Track
Excel TEXTSPLIT() is a function that allows you to split text into multiple cells based on a specified delimiter of your choice. In my experience, it's useful when you need to break apart data that sometimes gets clumped together, like a name, address, and postal code that gets combined all into one cell, for whatever reason. Take a look at the following, which I expect will answer your most pressing questions.
Understanding the Excel TEXTSPLIT() Function
The TEXTSPLIT() function is designed, as its name really tells us, to divide a text string into separate cells. It does this by using one or more delimiters. WhatTEXTSPLIT() then accomplishes is that it makes it extracts specific pieces of information from a single cell and distributes them across columns or, if you want, rows.
Here’s the syntax:
=TEXTSPLIT(text, col_delimiter, [row_delimiter], [ignore_empty], [pad_with])-
text: The text you want to split. -
col_delimiter: The character(s) that separate columns. -
row_delimiter: (Optional) The character(s) that separate rows. -
ignore_empty: (Optional) TRUE to ignore empty values. -
pad_with: (Optional) Value to use for missing values.
Excel TEXTSPLIT() for Basic Splitting
It's best to try it. Let’s look at a simple example of splitting a full name into first and last names. This is also probably the most common case.
Suppose cell A2 contains the name of a well-known English statistician and social reformer: "Florence Nightengale," but you want "Florence" and then "Nightengale".
To split her name into two cells (first name and last name), use:
=TEXTSPLIT(A2, " ")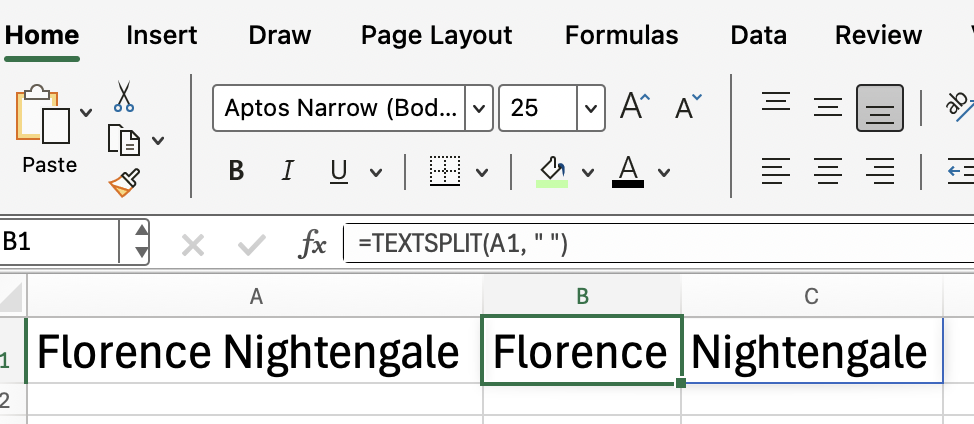
Excel TEXTSPLIT() for Splitting Text into Rows
You can also split text into rows instead of columns by using the row_delimiter argument which I listed earlier under the function syntax.
So, if cell A3 contains: "Apple;Banana;Cherry" and you want to split each fruit into a separate row, try again with the argument specified.
=TEXTSPLIT(A1, , ";")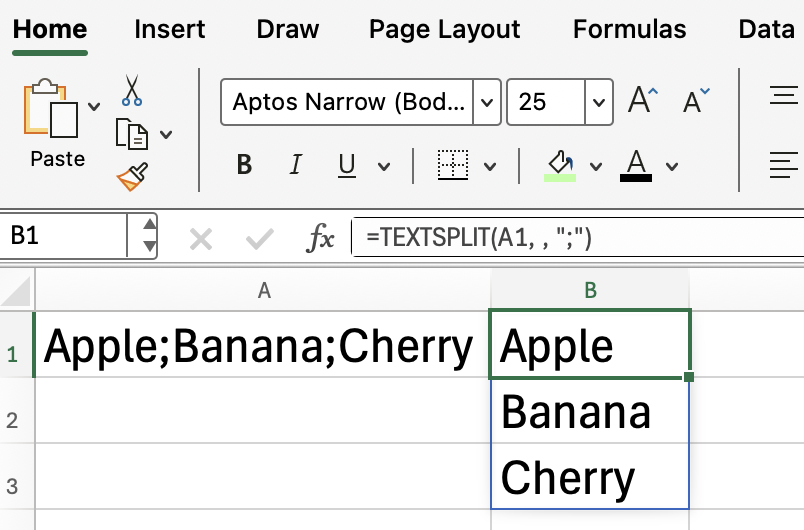
This formula leaves the column delimiter blank. Just for variety, I made the delimiter a semicolon this time.
Excel TEXTSPLIT() with Multiple Delimiters
Sometimes, your data may use more than one delimiter. TEXTSPLIT() allows you to specify an array of delimiters.
If you look closely, you can see that the next example is the same, except that it has both a comma and a semicolon.
=TEXTSPLIT(A4, {",",";"})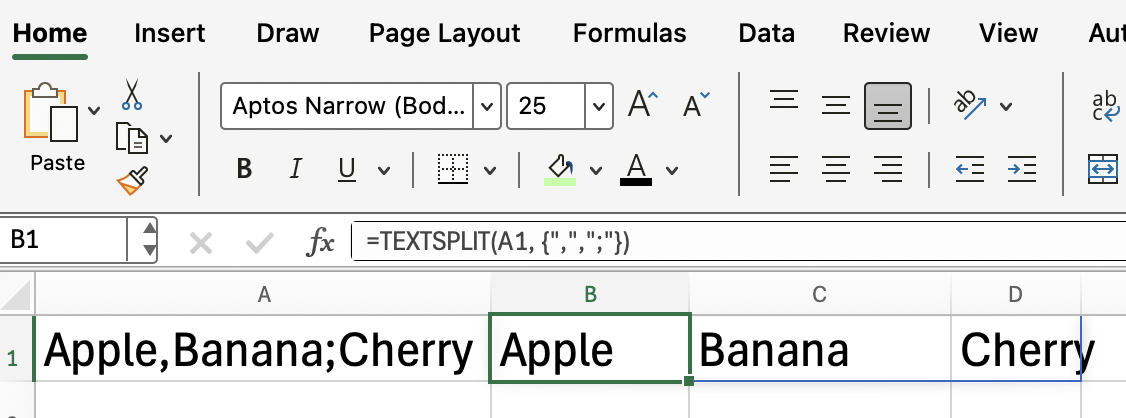
Dealing with Empty Values
If your text contains consecutive delimiters, you might get empty cells in your results. You can use the ignore_empty argument to control this behavior.
=TEXTSPLIT("A,,B", ",", , TRUE)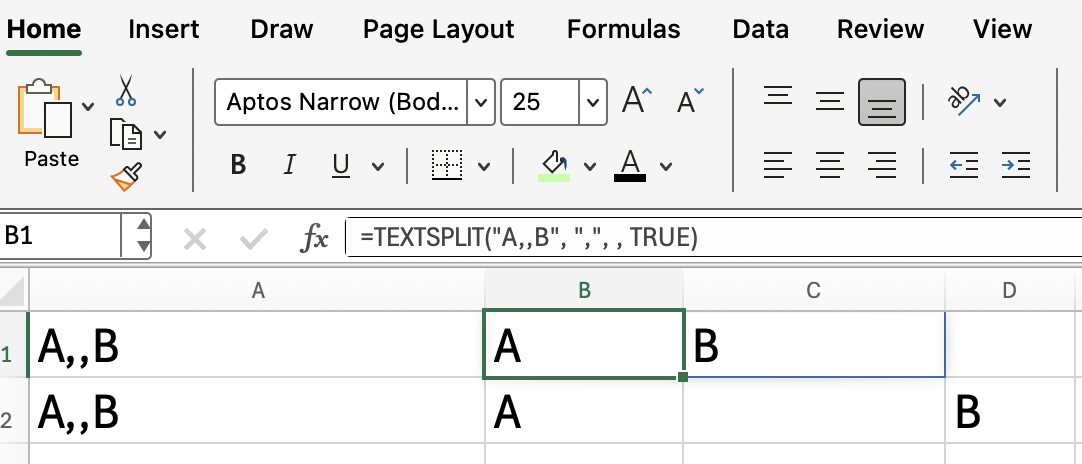
The first row has the ignore_empty argument as TRUE; in the second row, it's set to FALSE, and you can see the difference.
Tips for More Advanced Use
Here are some additional tips for using TEXTSPLIT() in more complex scenarios:
-
Combine with TRIM() to remove extra spaces from results.
-
Use SEQUENCE() to dynamically reference split results.
-
Pair with TEXTJOIN() to recombine split data if that's what you need.
Sometimes you have to combine multiple functions if your datasets are especially messy or inconsistent.
Conclusion
The TEXTSPLIT() function in Excel is a useful tool for breaking apart text into multiple cells, whether by columns or rows.
Keep learning Excel with us! We have some great courses such as Financial Modeling in Excel and Advanced Excel Functions.

I'm a data science writer and editor with contributions to research articles in scientific journals. I'm especially interested in linear algebra, statistics, R, and the like. I also play a fair amount of chess!
Advance Your Career with Excel
Gain the skills to maximize Excel—no experience required.
