Track
Speed and efficiency are becoming more important across all aspects of business. As such, many companies are turning to artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize their supply chains. The recent advancements in AI have the potential to transform how goods are produced, shipped, and delivered.
But what exactly does AI mean for supply chain management, and how can it be harnessed effectively?
We’ll explore these questions and more, providing insights and advice for businesses keen on leveraging AI in their operations in the supply chain. If you're eager to learn more about the impact of AI, check out our webinar, The Learning Leader's Guide to AI Literacy.
Elevate Your Organization's AI Skills
Transform your business by empowering your teams with advanced AI skills through DataCamp for Business. Achieve better insights and efficiency.

Introduction to AI in the Supply Chain
AI is developing rapidly, making its applications and potential far-reaching, particularly its impact on the supply chain industry. Let's explore more below.
What is AI in supply chain?
AI is a branch of computer science that refers to the development of algorithms and models that enable machines to display human-like intelligence. In supply chain management, AI is used to analyze, predict, and optimize operations to achieve maximum efficiency.
With its ability to process large amounts of data at high speeds, AI has become an invaluable tool in managing complex supply chains.
The importance of AI in modern supply chain management
Supply chains have seen increased scrutiny in recent years, particularly in the US. In 2021, an Executive Order on America’s Supply Chains was signed. This order aimed to secure US supply chain resilience in critical sectors like ICT and semiconductors, ensuring the secure development, deployment, and competitiveness of AI technologies while mitigating risks from geopolitical, cyber, and environmental threats.
Then, in 2023, a progress report by the USA White House on building resilient supply chains and an Executive Order on Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence was released.
The report showed that the CHIPS and Science Act allocated $52.7 billion to strengthen domestic semiconductor production, vital for AI development, while investments in workforce training and research aim to support innovation in AI-related fields.
International partnerships, such as the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework, have promoted secure and resilient supply chains for digital and ICT products, ensuring the US remains competitive in the global AI landscape. These efforts address vulnerabilities in critical materials, foster AI-enabled innovation, and secure the technologies driving the AI economy.
A recent McKinsey survey also showed that a majority of respondents reported that AI has led to meaningful revenue increase of over 5% in supply chain and inventory management.
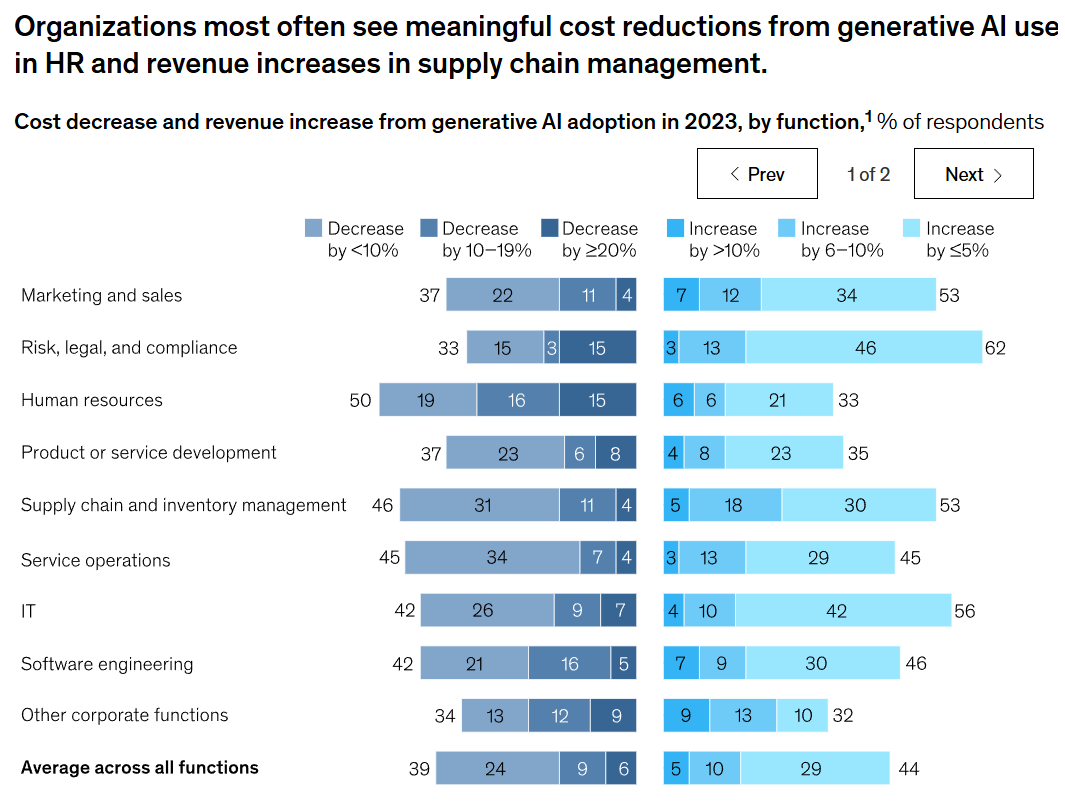
Why use AI in supply chains?
AI presents a unique opportunity for companies to streamline their operations and gain a competitive edge in the supply chain. Businesses can accurately forecast demand, identify potential risks and disruptions, and make data-driven decisions that lead to better efficiency and cost savings.
Additionally, AI can automate tasks such as inventory management, routing optimization, and supplier selection, freeing up human resources to focus on more strategic activities.
Without the use of AI, achieving such high levels of efficiency and accuracy would be near impossible, considering the fast pace of supply chains.
What is AI in logistics?
AI has a particularly significant impact on logistics, the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the flow of goods. It enables logistics companies to optimize their transportation routes, warehouse operations, and delivery schedules based on real-time data and predictive analytics.
AI in logistics enables companies to achieve faster delivery times, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Key Applications of AI in Supply Chain
AI is already revolutionizing supply chain management through several key applications. Here are some common uses:
1. Demand forecasting
AI-powered demand forecasting enables companies to predict future demand for products with high accuracy by analyzing a wide range of data sources, including historical sales, market trends, economic factors, and customer behavior.
Unlike traditional forecasting methods, AI models can adapt to new patterns and react to real-time data, making forecasts more dynamic and reliable.
- Predictive models: Machine learning algorithms, such as time-series analysis and neural networks, identify complex demand patterns and generate more precise predictions.
- Real-time adjustments: AI allows for on-the-fly adjustments to forecasts based on changes in demand drivers, such as new promotions, market shifts, or external events (e.g., weather conditions or holidays).
- Reduced stockouts and overstocks: Accurate demand forecasting ensures that companies have the right products available at the right time, improving customer satisfaction and reducing the costs associated with excess inventory or lost sales.
Models like the following can be used:
- Seasonal ARIMA: Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) models are used for time series forecasting, which is the process of predicting future values based on past data. These models take into account both trend and seasonal components.
- Random forests: Random forests are a type of machine learning algorithm that uses multiple decision trees to generate predictions. They can handle large datasets with many variables and have high prediction accuracy.
One good example of AI in this use case is Amazon’s use of AI in forecasting daily demands in shipping of over 400 million products during the 2023 holiday season.
2. Inventory management

AI optimizes inventory management as well. This is done by analyzing sales data, supply chain dynamics, and external variables to maintain ideal stock levels. This helps businesses achieve the delicate balance between having enough inventory to meet demand and avoiding excess stock that incurs holding costs.
Here are some common ways inventory can be managed using AI.
- Automated replenishment: AI systems can automatically reorder products when stock levels reach predefined thresholds, ensuring that inventory is consistently replenished without manual intervention.
- Demand-driven stocking: By forecasting demand more accurately, AI helps businesses stock high-demand products while minimizing less popular items, leading to optimized use of storage space and reduced holding costs.
- Warehouse efficiency: AI-driven systems optimize warehouse layout and product picking routes, improving fulfillment speed and reducing the time and resources spent on order processing.
Inventory management is also a common application for the use of AI in healthcare, where many disposable materials are consumed rapidly.
3. Supply chain optimization
AI enhances the overall supply chain optimization process and simplifies it.
AI can provide end-to-end visibility and automate complex processes, from production planning to logistics. The AI algorithms can analyze data across various touchpoints, allowing for optimal decision-making regarding production schedules, transportation routes, and resource allocation.
More specifically, here are some ways AI can be used:
- Route and logistics optimization: AI-powered systems can optimize transportation routes, consolidate shipments, and factor in real-time traffic and weather data, reducing delivery times and fuel costs.
- Production planning: AI algorithms balance production capacity with demand, adjusting schedules and resources to prevent bottlenecks and meet deadlines more efficiently.
- End-to-end visibility: With AI, companies gain real-time visibility across the supply chain, enabling better tracking of orders, shipments, and stock levels, which helps identify and mitigate potential disruptions early.
4. Supplier relationship management
AI can also work to strengthen supplier relationship management (SRM).
An AI model can provide insights into supplier performance, risk factors, and collaboration opportunities. This insight can be generated by analyzing large amounts of enterprise data.
These aspects can be enhanced in particular:
- Supplier performance monitoring: AI tracks key performance indicators (KPIs) such as lead times, defect rates, and compliance records, providing a comprehensive view of each supplier's reliability and quality.
- Risk assessment: AI identifies and assesses risks within the supplier base by analyzing external factors (e.g., geopolitical changes, financial health) that might affect supplier stability, enabling proactive risk management.
- Collaborative planning: AI can enhance collaboration by sharing demand forecasts and production plans with suppliers, improving coordination, and ensuring suppliers can meet demand efficiently.
This can be especially useful for supply chains in e-commerce, where multiple supplier partners are involved.
The Benefits of AI in Supply Chain Management
Using AI in the supply chain provides great benefits, including improved decision-making, cost reduction, operational efficiency, and enhanced sustainability.
Each of these benefits helps businesses navigate complex supply chain challenges and remain competitive in dynamic markets.
1. Improved decision-making
AI transforms decision-making in supply chains by delivering real-time, data-driven insights that allow companies to make proactive rather than reactive decisions.
AI systems can analyze large volumes of data from multiple sources—including historical data, market trends, and external factors like weather and economic shifts—to generate predictive insights and recommend actions.
- Predictive analytics: AI-powered predictive models forecast demand, helping businesses adjust inventory, optimize production schedules, and reduce the likelihood of stockouts or overstock.
- Scenario planning: By simulating various scenarios (e.g., changes in demand, supply disruptions), AI allows companies to evaluate the potential impacts of different choices, improving their ability to plan for uncertainties.
- Faster response to changes: AI-enabled decision support tools can detect issues or trends in real-time, such as a sudden demand increase or logistical bottleneck, allowing for quick adjustments to maintain smooth operations. AI is also able to analyze larger datasets faster than through manual analysis.
For example, IBM’s cognitive supply chain technology architecture enabled them to respond to issues in supply chain rapidly before disruption occurs.
It essentially uses AI to crawl the web and if there is a disruption, we can take action quickly to secure a second supply source.
Rob Cushman, Senior Partner, IBM Supply Chain Transformation
Through this, quick actions could be taken to look for a second supply source of one fails. Their cognitive supply chain technology that leverages AI resulted in a 100% order fulfillment rate even during the 2020 pandemic.
2. Cost reduction and operational efficiency
Through the same AI-based cognitive supply chain technology, IBM reduced their supply chain costs by USD 160 million.
AI significantly reduces costs and enhances operational efficiency by automating and optimizing core supply chain processes. From managing inventory to planning logistics, AI-driven automation minimizes manual tasks, reducing human error and improving process efficiency.
- Inventory optimization: AI systems can maintain optimal stock levels by analyzing factors like sales history, lead times, and seasonality, which reduces excess inventory costs and minimizes storage expenses.
- Automated scheduling: AI streamlines production and logistics schedules, minimizing downtime and improving resource utilization. For example, AI algorithms can optimize truck loads, shipping routes, and delivery times, leading to lower fuel costs and quicker delivery.
- Waste reduction: Through precise forecasting and efficient resource allocation, AI reduces waste in manufacturing and logistics. This not only lowers disposal costs but also contributes to environmental sustainability.
3. Enhanced sustainability
As we’ve discussed in a separate article AI can enhance sustainability in various areas. In supply chains, AI can enable more efficient resource use and reduce waste and emissions.
As companies aim to meet sustainability goals, AI offers tools to track, measure, and optimize sustainable practices within the supply chain.
- Lower carbon emissions: AI-powered routing and logistics optimization can reduce fuel consumption by selecting efficient routes, consolidating shipments, and minimizing unnecessary transportation, leading to reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy efficiency: In manufacturing, AI can optimize equipment usage, minimize idle times, and schedule production based on energy availability and cost, which reduces energy consumption and improves operational sustainability.
- Waste minimization: By accurately forecasting demand, AI helps reduce overproduction and unnecessary inventory, which minimizes waste and supports a circular economy approach, where resources are reused or repurposed.
The transport and supply chain sector accounts for 25% of global greenhouse emissions, according to a UN report. With the reduction in waste and improvements in managing inventory through the use of AI, possible reductions in greenhouse gas emissions may result.
Incorporating AI into supply chain management ultimately leads to more agile, cost-effective, and environmentally responsible operations.
These improvements help businesses not only save money and optimize resources but also align with global efforts toward sustainability, enhancing their brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
Ready to implement AI in your organization? Our AI Fundamentals course would be the perfect entry point for learning all the necessary AI skills.
Generative AI in Supply Chain
Generative AI is an advanced form of artificial intelligence that uses deep learning to create new, unique outputs based on a set of training data. In supply chain management, generative AI can help optimize processes by generating multiple scenarios and suggesting the most efficient course of action.
Here are some potential use cases:
- Generating alternate transportation routes to minimize costs and improve efficiency
- Creating optimized production schedules based on varying demand levels
- Generating potential solutions for supply chain disruptions in real-time
Case studies
Generative AI is transforming supply chain management by enabling businesses to optimize operations, enhance efficiency, and improve decision-making. Here are some real-world examples of companies leveraging generative AI in their supply chains:
1. DHL Supply Chain
DHL has partnered with Boston Consulting Group to deploy generative AI applications aimed at enhancing data management and analytics. One application is a data cleansing tool that processes and analyzes data from potential customers, enabling DHL engineers to design logistics solutions more efficiently.
Another application assists sales teams by providing insights during proposal development, allowing for quicker and more personalized customer proposals.
2. Mars Incorporated
Mars is collaborating with Celonis to utilize generative AI to optimize truck loads. By analyzing factors such as weather and shipment details, the AI system recommends load consolidations, reducing manual efforts by 80% and lowering shipping costs and emissions.
3. ThredUp
The secondhand apparel retailer ThredUp employs AI in its distribution centers to enhance throughput and productivity. AI is used to generate detailed item descriptions for products, streamlining operations and improving efficiency.
4. UPS
UPS utilizes its On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation (ORION) system, which leverages AI and advanced algorithms to optimize delivery routes in real time. The system considers factors such as package volume, delivery windows, real-time traffic conditions, and weather to generate efficient routes, saving over 10 million gallons of fuel annually and reducing costs and carbon emissions.
These examples demonstrate how generative AI is being applied across various industries to enhance supply chain efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall operational effectiveness.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing AI
Despite its many benefits, implementing AI in supply chains is not without challenges. These challenges may pose a difficulty for organizations that are not prepared for this change.
Data privacy
Data privacy and security are significant concerns, as AI systems rely on processing vast amounts of potentially sensitive information. Companies must ensure that their data handling practices comply with international regulations and standards.
If you’re an organization that resides in the EU, the EU AI Act is a key guideline with strict data privacy rules that must be abided to. You can read more on this in our EU AI Act guide for leaders.
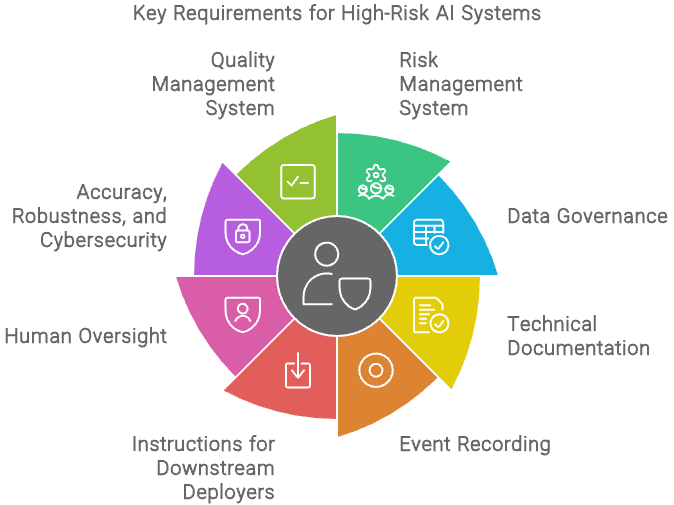
As you can see from the image above, the EU AI Act enforces good data governance, which can prove to be a challenge for many small businesses.
Data quality and complexity
AI algorithms are only as good as the data they are trained on. Companies must ensure that their data is accurate, relevant, and constantly updated to avoid erroneous predictions.
Across all industries, data quality is a key challenge when it comes to AI adoption. These issues with data accuracy and integration are especially true in complex supply chains.
For example, in a global supply chain, data must be collected and analyzed from various suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors across different countries and time zones. This presents challenges for data integration, standardization, and interoperability.
High implementation costs
With the implementation of any new technology, there is an initial cost. Companies must carefully consider the return on investment and potential benefits before investing in AI.
Some of these costs can come from:
- Hiring skilled professionals to develop and maintain AI systems
- Upgrading existing infrastructure to support AI technology
- Upkeeping of large AI models on-premise
However, the positive outcomes of AI far outweigh the financial and operational challenges of adopting AI solutions.
Workforce training and adaptation
The impact on the workforce is another consideration. While AI can automate many tasks, it can also lead to the need for AI reskilling and upskilling. Companies need to find a balance between technological advancement and maintaining the skill base of their workforce.
Organizations must be prepared to equip employees to work alongside AI and use these new AI tools to fill any skills gaps that may arise.
This is where DataCamp for Business can help. DataCamp for Business provides a comprehensive solution for corporate training in data science and AI skills that are in high demand in this growing area of AI in the supply chain. Get started with a demo today.
Elevate Your Organization's AI Skills
Transform your business by empowering your teams with advanced AI skills through DataCamp for Business. Achieve better insights and efficiency.

The Future of AI in the Supply Chain
Looking ahead, the role of AI in supply chain management will likely expand. Emerging technologies will further enhance AI capabilities, offering even more sophisticated solutions for supply chain challenges.
Autonomous supply chains
For example, supply chains will move towards autonomy, with AI-driven processes and machines working independently. This could lead to near-perfect accuracy and efficiency, reducing the need for human intervention.
Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics will continue to evolve, enabling companies to anticipate disruptions further in advance and make necessary adjustments quickly. This will help companies proactively manage risks and avoid potential setbacks.
Generative AI-driven innovation
Generative AI will also play a more significant role in supply chain innovation. Generative AI may be useful in drafting out multiple design options for products and processes. Companies can then find the most optimal solutions that may not have been possible with traditional methods.
Final Thoughts
AI has already made substantial inroads into supply chain management, and its role will continue to expand. For organizations and individuals, it’s crucial to keep up-to-date with these developments. DataCamp for Business will equip your teams and employees with the AI skills they need to capitalize on the exciting developments in the industry.
AI in Supply Chain FAQs
How is AI used in supply chain?
AI can be used in supply chain operations such as demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics optimization.
What is the future of supply chain AI?
Supply chain AI will continue to evolve and become more advanced, with the potential to improve efficiency and reduce costs for businesses. More businesses will adopt AI as it becomes a must-have for organizations of all sizes.
Is AI in supply chain a threat to jobs?
While some low-skill jobs may be replaced by AI in the supply chain industry, it will also create new job opportunities in areas such as data analysis and algorithm development. Overall, it has the potential to increase productivity and create a more efficient workforce.
How is generative AI used in supply chains?
Generative AI can be used to generate and optimize supply chain designs and processes, improving efficiency and reducing costs. It can also be used for predictive maintenance and risk management.
How can AI make supply chains more sustainable?
AI can help make supply chains more sustainable by optimizing routes and reducing carbon emissions through smart logistics. It can also aid in identifying and reducing waste in the supply chain, leading to a more environmentally friendly process.

I'm Austin, a blogger and tech writer with years of experience both as a data scientist and a data analyst in healthcare. Starting my tech journey with a background in biology, I now help others make the same transition through my tech blog. My passion for technology has led me to my writing contributions to dozens of SaaS companies, inspiring others and sharing my experiences.