Track
Up until recently, fine-tuning GPT-4o was only possible with text. Now, with OpenAI’s latest fine-tuning API, we can customize GPT-4o with images, too. This means we can adapt GPT-4o’s capabilities to our use case.
This update opens up new possibilities—imagine fine-tuning GPT-4o for more accurate visual searches, object detection, or even medical image analysis.
In this tutorial, I’ll provide step-by-step guidance on fine-tuning GPT-4o with images. Specifically, we will fine-tune the model to correctly identify Georgian Orthodox churches.
GPT-4o Visual Fine-Tuning Pricing
OpenAI is offering one million free tokens per day until October 31st to fine-tune the GPT-4o model with images, which is a good opportunity to explore the capabilities of visual fine-tuning GPT-4o.
After October 31st, training costs will transition to a pay-as-you-go model, with a fee of $25 per million tokens. Additionally, inference costs will be incurred for each input ($3.75 per million tokens) and output ($15 per million tokens).
It's important to note that this information is accurate as of October 10th, so be sure to refer to OpenAI's pricing page for the most up-to-date details on pricing and availability.
GPT-4o's Visual Problem Challenge
Let’s jump to the interesting part. How do we actually do visual fine-tuning for GPT-4o?
Let’s begin by evaluating how well GPT-4o recognizes this Georgian church:

When asked, the model thought the image was of St. Nicholas Church in Georgia, when in reality, it is the Kutaisi Holy Annunciation temple.
Clearly, there’s room for improvement, and this is where fine-tuning comes in.
Prepare the JSONL file
We first need to prepare our training dataset to get started with fine-tuning. According to the official documentation, we need a JSONL file structured like this:
{
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are an assistant that identifies Georgian orthodox churches."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is this church called?"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/e8/Khareba_church.jpg"
}
}
]
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Kutaisi Holy Annunciation temple"
}
]
}
//second example
{
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are an assistant that identifies Georgian orthodox churches."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is this church called?"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/a/af/Holy_Trinity_Cathedral_of_Tbilisi.jpg"
}
}
]
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Holy trinity cathedral"
}
]
}
//other examples below
For the sake of readability and space, I only included a snippet of my training JSONL with two entries; the other training examples should be added on a separate line.
Note that we need at least 10 examples to run the fine-tuning. Each line represents an independent JSON object with a messages array.
Note also that JSONL does not support comments, so I decided to add comments after the // for the sake of the guide. Make sure to remove them before training.
You can use a regular text editor like Notepad, or if you're working with many examples, it’s a good idea to automate the creation of this file using a script. Once your JSONL file is ready, you can begin the fine-tuning process.
Develop AI Applications
Fine-tuning GPT-4o With Images
Now, with the ready JSONL, we need to log into our OpenAI dashboard and choose the Create option:
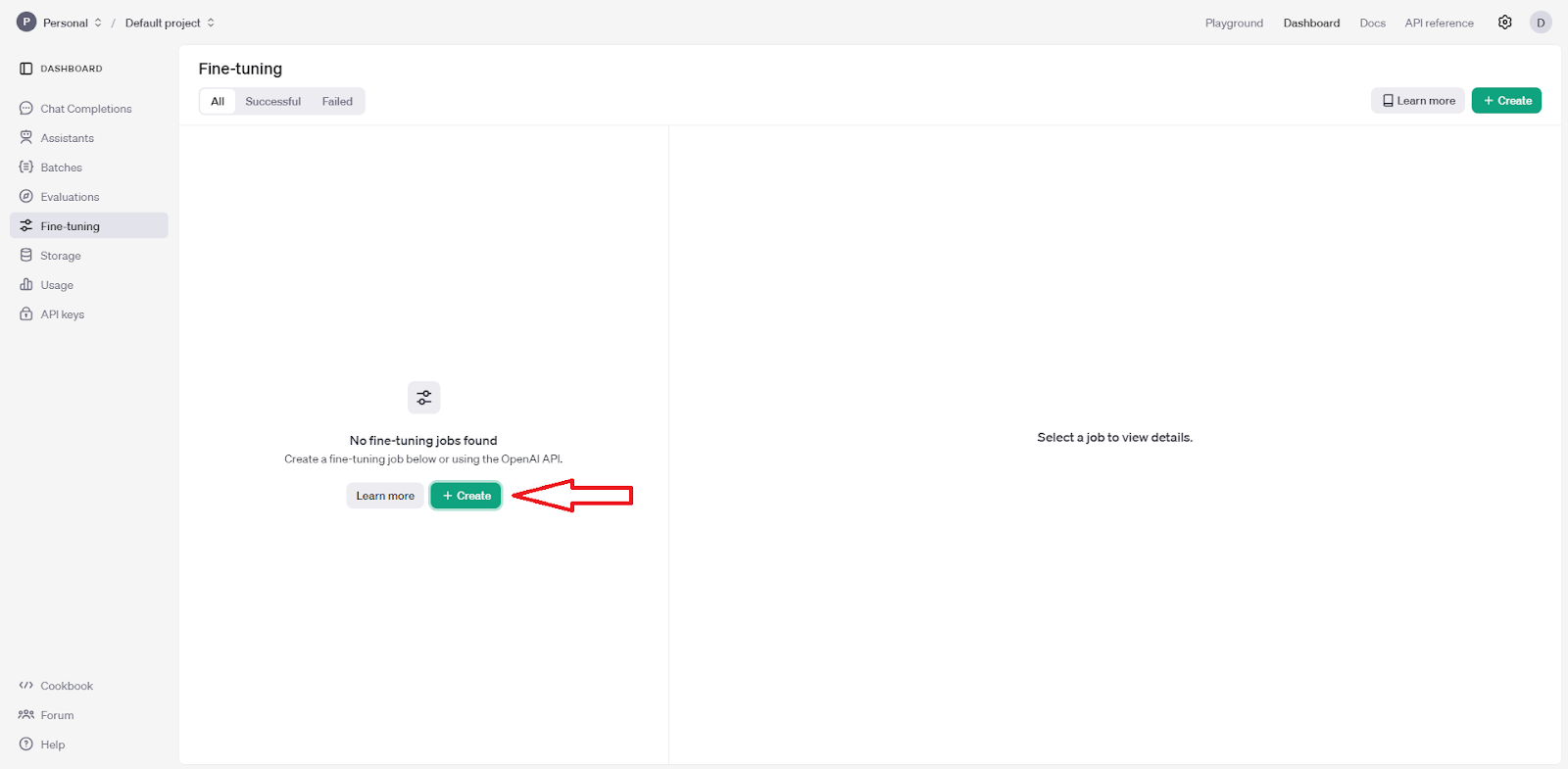
In the menu that pops up:
- Choose the
gpt-4o-2024-08-06model. - Upload the training JSONL file.
- You can also set the hyperparameters or leave everything on auto.
Once we create the job, fine-tuning should start automatically:
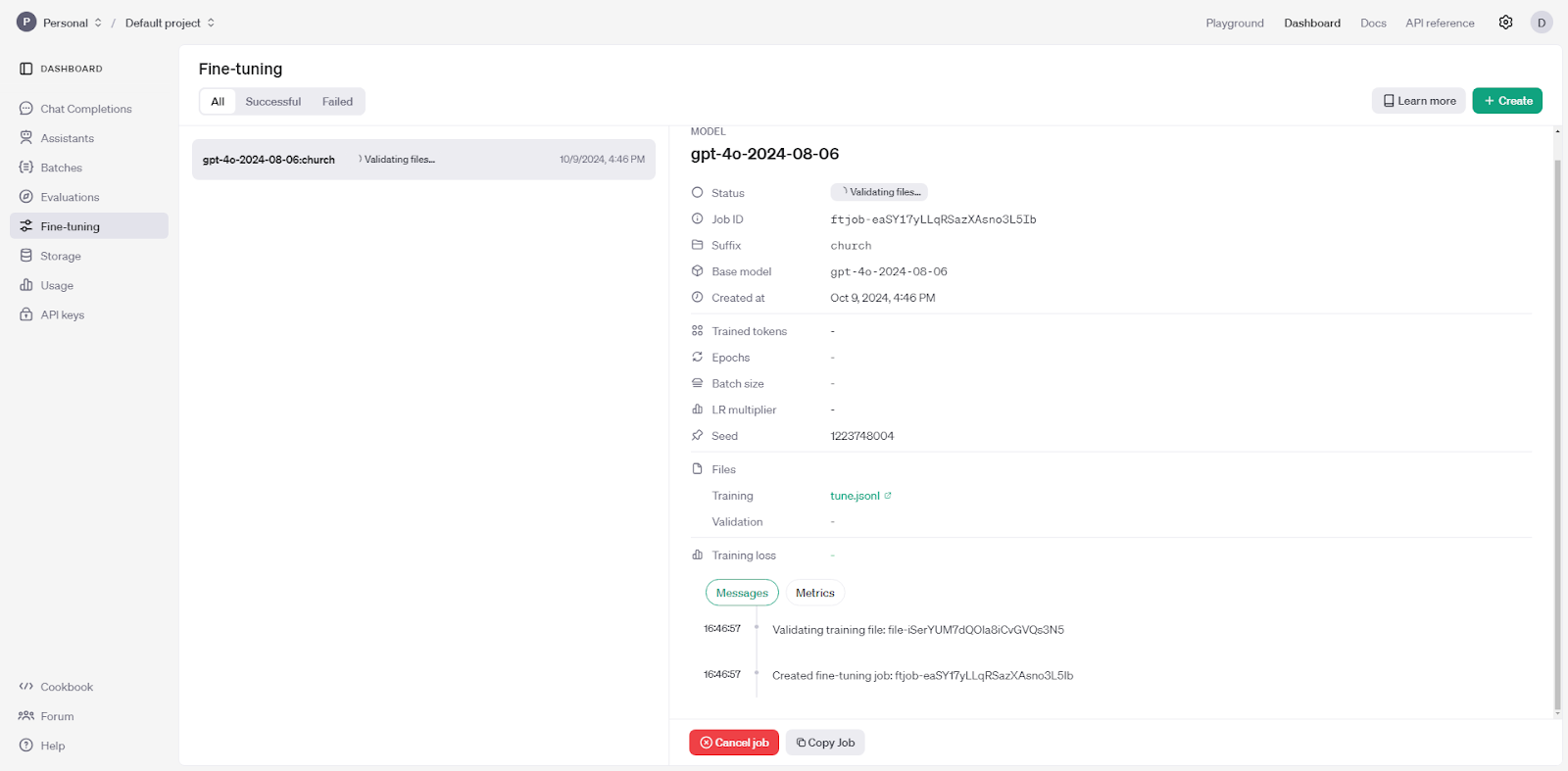
My fine-tuning routine took approximately 20 minutes (the number of epochs was automatically set to 9). Depending on the dataset size and model complexity, this could vary, but you’ll be notified once it’s complete.
Testing the Fine-Tuned GPT-4o Model
Once you’re done, you can access the fine-tuned agent through the API or the Playground.
For simplicity, I’ll be using the Playground for testing. Let’s see if the model can correctly identify the church this time:
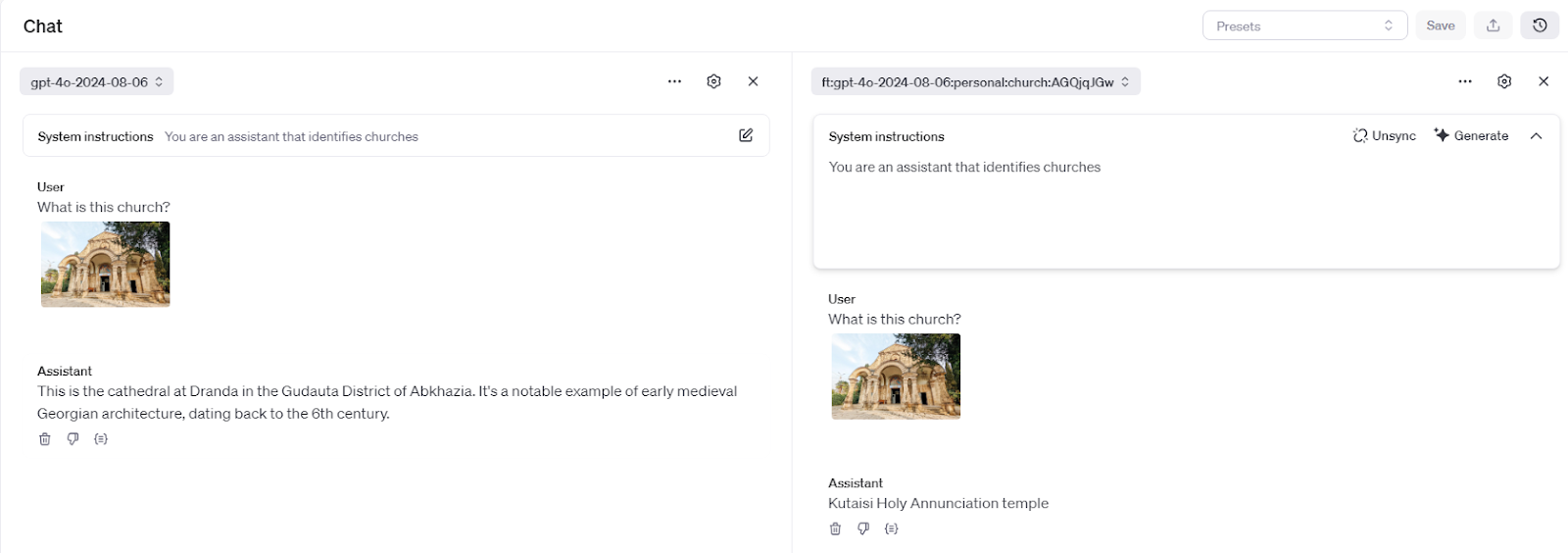
As you can see, the fine-tuned agent (on the right) identified the church correctly, even though that picture was not in the training dataset. The regular model (on the left) still gets it wrong!
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we explored the process of fine-tuning GPT-4o with images.
We started by highlighting the model's initial limitations in identifying a specific type of church. To address this, we prepared a JSONL file containing image-text pairs for training. We then utilized OpenAI's fine-tuning API to create a customized model.
Finally, we tested the fine-tuned model and observed its improved accuracy in identifying the church.
While this example focused on a specific use case, the underlying principles and techniques can be applied to a wide range of image-related tasks, demonstrating the potential of GPT-4o's visual fine-tuning capabilities. I recommend reading the use cases in the OpenAI’s announcement article.
To learn more about working with OpenAI’s products, I recommend these resources:




