Track
In Excel, hyperlinks are not only useful to include references to external websites, they offer an intuitive and handly way to navigate between sheets and link information cells, thereby enabling interactive spreadsheets.
In this tutorial, we will analye how to create hyperlinks in Excel and how to manage the information they contain. We will cover the three main ways to create hyperlinks, whether through the Insert menu, the HYPERLINK() function, and VBA/macros. Finally, we will cover some interesting use cases to make the most out of Excel hyperlinks.
For this tutorial, we will use a simple spreadsheet with a subset of articles published in the DataCamp Blog. It contains two sheets, the first with information about the articles, and the second with basic information about the authors.
How to Insert a Hyperlink in Excel
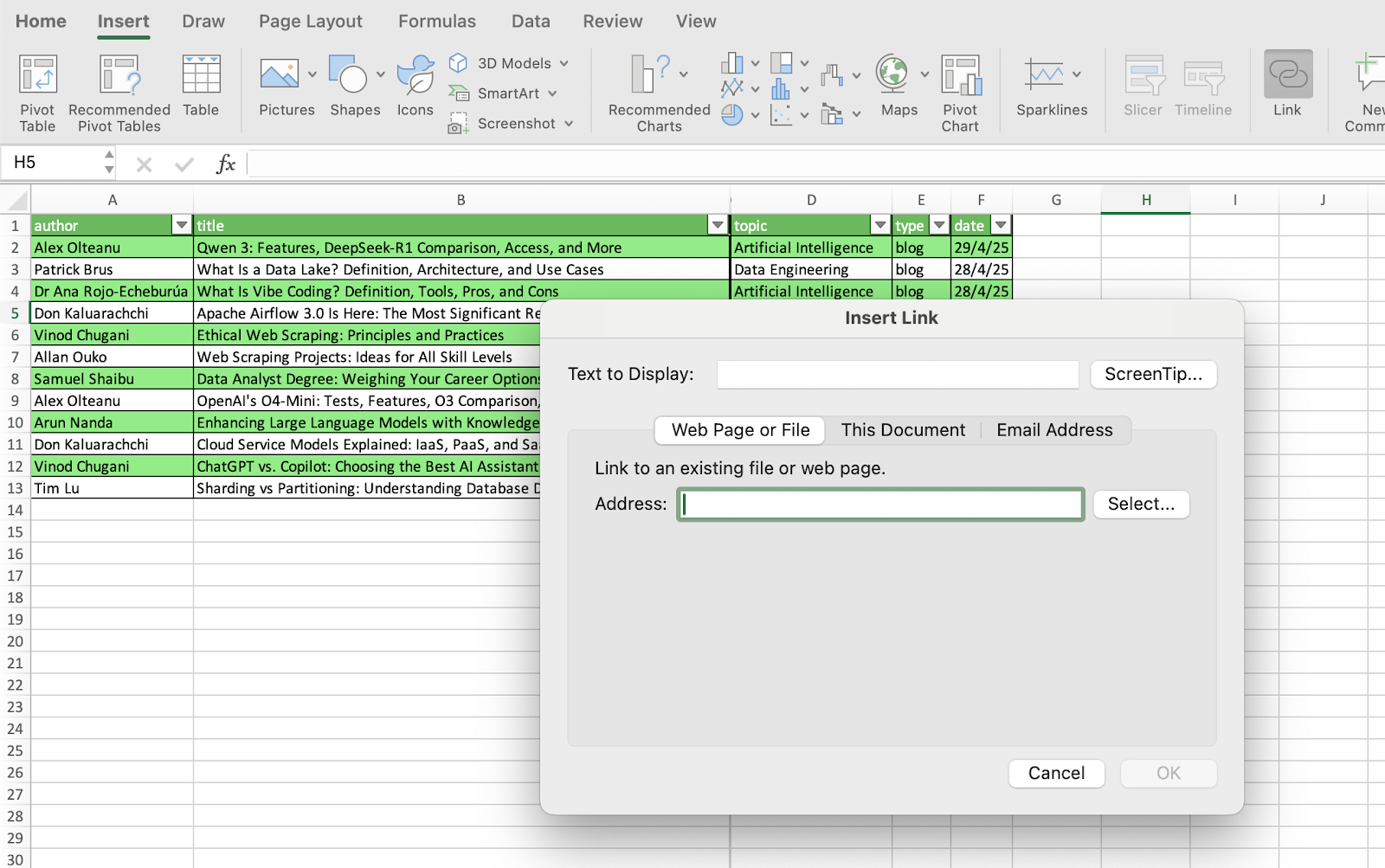
The fastest way to create a hyperlink in Excel is to go to Insert > Link. Then, you will access a box with several options to create hyperlinks, including:
- Webpage or file
- This document
- Email address
How to insert a webpage or file hyperlink
To create a webpage or file hyperlink, just add the URL or location of the file in your computer in the Address box.
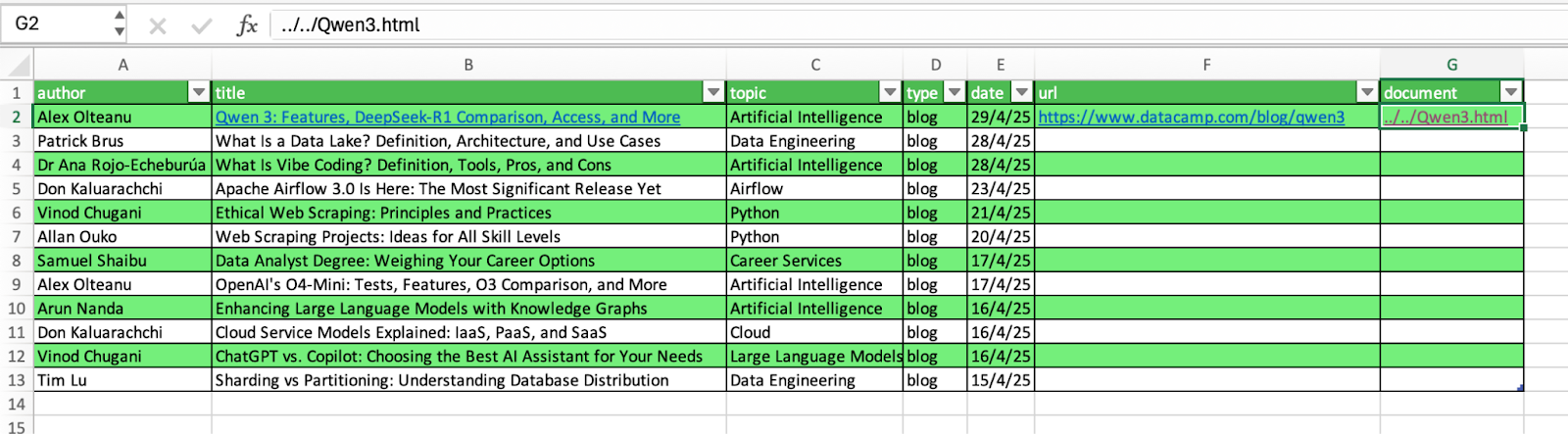
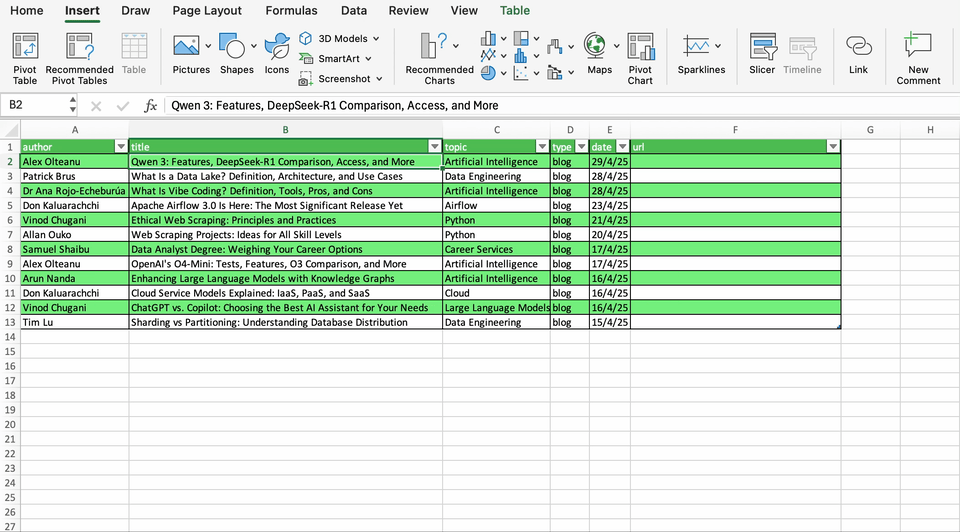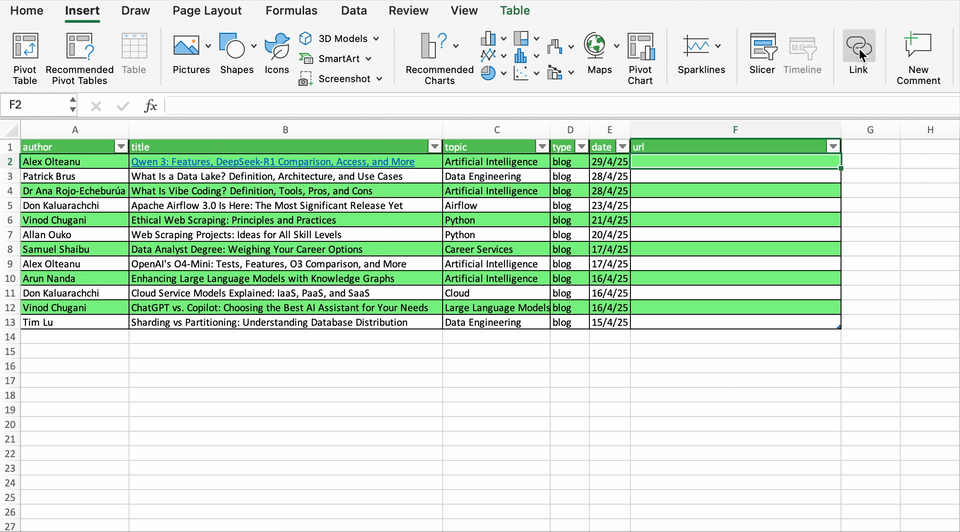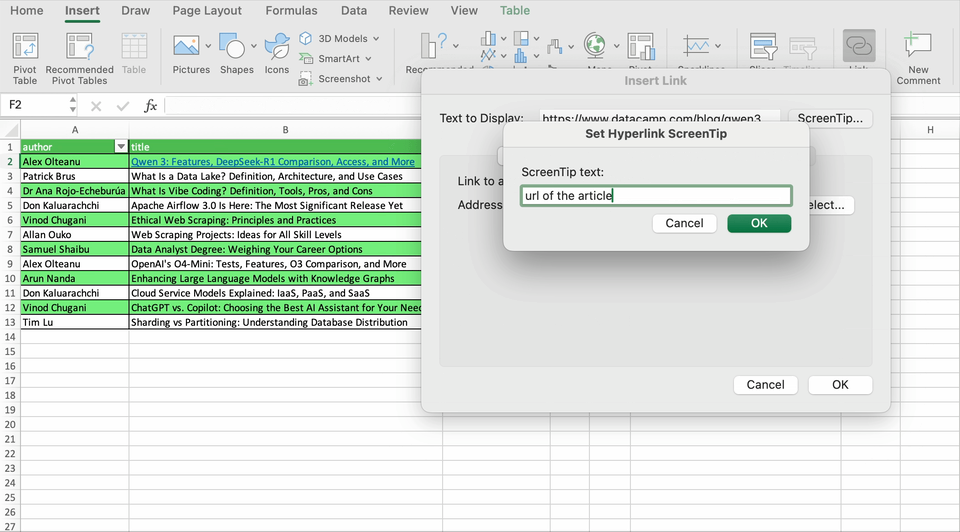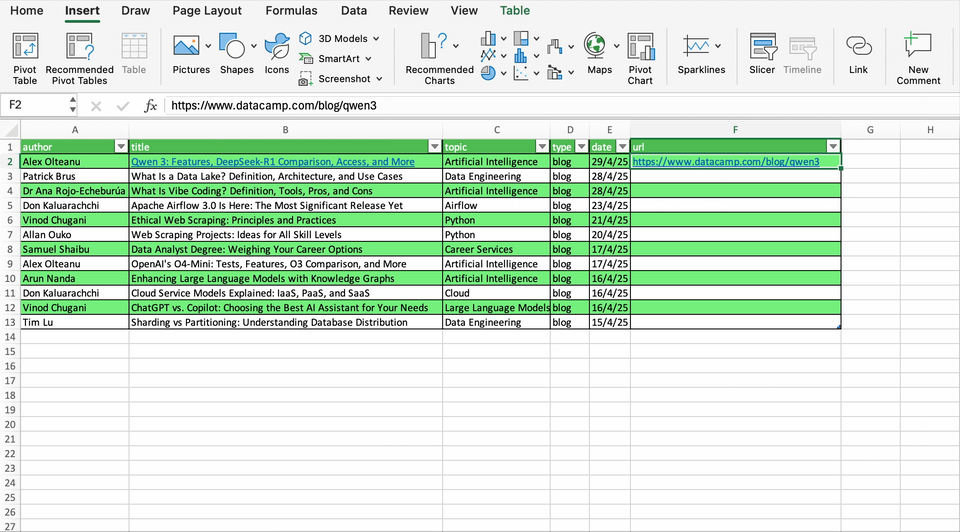
For example, let’s create a link to the first article in our sample. We can directly create the hyperlink in the cell with the title of the article (B2) or in a separate column. When we add the URL, Text to Display will return by default the title of the article. Once you finish the operation, you will see the title with a new formatting, indicating it has an hyperlink.
In case we create the hyperlink in a separate blank cell, Text to Display will return the URL. However, you are free to choose the wording of the text that will contain the hyperlink.
Finally, to display helpful information when you rest the pointer on the link, your can use the ScreenTip button.
The process to include a file is the same. Just choose the local file you want to insert and Excel will create the hyperlink with the full path.
Below you can find a hyperlink with the location of an HTML file with the article.
Notice that the hyperlink references the path in your computer, so it will not work in the computer of other users you may share the worksheet with, unless it's in shared drive.
How to link a specific location in your worksheet
Excel also allows you to create hyperlinks containing internal references within your worksheets. In this case, you will have to specify the cell reference (it can be a single cell or a range) in the worksheet of your interest.
You can also create defined names with a group of cells and use it instead of the cell reference.
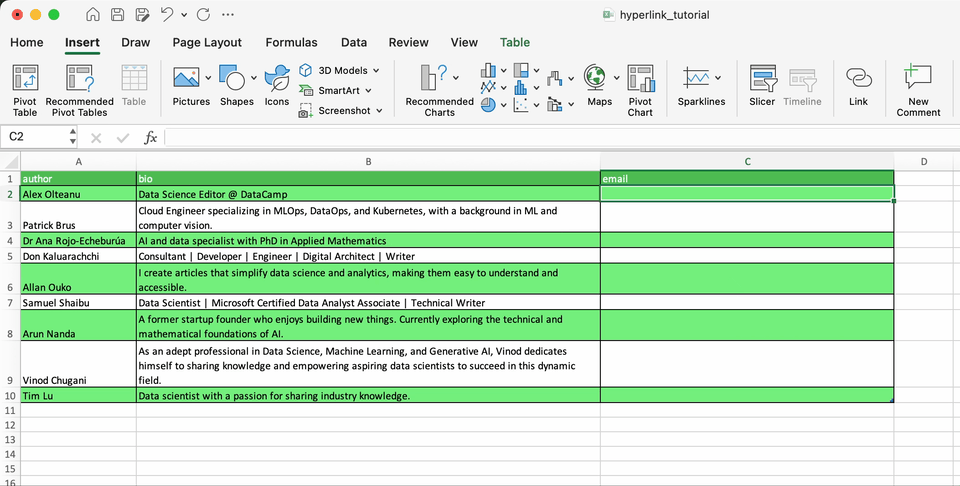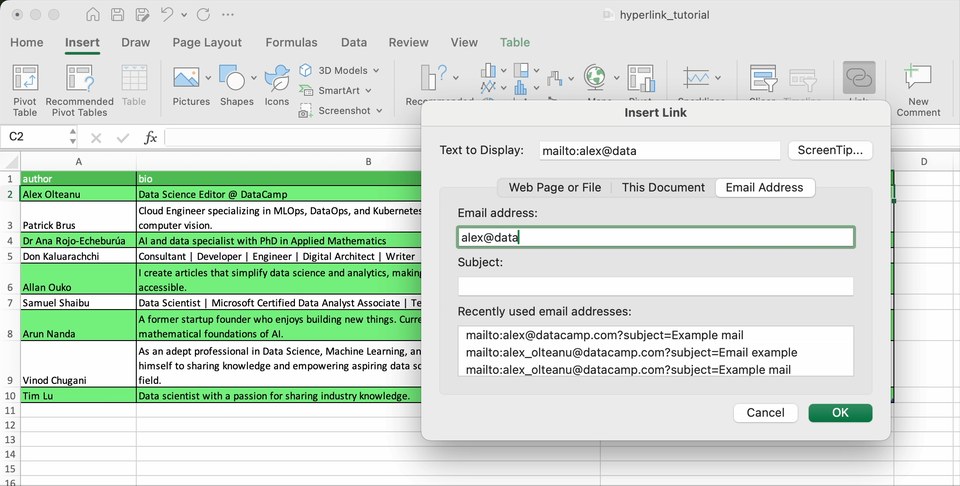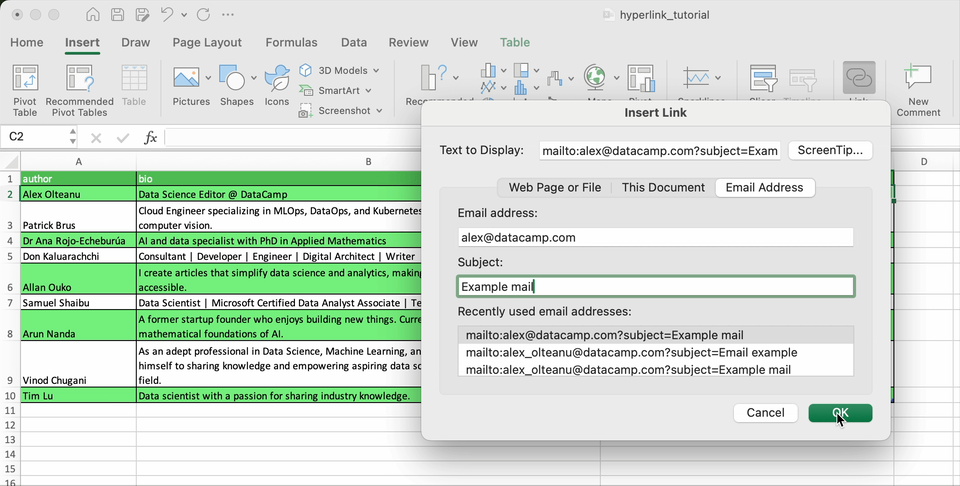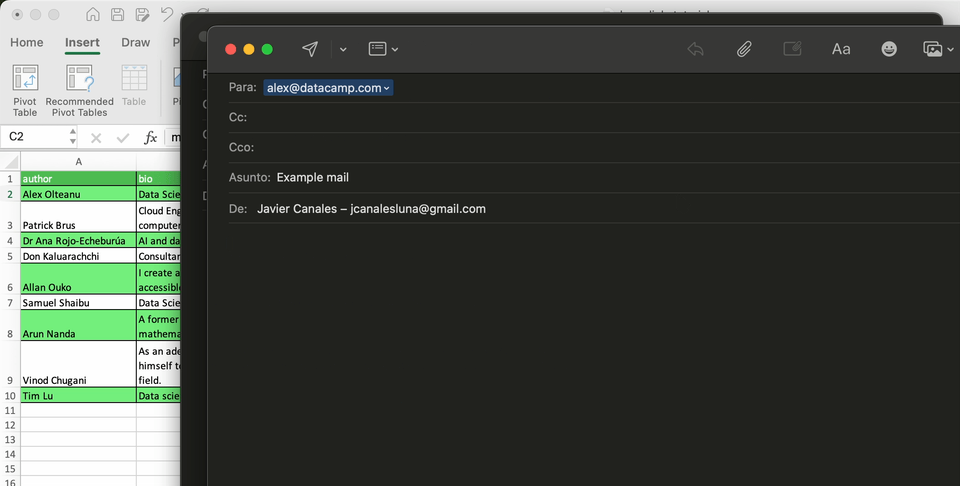
How to link email addresses
It’s very common to have a column containing emails. Excel allows you create hyperlinks that automatically launch your email program and create an email messages with the provided address and, optionally, a subject.
Let’s see how it works with a fictional email address.
Managing and Formatting Existing Hyperlinks in Excel
Once you create your hyperlinks, Excel provides you with different tools to manage and formate them. Let’s see how to perform some basic operations.
Editing a hyperlink
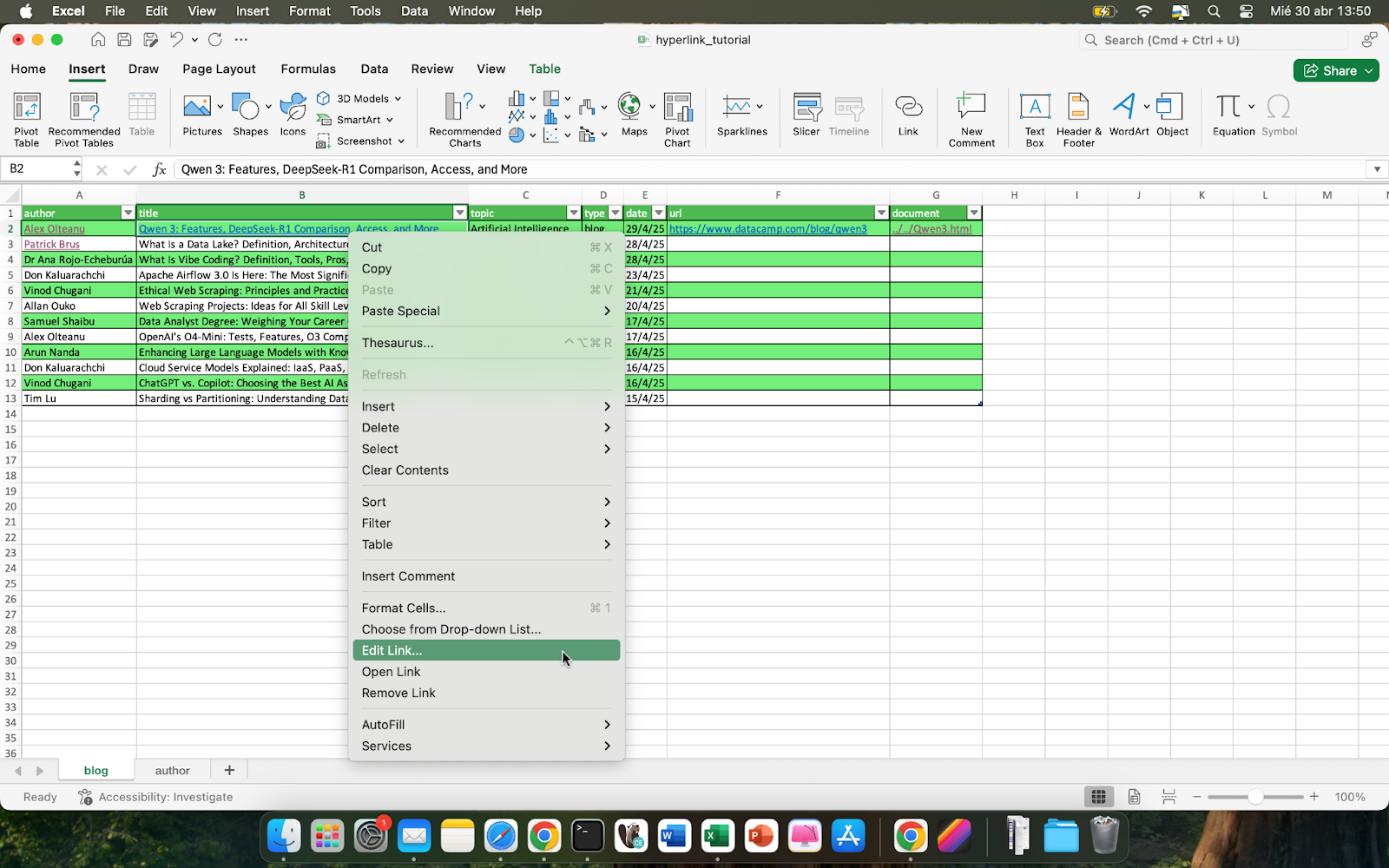
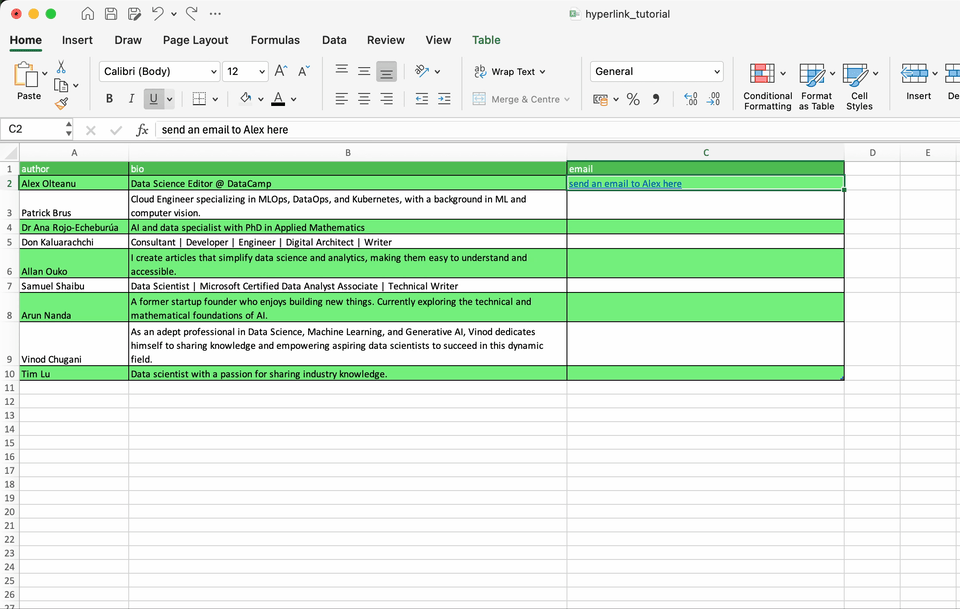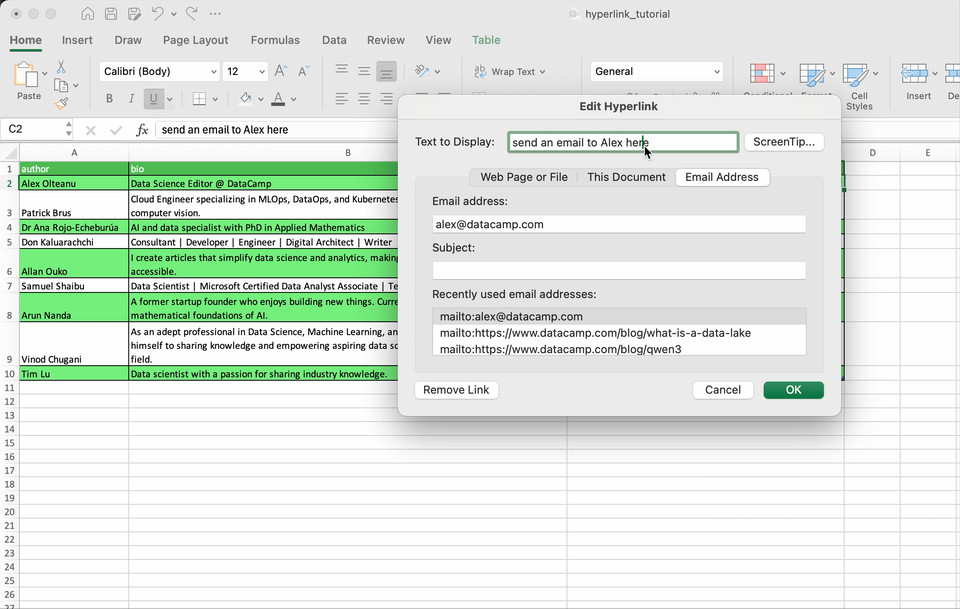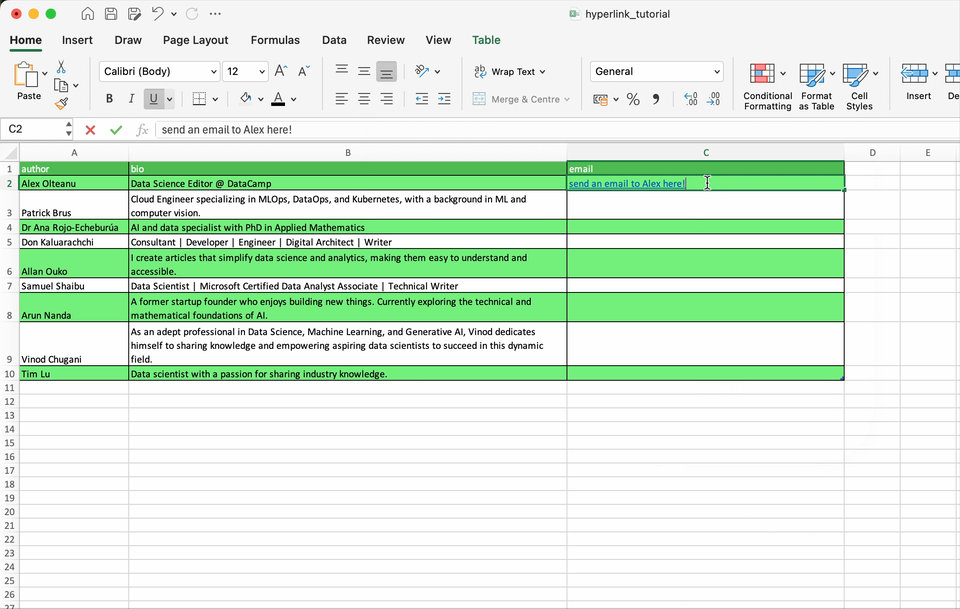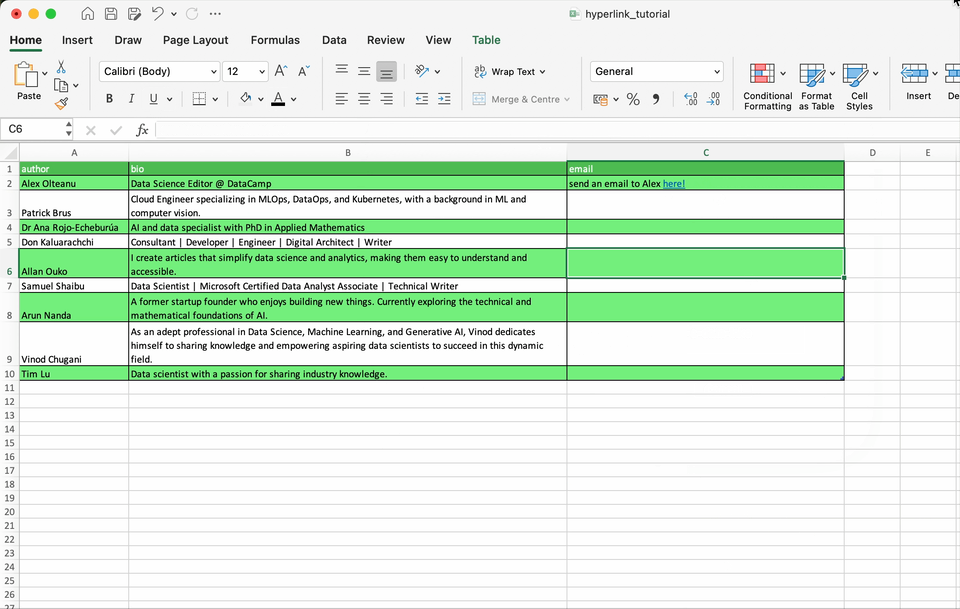
To edit an existing hyperlink, right-click the hyperlink and select Edit Hyperlink to update the address or display text.
Removing a hyperlink
To remove an existing hyperlink, right-click and choose Remove Hyperlink.
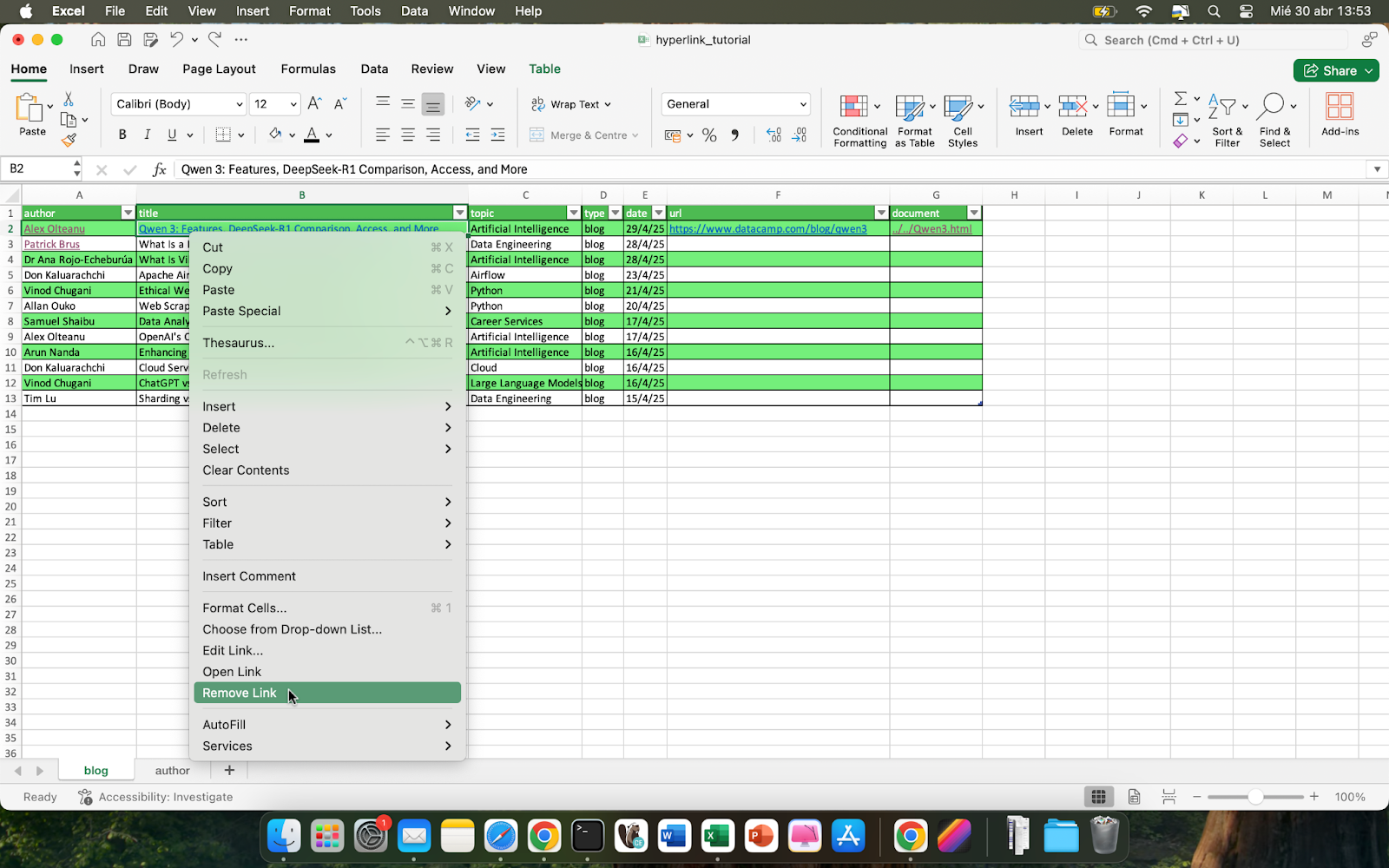
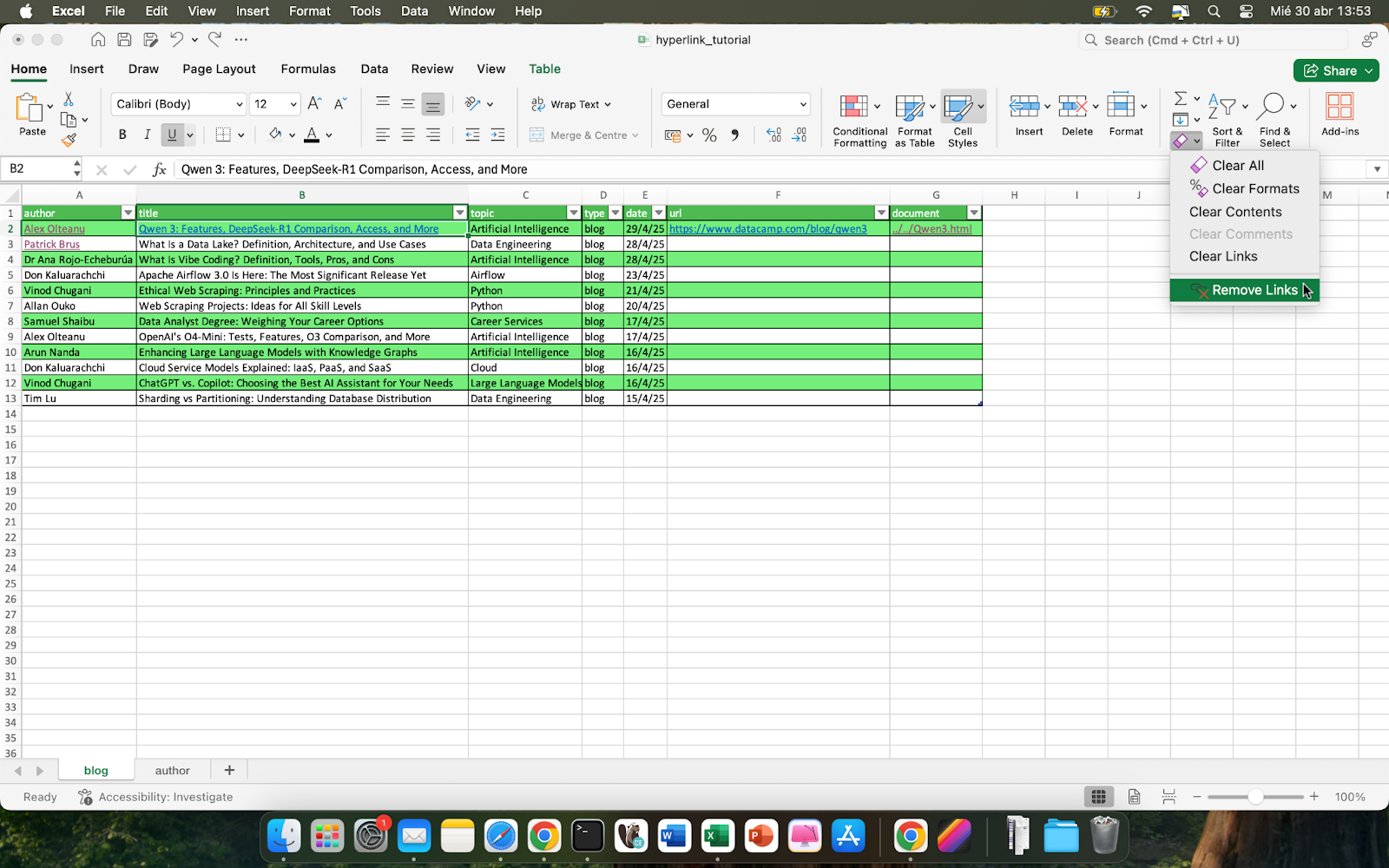
Or, if you want to remove multiple hyperlinks at once, select the cells of your interest and go to Home > Clear > Remove Hyperlinks.
Formatting hyperlinks
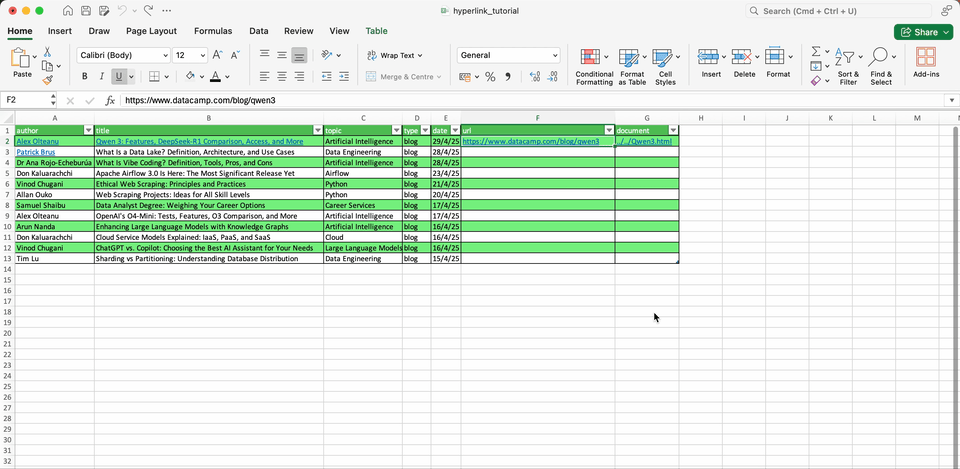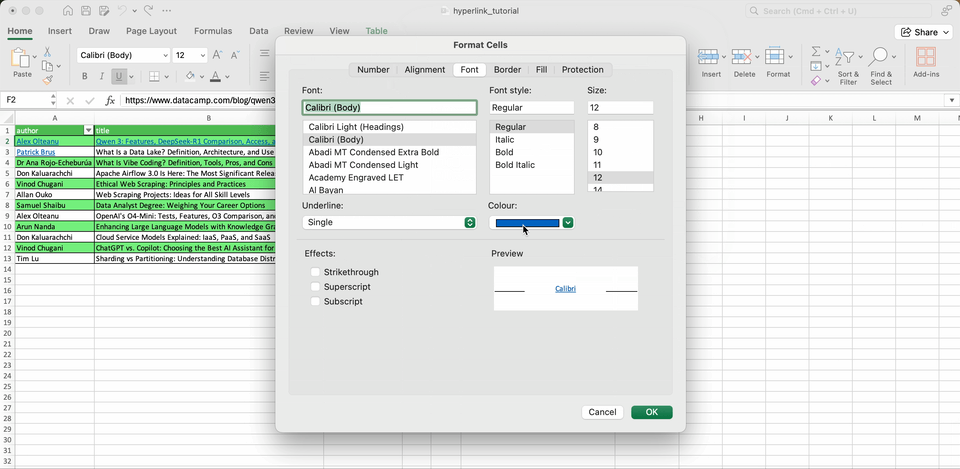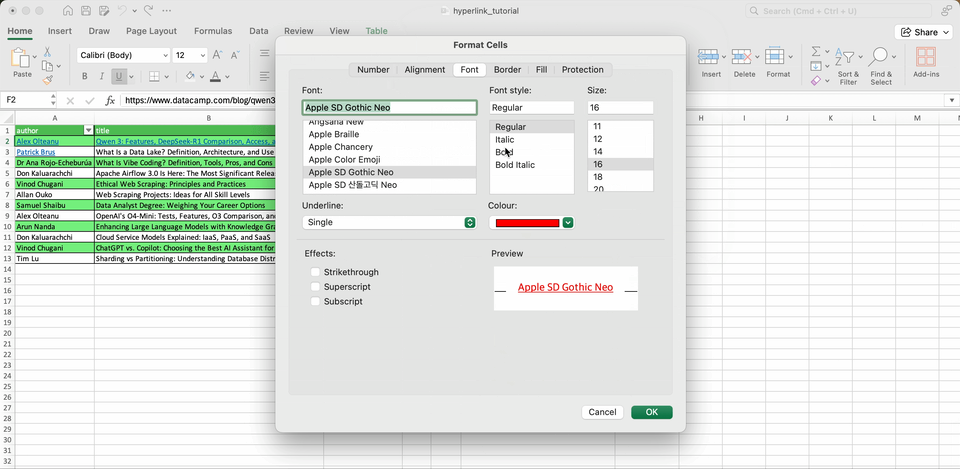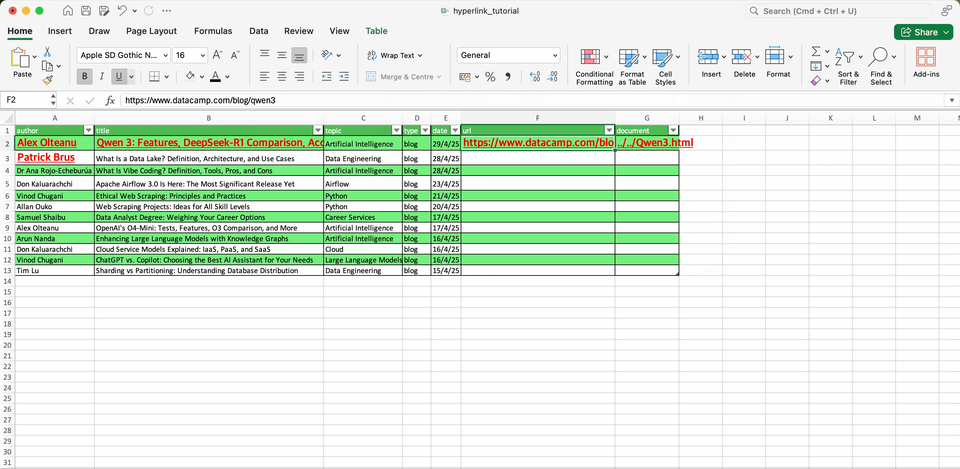
Excel uses a default style for hyperlinks, but you are free to use other styles. Just go to Cell Styles > Hyperlink for manually adjust font color and underline settings, or even create new styles.
Building Links with the HYPERLINK() Function
The ribbon menu will normally suffice to create and change hyperlinks. However, in certain scenarios, you may want to manually create hyperlinks using the HYPERLINK() function.
This function will help you either create new hyperlinks from scratch or convert existing plain text into clickable links, depending on the starting point of the data.
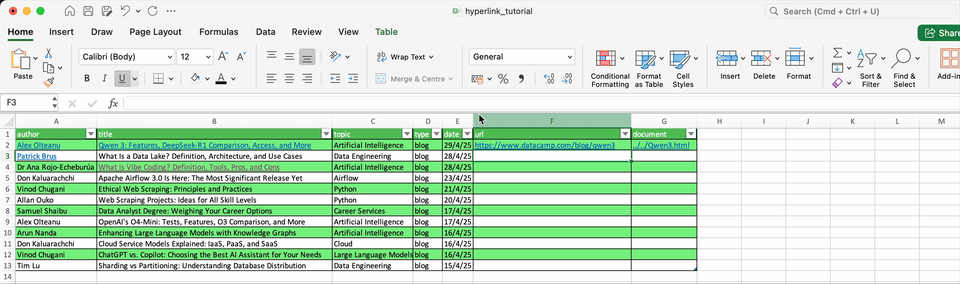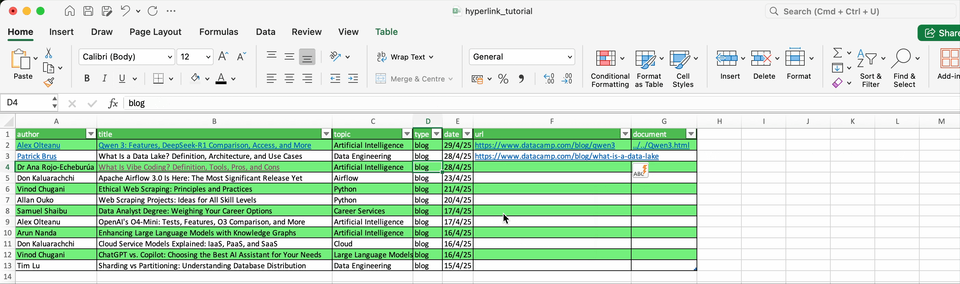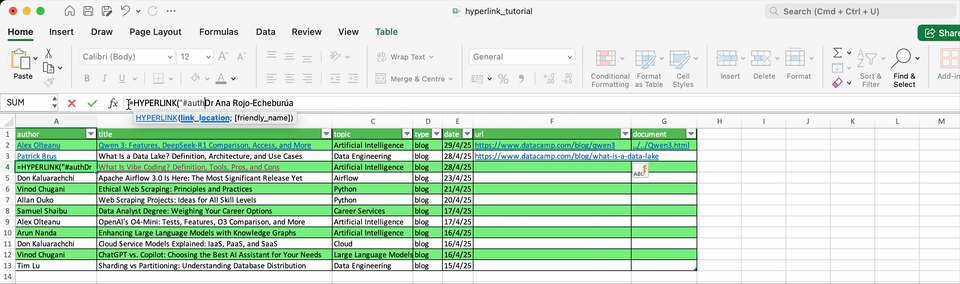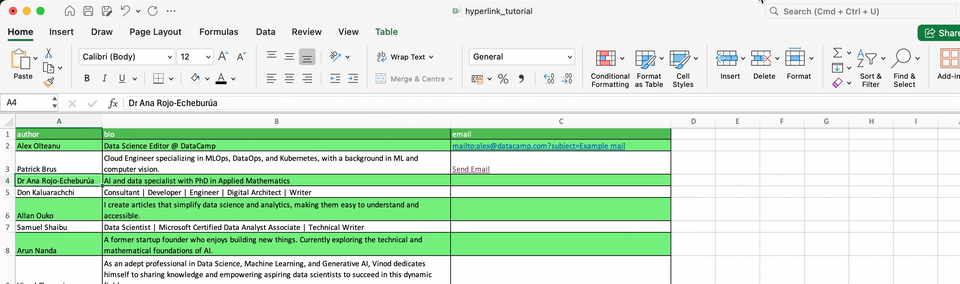
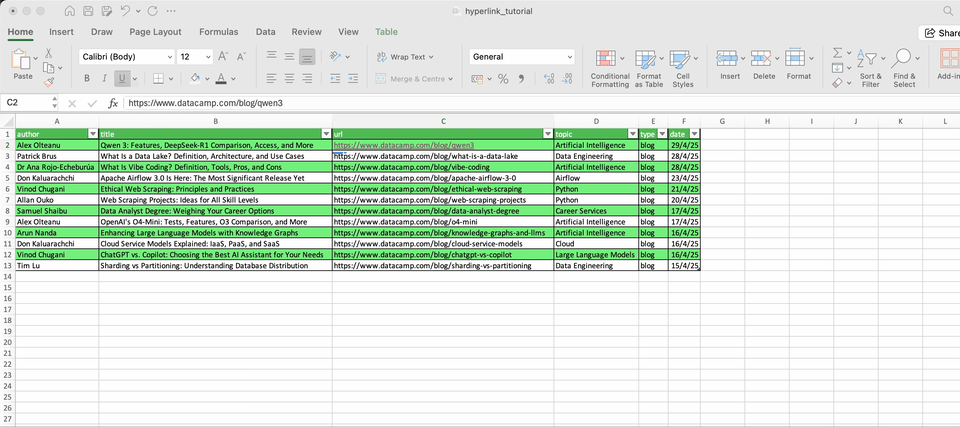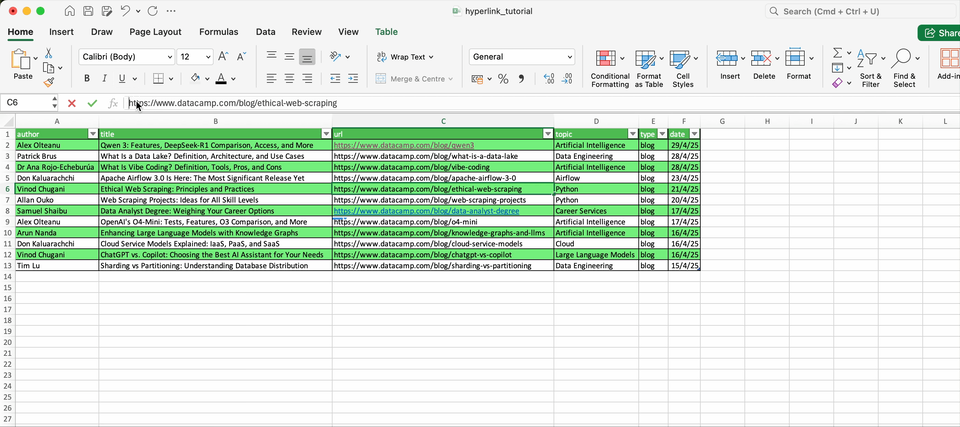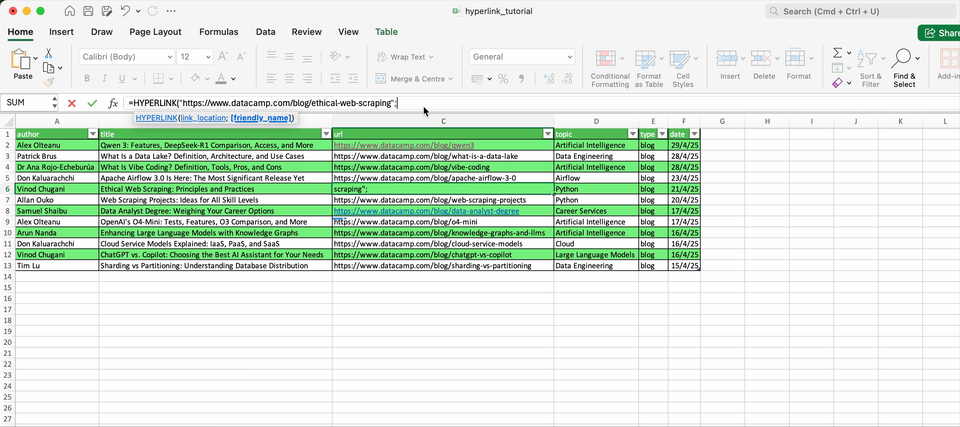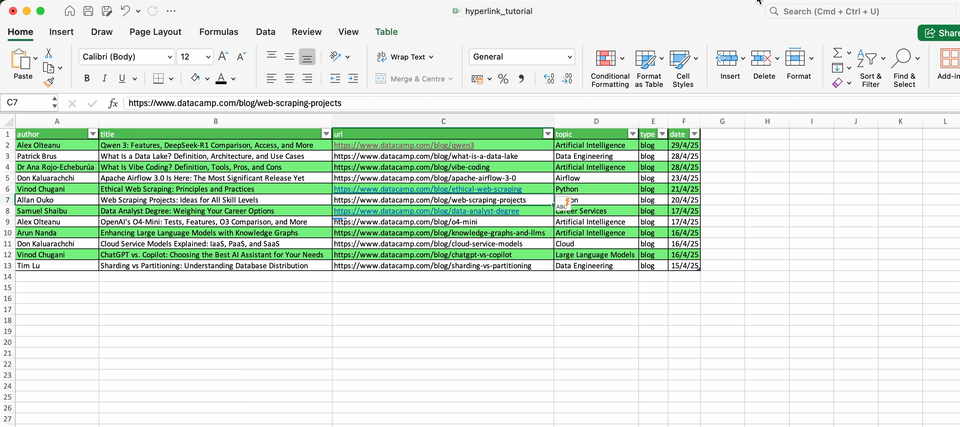
Here is the syntax of the HYPERLINK() function:
=HYPERLINK(link_location, [friendly_name]). Where link_location is the URL or path to the link destination, and the optional friendly_name allows to choose the text to display.
For dynamic internal linking, you can use the # symbol before the cell and sheet reference. You could also link to another working by adding the full path in the link_location parameter
Below you can find several examples on how to use this function:
Other Interesting Things You Can Do with Hyperlinks
Creating internal links to locations in the same workbook
We already mentioned how to created defined names to reference other cells or sheet tabs. Defined names are great to create resilient internal links that don’t break when rows or columns are moved.
To see all the defined names you created and edit or delete them, you can go to Formulas > Name Manager.
Converting existing text into clickable hyperlinks
Excel automatically detects URLs starting with http://, www., or mailto. However, sometimes this may not be the case and you will have to convert plain text to hyperlinks. You can do this manually by double clicking in the cell with the hyperlink. Then, when you click on another cell, Excel will change the text cell to hyperlink style.
You could also make do the change explicitly by using the HYPERLINK() function, as we saw previously.
Workarounds for embedding links in partial text
Excel does not allow hyperlinking part of the text within a cell. However, there are some tricks you can use to give the impresion that only part of the text has a hyperlink.
For example, you can select the text you don’t want to be (seem) hyperlinked, remove its underline, and change the color to black.Otherwise, you can place the text and the hyperlink in adjacent cells for visual similarity.
Conclusion
Many Excel spreadsheets make use of hyperlinks, whether for referencing external websites and documents, or to create dynamic worksheets with internal references. Hence, learning how to use hyperlinks in Excel can be a helpful way to stay organized and help your notebook stand out.
I hope you enjoyed it and look forward to seeing you around. If you want to keep improving your Excel skills, know that we have updated and best-in-class courses and skill tracks. Here is a list of some of our curated Excel content:
- Introduction to Excel course
- Data Analysis in Excel course
- Excel Fundamentals skill track
- Data Visualization in Excel course
Advance Your Career with Excel
Gain the skills to maximize Excel—no experience required.

I am a freelance data analyst, collaborating with companies and organisations worldwide in data science projects. I am also a data science instructor with 2+ experience. I regularly write data-science-related articles in English and Spanish, some of which have been published on established websites such as DataCamp, Towards Data Science and Analytics Vidhya As a data scientist with a background in political science and law, my goal is to work at the interplay of public policy, law and technology, leveraging the power of ideas to advance innovative solutions and narratives that can help us address urgent challenges, namely the climate crisis. I consider myself a self-taught person, a constant learner, and a firm supporter of multidisciplinary. It is never too late to learn new things.