Track
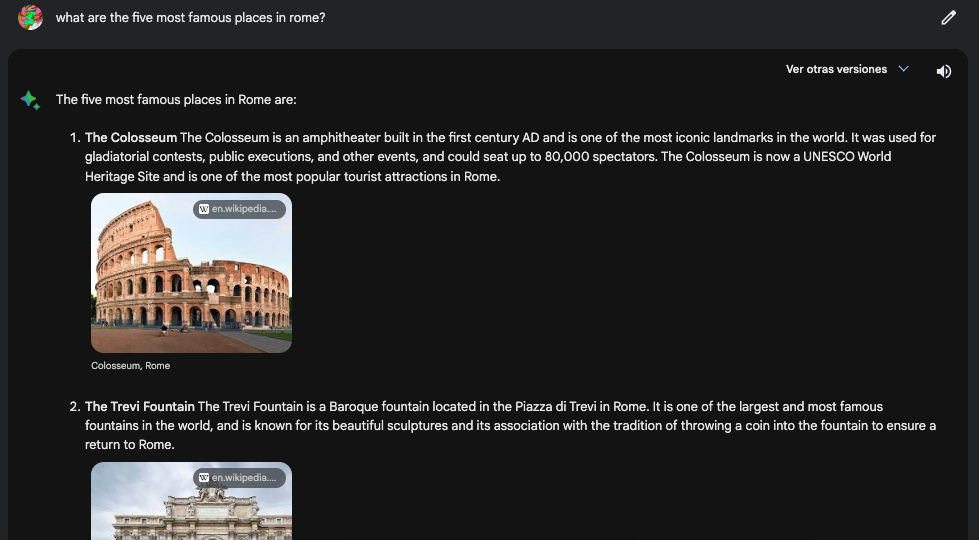
If you ask somebody about AI these days, sooner rather than later, they will probably mention ChatGPT. Undoubtedly, ChatGPT is the most famous AI star on the red carpet these days. However, it’s important to know that there are other cool tools that are attending the ongoing AI revolution. In particular, one tool that can compete in popularity and capabilities with ChatGPT is Bard, the conversational large language model (LLM) developed by Google.
In this article, we will take you through the main features and differences between ChatGPT vs Google Bard. What is the underlying technology behind these powerful tools? Where are the pros and cons of ChatGPT vs Bard? In what areas do they perform better?
Keep reading to discover these answers and more!
Understanding Bard and ChatGPT
What is Bard?
Following the release of ChatGPT and its integration into Microsoft search engine Bing, it wouldn’t take much for Google to launch its own chatbot to compete with ChatGPT.
In February 2023, it announced the release of a new generative AI tool called Bard AI, powered by Google’s language model LaMDA.
However, as Google has reportedly admitted, Bard is still experimental, delivering only a fraction of its full potential. In the last months, Google has continuously upgraded Bard, powering it with the more powerful PaLM 2 model, offering improved performance in reasoning, coding, and multilingual capabilities. It’s well suited for creative tasks, provides cited sources, and it’s available for free.
In the coming versions, Bard will include multimodality, combining text and images in its answers. Equally, you will be able to include images in your prompts and integrate them with other Google tools, like YouTube, Maps, and Google Lens.
What is ChatGPT?
Developed in partnership with OpenAI and Microsoft, ChatGPT is an AI-powered chatbot designed to answer questions and perform tasks in a conversational way.
Launched in late 2022, ChatGPT took the world by storm with its unique and unprecedented ability to generate human-like text of all sorts, from code, document summaries, and lyrics to detailed essays, trip plans, and jokes. This is thanks to its underlying LLM, GPT3.5 in the free version of ChatGPT, and GPT4 in the pro, paid version.
The list of possibilities offered by ChatGPT is infinite, which is why, in just two months, it became the fastest-growing web application ever, reaching 100 million users. If you want to get your hands dirty with this wonderful AI tool, we highly recommend you check our Introduction to ChatGPT Course.
Key Similarities and Differences
Technically speaking, ChatGPT and Bard are very similar. They are both generative AI products with general-purpose capabilities that compete for the same market. They share the same underlying technology, the so-called LLMs.
OpenAI GPT-4 model powers the most advanced version of ChatGPT, while the Google counterpart is powered by the PaLM 2 model. To know more about LLMs, the foundational technology of the ongoing AI revolution, we highly recommend you to check out our Large Language Models (LLMs) Concepts Course.
However, when we compare Bard vs ChatGPT, we see many differences. We’ve summarised some of the most significant differences in the table below.
|
ChatGPT |
Bard |
|
|
Created by |
OpenAI, Microsoft |
|
|
Underlying LLM |
GPT-3.5 free version GPT-4 Pro version |
PaLM 2 |
|
Data sources |
A wide collection of data sources from the Internet, including Wikipedia and scientific papers until 2021 |
Infiniset, a curated list of Internet content. Bard has a direct connection to up-to-date information through Google |
|
Connected to the Internet |
Only Pro version, through plugins. |
Yes |
|
Multimodality |
Yes, image and voice inputs. Beta Image generation with new Dall-E integration |
Yes, voice inputs and image outputs |
|
Integration with other tools |
Only Pro version, through plugins |
Mainly Google tools, including Maps, Youtube, and Lens. More to come with brand-new plugins. |
|
Price |
Free Pro: $20/month |
Free |
Diving Deeper into Bard
The mechanism behind Bard
Let’s get a bit more into the technicalities of Bard.
Initially, Bard was powered by the LaMDA family of language models, but it performed poorly compared to GPT-3.5, the LLM that powered the first ChatGPT. In order to compete with ChatGPT in the generative AI industry, Google has now switched to the more advanced PaLM 2 for all its AI products, including Bard.
The name "PaLM'' refers to Pathways Language Model. PaLM leverages Google's AI framework to teach machine learning models how to carry out various tasks. Unlike its predecessor, the PaLM model, PaLM 2 has been trained on a more diverse corpus of data, including an extensive number of human and programming languages, mathematical equations, scientific papers, and web pages. This allows PaLM 2 to deliver improved expertise in coding, enhanced logical reasoning, and mathematical abilities.
Another cool thing that distinguishes Bard from other chatbots is its internet access feature. Every time you prompt a question to Bard, it will browse Google to provide accurate and real-time responses. You can also use the “Google it” button to search for information on Google within Bard.
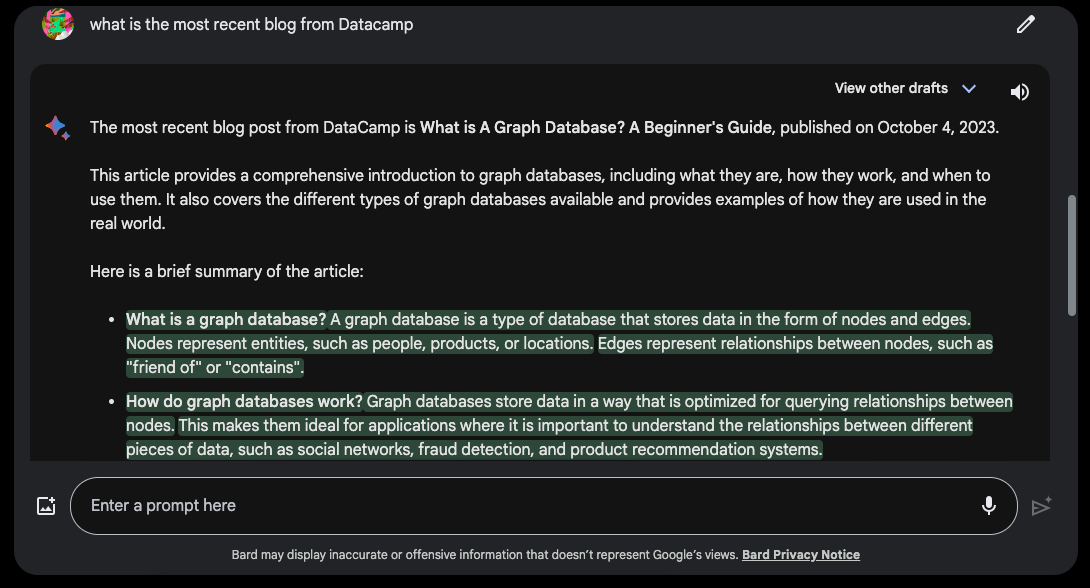
Bard can access up-to-date information through Google
Bard pros and cons
Since its official launch at the beginning of 2023, Bard has improved dramatically, and more is about to come as Google keeps integrating Bard within its powerful technology stack.
Among its current strengths, we can highlight:
- Access to the internet.
- Possibility to resume a previous chat.
- Progressive integration with other Google tools, like YouTube, Maps, Lens, and Gmail.
- Support over 40 human languages and more than 20 programming languages.
- Voice inputs.
- Text inputs enriched with images.
- Multiple draft responses.
- Free access.
However, as already mentioned, Google Bard is in its infancy, with weaknesses and limitations that require improvement in future versions, such as:
- Inaccurate results, including hallucinations, especially with complex questions. To ensure higher accuracy, providing easily-interpretable prompts with sufficient context can make a big difference. Check out our article to discover the best practices in prompt engineering.
- Lower performance in many tasks compared to other AI-powered chatbots.
- Lack of sources for responses. However, it's possible to use the “Google it” button to fact-check results.
- Limited integrations with other tools. However, this will soon be possible following the recent announcement of Bard extensions.
Exploring ChatGPT
The technology powering ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a generative AI tool based on the GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer) architecture. Developed by OpenAI, the GPT architecture extends to transformers with a focus on generating coherent and contextually accurate text. You can learn all the details about transformers in our Large Language Models Course.
The first version of ChatGPT, and still available as the free version, is based on the GPT-3.5 architecture. This is an upgraded version of the GPT-3 architecture model. The GPT-3 model is based on 175 billion parameters, providing unique capabilities in natural language processing and understanding tasks. By contrast, GPT-3.5 has fewer parameters to make it more efficient and is designed to work within policies based on human values.
The latest version of ChatGPT (GPT Plus) is based on GPT-4, a more advanced version of GPT-3. Although the specifics of GPT-4's size and improvements are not publicly disclosed, it is expected to have even more parameters (some have estimated it has up to 1.76 trillion parameters), further fine-tuning its language generation abilities and performance across various tasks. Curious about the differences between GPT-3 and GPT-4? Check out our article, where we directly asked ChatGPT about the differences.
Since its first launch, OpenAI has been constantly upgrading ChatGPT, with promising innovations, such as the creation of the OpenAI GPT API for developers to build applications on top of OpenAI models, the possibility of third-party ChatGPT plugins, and the integration with other OpenAI LLMs. For example, OpenAI recently announced the integration of ChatGPT with Dall-E, the powerful image generation model.
ChatGPT Pros and cons
Using ChatGPT comes with many advantages, including:
- Wide range of internal business use cases.
- Possibility to resume a previous chat.
- Ever-increasing catalog of plugins and integrations.
- Support over 95 human languages and a wide variety of programming languages.
- Voice inputs
- Image generation
As for the cons of ChatGPT:
- Only the ChatGPT Plus version has access to real-time information.
- Sometimes inaccuracy or false claims, including LLM hallucinations.
- Lack of sources for responses.
- Privacy and copy-rights concerts regarding the training data.
- Paid version to use ChatGPT at full capacity.
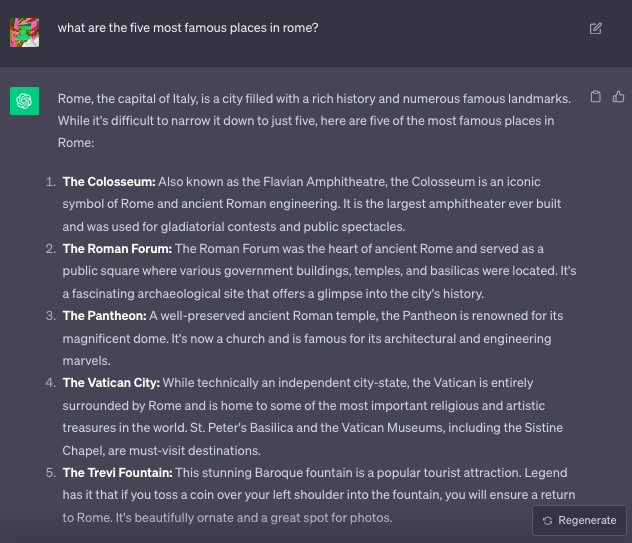
Bard vs. ChatGPT: A Comparative Analysis
Let’s analyze how Bard vs ChatGPT perform in different scenarios:
Data science and coding
Making data science accessible to everyone is at the core of DataCamp’s mission. When ChatGPT and Bard launched the tech space, we wondered whether these next-generation tools could help us achieve this mission.
Over recent months, we have tested Google Bard and ChatPT in a wide variety of data science and coding tasks. Overall, our analyses show that ChatGPT, especially its Pro version powered by GPT-4, is currently and overall a more suitable tool for data science and coding tasks than Google Bard. This applies to a wide range of areas, including programming workflows, data analysis, data visualization, machine learning, and natural language processing tasks. This is largely due to the ChatGPT Code Interpreter feature.
Some of our experiments have been published in our blog. Don’t miss the opportunity to read our Bard vs ChatGPT for Data Science post and our Guide to Using ChatGPT For Data Science Projects.
Research capabilities
Both ChatGPT vs Google Bard stand out as great research assistants. They can help you in many aspects, including suggesting and framing research questions, performing preliminary literature reviews, or rewriting texts to improve clarity and accessibility.
However, they are still very far from replacing the work of researchers. Despite their impressive capabilities, neither ChatGPT nor Bard would meet the quality standards for academic publishing.
First, there’s the question of reliability. These tools often provide misleading, inaccurate information, and can fall into LLM hallucination out of the blue (generating information that is incorrect, misleading, or not based on real-world facts). This kind of behavior is unacceptable in a task like academic research, where everything is about precision and integrity.
This links to the second problem of these tools: authenticity and authorship. Scientific research is an evolving process where every new idea is grounded on previous, accumulated research. To support their ideas, researchers always have to provide references to previous research on the topic.
A common problem of Bard and ChatGPT is the absence of citations or references of the source. While Bard provides citations when it directly quotes at length from a webpage, more is needed in scientific research, where every statement based on previous knowledge needs to be referenced.
Finally, to provide relevant scientific publications, researchers have to be aware of the latest publications. However, this is not possible with ChatGPT, at least in its free version, as it is not connected to the internet, and its knowledge doesn't go beyond September 2021, as shown in the image below.

In this regard, the possibility of Google Bard providing up-to-date information makes it a better research assistant than ChatGPT.
Writing assistance
The underlying technology of ChatGPT and Google Bard is specifically designed to excel in writing tasks. Every writing task you can think of can be performed by these tools, from writing essays, cooking recipes, and newsletters to poems, summaries, and even jokes.
It’s difficult to measure what tool provides the best replies, for both ChatGPT and Bard have great quality standards.
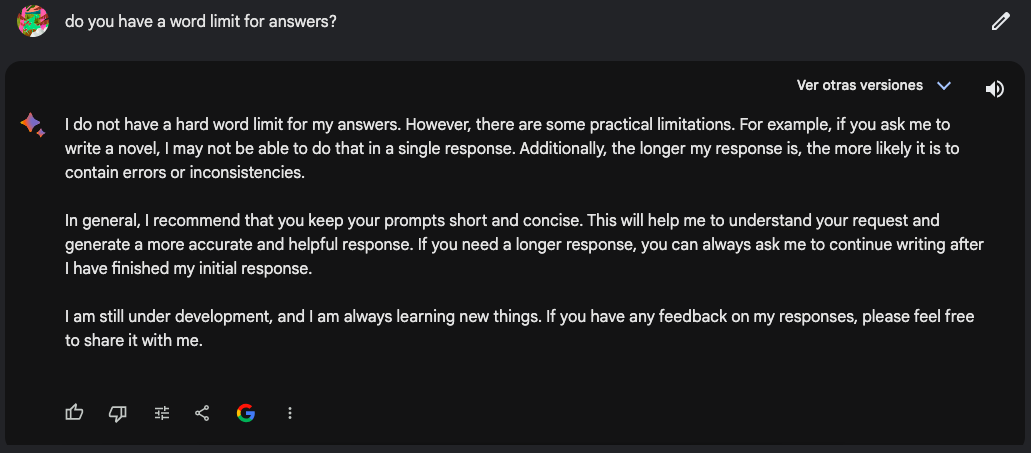
However, some differences are worth mentioning. First, the word limit. Currently, the free version of ChatGPT has a word limit of around 500 words or 4000 characters. The pro version comes with more tokens. By contrast, Google Bard claims not to have a word limit for answers. This can make a great difference, especially if you expect these tools to provide lengthy answers.
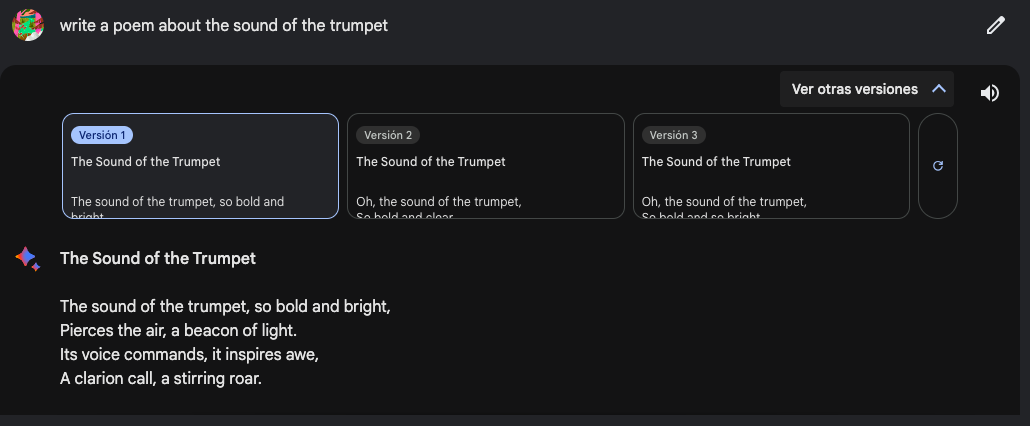
Another interesting feature that makes Google Bard different from ChatGPT is its ability to provide multiple draft answers, so you can choose the one you like the most.
User experience
Overall, both ChatGPT and Bard are simple, easy-to-use, and intuitive tools. They come with a user-friendly, chat-based interface where you just have to write your prompt as if you were speaking to a friend on WhatsApp. Both also include a sidebar where you can resume previous chats.
Hence, we cannot say one is better than the other. In my case, I like the Google Bard interface better, but it’s just a matter of personal taste.
Integration, plugins, and collaboration
To become the leader in the new LLM-powered chatbot market, you need a huge pool of users. Not only direct users who use the tool to prompt questions but also developers who can plug their applications on top of the chatbot.
This is something that OpenAI understood from the very beginning, and that’s why the company rapidly launched OpenAI GPT API, a tool that enables developers to integrate the power of ChatGPT into their applications, products, or services.
Check out our Working with the OpenAI API Course to learn how to develop AI-powered applications with GPT models.
The same idea underpinned the announcement of ChatGPT plugins. Aimed at unlocking the vast range of possible use cases of ChatGPT, plugins are designed to add functionality and features, such as access to up-to-date information, run computations, or use third-party services. So far, ChatGPT is testing plugins with a limited number of developers and is only available for Pro versions.
Google Bard is taking a different strategy to achieve the same goal. The core advantage of Google is its widely-used technology stack. To increase the pool of users of Bard, Google is steadily integrating the tool into other Google applications, including Drive, Gmail, Maps, and Google Lens.
Also, Google recently announced the launch of Bard third-party plugins, also called Bard extensions, which will allow new integrations with third-party services and applications.
Images
An important difference between Bard vs ChatGPT is the ability of Bard to provide answers with images. This is a cool feature to enrich the generated text.
By contrast, ChatGPT has recently increased its image generation capabilities by integrating Dall-E. This will allow ChatGPT Plus users to describe an image and ChatGPT will create it, as shown below:

ChatGPT vs Bard: Practical Applications and Use-Cases
Bard in action
Although Bard is still in an experimental phase, it is already one of the best chatbots in the market. You can use it in a wide range of scenarios, from customer support and medical assistance to e-learning and content creation.
However, the full potential of Bard will be unblocked as it keeps its integration process with other Google tools. This will make Bard a unique chatbot. Thanks to these integrations with popular and widely-used Google services, Bard will be able to find, combine, and show relevant information from different sources, including Gmail, Docs, Drive, Google Maps, and YouTube.
For example, if you’re planning a business trip to the Greek Islands (a project that takes up many tabs), you can now ask Bard to recommend the dates that work for everyone from Gmail, look up real-time flight and hotel information, see Google Maps directions to the airport, and even watch YouTube videos of things to do there.

Source: Google
Leveraging ChatGPT
OpenAI has managed to keep its momentum after the initial launch of ChatGPT. Today, ChatGPT is no doubt the most popular and widely used LLM-powered chatbot. The use cases are endless and will be more as developers create new plugins and build their applications on top of the OpenAI GPT API.
For example, at DataCamp we are already leveraging ChatGPT in our cloud-based IDE, DataLab. With the new ChatGPT-based AI Assistant, DataLab aims to make data science even more accessible and productive for its users. Key features of the AI Assistant include the "Fix Error" button, which not only corrects code errors but also explains them, allowing users to learn and avoid repeating mistakes.
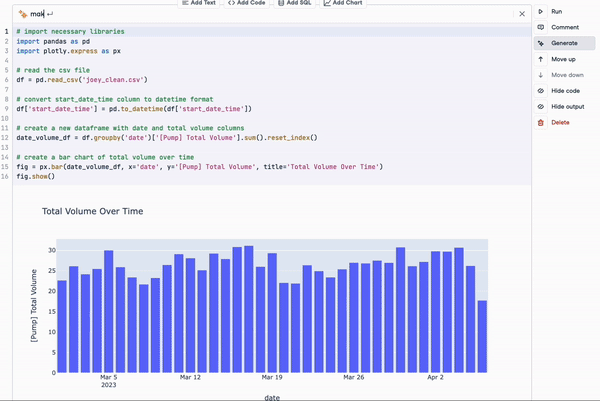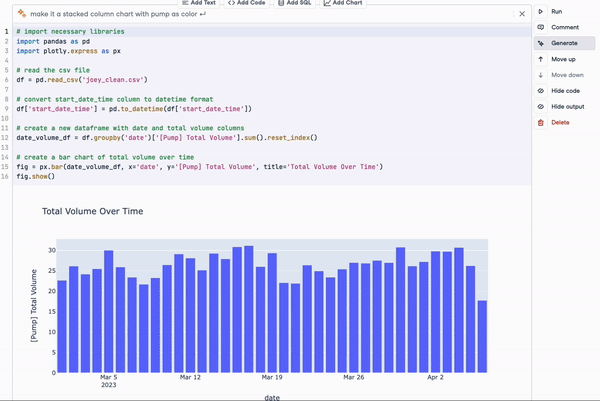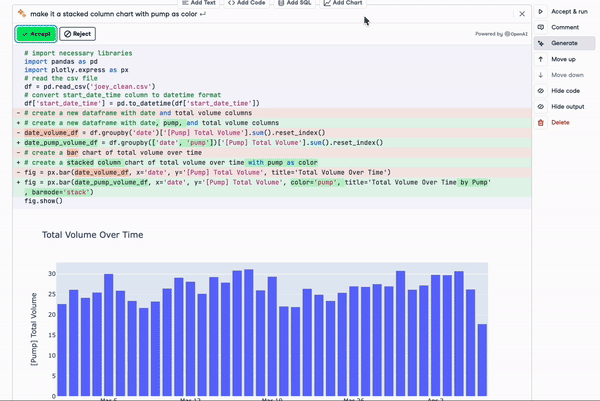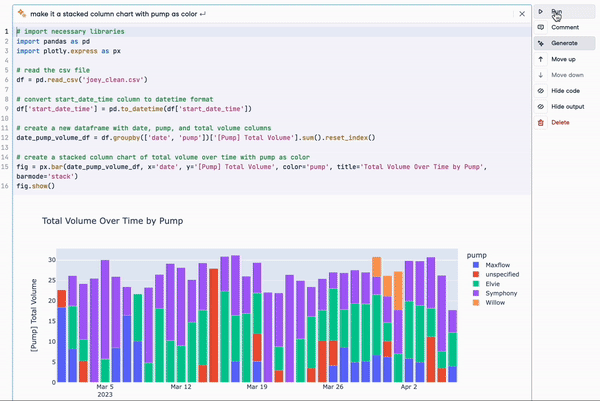
Either as a standalone product or as the foundation model of other applications, ChatGPT is leading the generative AI revolution, and more is to come as the product keeps evolving with more powerful technology. For example, there are already conversations on the next-generation GPT-5 that may reach the market in 2024.
Conclusion: ChatGPT vs Google Bard, Which is Better?
With the launch of ChatGPT in late 2022, OpenAI took everyone by storm. One year later, OpenAI has managed to keep its momentum. ChatGPT is still by far the most popular and widely-used LLM-powered chatbot, and this is unlikely to change in the near future, especially if OpenAI keeps improving the product with new features. This is the case with the recently announced integration with Dall-E, which will help ChatGPT to compete with other image generation tools, like Midjourney.
Yet while Bard’s PaLM 2 model doesn’t seem to rival the GPT-4 model that powers the most advanced version of ChatGPT, Bard is much more than a standalone chatbot. With its vast pool of users, Bard already has the most important ingredient for success. As the tool keeps integrating with other Google products, Bard can easily become ubiquitous, and once users get used to it, sooner or later, they will start using it. Hence, in the long run, Bard may be able to overcome ChatGPT.
In the meantime, if you want to keep posted on the latest developments in generative AI, at DataCamp, we have you covered. Check out our dedicated materials and start your generative AI journey today:

I am a freelance data analyst, collaborating with companies and organisations worldwide in data science projects. I am also a data science instructor with 2+ experience. I regularly write data-science-related articles in English and Spanish, some of which have been published on established websites such as DataCamp, Towards Data Science and Analytics Vidhya As a data scientist with a background in political science and law, my goal is to work at the interplay of public policy, law and technology, leveraging the power of ideas to advance innovative solutions and narratives that can help us address urgent challenges, namely the climate crisis. I consider myself a self-taught person, a constant learner, and a firm supporter of multidisciplinary. It is never too late to learn new things.