Course
Imagine you're building a complex, multi-agent large language model (LLM) application. It's exciting, but it comes with challenges: managing the state of various agents, coordinating their interactions, and handling errors effectively. This is where LangGraph can help.
LangGraph is a library within the LangChain ecosystem designed to tackle these challenges head-on. LangGraph provides a framework for defining, coordinating, and executing multiple LLM agents (or chains) in a structured manner.
It simplifies the development process by enabling the creation of cyclical graphs, which are essential for developing agent runtimes. With LangGraph, we can easily build robust, scalable, and flexible multi-agent systems.
If you want to learn more about the LangChain ecosystem, I recommend this introduction to LangChain. You can also check out our LangGraph video tutorial below.
What Is LangGraph?
LangGraph enables us to create stateful, multi-actor applications utilizing LLMs as easily as possible. It extends the capabilities of LangChain, introducing the ability to create and manage cyclical graphs, which are pivotal for developing sophisticated agent runtimes. The core concepts of LangGraph include: graph structure, state management, and coordination.
Graph structure
Imagine your application as a directed graph. In LangGraph, each node represents an LLM agent, and the edges are the communication channels between these agents. This structure allows for clear and manageable workflows, where each agent performs specific tasks and passes information to other agents as needed.
State management
One of LangGraph's standout features is its automatic state management. This feature enables us to track and persist information across multiple interactions. As agents perform their tasks, the state is dynamically updated, ensuring the system maintains context and responds appropriately to new inputs.
Coordination
LangGraph ensures agents execute in the correct order and that necessary information is exchanged seamlessly. This coordination is vital for complex applications where multiple agents need to work together to achieve a common goal. By managing the flow of data and the sequence of operations, LangGraph allows developers to focus on the high-level logic of their applications rather than the intricacies of agent coordination.
Why LangGraph?
As I mentioned above, LangGraph offers several significant advantages for developers working with complex LLM applications. Here are some of the real-world benefits LangGraph offers.
Simplified development
LangGraph abstracts away the complexities associated with state management and agent coordination. This means developers can define their workflows and logic without worrying about the underlying mechanisms that ensure data consistency and proper execution order. This simplification accelerates the development process and reduces the likelihood of errors. It’s a game-changer!
Flexibility
With LangGraph, developers have the flexibility to define their own agent logic and communication protocols. This allows for highly customized applications tailored to specific use cases. Whether you need a chatbot that can handle various types of user requests or a multi-agent system that performs complex tasks, LangGraph provides the tools to build exactly what you need. It’s all about giving you the power to create.
Scalability
LangGraph is built to support the execution of large-scale multi-agent applications. Its robust architecture can handle a high volume of interactions and complex workflows, enabling the development of scalable systems that can grow with your needs. This makes it suitable for enterprise-level applications and scenarios where performance and reliability are critical.
Fault tolerance
Reliability is a core consideration in the design of LangGraph. The library includes mechanisms for gracefully handling errors, ensuring that your application can continue to operate even when individual agents encounter issues. This fault tolerance is essential for maintaining the stability and robustness of complex multi-agent systems. Peace of mind is just a feature away.
Getting Started With LangGraph
Let’s see how we can set up LangGraph and what the basic concepts are.
Installation
To install LangGraph, you can use pip:
pip install -U langgraphBasic Concepts
Nodes: Nodes represent units of work within your LangGraph. They are typically Python functions that perform a specific task, such as:
- Interacting with an LLM
- Calling a tool or API
- Performing some data manipulation
- Receiving user input
- Executing business logic
In LangGraph, you can add nodes using the graph.add_node(name, value) syntax.
Edges: Edges are communication channels between nodes. They define the flow of information and the order of execution. You can add edges using the graph.add_edge(node1, node2) syntax.
State: The state is a central object updated over time by the nodes in the graph. It manages the internal state of your application and can be overridden or added to, depending on the application's requirements. This state can hold things such as:
- Conversation history: A list of messages between the agent and the user.
- Contextual data: Information relevant to the current task or interaction.
- Internal variables: Flags, counters, or other variables to track the agent's progress and behavior.
Building a Simple LangGraph Application
Here’s a step-by-step example of creating a basic chatbot application using LangGraph.
Step 1: Define the StateGraph
Define a StateGraph object to structure the chatbot as a state machine. The State is a class object defined with a single key messages of type List and uses the add_messages() function to append new messages rather than overwrite them.
from typing import Annotated
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
class State(TypedDict):
# messages have the type "list".
# The add_messages function appends messages to the list, rather than overwriting them
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)Step 2: Initialize an LLM and add it as a Chatbot node
Here, we initialize the AzureChatOpenAI model and create a simple chatbot function that takes in the state messages as input and generates a message response (which is subsequently appended to the state).
This chatbot function is added as a node named “chatbot” to the graph.
from langchain_openai import AzureChatOpenAI
llm = AzureChatOpenAI(
openai_api_version=os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_API_VERSION"],
azure_deployment=os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_CHAT_DEPLOYMENT_NAME"],
)
def chatbot(state: State):
return {"messages": [llm.invoke(state["messages"])]}
‘’’The first argument is the unique node name
# The second argument is the function or object that will be called whenever the node is used.’’’
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", chatbot)Step 3: Set edges
Since we are building a simple chatbot, we set the chatbot node as both the entry and finish points of the graph to indicate where to start and end the process.
# Set entry and finish points
graph_builder.set_entry_point("chatbot")
graph_builder.set_finish_point("chatbot")Step 4: Compile and Visualize the Graph
Compile the graph to create a CompiledGraph object, and optionally, we can visualize the graph structure using the code below:
graph = graph_builder.compile()
from IPython.display import Image, display
try:
display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
except Exception:
pass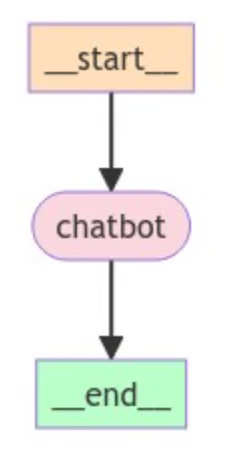
Step 5: Run the chatbot
Finally, we implement a loop to continuously prompt the user for input, process it through the graph, and print the assistant's response. The loop exits when the user types "quit", "exit", or "q".
# Run the chatbot
while True:
user_input = input("User: ")
if user_input.lower() in ["quit", "exit", "q"]:
print("Goodbye!")
break
for event in graph.stream({"messages": [("user", user_input)]}):
for value in event.values():
print("Assistant:", value["messages"][-1].content)Advanced LangGraph Features
Now that we've covered the basics, let’s take a look at some advanced features.
Custom node types
LangGraph allows you to create custom node types to implement complex agent logic. This provides flexibility and control over your application's behavior.
from typing import Annotated
from langchain_anthropic import ChatAnthropic
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
class MyCustomNode:
def __init__(self, llm):
self.llm = llm
def __call__(self, state):
# Implement your custom logic here
# Access the state and perform actions
messages = state["messages"]
response = self.llm.invoke(messages)
return {"messages": [response]}
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
llm = ChatAnthropic(model="claude-3-haiku-20240307")
custom_node = MyCustomNode(llm)
graph_builder.add_node("custom_node", custom_node)Here, we define a class MyCustomNode that encapsulates custom logic and interacts with the LLM. This provides a more structured and maintainable way to implement complex node behaviors.
Edge types
LangGraph supports different edge types to handle various communication patterns between nodes. One useful type is the conditional edge, which allows for decision-making based on a node's output.
To create a conditional edge, you need three components:
- The upstream node: The node's output decides the next step.
- A function: This function evaluates the upstream node's output and determines the next node to execute, returning a string that represents the decision.
- A mapping: This mapping links the possible outcomes of the function to the corresponding nodes to be executed.
Here's an example in pseudocode:
graph.add_conditional_edge(
"model",
should_continue,
{
"end": END,
"continue": "tools"
}
)Here, after the “model” node is called, we can either exit the graph (”end”) and return to the user, or we can continue (”continue”) and call a tool—depending on what the user decides!
State management
LangGraph offers powerful state management techniques, which include using external databases like SQLite, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB, or cloud storage solutions like Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Azure Blob Storage to store and retrieve your agent's state, enabling reliability and scalability.
Here's an example of using a SQLite database for state management:
from langgraph.checkpoint.sqlite import SqliteSaver
# Connect to the SQLite database
memory = SqliteSaver.from_conn_string(":memory:")
# Compile the graph with the checkpointer
graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=memory)Error handling
LangGraph also provides mechanisms for error handling:
- Exceptions: Node functions can raise exceptions to signal errors during execution. You can catch and handle these exceptions to prevent your graph from crashing.
- Retry mechanisms: You can implement retry logic within your nodes to handle transient errors, such as network issues or API timeouts.
- Logging: Use logging to record errors and track the execution of your graph.
Real-World Applications of LangGraph
LangGraph can be used to build a wide range of applications.
Chatbots
LangGraph is ideal for developing sophisticated chatbots that can handle a wide array of user requests. By leveraging multiple LLM agents, these chatbots can process natural language queries, provide accurate responses, and seamlessly switch between different conversation topics. The ability to manage state and coordinate interactions ensures that the chatbot maintains context and delivers a coherent user experience.
Autonomous agents
For applications requiring autonomous decision-making, LangGraph enables the creation of agents that can perform tasks independently based on user inputs and predefined logic.
These agents can execute complex workflows, interact with other systems, and adapt to new information dynamically. LangGraph's structured framework ensures that each agent operates efficiently and effectively, making it suitable for tasks like automated customer support, data processing, and system monitoring.
Multi-Agent systems
LangGraph excels in building applications where multiple agents collaborate to achieve a common goal. For example, different agents can manage inventory, process orders, and coordinate deliveries in a supply chain management system. LangGraph's coordination capabilities ensure that each agent communicates effectively, sharing information and making decisions in a synchronized manner. This leads to more efficient operations and better overall system performance.
Workflow automation tools
With LangGraph, automating business processes and workflows becomes straightforward. Intelligent agents can be designed to handle tasks such as document processing, approval workflows, and data analysis. By defining clear workflows and leveraging LangGraph's state management, these tools can execute complex sequences of actions without human intervention, reducing errors and increasing productivity.
Recommendation systems
Personalized recommendation systems can greatly benefit from LangGraph's capabilities. By employing multiple agents to analyze user behavior, preferences, and contextual data, these systems can deliver tailored suggestions for products, content, or services. LangGraph's flexibility allows for integrating various data sources and algorithms, enhancing the accuracy and relevance of recommendations.
Personalized learning environments
In educational platforms, LangGraph can be used to create adaptive learning environments that cater to individual learning styles and needs. Multiple agents can assess a student's progress, provide customized exercises, and offer real-time feedback. The stateful nature of LangGraph ensures that the system retains information about each learner's performance and preferences, enabling a more personalized and effective educational experience.
Conclusion
LangGraph significantly simplifies the development of complex LLM applications by providing a structured framework for managing state and coordinating agent interactions.
Potential developments for LangGraph include integration with other LangChain components, support for new LLM models, and the introduction of more advanced agent runtimes from academia.
If you want to learn more about developing applications within the LangChain ecosystem, I recommend this course on developing LLM applications with LangChain.
Multi-Agent Systems with LangGraph
Ryan is a lead data scientist specialising in building AI applications using LLMs. He is a PhD candidate in Natural Language Processing and Knowledge Graphs at Imperial College London, where he also completed his Master’s degree in Computer Science. Outside of data science, he writes a weekly Substack newsletter, The Limitless Playbook, where he shares one actionable idea from the world's top thinkers and occasionally writes about core AI concepts.




