The term AI has been in vogue for a while now. Artificial intelligence is a concept that has existed for many years, and various technologies rely on AI to function. But with tools like ChatGPT and Google Bard making headlines, it feels like a new age of artificial intelligence is upon us. But what is AI? And how does it work?
Here, we take a brief look at what AI is, why it matters, and how you can learn more about this fascinating field. As well as examples of where artificial is used, we’ve included quotes from experts and resources for further reading.
What is AI?
Artificial Intelligence is a subfield of computer science that focuses on creating intelligent agents capable of performing tasks that would typically require human levels of intelligence. These tasks include problem-solving, speech recognition, and decision-making, among others.
AI is an interdisciplinary science with many approaches; it can be rule-based and operate under a predefined set or conditions, or it can use machine learning algorithms to adapt to its environment. The latter is particularly powerful, as it allows AI systems to learn from data, making them more versatile and capable of handling unforeseen scenarios.
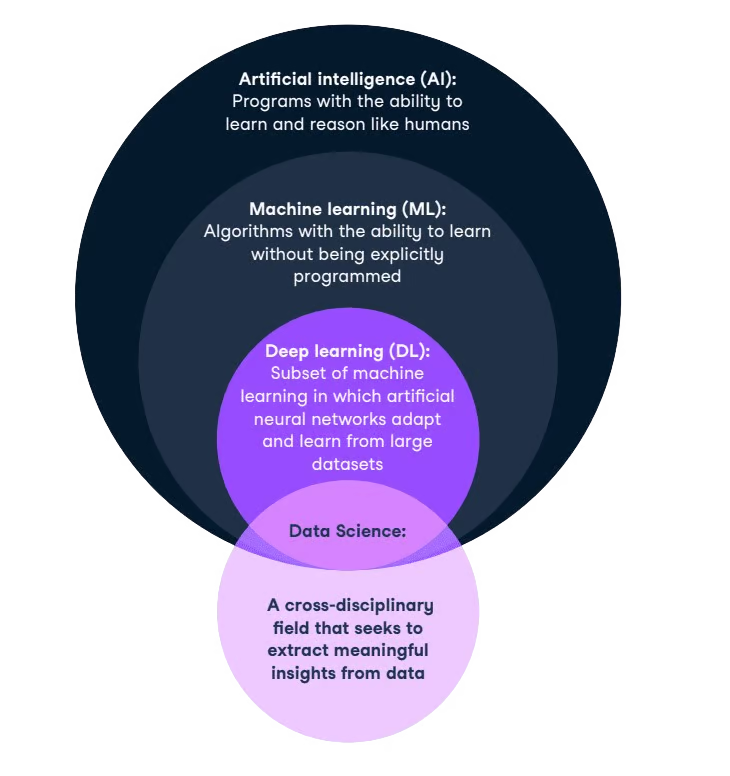
AI in relation to data science and other key concepts
Common misconceptions
It’s also worth mentioning what AI isn’t. There are a lot of misconceptions about what artificial is, and here are some common incorrect beliefs:
- AI is synonymous with robots. AI is not limited to robotics; it's a broader field that includes various technologies like search algorithms and natural language processing.
- AI can surpass human intelligence anytime soon. The idea that AI will soon outsmart humans is exaggerated; Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is still theoretical and far from realization.
- AI understands content like humans do. AI doesn't "understand" text or speech in the human sense; it processes data based on patterns but lacks comprehension.
- AI is unbiased. Contrary to belief, AI can inherit biases from its training data or designers, meaning it’s not inherently unbiased. Check out our guide on the ethics of generative AI to learn more.
- AI can replace all human jobs. While AI can automate specific tasks, it cannot replace jobs that require emotional intelligence, creativity, and other human-specific skills.
You can explore the differences between AI and machine learning, and machine learning and deep learning, in separate guides.
AI Glossary
We’ll use a range of terms in our exploration of artificial intelligence, some of which will be unfamiliar. We’ve created a list of key artificial intelligence terms and their meanings:
Algorithm
A set of rules or instructions that a computer follows to perform a specific task. Algorithms are the building blocks of all AI systems.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
A currently theoretical form of AI that has the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across different domains, reason through problems, have consciousness and even have emotional understanding. This is in contrast to Narrow AI, which is designed and trained for a specific task.
Deep Learning
A specialized type of machine learning that mimics the way our brain works, allowing computers to learn from experience and understand the world in terms of a hierarchy of concepts. In simple terms, deep learning is like a virtual brain that helps computers learn from data so they can make decisions on their own.
Machine Learning
A way to give computers the ability to learn from data and make decisions without being explicitly programmed. Think of it as teaching computers to learn from experience, much like how humans do. In essence, machine learning is the method by which AI gets the "intelligence" part of its name. You can learn more about the topic in our Understanding Machine Learning course.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
A field of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through natural language. The ultimate objective of NLP is to enable computers to understand, interpret, and generate human languages in a way that is both meaningful and useful. Check out our Introduction to Natural Language Processing in Python course to find out more.
Neural Network
A computing model inspired by the structure of neurons in the human brain. Neural networks are used in various applications that involve pattern recognition, such as image and voice recognition. We have a whole article exploring what neural networks are.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
AI can be categorized based on its capabilities and functionalities.
When it comes to capabilities, we can distinguish between between types of AI in the following ways:
Narrow AI
Also known as Weak AI, narrow AI is designed and trained to perform a specific task. It operates under a limited pre-defined set of conditions and doesn't possess the broad range of capabilities that humans have. Most current AI systems, including reactive machines and limited memory machines (see below), fall under this category.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Also known as General AI, this type of AI would have the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across different domains. It would be capable of self-awareness, reasoning, and emotional understanding. General AI remains largely theoretical at this point.
Artificial Super Intelligence
This is an advanced form of AI that would surpass human intelligence in nearly all aspects, from creativity and social intelligence to problem-solving abilities. Super AI is a concept that exists more in the realm of science fiction and future speculation than in current reality.
We can also explore the types of artificial intelligence based on its functionality:
Reactive machines
These are the most basic forms of AI, designed to perform specific tasks. For example, IBM's Deep Blue, a chess-playing supercomputer, falls under this category. Reactive machines cannot store memories or use past experiences to inform current decisions.
Limited memory
Limited Memory AI can store past data and use it to make better predictions or decisions. This type of AI is commonly found in recommendation systems like those used by Netflix or Amazon.
Theory of mind
This is a theoretical concept that refers to AI systems potentially understanding human emotions, beliefs, and thoughts. While intriguing, we have yet to achieve this level of AI sophistication.
Self-awareness
The pinnacle of AI development would be self-aware machines that understand their existence and can make decisions based on self-interest. This remains a subject of ongoing research and ethical debate.
Applications and Examples of AI
AI's reach extends far beyond academia and specialized industries. Here are some ways in which artificial intelligence is used in today’s world:
Everyday technology
AI is deeply integrated into the technologies we use daily. From Google Maps optimizing your route based on real-time traffic data to Siri and Alexa setting your alarms and answering your questions, AI is near omnipresent. These applications often use Narrow AI to perform specific tasks efficiently.
Business and industry
The business world is already embracing AI, with an IBM survey finding that more than a third of companies (35%) reported using AI in their business in 2022. Organizations across many sectors are finding uses for artificial intelligence, including:
- Healthcare. AI algorithms can analyze medical images to identify early signs of diseases like cancer. They can also assist in drug discovery by predicting how different compounds can treat diseases.
- Finance. Artificial intelligence is used in fraud detection, where machine learning algorithms can analyze transaction patterns to flag unusual activities. It also plays a role in algorithmic trading, optimizing portfolios, and personalizing banking services.
- Retail. Tools like recommendation systems in online shopping platforms are often powered by AI, helping businesses upsell and cross-sell products. It can also assist in inventory management and demand forecasting.
Large Language Models like ChatGPT are revolutionizing the way we interact with software. Whether it's customer service, project management, or data analysis, these AI tools are enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and productivity across all sectors.
Noelle Silver Russel, Global AI Solutions & Generative AI & LLM Industry Lead at Accenture
Gaming and entertainment
As we saw in our article on creativity and generative AI, there is a whole new frontier of art that artificial intelligence can help facilitate. Here are some of the ways it's currently in use:
- Video games. Algorithms control non-player characters (NPCs), making them more responsive and realistic. Advanced AI can even adapt to individual players' behaviors to adjust the game's difficulty level.
- Music and film. Content recommendations on platforms like Spotify and Netflix use AI, and it can even assist in the creative process, such as composing music or helping in film editing.
Public services and infrastructure
We’re seeing government agencies and similar organizations using artificial intelligence for a host of different tasks:
- Traffic management. AI algorithms can analyze traffic data in real-time to optimize signal timings, reducing congestion and improving road safety.
- Emergency response. Areas such as natural disaster prediction and response can benefit from artificial intelligence, such as forecasting hurricanes and optimizing evacuation routes.
How Does AI Work?
To truly grasp the essence of Artificial Intelligence, it's helpful to understand the steps that go into making an AI system function. Let's break it down in a beginner-friendly manner. You can get a full understanding of the AI fundamentals with our skill track, which covers actionable knowledge on popular AI topics like ChatGPT, large language models, generative AI, and more.
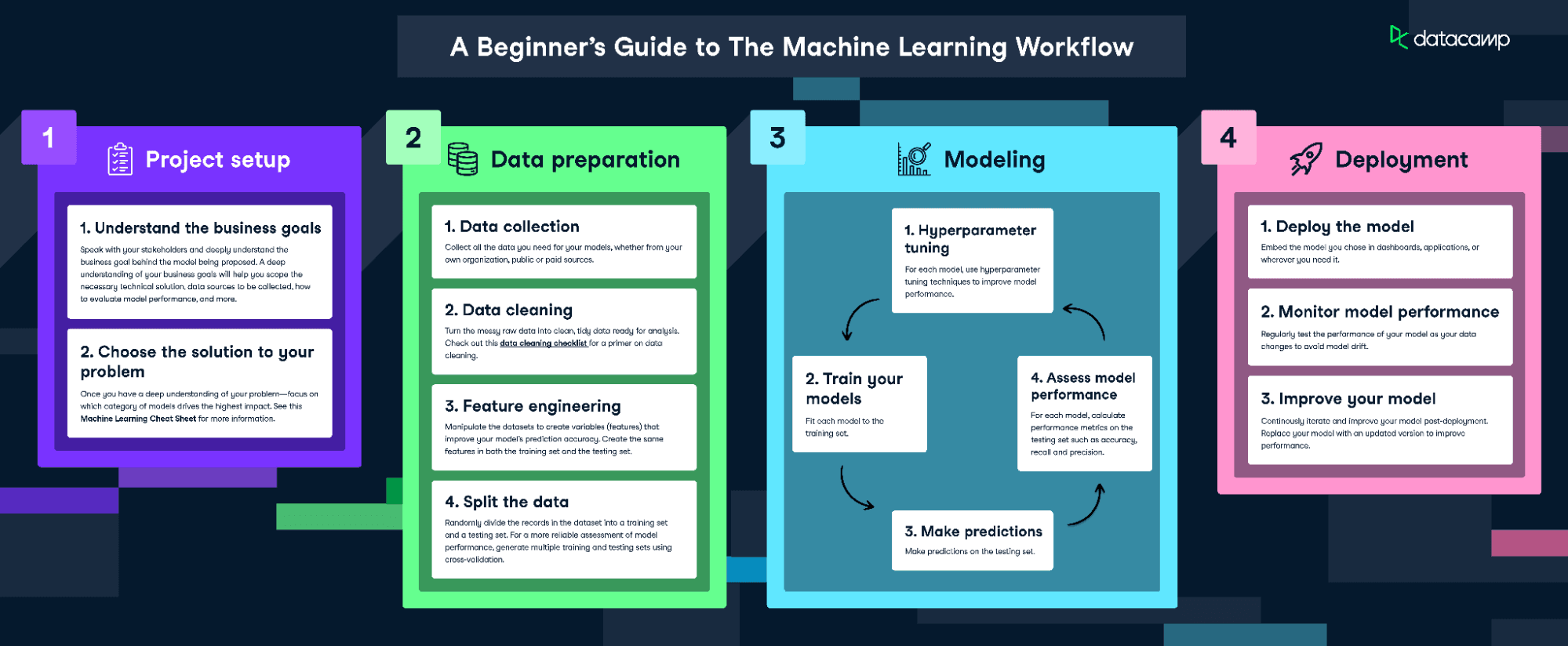
The AI and machine learning workflow
Step 1: Data collection
The first step in any AI project is gathering data. This could be anything from pictures and text to more complex data like human behavior. The data serves as the raw material that the AI system will learn from.
Step 2: Data preparation
Once the data is collected, it needs to be prepared and cleaned. This means removing any irrelevant information and converting the data into a format that the AI system can understand.
Step 3: Choosing an algorithm
An algorithm is like a recipe for how the AI system will process the data. Different algorithms are better suited for different tasks. For example, you might use a specific algorithm for image recognition and another for natural language processing. You can explore various types of algorithms in a separate article.
Step 4: Training the model
The prepared data is fed into the chosen algorithm to "train" the AI model. During this phase, the model learns to make predictions or decisions based on the data. Think of this as the AI system studying for an exam.
Step 5: Testing the model
After training, the model is tested to see how well it performs. If it's not accurate enough, it may need to be trained further or adjusted.
Step 6: Deployment
Once the model is trained and tested, it's ready to be deployed into a real-world application. This could be anything from a chatbot answering customer queries to a medical AI analyzing X-rays.
Step 7: Ongoing learning
Many modern AI systems have the ability to learn and adapt over time. This means they can improve their performance as they gather more data, making them more efficient and accurate.
Getting Started With AI
This article has covered some of the very basics of AI. If you’re intrigued by what you’ve read so far and want to learn more about this fascinating field, we have a comprehensive guide on how to learn AI from scratch, which covers everything you need to know to get started on the path to AI mastery. You’ll find resources to help you make a start, as well as a sample learning plan that can guide you through your first few months of learning AI.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Concepts in Python

A senior editor in the AI and edtech space. Committed to exploring data and AI trends.
