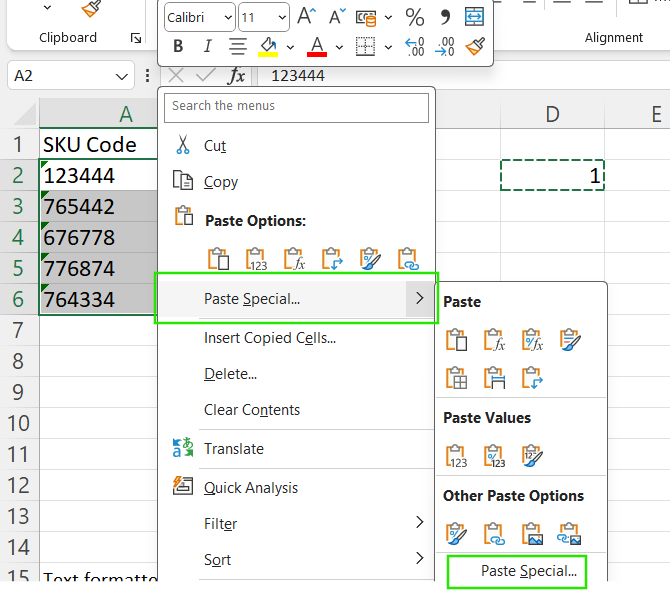
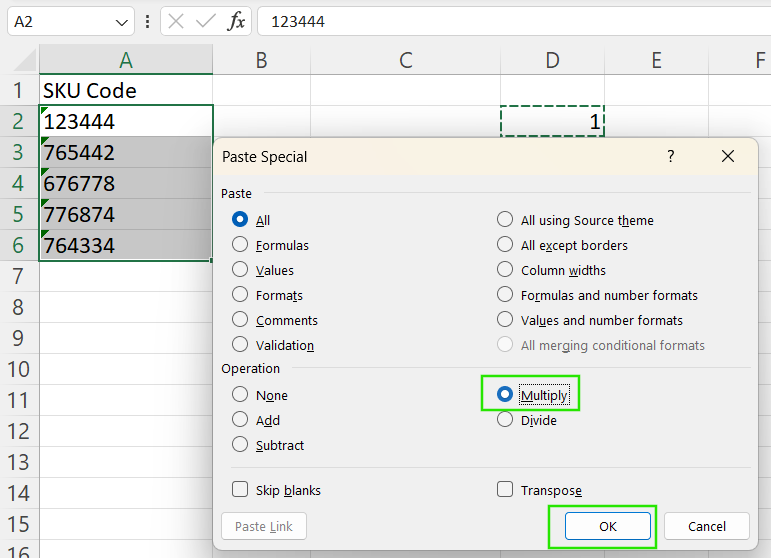
This operation multiplies each cell by 1, converting text to numbers, because multiplying by 1 preserves the original values while forcing Excel to re-evaluate the cell contents.
Perform simple arithmetic (Add 0, Multiply by 1)
This method is similar to the last one. Instead of multiplication, we could use addition.
- Enter
=A2+0in a new column to convert text to numbers. - Drag down to apply to other cells.
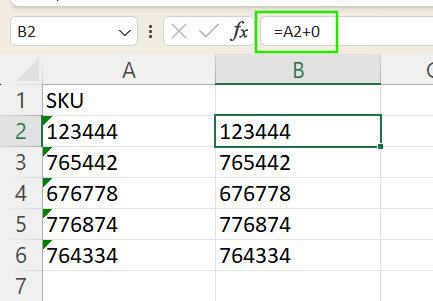
- Optionally, set the formula column’s format to General if needed.
Use Text to Columns
The Text to Columns tool can reset the format when other methods fail. This method re-parses the values and converts them into numbers even without splitting the data.
- Select the cells.
- Go to Data > Text to Columns.
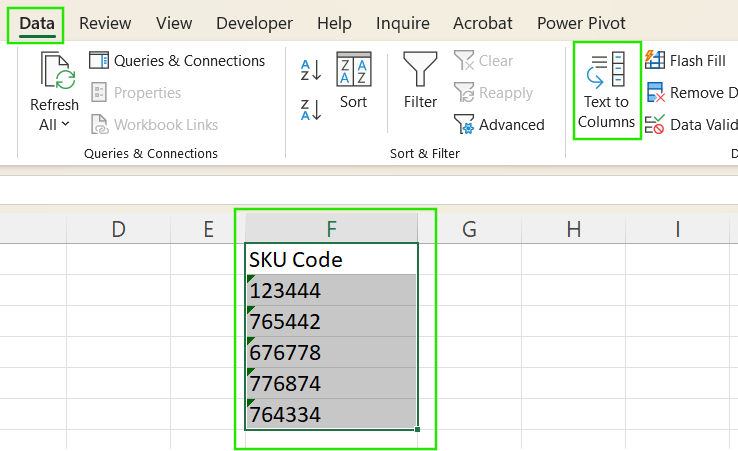
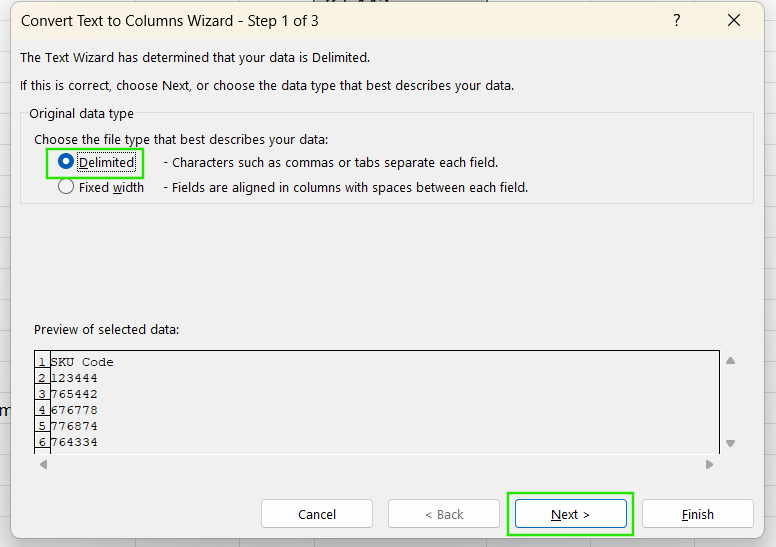
- Choose Delimited > Click Next (don't select any delimiters) > Finish
Use the VALUE() function
The VALUE() function converts text to numbers using a formula:
- Assume you have the cell “A2” with text-formatted numbers. In a blank cell, enter
=VALUE(A2). - Drag the formula down to apply it to more cells if needed.
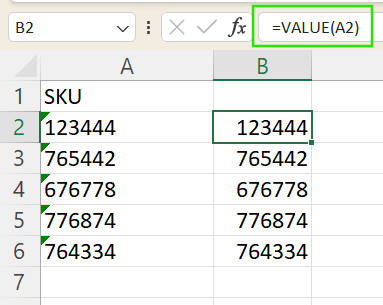
The VALUE() function can also handle text-formatted dates and times.
Troubleshooting Cases Where Standard Methods Fail
Standard conversion methods in Excel sometimes fail due to hidden issues like invisible spaces, non-printable characters, or unusual formatting, especially in data imported from PDFs, web pages, or after splitting cells. Common problems include leading or trailing spaces, non-breaking spaces, or hidden symbols that prevent Excel from recognizing values as numbers, even if they look correct on the surface.
To resolve these stubborn cases, Excel provides the following cleaning functions:
- The TRIM() function removes extra spaces from text, especially leading or trailing spaces that prevent correct conversion.
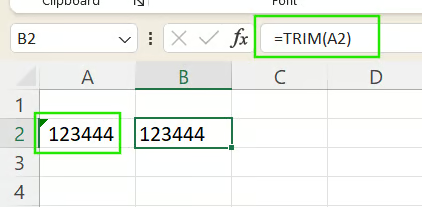
Check out our tutorial on How to Remove Spaces in Excel to learn different methods of removing spaces, and tips for handling special characters in your data.
- The CLEAN() function strips out non-printable characters that may have come from external sources, such as PDFs.
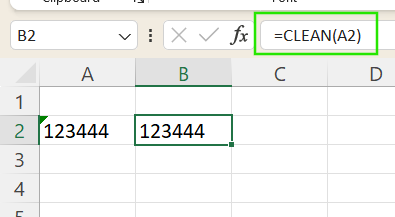
- If you suspect invisible formatting or strange symbols, you can use
=UNICODE(LEFT(A2, 1))to check the character code of the first character in a cell.
Check out our tutorial How to Extract a Number from a String in Excel to understand how to separate text from numbers to clean your data.
Key Points to Remember
When dealing with numbers stored as text in Excel, always start by checking whether the issue is simple formatting or true text storage. Begin with the easiest solutions, like using Error Checking or changing the cell format, and move to formulas or manual fixes if needed for more stubborn cases. For data coming from external sources like the web, PDFs, or databases, be sure to clean it thoroughly using tools like TRIM() and CLEAN() to ensure accurate conversion and reliable calculations.
I recommend taking our Data Analysis in Excel course to keep practicing your skills and our Excel Fundamentals skill track to learn advanced data cleaning techniques and the functions available in the latest Excel versions.
Advance Your Career with Excel
Gain the skills to maximize Excel—no experience required.
Excel FAQs
How can I quickly spot numbers stored as text?
Look for left-aligned cells, green error triangles, or use the =ISNUMBER() formula returning FALSE.
How does Paste Special multiply by 1 work?
Multiplying by 1 forces Excel to reinterpret text as numbers. Copy 1, select text-cells, and use Paste Special > Multiply.
When should I use Text to Columns?
Use it when other methods fail. It reprocesses text into numbers, even with hidden formatting issues.
How do I fix numbers from messy PDF imports?
Use TRIM() and CLEAN() to remove hidden spaces or non-printable characters.
How do I detect invisible characters?
Use =UNICODE(LEFT(A1,1)) to find hidden symbols at the start of a cell.