Course
In this article, I’ll explain how the Excel NOW() function works. I'll walk you through formatting options and I'll show you some useful ways you can it for time-stamping, scheduling, and more.
Understanding the Excel NOW() Function
The NOW() function in Excel is designed to return the current date and time based on your system clock. This is useful for time-stamping data, tracking changes, or creating dynamic reports that update automatically.
How Excel NOW() works
When you enter the NOW() function in a cell, Excel displays the current date and time. The value updates every time the worksheet recalculates. Because it's always recalculating, NOW() is best for cases where real-time values are useful or required, like in dashboards, or for clocks, or in combination with bigger and also time-sensitive formulas.
Syntax for Excel NOW()
The syntax for the NOW() function is straightforward. It does not require any arguments.
=NOW()After entering the formula, press Enter to display the current date and time.
Formatting the Result of Excel NOW()
By default, Excel may display the result as a date and time or just a date, depending on your cell formatting. You can always see how it looks and then change the display format if you want something different.
To format the cell:
-
Select the cell with the
NOW()formula -
Press Ctrl+1 to open what is called the Format Cells dialog box
-
Choose Date or Custom
Some Ways You Can Use Excel NOW()
There are many ways to use the NOW() function in your own spreadsheets. Here are some common ideas:
- Time-stamping entries in a log or database
- Calculating elapsed time since a specific event
- Creating dynamic headers or footers with the current date and time
Combining Excel NOW() with Other Functions
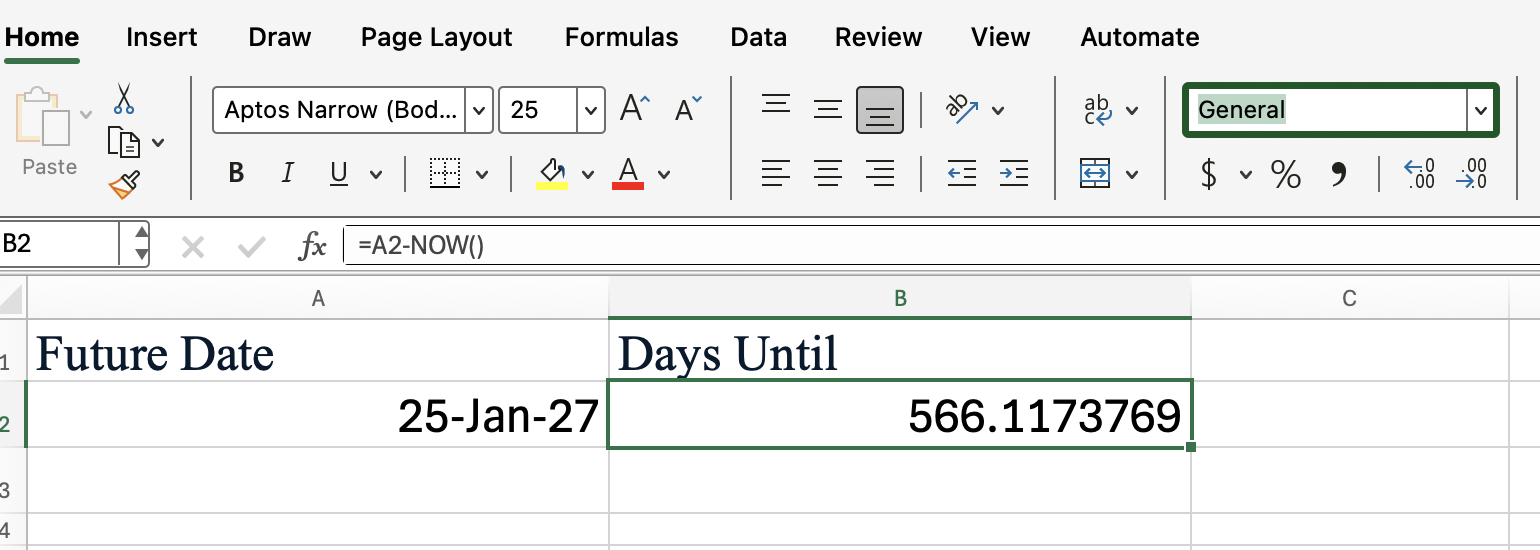
You can combine NOW() with other Excel functions to perform more advanced calculations. For example, to calculate the number of days between now and a future date, just subtract NOW() from the future date.
=A2 - NOW()This formula returns the difference in days (and fractions of days) between the specified future date and the current date and time.
The Excel ROUND() function would be useful here, also, as you can see:
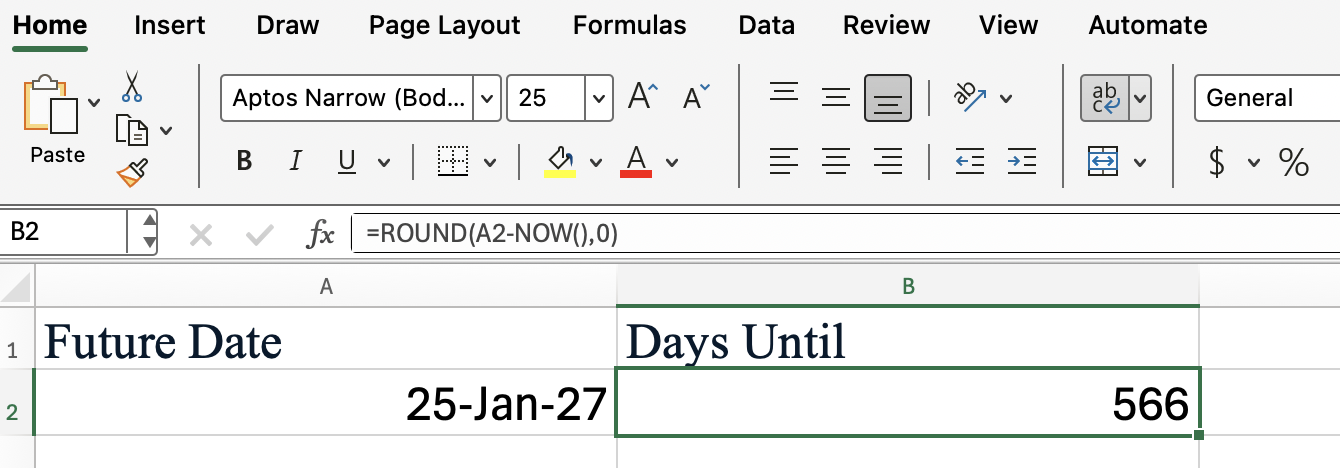
Here's another, maybe more interesting example:
You can combine NOW() with the IF() function to create deadlines or alerts. For instance, imagine you have a due date in cell A2, and you want to know if it's overdue:
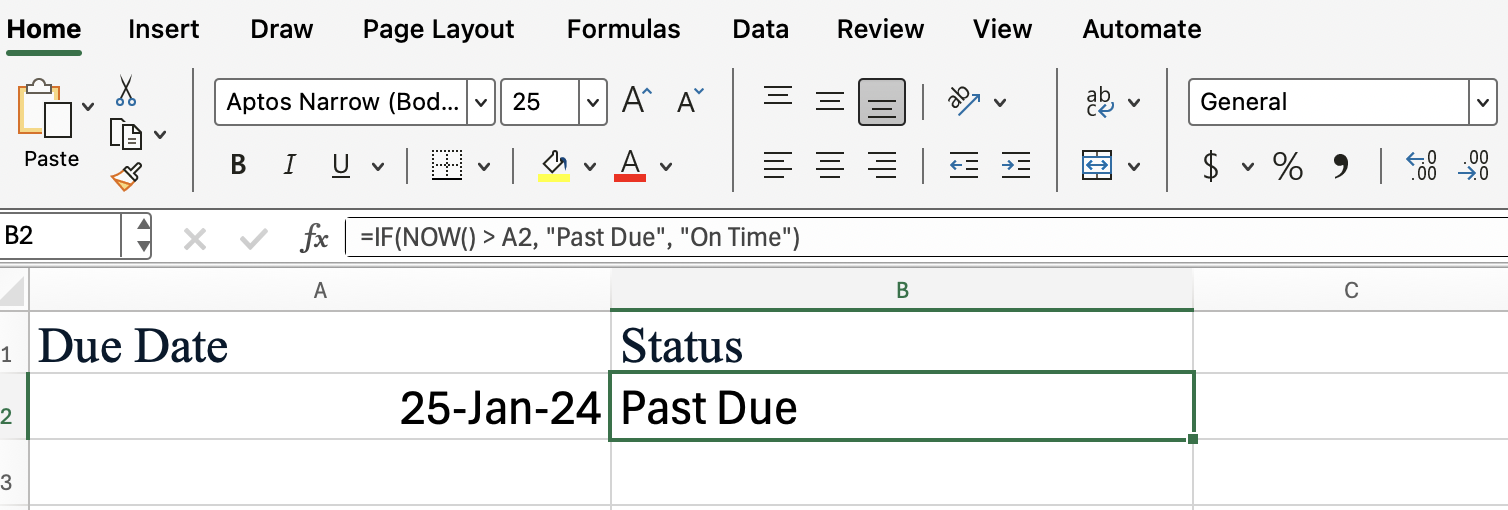
This formula compares the current date and time to the value in A2. If the due date has already passed, it returns "Past Due"; otherwise, it shows "On Time."
Updating and Recalculating Excel NOW()
The value returned by NOW() updates whenever the worksheet recalculates. This can happen when you:
- Open the workbook
- Enter new data
- Press F9 to recalculate manually (This is a nice trick if you don't know it.)
If you want the value to remain static, consider using Ctrl + ; for the current date or Ctrl + Shift + ; for the current time.
Limitations of Excel NOW()
NOW() is useful but there are a couple things you should keep top of mind:
- It relies on your system clock, so incorrect system time affects results. Double-check your workbook if you are traveling.
- It updates with every recalculation, so it's what is called a volatile function. This behavior might not be desirable for all cases. If, for example, you're logging when a task was completed, a always-recalculating timestamp would overwrite the original time and might not give you the result you want.
Conclusion
The NOW() function in Excel is a good tool for adding dynamic date and time info to your spreadsheets. I like the NOW() function because it lets you create more responsive and in some cases much more useful Excel documents.
To learn other great and useful tricks, take our Advanced Excel Functions course. You will learn referencing, database functions, and much more. Give it a try!
Learn Excel Fundamentals

I'm a data science writer and editor with contributions to research articles in scientific journals. I'm especially interested in linear algebra, statistics, R, and the like. I also play a fair amount of chess!