Track
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just a concept from science fiction; it’s a driving force behind innovations we find in our daily lives. From Netflix recommending your next favorite series to Tesla's self-driving cars and Amazon Alexa's virtual assistant, AI powers the cutting-edge technologies shaping our lives. But have you ever wondered:
What’s behind these systems?
How do they become a reality?
The answer lies in the AI project cycle, a structured framework that transforms ideas into impactful solutions.
This article breaks down the seven key stages of the AI project cycle, explaining how each step—from problem scoping to deployment—contributes to building effective AI systems. If you’re new to the topic of AI, be sure to check out our AI Fundamentals skill track to master the foundations.
What is the AI Project Cycle?
The AI project cycle is a step-by-step framework for developing and deploying artificial intelligence (AI) solutions to address specific problems, transforming ideas into impactful, real-world applications.
Spanning multiple stages, it guides organizations and individuals through tasks ranging from problem identification to model deployment. Each step plays a critical role in ensuring the success of an AI solution by providing a clear roadmap for achieving defined goals and final success.
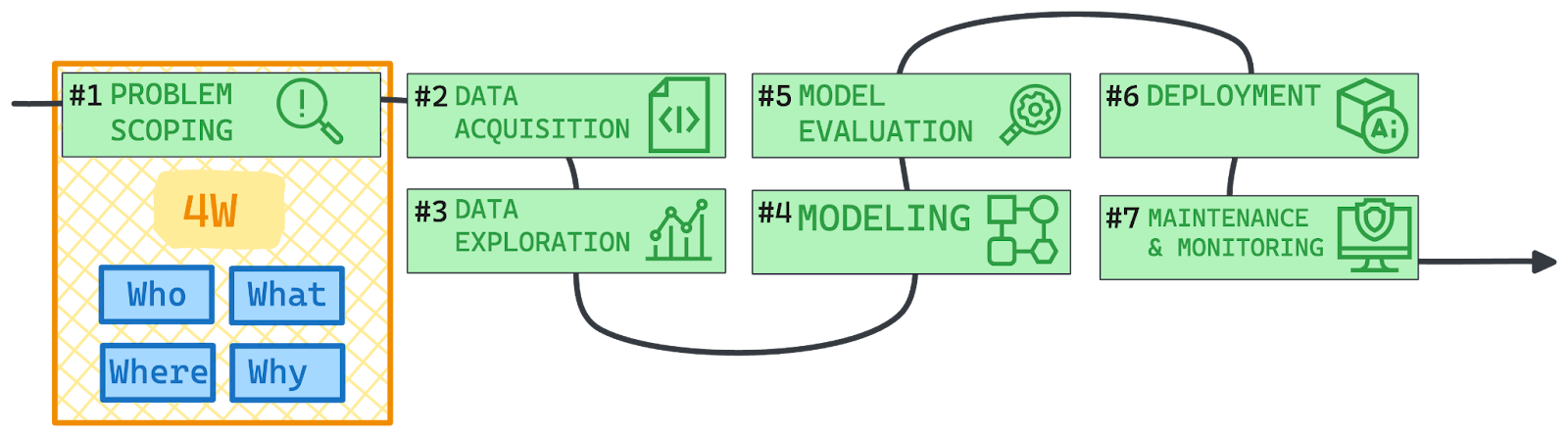
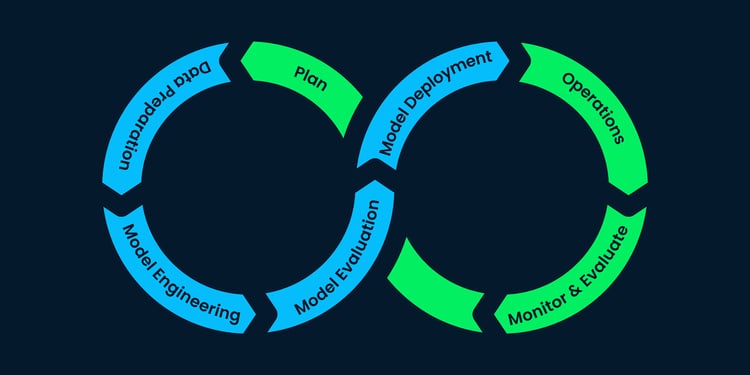
Image by Author
AI Project Lifecycle Step-by-Step
Let’s break down each section of the AI project lifestyle to understand it in more detail.
Stage 1 - Problem scoping
Before starting any project, no matter what field, identifying the problem we aim to solve is one of the core actions to perform. This is why the AI Project cycle is not different and needs to be started with a Problem Scoping stage.
It is the process of defining the challenge or opportunity that AI can address, setting specific objectives, and establishing clear criteria for success.
4Ws problem canvas
To effectively scope the problem, it’s essential to gather detailed requirements and analyze the context using the 4Ws Problem Canvas—a structured framework that ensures a thorough understanding of the problem:
- Who: Begin by identifying the stakeholders affected by the problem—individuals or organizations that stand to benefit from the proposed solution.
- What: Then comes the understanding of the nature of the problem. Analyze its characteristics, validate its existence with evidence, and clarify why it’s an issue.
- Where: The next action is determining the locations and contexts where the problem arises. Understanding when and where it occurs helps identify patterns and trends critical for developing an effective solution.
- Why: Finally, we establish the purpose of addressing the problem. Define the benefits, expected outcomes, and the value the AI solution will bring to stakeholders.
By systematically addressing these questions, problem scoping lays the groundwork for aligning the AI project with business goals and stakeholder expectations.
Stage 2 - Data acquisition
In any AI project, data acts like the fuel that allows learning. This is why clean, well-organized, and relevant data provides a solid foundation for the subsequent stages, including exploration, modeling, and deployment. Properly acquired data ensures your AI project starts on the right track, minimizing errors and maximizing impact.
This is exactly what data acquisition is about; it involves sourcing, cleaning, and organizing the data needed to train and validate your AI system. The goal is to ensure the data is comprehensive, accurate, and suitable for the problem at hand while addressing privacy and ethical considerations.
Here are the key steps:
- Data collection: Identify and gather data from diverse sources, such as:
- Surveys
- Web scraping
- Sensors and cameras
- Observational studies
- APIs
- Data quality assurance: Raw data often contains errors, missing values, or inconsistencies. Before using it, we must be sure the data is clean. High-quality data ensures the AI model can learn effectively and deliver accurate predictions.
- Feature selection: Identify the specific data attributes—called features—needed for the AI model. Choosing relevant features is critical for the model’s success.
- Ethical considerations: Safeguard data privacy and ensure ethical handling of sensitive information. This includes compliance with regulations like GDPR and maintaining transparency about data usage.
Stage 3 - Data exploration
When observing data, we usually just see a bunch of numbers. However, it is important to make sense of it. This is where data exploration kicks in, allowing us to find hidden patterns. It’s all about turning those numbers into pictures that are easy for people to understand. Data exploration transforms raw data into actionable insights by uncovering patterns, trends, and anomalies.
There are several steps to this process:
- Spotting patterns: Identify correlations and trends that guide model development.
- Visualizing data: Simplify data with visuals to enhance understanding and highlight key insights.
- Handling anomalies: Detect and address outliers to ensure data integrity.
- Informing next steps: Choose the right analytical methods and tools for modeling.
Effective exploration ensures the data is ready for modeling and aligns with project objectives, which leads us to the following stage:
Stage 4 - Modeling
Modeling is the core of the AI project cycle, where data is transformed into actionable insights through algorithms and mathematical frameworks. This stage involves selecting, training, and fine-tuning AI models to solve the identified problem effectively.
The main components of this step include:
- Choosing the right model: Select an AI model tailored to the problem, such as Logistic Regression, Naive Bayes, or advanced options like Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs). The choice of model significantly impacts the solution's accuracy and effectiveness.
- Training the model: Use the prepared data to train the selected model. Training enables the AI to learn patterns and relationships in the data, forming the foundation for making predictions or decisions. This step may require significant computational resources and time, depending on the task's complexity.
- Fine-tuning and optimization: Refine the model by adjusting hyperparameters and tweaking its architecture to enhance performance. This iterative process ensures the model aligns with project objectives and delivers optimal results.
- Evaluating multiple models: Test and compare different models to identify the best-performing one. The evaluation ensures the chosen model is not only accurate but also robust and efficient for the given task.
Modeling bridges raw data and actionable insights, empowering AI solutions to deliver reliable and impactful outcomes in real-world scenarios.
Stage 5 - Evaluation
Evaluation is a pivotal stage in the AI project cycle, where the model’s performance is rigorously tested to ensure it operates as intended. This step involves assessing the model against key metrics, validating its reliability on unseen data, and confirming alignment with business objectives.
The key steps here are:
- Assessing performance metrics: Evaluate the model’s effectiveness using the following metrics:
- Accuracy: Measures the overall proportion of correct predictions.
- Precision: Indicates the model’s ability to minimize false positives by assessing the proportion of true positive predictions out of all positive predictions.
- Recall (Sensitivity): Reflects the model’s ability to identify all relevant positive cases, ensuring no important data is missed.
- F1 score: Balances precision and recall, especially valuable when working with imbalanced datasets.
- Cross-validation: Conduct cross-validation to test the model’s robustness across different subsets of data. This ensures the model performs consistently and avoids overfitting to specific datasets.
- Testing on unseen data: Use a separate testing dataset to simulate real-world conditions and evaluate the model’s ability to generalize beyond the training data.
- Business alignment: Verify that the model meets the project’s business goals and stakeholder expectations. A successful AI solution is not only technically sound but also impactful in achieving its intended objectives.
Thorough evaluation ensures the AI model is accurate, reliable, and aligned with the problem it aims to solve. This stage provides confidence in the model’s ability to perform effectively in real-world applications and lays the foundation for deployment.
Stage 6 - Deployment
Deployment is where the AI model moves from development to real-world application. This step integrates the model into systems or platforms, ensuring it operates effectively to solve practical problems.
The key stages of deployment are:
- Integration: Embed the model into existing infrastructure, applications, or services.
- Deployment options: Choose from cloud-based solutions, on-premises setups, or edge devices based on project needs.
- Performance monitoring: Track the model in real-world conditions to ensure accuracy and address potential issues like drift.
- Scalability and maintenance: Configure for increased data loads and establish protocols for regular updates.
Effective deployment ensures the model delivers its intended benefits while remaining reliable, scalable, and adaptable. For a hands-on approach to deploying and maintaining AI models, explore our course on MLOps deployment and life cycling.
Stage 7: Maintenance and monitoring
Maintenance ensures AI models stay accurate and effective over time by adapting to new data and evolving conditions.
The steps to follow here include:
- Regular updates: Retrain and refine the model with fresh data to maintain accuracy.
- Performance tracking: Monitor metrics to detect issues like drift or degradation.
- Feedback loops: Use real-world insights to improve the model iteratively.
Ongoing maintenance keeps the AI model reliable, relevant, and aligned with its objectives, ensuring long-term success. If you'd like to explore a similar framework specifically for machine learning, check out this comprehensive guide on the ML lifecycle.
Best Practices in the AI Project Cycle
Implementing AI effectively requires careful planning, collaboration, and a focus on ethics and scalability. Adopting best practices can help ensure success while minimizing risks.
- Prioritize ethics and responsibility: Develop AI systems with transparency, fairness, and explainability, ensuring compliance with ethical guidelines and regulations.
- Foster collaboration: Involve multidisciplinary teams, including technical experts, domain specialists, and non-technical stakeholders, to gain diverse perspectives and align expectations.
- Leverage robust testing: Use multiple datasets and adversarial testing to evaluate models across diverse scenarios and identify potential failure modes.
- Benchmark regularly: Continuously compare your model’s performance against others to ensure competitiveness and adaptability.
- Define Success Clearly: Establish clear, measurable success metrics to avoid ambiguity and scope creep.
- Adopt an incremental approach: Think big but start small—focus on simple, impactful use cases as a foundation for future growth.
- Invest in MLOps: Build a robust MLOps framework early to manage the complexities of deploying and maintaining AI models in production effectively.
For additional strategies on managing AI initiatives, read this insightful blog on managing AI projects effectively.
Common AI Project Cycle Challenges and How to Overcome Them
AI projects often encounter technical, ethical, and operational challenges. Addressing these proactively can enhance the project’s success and long-term value. This is why I designed a table containing some of the most common challenges you will face and how to assess them.
|
Main Challenge |
Suggested Solutions |
|
Data Scarcity or Imbalance |
Use data augmentation, synthetic data generation, or transfer learning to improve dataset diversity. |
|
Bias in Data and Models |
Regularly monitor for bias using specialized tools, and employ reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to mitigate ethical risks. |
|
Compliance and Regulation |
Ensure compliance with legal standards through rigorous audits and maintain documentation for transparency. |
|
Overfitting and Loss of Generalizability |
Use techniques like cross-validation and regularization to create models that generalize well across various inputs. |
|
Latency in Real-Time Applications |
Optimize models with quantization and distillation techniques to improve speed without sacrificing accuracy. |
|
Integration Complexity |
Implement modular architectures and well-defined APIs to streamline integration into existing systems. |
|
Cost Management |
Optimize model architecture and operations for efficiency, and select cost-effective cloud solutions. |
AI Project Cycle Case Studies and Real-World Applications
The AI project cycle finds its relevance across diverse applications, from eCommerce to specialized domains like healthcare. Here are two examples that illustrate its implementation:
1. Recommendation system for an eCommerce platform
Objective: Enhance user engagement and increase sales through personalized recommendations.
AI project cycle in action:
- Problem scoping: Define the goal of recommending products that align with user preferences and behaviors, identifying stakeholders such as customers and the business team.
- Data acquisition: Collect customer data, including purchase history, browsing patterns, and demographics, while ensuring data privacy compliance.
- Data exploration: Analyze the data for patterns, such as frequently bought items or seasonal trends, and identify potential anomalies.
- Modeling: Develop and train machine learning models, such as collaborative filtering or neural networks, to predict product preferences accurately.
- Evaluation: Test the model using metrics like precision and recall to ensure accurate and meaningful recommendations.
- Deployment: Integrate the model into the eCommerce platform, ensuring seamless operation alongside existing systems.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: Continuously update the model with new data and track performance to address issues like drift or changing user behavior.
Outcome: A dynamic recommendation system that improves customer experience and drives revenue growth.
2. A chatbot like ChatGPT specialized in the healthcare domain
Objective: Provide users with accurate and reliable health information through a conversational AI interface.
AI project cycle in action:
- Problem scoping: Establish the chatbot’s purpose to answer health-related queries while ensuring it complies with ethical and legal standards. Stakeholders include patients, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies.
- Data acquisition: Gather diverse, high-quality medical datasets, including clinical guidelines, medical literature, and user interaction logs, while safeguarding patient privacy.
- Data exploration: Analyze the data to identify common health concerns, frequently asked questions, and language patterns for effective model training.
- Modeling: Fine-tune a large language model like ChatGPT on domain-specific datasets, incorporating reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF) to align responses with expert advice.
- Evaluation: Assess the model using metrics such as accuracy, relevance, and safety of responses to ensure reliable information delivery.
- Deployment: Deploy the chatbot as a web or app-based service, integrating it into existing healthcare systems for accessibility.
- Maintenance and monitoring: Monitor interactions to refine responses, address misinformation, and retrain the model with updated medical knowledge.
Outcome: A reliable health-focused chatbot that provides accurate, accessible, and ethical information, empowering users to make informed health decisions.
For those keen on understanding AI's role in business, this AI Business Fundamentals track is a great starting point.
Conclusion
The AI project cycle provides a structured roadmap for turning innovative ideas into impactful real-world solutions. From problem scoping to deployment and ongoing maintenance, each stage plays a critical role in ensuring the success and reliability of AI systems. This systematic approach allows us to both define clear objectives and uncover valuable insights while supporting the creation of robust, ethical, and effective AI models.
By adopting the AI project cycle, organizations can navigate the complexities of AI development with confidence. It encourages collaboration, fosters ethical responsibility, and aligns technical efforts with business goals. Whether you're launching a new AI initiative or refining an existing solution, embracing this lifecycle is key to achieving meaningful and sustainable results in the ever-evolving field of artificial intelligence. If you’re totally new to the AI field, you can start with DataCamp’s AI Fundamentals track. For more advanced users, some other good resources to improve your AI skills are:
Josep is a freelance Data Scientist specializing in European projects, with expertise in data storage, processing, advanced analytics, and impactful data storytelling.
As an educator, he teaches Big Data in the Master’s program at the University of Navarra and shares insights through articles on platforms like Medium, KDNuggets, and DataCamp. Josep also writes about Data and Tech in his newsletter Databites (databites.tech).
He holds a BS in Engineering Physics from the Polytechnic University of Catalonia and an MS in Intelligent Interactive Systems from Pompeu Fabra University.