Track
As someone new to Power BI, you might not be familiar with Power BI Report Builder, considering how it’s vastly different from the popular Power BI Desktop software.
In this guide, we’ll cover a walkthrough tutorial for setting up the software, getting data sources, creating and formatting a report, and exporting reports.
What is Power BI Report Builder?
Power BI Report Builder is a stand-alone tool provided by Microsoft that allows users to create paginated reports. These reports are formatted to fit well on a printed page and are ideal for operational or printable documents.
Unlike interactive dashboards in Power BI Desktop, paginated reports are highly structured and are best for invoices, statements, or tabular-style data that spans multiple pages.
These reports can be created using data from a variety of sources and published to the Power BI Service for secure sharing and scheduled delivery.
1. Installing Power BI Report Builder
To create reports, you must first obtain a copy of the latest version of Power BI Report Builder. Let’s run through the steps below.
Downloading and installing
- Visit the official Microsoft download page for Power BI Report Builder.
- Click Download, select the installer file, and run the installation wizard.
- Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the installation.
Once installed, launch Power BI Report Builder from your start menu. You should be greeted with this welcome screen, as shown below.
Next, sign up for a free Power BI account and sign in to your account in the software.
2. Connecting to Data Sources
Creating a data source
A data source is your connection to a database or service, such as SQL Server, Azure SQL, or Power BI datasets.
- Go to the Report Data pane (on the left) and right-click Data Sources > Get data….
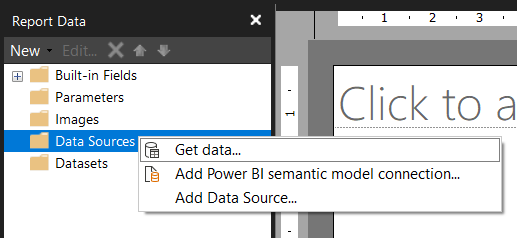
- Select Blank Table on the left pane.
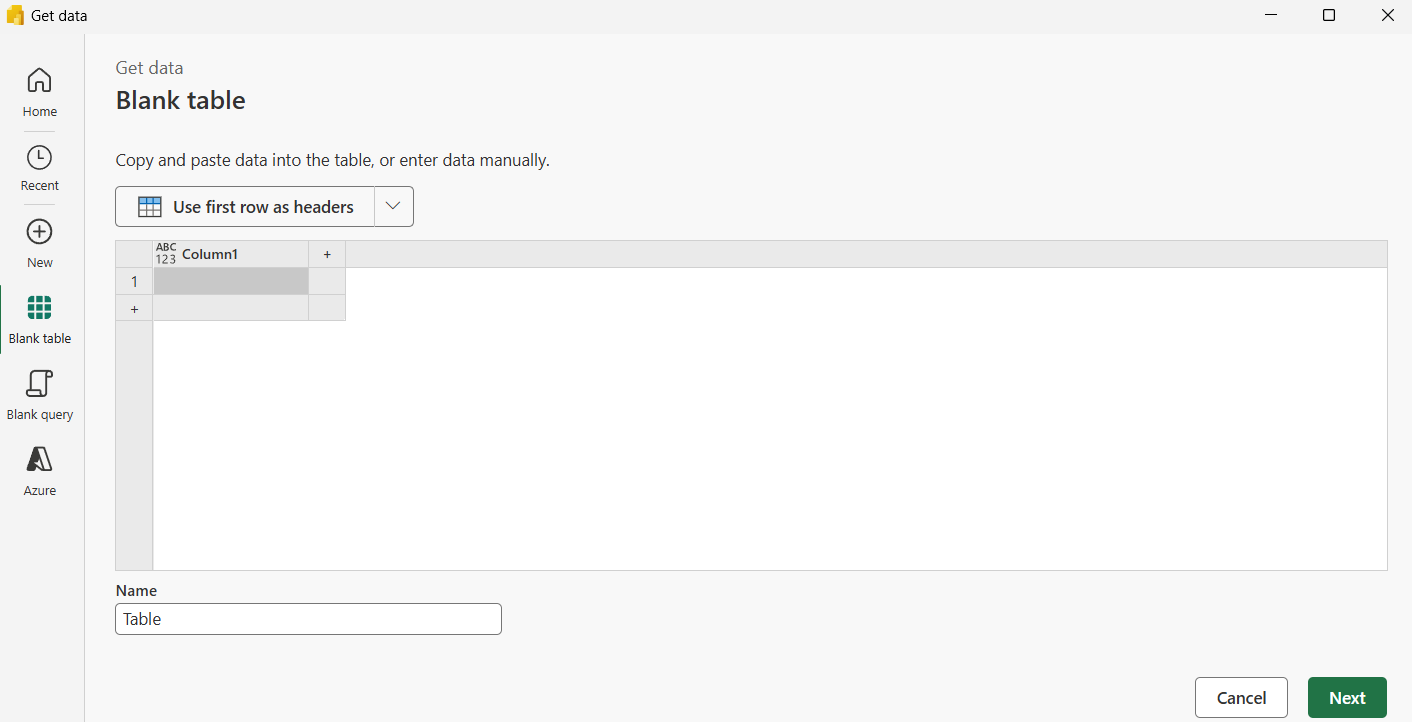
- Copy and paste the following sample data into the table.
Region,Product,SalesAmount
East,Widget A,3200
East,Widget B,2700
West,Widget A,1800
West,Widget C,3900
South,Widget B,2100
North,Widget A,2400
North,Widget C,3100- Click on Use first row as headers.
- Enter a table name (e.g., SalesData) and click Next, then Create.
- In the left-side panel, right-click on the new data source named PowerQuery and rename it as “SalesData”.
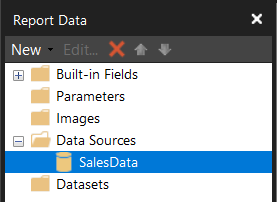
Defining a dataset
A dataset is a specific query or table that defines what data will be used in your report.
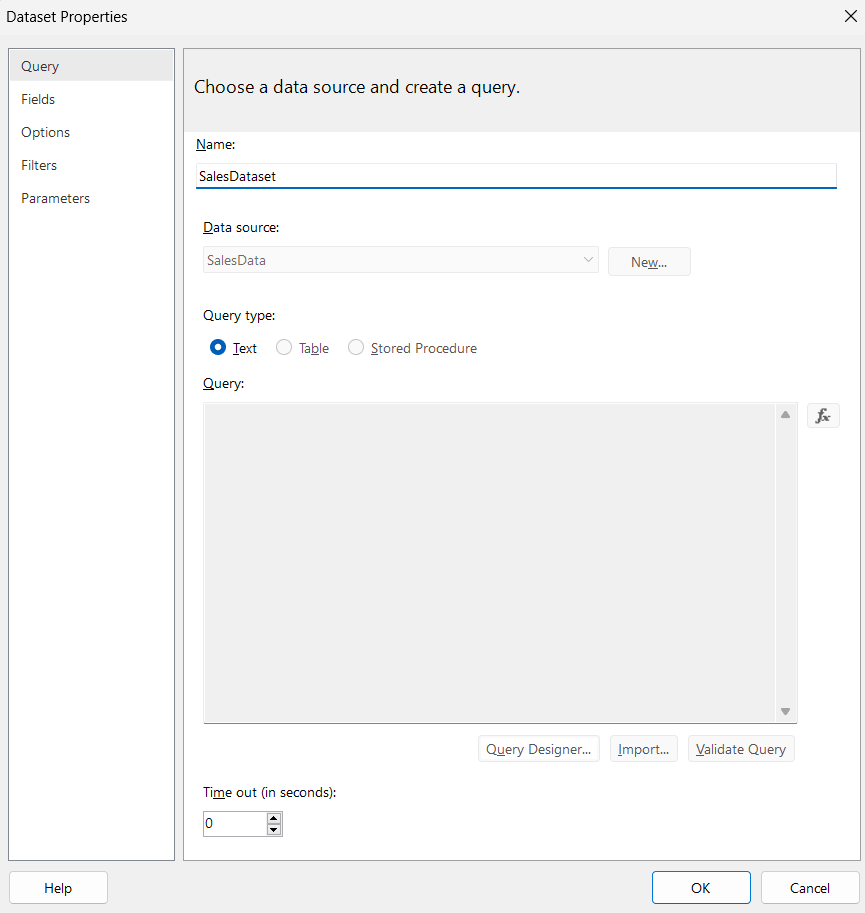
- Right-click Datasets > Add Dataset.
- Name your dataset as Sales Dataset.
- Select SalesData for your Data source to reference the Data Source that you created previously and click OK.
3. Creating Your First Paginated Power BI Report
Using the table wizard
- Go to Insert > Table > Table Wizard.
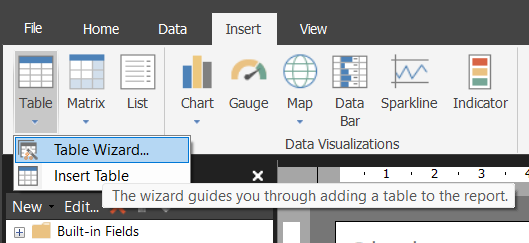
- Select your dataset “Sales Dataset” and click Next.
- Drag Region to Row Groups.
- Drag SalesAmount into Values and select the Sum aggregate.
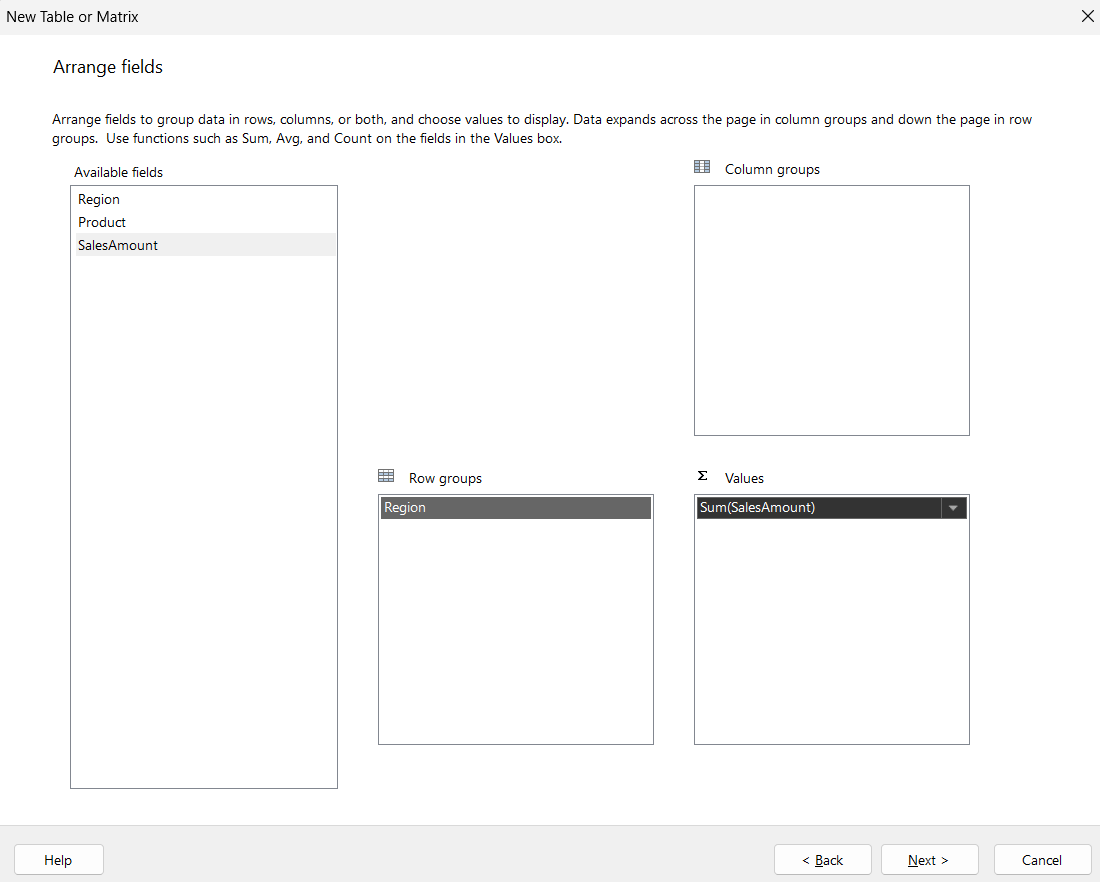
- Click Next, Next, and then Finish.
You now have a basic table displaying data from your dataset.
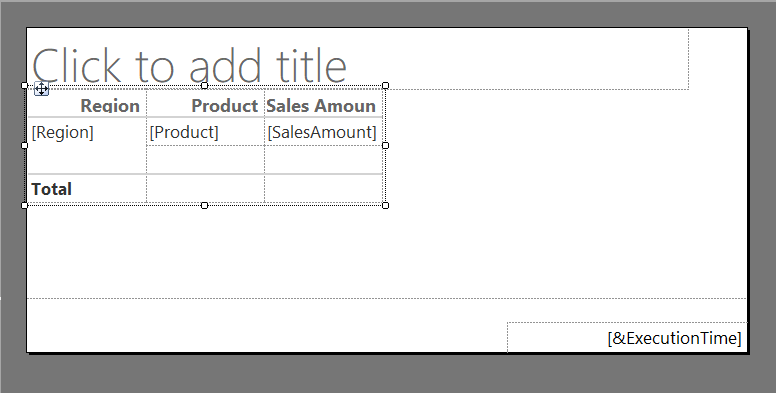
You can also resize the table by dragging the corners with your mouse, as shown below.
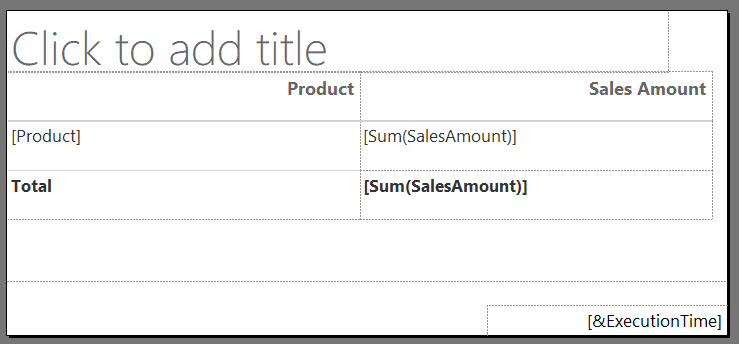
You can preview the data in the table by clicking Run.
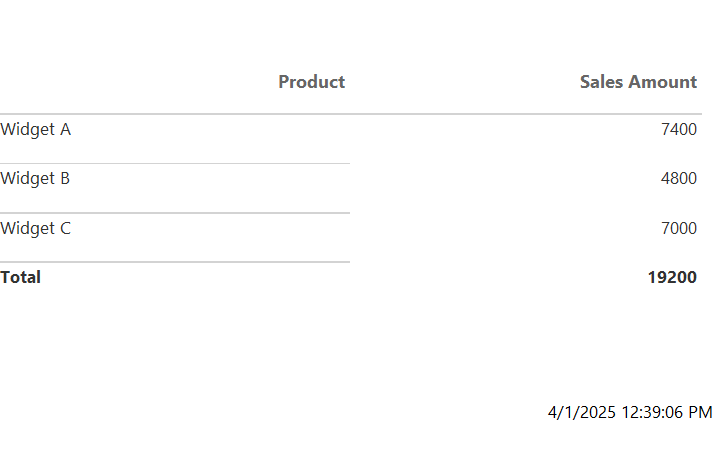
You should be able to achieve a printed data table like this:
Adding charts and visuals
Next, we can beautify the report with some visuals to better present the data.
- Go to Insert > Chart > Chart Wizard.
- Choose the “SalesDataset” option and click on Next.
- Choose a chart type (e.g., bar, line, pie). In this case, we’ll go with Pie.
- Drag the fields into the following arrangements.
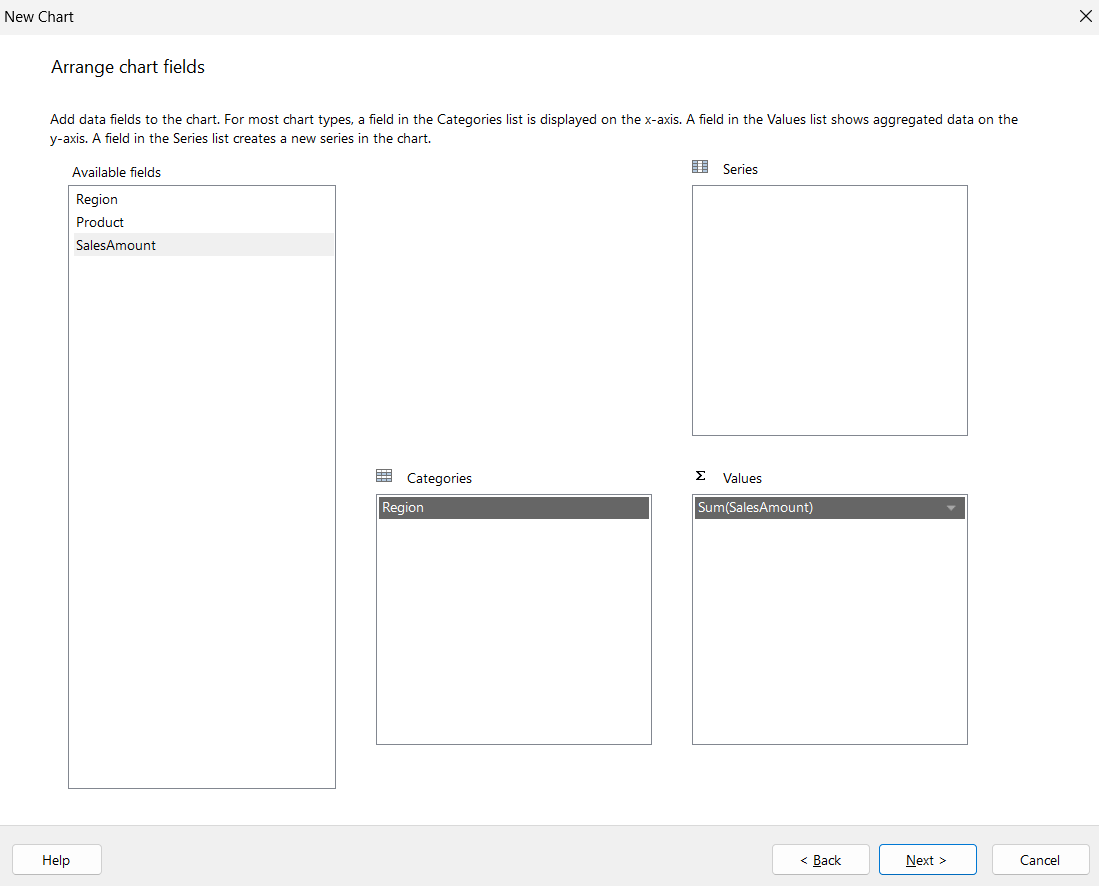
- Click Next and Finish.
- Resize the chart you’ve created to fit the report using the corners.
Once you’re done, hit Run, and you should see a printout of the chart in your report.
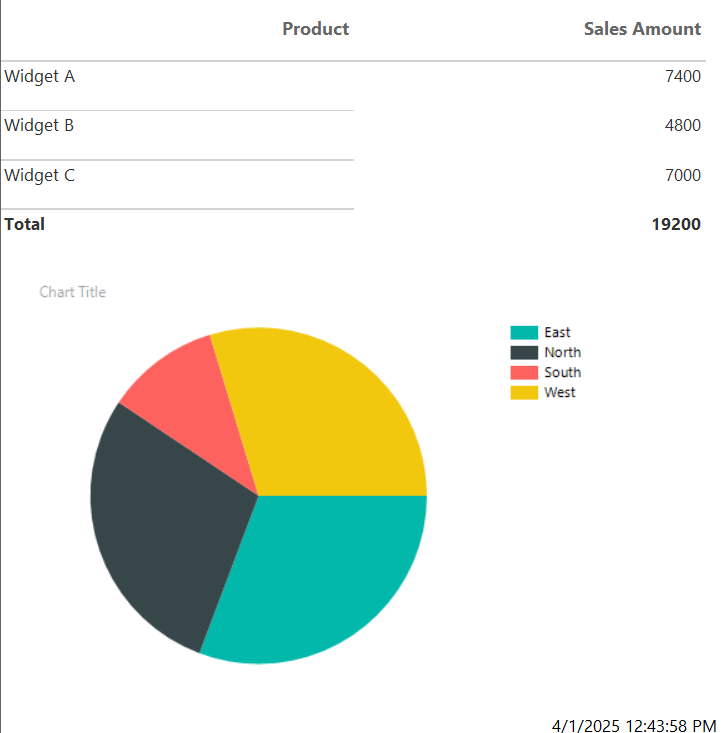
Charts like these can help visualize trends and are useful for summary sections. If you’re building reports, having a mixture of some charts and graphs like bar charts, line graphs, and pie charts can help your readers understand the data better.
4. Formatting and Designing Reports
Before you can start sending these reports out, you’ll need to see how you can make things easier for your readers to view the data. This will involve some basic formatting and designing. If you’re looking for some hands-on practice, be sure to check out our Data Visualization in Power BI Course.
Here are some areas to modify.
Applying styles and themes
You can modify the font size, color, borders, and background color using the Properties pane. This pane is especially useful for the detailed designing of reports that can be used to clean up and enhance the appearance of your report.
To enable the Properties pane, go to View on the top ribbon and check to enable Properties. A Properties pane should appear on the right side of your screen.
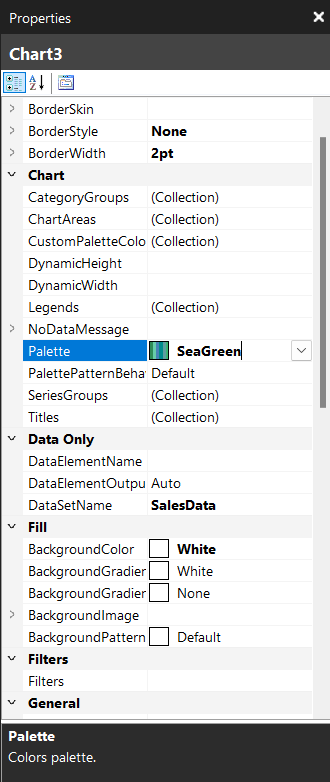
- Select the pie chart you created previously.
- Go to Properties > Chart > Palette. Select on Seagreen in the dropdown to modify the chart colors.
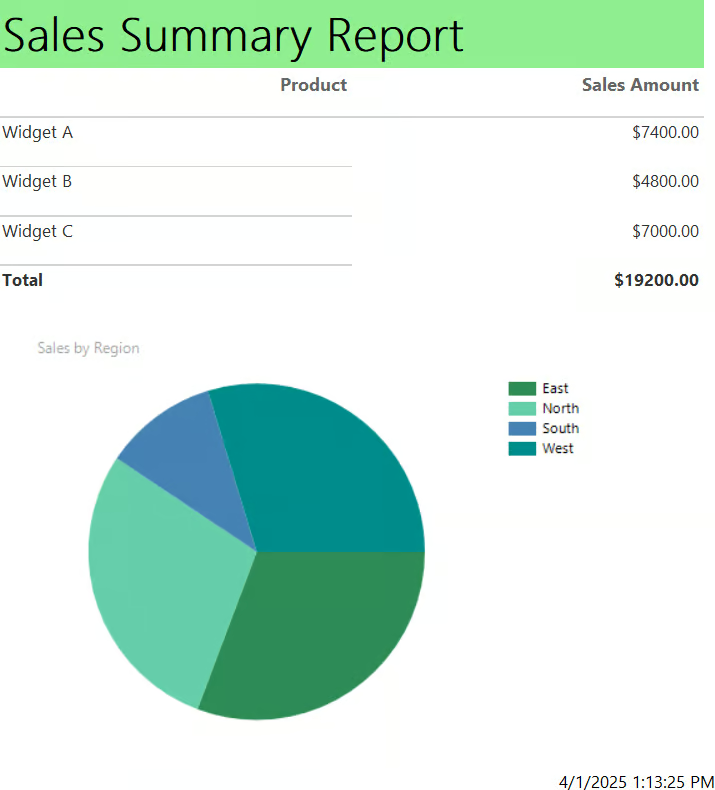
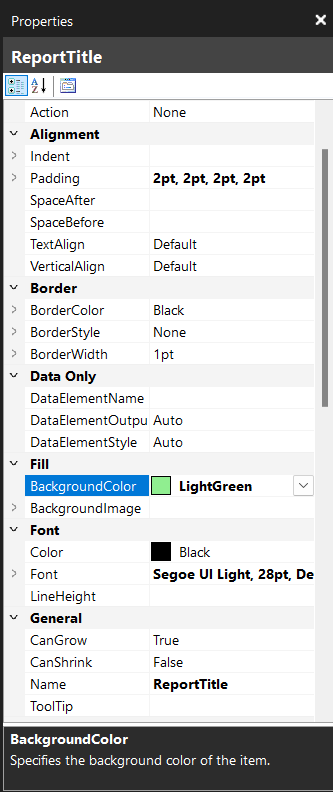
- Click on the Chart Title box in your chart and rename it to Sales by Region.
- Click on the title box and change the FillColor to LightGreen.
- Right-click on the Sales Amount fields of your table and click on Placeholder Properties.
- Click on Number > Currency > OK.
- Right-click on the values in the Totals row of your table and click on Text Box Properties.
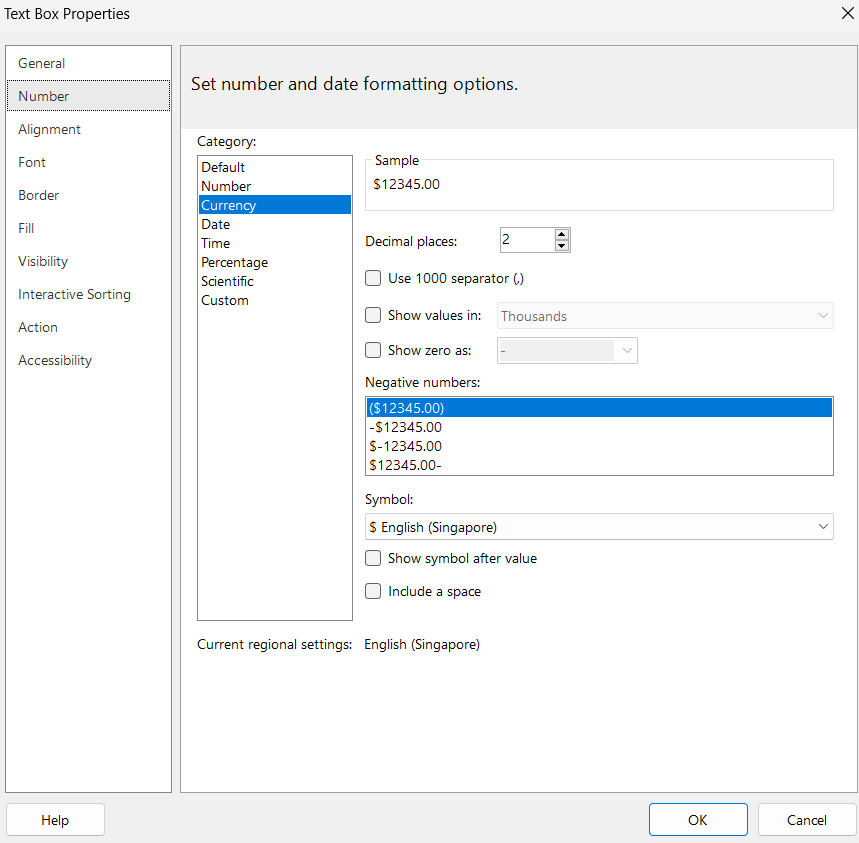
- Click on Number > Currency > OK.
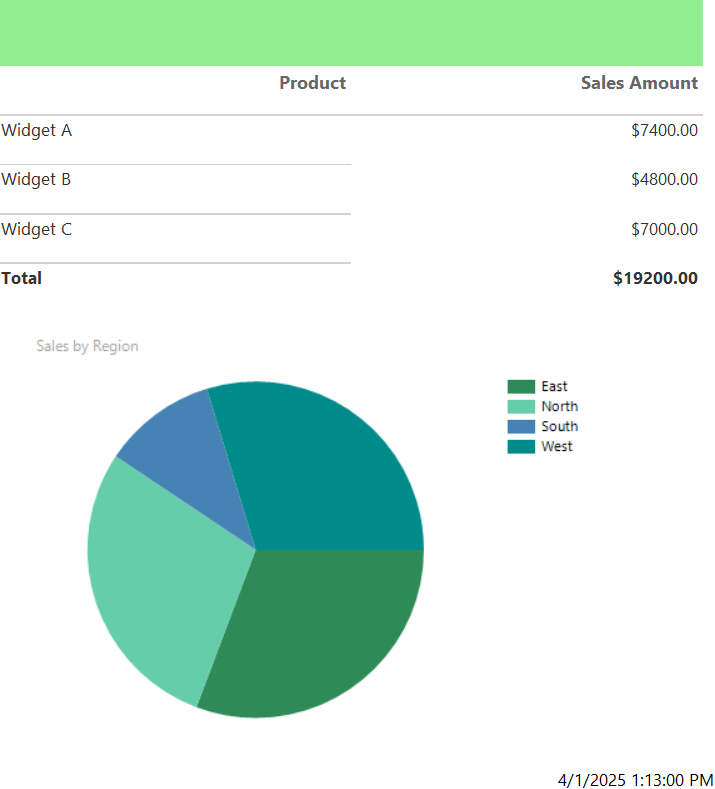
After all that editing, hit Run again to preview your report. It should look something like this:
Setting Up page layout
You can make your report look more professional with a proper header title so your readers can quickly grasp what they’re looking at.
To add a title, click on the “Click to add title” box and fill in “Sales Summary Report”
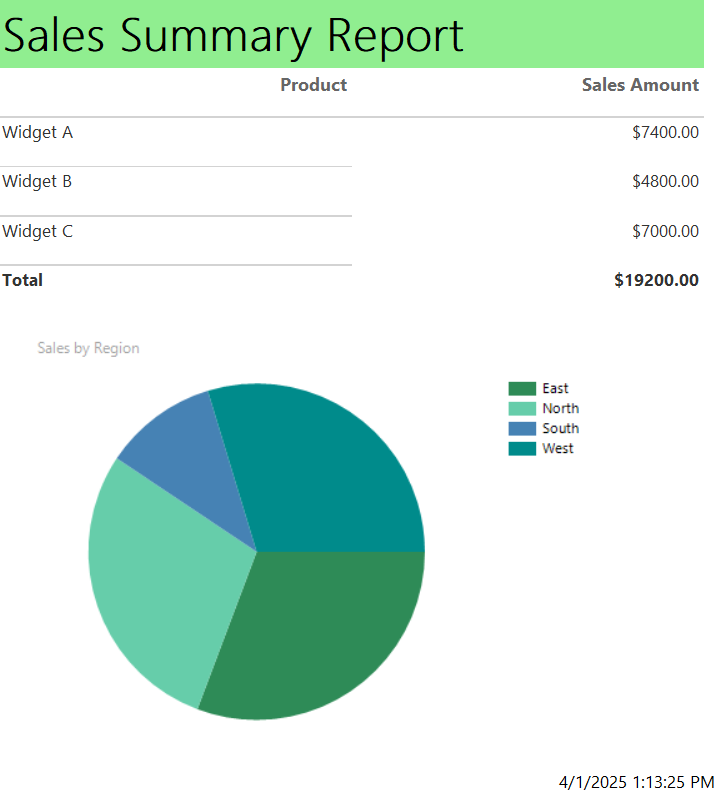
You may also choose to modify the sizing of your report and set a page size to make it easily printable.
Here is how you can do it:
- In the run screen, go to Page Setup.
- Set Page Size (A4, Letter, etc.) and Margins.
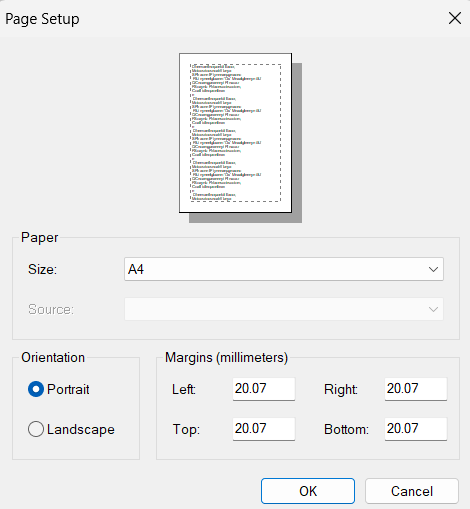
These steps ensure the report prints neatly and is optimized for paginated formats like PDFs. To double-check your sizing, you can use the Print Layout button to preview how your report will look when printed.
5. Publishing Reports to Power BI Service
Saving and exporting reports
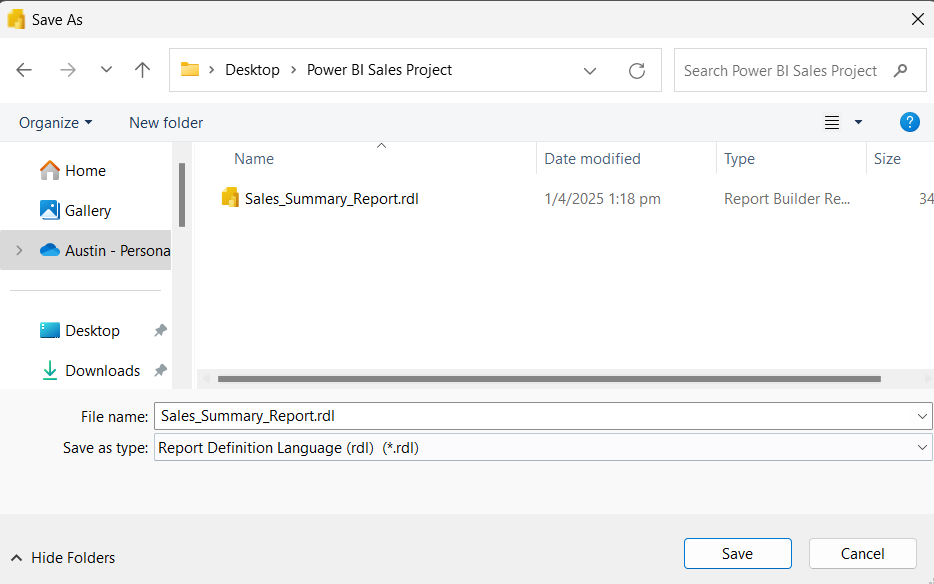
You can save your report as an .rdl file for reuse or editing.
- Go to File > Save As.
- Choose a local folder or OneDrive location.
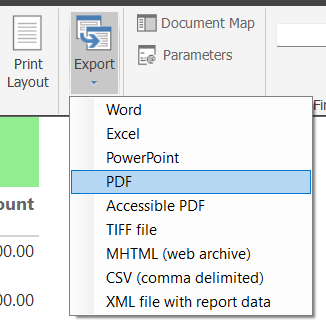
To export as PDF, Word, or Excel:
- Go to Home > Run > Export and select your desired format.
Publishing to Power BI
To publish your report to the Power BI Service:
- Go to File > Publish > Power BI Service.
- Sign in to your Power BI account.
- Select the workspace where you want to publish.
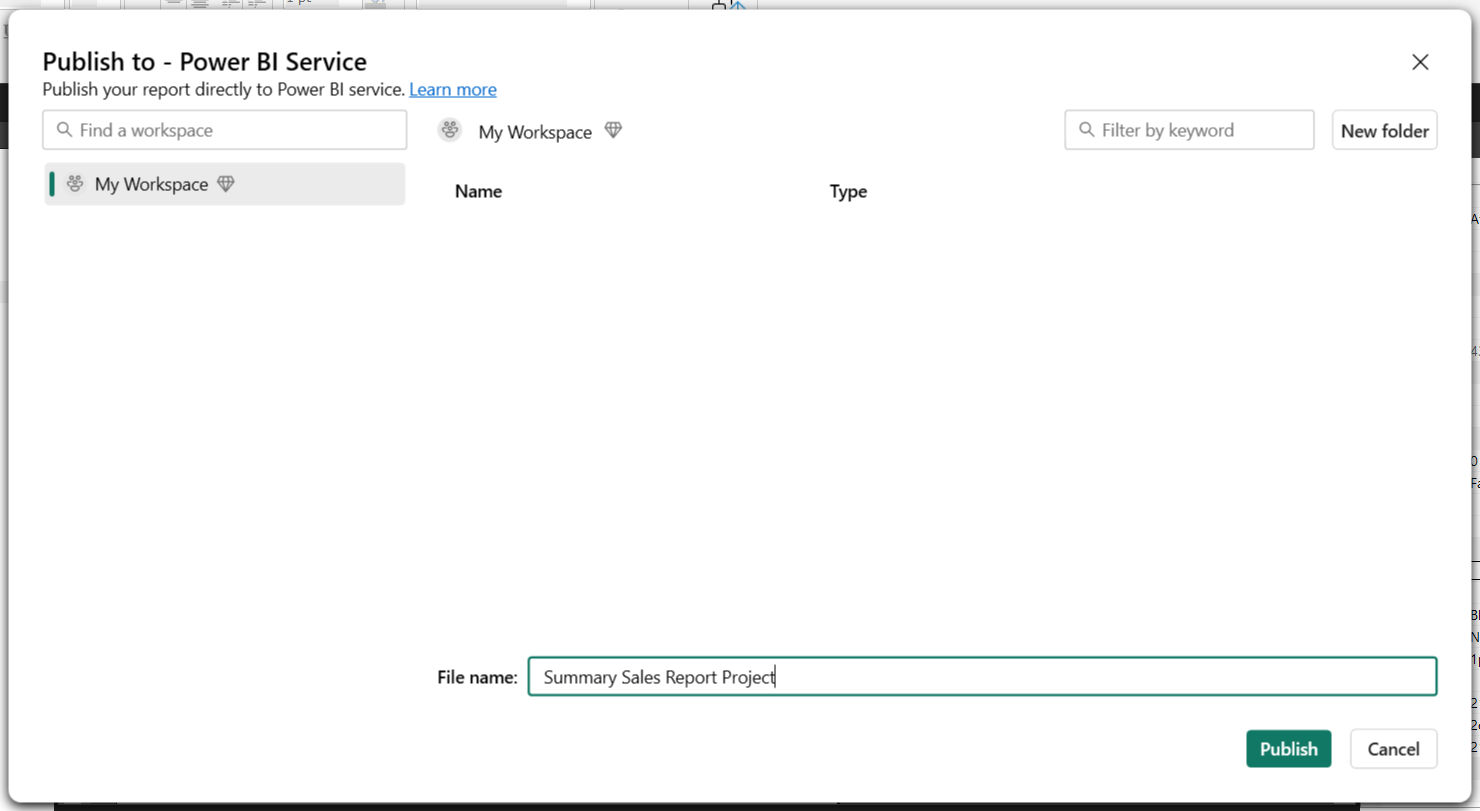
- Name your project and click Publish.
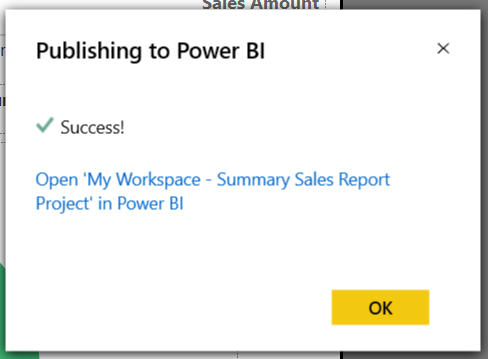
Once uploaded, the report is available in the Power BI Service and can be scheduled, shared, or embedded in dashboards.
Power BI Report Builder vs. Power BI Desktop
Power BI Report Builder is often mixed up with Power BI Desktop, especially for beginners who aren’t familiar with both of them.
To help you make things clearer, here’s a table of some differences between the two standalone software:
|
Feature |
Power BI Report Builder |
Power BI Desktop |
|
Report Type |
Paginated |
Interactive, dynamic reports |
|
Best For |
Printable reports, invoices |
Dashboards, visual analytics |
|
Export Options |
PDF, Word, Excel, etc. |
PDF, PowerPoint, Excel |
|
Data Interactivity |
Limited |
Highly interactive |
|
Charting and Visuals |
Basic |
Advanced |
|
Publishing Destination |
Power BI Service (Paginated) |
Power BI Workspaces |
In short, you should use Report Builder for structured, print-ready reports and Power BI Desktop for exploration and storytelling with data.
Learn more about Power BI Desktop in this Power BI tutorial for beginners. You can also get some visual inspiration with our guide to the Top 9 Power BI Dashboard Examples.
Conclusion
Power BI Report Builder is a powerful tool for creating professional, paginated reports. It also offers tight integration with SQL-based data sources and Power BI Service, making it ideal for generating printable documents and regulatory reports.
Looking to explore more about Power BI’s potential or learn more about its related products and services? Check out our Introduction to Power BI course or the Data Analyst in Power BI track.
Power BI Report Builder FAQs
What is the difference between Power BI Desktop and Power BI Report Builder?
Power BI Report Builder is a standalone desktop application that allows you to build and publish paginated reports, while Power BI Desktop is used for creating interactive visualizations and dashboards.
Is Power BI Report Builder free?
Yes, it is free to download and use with your Power BI Desktop license.
Can I create custom report templates in Power BI Report Builder?
Yes, you can create custom report templates using the built-in Report Definition Language (RDL) format.
Does Power BI Report Builder have data refresh capabilities?
No, data refresh must be done through Power BI Desktop or the online service.
How does Power BI Report Builder compare to other reporting tools?
Power BI Report Builder offers a user-friendly interface and powerful features for creating highly formatted, pixel-perfect reports. It also integrates seamlessly with the rest of the Power BI suite, making it a popular choice among users. However, it may not have the same advanced capabilities as more specialized reporting tools in terms of data manipulation and analysis.

I'm Austin, a blogger and tech writer with years of experience both as a data scientist and a data analyst in healthcare. Starting my tech journey with a background in biology, I now help others make the same transition through my tech blog. My passion for technology has led me to my writing contributions to dozens of SaaS companies, inspiring others and sharing my experiences.