Run and edit the code from this tutorial online
Run codeAnaconda is a package manager, an environment manager, and Python distribution that contains a collection of many open source packages. This is advantageous as when you are working on a data science project, you will find that you need many different packages (numpy, scikit-learn, scipy, pandas to name a few), which an installation of Anaconda comes preinstalled with.
If you need additional packages after installing Anaconda, you can use Anaconda's package manager, conda, or pip to install those packages. This is highly advantageous as you don't have to manage dependencies between multiple packages yourself. Conda even makes it easy to switch between Python 2 and 3 (you can learn more here). In fact, an installation of Anaconda is also the recommended way to install Jupyter Notebooks which you can learn more about here in this Jupyter Notebook tutorial.
With that, let's get started!
Start Learning Python For Free
Introduction to Data Science in Python
How to Download and Install Anaconda
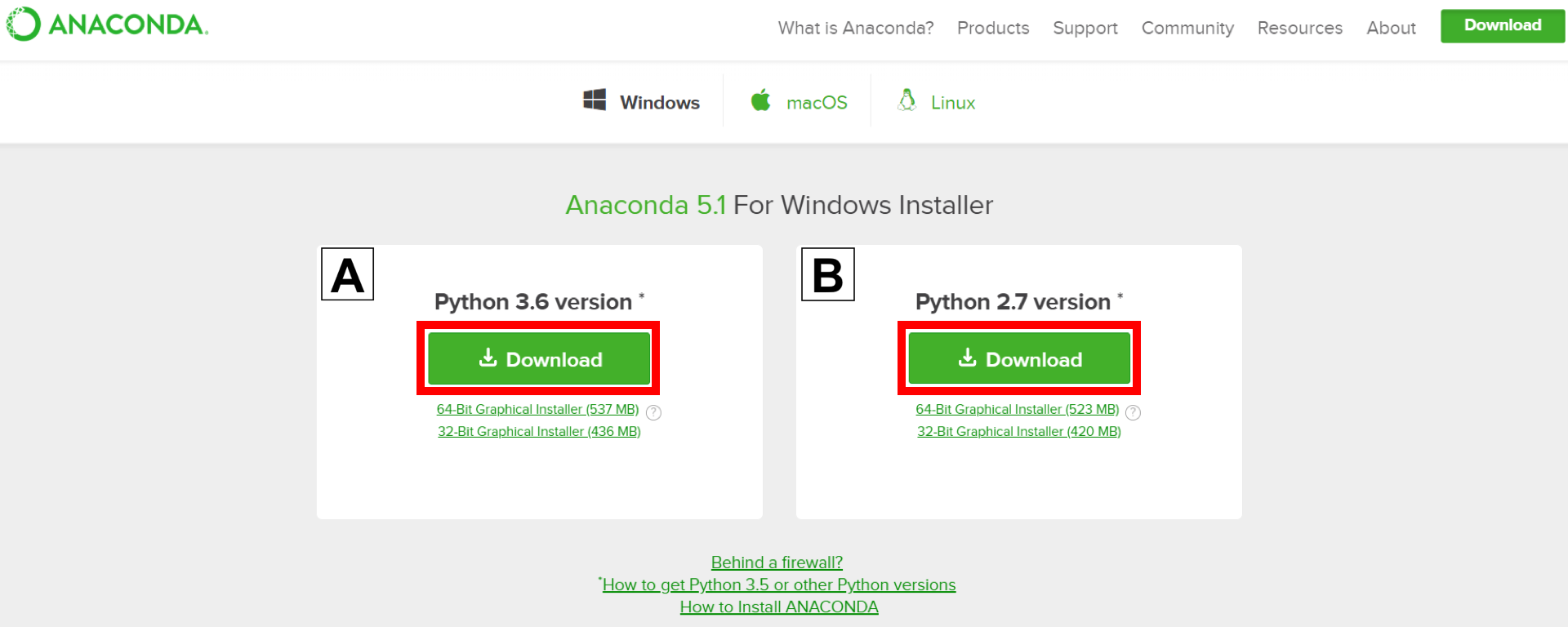
1. Go to the Anaconda Website and choose a Python 3.x graphical installer (A) or a Python 2.x graphical installer (B). If you aren't sure which Python version you want to install, choose Python 3. Do not choose both. Note: see our installing anaconda on Mac OS X tutorial if you're not on Windows.
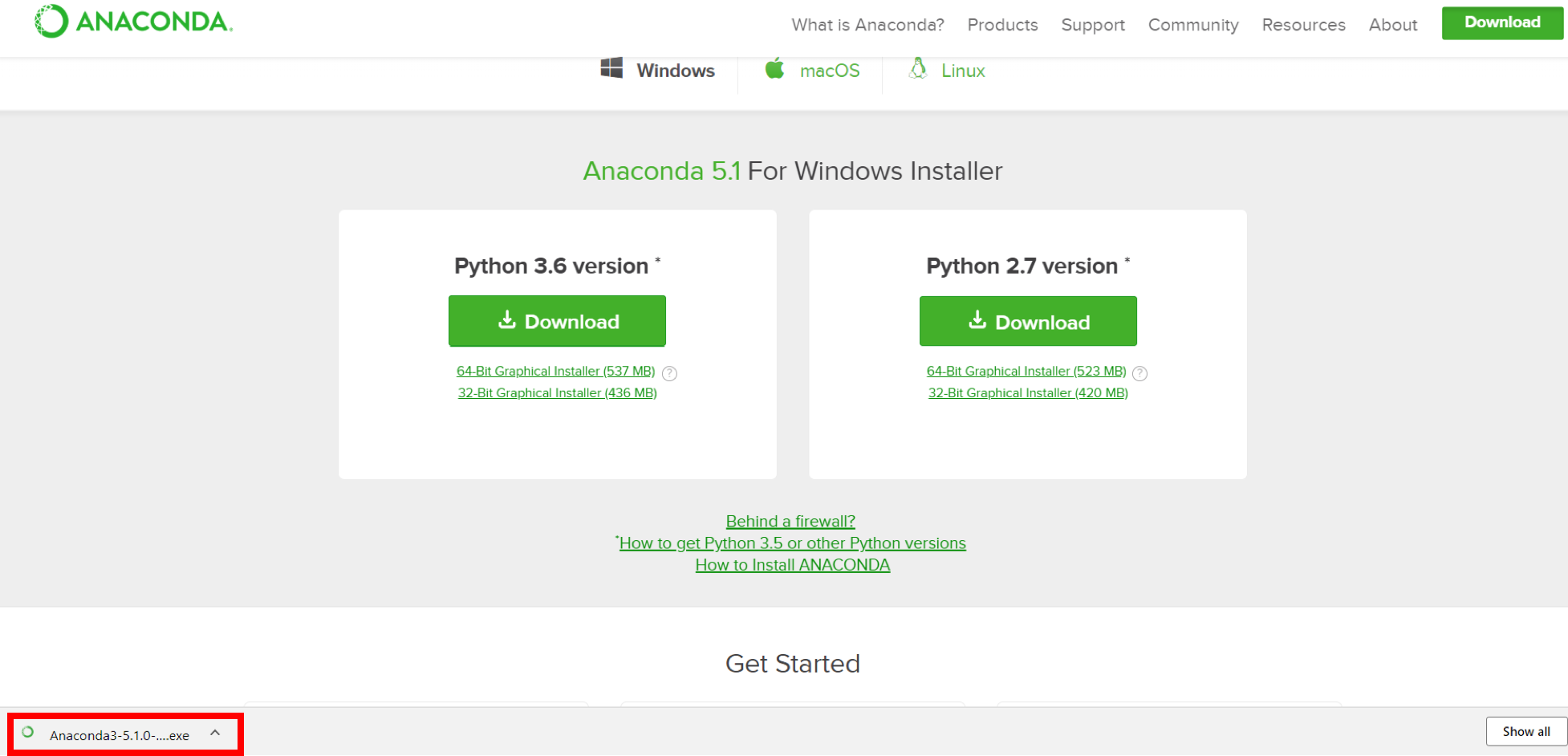
2. Locate your download and double click it.
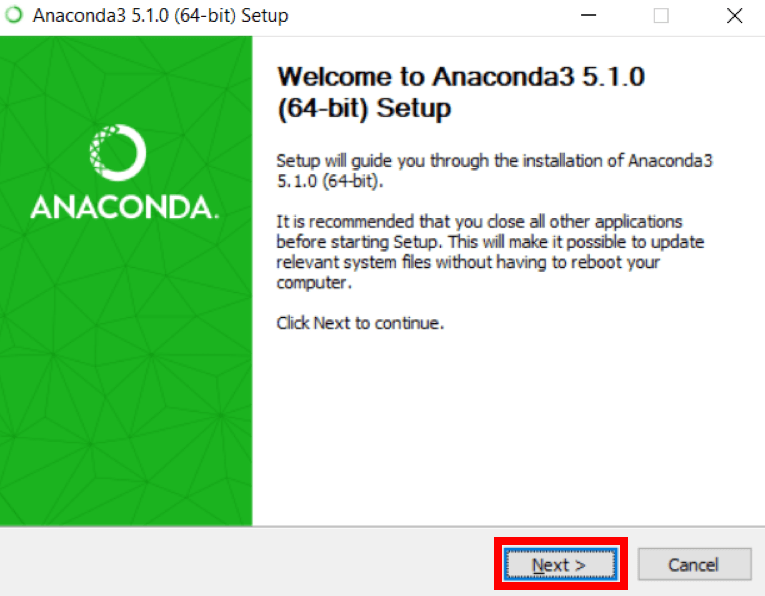
When the screen below appears, click on Next.
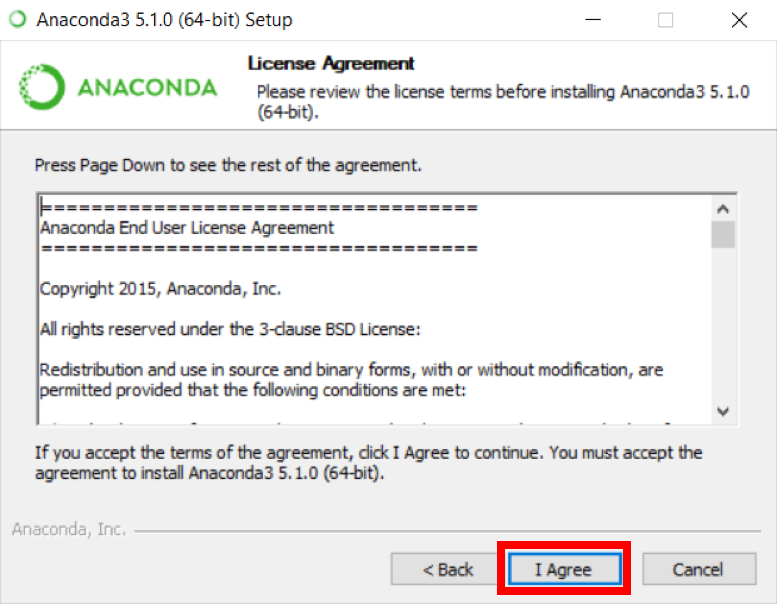
3. Read the license agreement and click on I Agree.
4. Click on Next.
5. Note your installation location and then click Next.
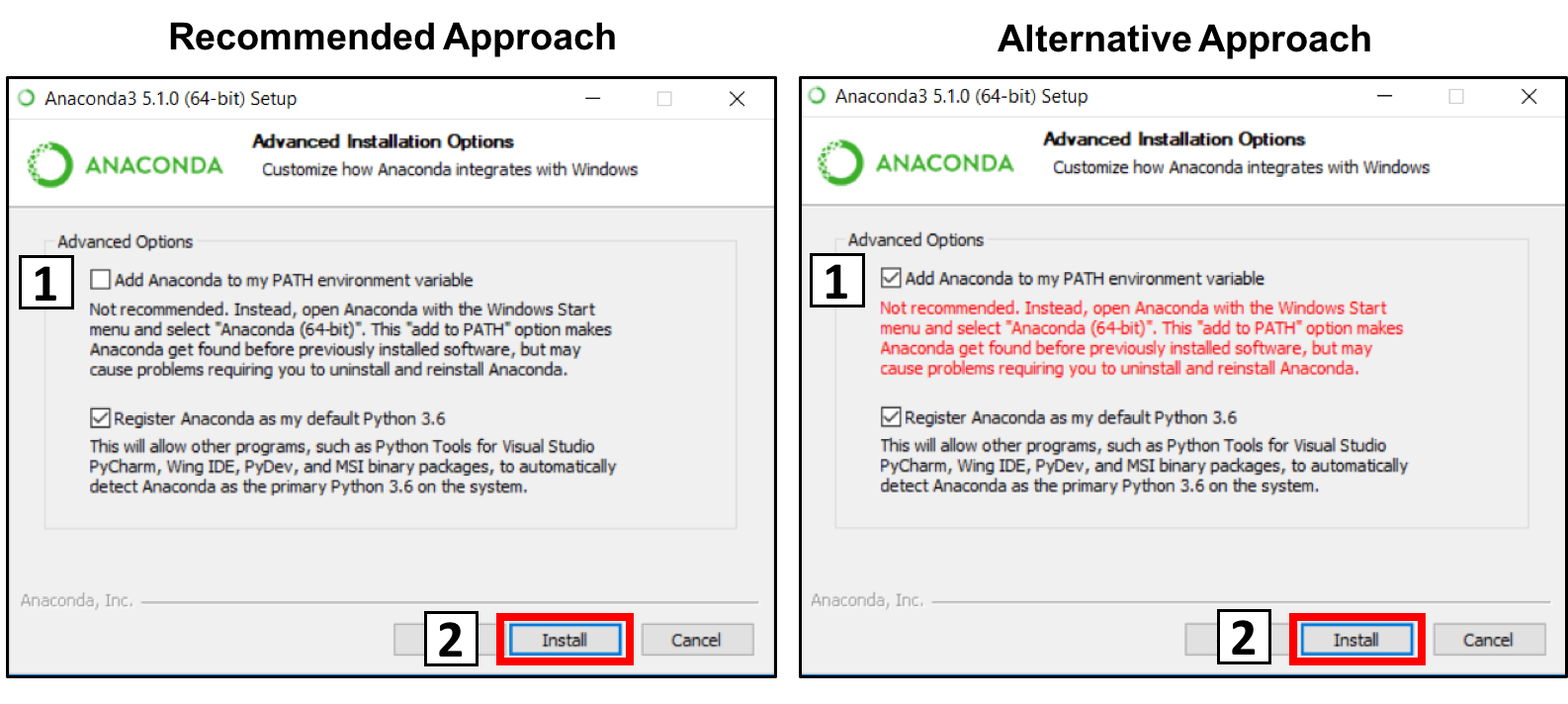
6. This is an important part of the installation process. The recommended approach is to not check the box to add Anaconda to your path. This means you will have to use Anaconda Navigator or the Anaconda Command Prompt (located in the Start Menu under "Anaconda") when you wish to use Anaconda (you can always add Anaconda to your PATH later if you don't check the box). If you want to be able to use Anaconda in your command prompt (or git bash, cmder, powershell etc), please use the alternative approach and check the box.
8. You can install Microsoft VSCode if you wish, but it is optional.
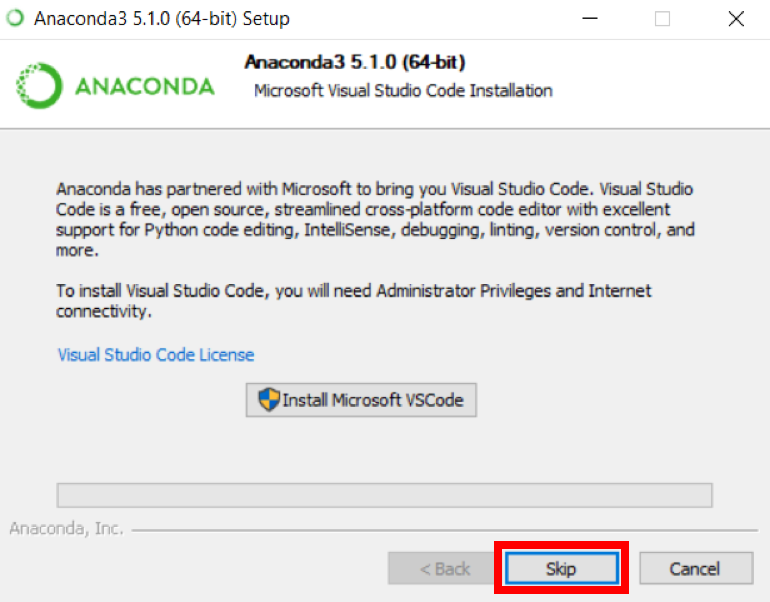
9. Click on Finish.
How to Add Anaconda to Path (Optional)
This is an optional step. This is for the case where you didn't check the box in step 6 and now want to add Anaconda to your Path. The advantage of this is that you will be able to use Anaconda in your Command Prompt, Git Bash, cmder etc.
1. Open a Command Prompt.
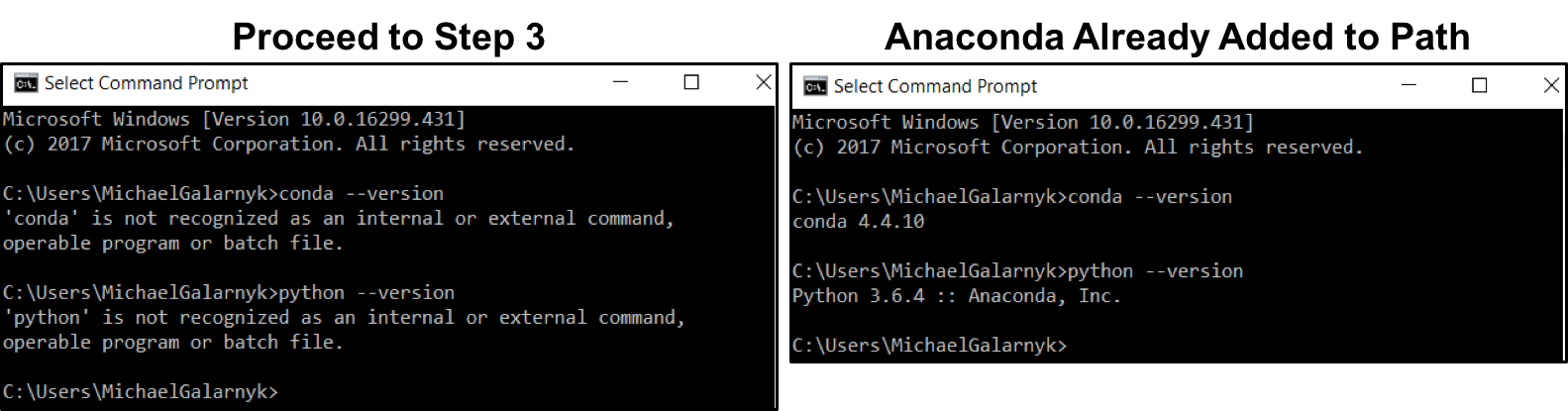
2. Check if you already have Anaconda added to your path. Enter the commands below into your Command Prompt. This is checking if you already have Anaconda added to your path. If you get a command not recognized error like in the left side of the image below, proceed to step 3. If you get an output similar to the right side of the image below, you have already added Anaconda to your path.
conda --version
python --version
3. If you don't know where your conda and/or python is, open an Anaconda Prompt and type in the following commands. This is telling you where conda and python are located on your computer.
where conda
where python
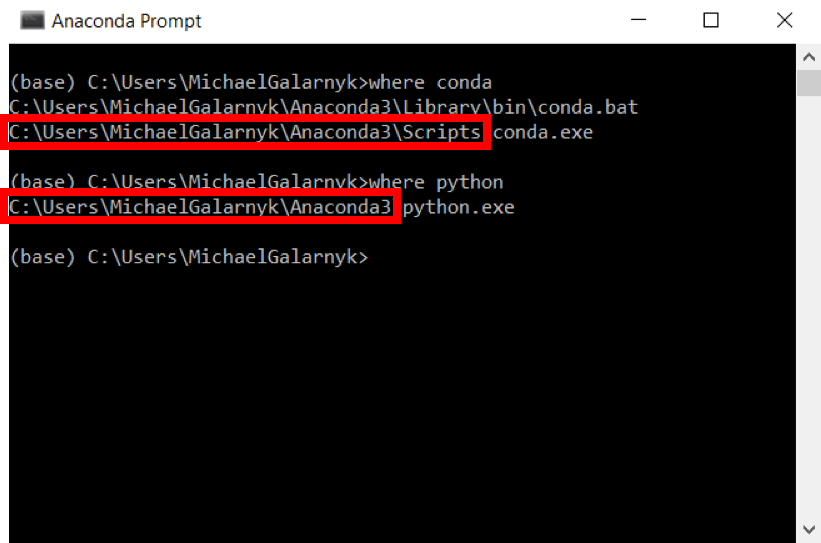
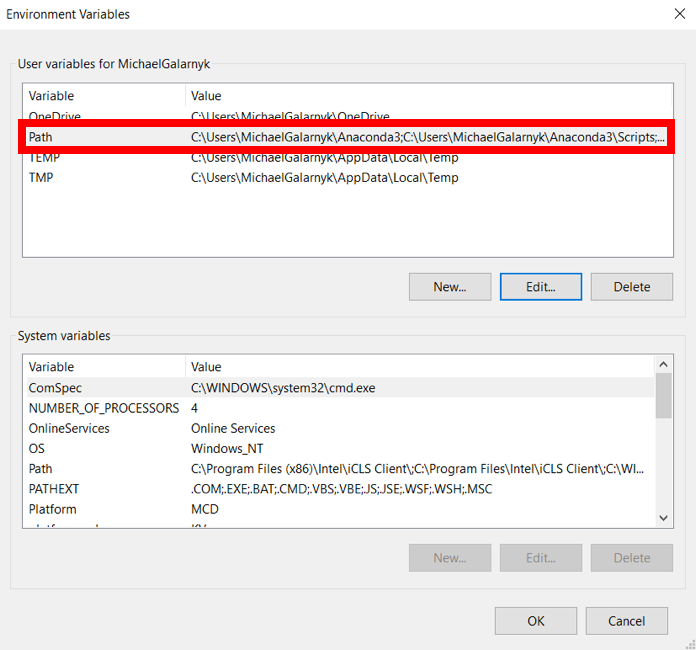
4. Add conda and python to your PATH. You can do this by going to your Environment Variables and adding the output of step 3 (enclosed in the red rectangle) to your path. If you are having issues, here is a short video on adding conda and python to your PATH.
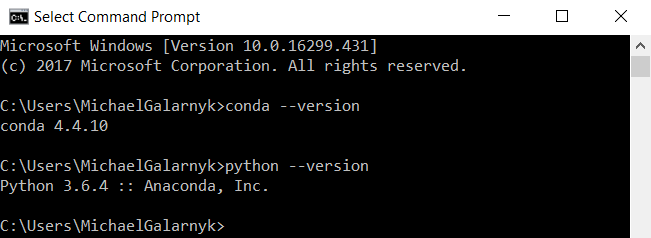
5. Open a new Command Prompt. Try typing conda --version and python --version into the Command Prompt to check to see if everything went well.
Conclusion
This tutorial provided a quick guide on how to install Anaconda on Windows as well as how to deal with a common installation issue. If you would like to learn more about Anaconda, you can learn more about it here. If you aren't sure what to do to start coding on your computer, I recommend you check out the the Jupyter Notebook Definitive Guide to learn how to code using Jupyter Notebooks.
If you want to learn about Python for Data Science, I suggest you check out the DataCamp course Intro to Python for Data Science. If you any questions or thoughts on the tutorial, feel free to reach out in the comments below or through Twitter.