Course
Over the past few years, we’ve seen cloud computing become a cornerstone of digital transformation. The market is growing at an incredible pace; public cloud spending is projected to hit over $900 billion in 2026, up from $781.3 billion in 2025, and could approach $1 trillion soon after. Businesses of all sizes are using the cloud to boost agility, cut IT costs, and drive innovation across industries from healthcare to finance, manufacturing, and media.
This shift from on-premises infrastructure to scalable, on-demand services has completely changed how organizations think about computing. Choosing the right cloud service provider (CSP) can shape everything from cost efficiency to system performance, security, and long-term strategy.
While AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud lead the way, other players like IBM Cloud and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure fill important niches.
In this article, I’ll break down what CSPs are, review the leading providers in 2026, and share insights to help you choose the best partner for your needs.
If you are new to cloud service providers, consider taking one of our courses, such as Understanding Cloud Computing, Introduction to GCP, Introduction to AWS, or Understanding Microsoft Azure Architecture and Services.
What Is a Cloud Service Provider?
In simple terms, a cloud service provider (CSP) is a company that delivers computing services over the internet (what we call "the cloud"). These services include data storage, servers, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence. From my perspective, the core function of a CSP is to eliminate the need for on-premise infrastructure, offering scalable and reliable solutions on a pay-per-use or subscription basis.
From my experience working with various CSPs, the typical services they offer include:
- Compute: Virtual machines, containers, and serverless computing for running applications
- Storage: Scalable file, block, and object storage solutions
- Networking: Load balancers, VPNs, and content delivery networks (CDNs)
- Managed services: Database management, machine learning, IoT, DevOps
Importance of CSPs in data science
Having worked extensively in data science, I can say the significance of cloud service providers cannot be overstated, as they address three critical challenges that have historically limited data science initiatives: scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Scalability: Data science workloads often require varying levels of compute power, including access to specialized hardware like GPUs and TPUs, which allow users to scale up or down based on demand.Cost-effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go models minimize waste by only charging for what is used. This shift has enabled smaller organizations and individual researchers to access the same powerful tools and infrastructure previously available only to large corporations with substantial IT budgets.
- Flexibility: CSPs support various programming environments, tools, and integrations crucial for data analytics and machine learning projects.
Popular services include Google BigQuery, Azure Machine Learning, and Amazon SageMaker, which empower data scientists to build models, run queries, and deploy solutions efficiently.
Types of cloud services
Cloud services are typically categorized into three fundamental models, each offering different levels of control and management responsibility.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides the most basic level of cloud computing, offering virtualized computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking components. Organizations using IaaS maintain control over operating systems, applications, and data while the cloud provider manages the underlying physical infrastructure.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Abstracts away the underlying infrastructure and provides a complete development and deployment environment. This model allows developers to focus on building applications without worrying about server management, operating system updates, or infrastructure scaling.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Represents the highest level of abstraction, delivering complete applications over the internet. Users access these applications through web browsers or mobile apps, while the provider handles all aspects of infrastructure, platform management, and application maintenance.
What I typically see is organizations starting with SaaS solutions, then gradually moving to PaaS for custom development, and finally adopting IaaS when they need maximum control over their infrastructure stack.
Top Cloud Service Providers in 2026
Let’s look at some of the top cloud service providers you can choose from today, exploring what makes them unique. This list is in no particular order, as the exact ‘best’ choice will depend on your needs.
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services maintains its position as the undisputed market leader in cloud computing, commanding approximately 32% of the global cloud infrastructure market. AWS offers the most comprehensive suite of cloud services, with over 200 fully featured services spanning compute, storage, databases, networking, analytics, machine learning, and IoT capabilities.
The primary strengths of AWS lie in its unmatched scalability and global reach. With data centers in over 115 availability zones across 37 geographic regions (as of July 2025), AWS provides the infrastructure necessary for organizations to deploy applications globally while maintaining low latency and high availability. This extensive global presence, combined with a mature ecosystem of services and tools, makes AWS particularly attractive for enterprises requiring complex, multi-region deployments.

AWS Regions and Availability Zones
However, from my perspective, organizations considering AWS must be prepared for complex pricing models that can be challenging to predict and optimize. The sheer breadth of services and configuration options, while powerful, can lead to unexpected costs if not properly managed. Additionally, the learning curve for AWS can be steep, particularly for organizations new to cloud computing.
2. Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure has emerged as a formidable competitor to AWS, particularly among enterprises already invested in Microsoft's ecosystem. Azure's strength lies in its seamless integration with Microsoft products, including Office 365, Windows Server, and SQL Server, making it an attractive choice for organizations heavily reliant on Microsoft technologies.
Azure excels in enterprise solutions and hybrid cloud deployments, offering robust tools for organizations that need to maintain some on-premises infrastructure while leveraging cloud capabilities. The platform provides excellent support for both Windows and Linux environments, with strong identity management and security features that integrate well with existing Microsoft infrastructure.
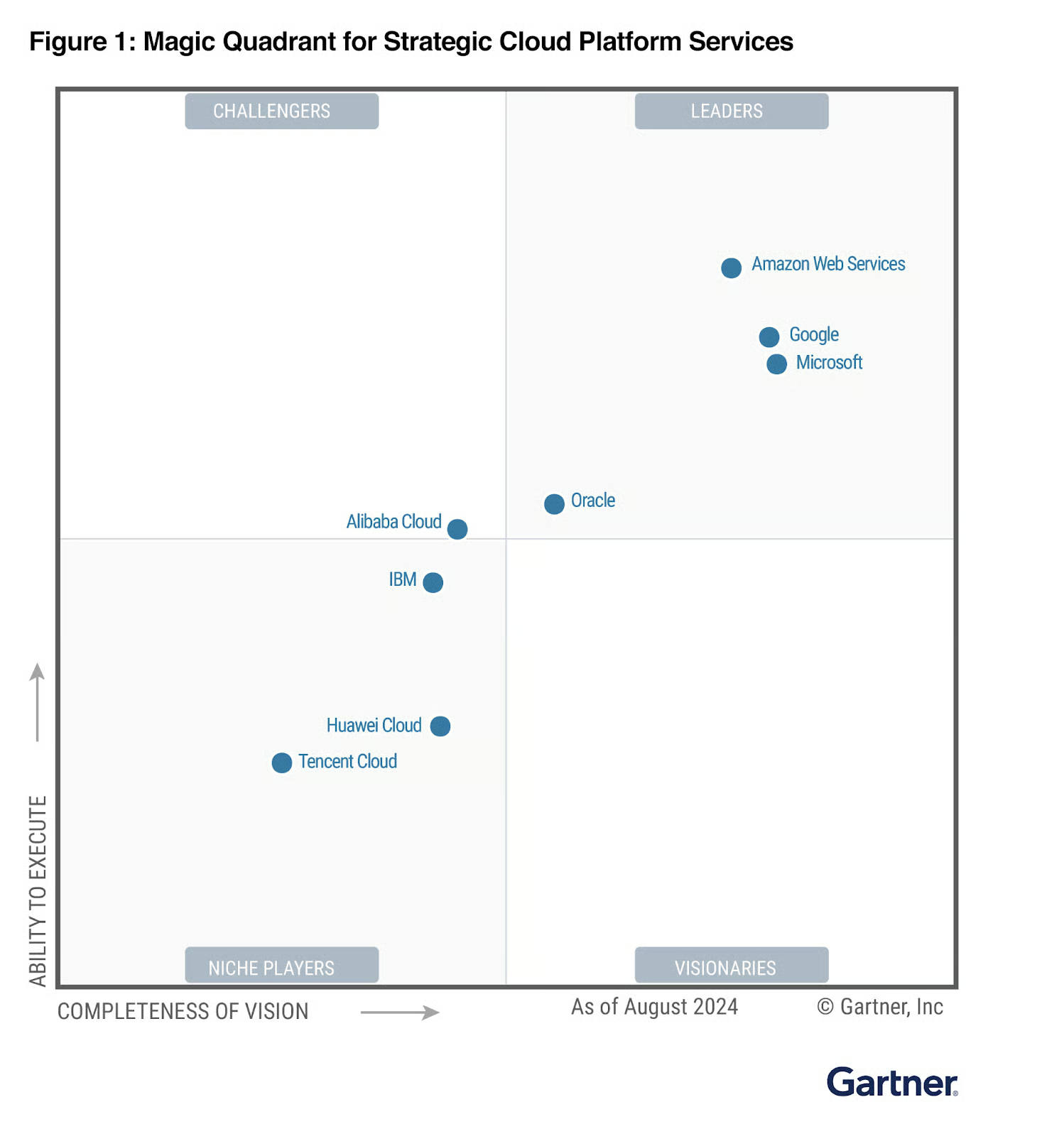
Magic Quadrant for Strategic Cloud Platform Services: Microsoft was named a Leader for Completeness of Vision in 2024
From what I have observed, one of the key considerations for Azure adoption is the learning curve for organizations and developers not familiar with Microsoft technologies. While Azure has made significant strides in supporting open-source technologies, some users may find the platform more intuitive if they already have experience with Microsoft development tools and practices.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google Cloud Platform has carved out a significant niche in the market, particularly among organizations focused on data analytics and machine learning. GCP is renowned for its advanced data analytics capabilities, with BigQuery serving as one of the most powerful and cost-effective data warehouse solutions available in the market.
GCP's integration with TensorFlow and other Google-developed machine learning frameworks makes it particularly attractive for organizations building AI and machine learning applications. The platform offers sophisticated tools for data processing, including Dataflow for both stream and batch processing, as well as Cloud AI Platform for building and deploying machine learning models at scale.
One thing I often mention when discussing GCP is that it has a smaller market share compared to AWS and Azure, which can translate to a smaller ecosystem of third-party tools and services. However, for organizations prioritizing data analytics and machine learning capabilities, GCP often provides superior tools and performance.
4. IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud focuses heavily on AI and machine learning services, leveraging IBM's expertise in artificial intelligence through its Watson platform. The service offers enterprise-grade solutions with a strong emphasis on security and compliance, making it attractive for regulated industries such as healthcare and financial services.
IBM Cloud's Watson AI services provide pre-built models for natural language processing, computer vision, and speech recognition, allowing organizations to quickly integrate AI capabilities into their applications. The platform also offers strong support for hybrid and multi-cloud deployments, reflecting IBM's understanding of enterprise IT complexity.
In my experience, one of IBM Cloud’s main limitations is its limited third-party integrations compared to larger competitors. Organizations may find fewer pre-built connectors and marketplace solutions, potentially requiring more custom development work.
5. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure emphasizes database services and high-performance computing, leveraging Oracle's decades of database expertise. OCI is particularly strong for organizations running Oracle applications and databases, offering optimized performance and cost advantages for these workloads.
The platform provides high-performance computing capabilities with bare metal servers and low-latency networking, making it suitable for demanding applications such as financial modeling and scientific computing. Oracle's autonomous database services reduce administrative overhead while maintaining high performance.
In my view, OCI's niche focus means it may not be the best choice for organizations requiring diverse cloud services beyond database and compute capabilities. The platform's ecosystem is more limited compared to the major cloud providers.
Comparative Analysis
Let’s take a deeper look at some of the key areas where these cloud service providers compete.
Performance and reliability
All major cloud service providers offer robust uptime guarantees, typically promising 99.9% to 99.99% availability for their core services. However, performance characteristics can vary significantly based on workload types and geographic location.
AWS's extensive global infrastructure provides the most consistent performance across regions, while GCP often delivers superior performance for data analytics workloads. Azure's performance is particularly strong for Microsoft-centric applications and services.
Security and compliance
Security and compliance capabilities are increasingly important differentiators among cloud providers. All major CSPs invest heavily in security infrastructure and offer comprehensive compliance certifications, including SOC 2, ISO 27001, and industry-specific standards like HIPAA and PCI DSS.
AWS provides the most granular security controls, while Azure offers excellent integration with existing Microsoft security tools. GCP emphasizes security by default with automatic encryption and advanced threat detection.
Pricing models
From what I have seen, cloud pricing models have evolved from simple pay-as-you-go structures to sophisticated options including reserved instances, spot pricing, and commitment-based discounts.
AWS offers the most complex but potentially cost-effective pricing options, while Azure provides good value for organizations already using Microsoft software. GCP often delivers competitive pricing for compute and storage, with particularly attractive rates for sustained workloads.
Ease of use
As I have seen across many projects, user experience varies significantly among providers, with each offering different strengths in interface design, documentation, and support.
AWS provides the most comprehensive documentation and the largest community, but it can be overwhelming for newcomers. Azure offers intuitive interfaces for users familiar with Microsoft products, while GCP provides clean, developer-friendly interfaces with excellent API documentation.
Comparison table
In the table below, we’ve compared the key features of the ‘big three’ cloud service providers. You can also find our detailed AWS vs Azure vs GCP comparison guide:
|
Criteria |
AWS |
Azure |
Google Cloud (GCP) |
|
Performance & Reliability |
Most consistent performance across regions due to extensive global infrastructure |
Strong performance for Microsoft-centric applications and hybrid environments |
Superior performance for data analytics workloads |
|
Security & Compliance |
Most granular security controls; broad compliance coverage |
Excellent integration with Microsoft security tools |
Security by default with automatic encryption and advanced threat detection |
|
Pricing Models |
Most complex but potentially most cost-effective (reserved instances, spot pricing, discounts) |
Good value for organizations already using Microsoft software |
Competitive compute/storage pricing; attractive sustained workload rates |
|
Ease of Use |
Largest community and most comprehensive documentation, but steep learning curve for newcomers |
Intuitive for Microsoft users; strong integration with existing Microsoft tools |
Clean, developer-friendly interface with excellent API documentation |
Choosing the Right CSP for Your Needs
Now that we’re familiar with the main players and their USPs, let’s take a closer look at how you can choose the right cloud service provider for your needs.
Assessing your project requirements
In my experience, selecting the appropriate cloud service provider requires careful evaluation of your specific compute needs, storage requirements, and scalability expectations. Organizations should consider their current technology stack, development team expertise, and long-term growth projections when making this decision.
Compute requirements vary dramatically across applications, from simple web hosting to complex machine learning workloads requiring specialized hardware. Storage needs encompass not only capacity but also performance characteristics, backup requirements, and data sovereignty considerations. Scalability requirements should account for both predictable growth and unexpected traffic spikes.
Budget considerations
What I tend to focus on when estimating cloud costs is understanding both the obvious and hidden fees associated with different providers. Most CSPs offer pricing calculators and cost management tools, but organizations should also consider costs for data transfer, premium support, and third-party integrations.
Hidden costs often include charges for data egress, premium storage classes, and support services. Organizations should also factor in the cost of training staff and potentially hiring cloud-specialized personnel when evaluating the total cost of ownership.
Support and community
The availability of high-quality support and an active community can significantly impact the success of cloud adoption. This includes access to comprehensive tutorials, active forums, responsive customer service, and local support presence.
AWS offers the largest community and most extensive third-party ecosystem, while Azure provides excellent support for organizations already working with Microsoft partners. GCP, while having a smaller community, offers high-quality documentation and responsive support for technical issues.
Conclusion
We’ve seen that the cloud provider market is shifting quickly, with each major player doubling down on its strengths. AWS still leads with the broadest range of services, Azure excels in enterprise integration and hybrid setups, and GCP stands out in data analytics and machine learning. Providers like IBM Cloud and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure continue to serve important niche needs.
In my view, the right choice comes down to your organization’s specific requirements, existing tech stack, and long-term goals. It’s not just about features or pricing; performance, security, support, and ecosystem all matter.
As the market matures, the differences between providers are narrowing, and most can handle common use cases well. The real key to success is not just picking a provider, but building the skills and processes to get the most out of it.
To keep learning, be sure to check out the following resources:
Cloud Service Providers FAQs
What are the key differences between AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud?
AWS offers the most services and global reach, Azure excels in Microsoft integration and hybrid cloud, while Google Cloud leads in data analytics and AI capabilities.
How do cloud service providers ensure data security and compliance?
They implement encryption, identity management, threat detection, and comply with standards like ISO 27001, HIPAA, and SOC 2.
What are the benefits of using a multi-cloud strategy?
It reduces vendor lock-in, improves reliability, allows workload optimization, and enhances flexibility across services.
How is AI transforming cloud computing services?
AI enhances automation, optimizes resource usage, powers predictive analytics, and enables faster deployment of intelligent applications.
What are the emerging trends in cloud computing for 2026?
Key trends include expanded hybrid and multi-cloud adoption, greater AI and machine learning integration, edge computing growth, and more tailored industry-specific cloud solutions.
As the Founder of Martin Data Solutions and a Freelance Data Scientist, ML and AI Engineer, I bring a diverse portfolio in Regression, Classification, NLP, LLM, RAG, Neural Networks, Ensemble Methods, and Computer Vision.
- Successfully developed several end-to-end ML projects, including data cleaning, analytics, modeling, and deployment on AWS and GCP, delivering impactful and scalable solutions.
- Built interactive and scalable web applications using Streamlit and Gradio for diverse industry use cases.
- Taught and mentored students in data science and analytics, fostering their professional growth through personalized learning approaches.
- Designed course content for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) applications tailored to enterprise requirements.
- Authored high-impact AI & ML technical blogs, covering topics like MLOps, vector databases, and LLMs, achieving significant engagement.
In each project I take on, I make sure to apply up-to-date practices in software engineering and DevOps, like CI/CD, code linting, formatting, model monitoring, experiment tracking, and robust error handling. I’m committed to delivering complete solutions, turning data insights into practical strategies that help businesses grow and make the most out of data science, machine learning, and AI.

