Track
So you're curious about the different data careers and have stumbled upon a few different titles, like data analysts and business analysts.
You may be wondering, "What's the difference between these roles?".
Well, their differences are quite distinct, but they also have some similarities. In this blog post, we'll cover their differences, an overview of both roles and the skills needed for each role.
Let's start with the main difference.
Data Analyst vs Business Analyst: Key Differences
The main difference between a data analyst and a business analyst lies in their primary focus. Data analysts are responsible for analyzing complex datasets to identify patterns and trends, while business analysts focus on understanding business needs and providing strategic recommendations using data.
Business Analyst vs Data Analyst: Roles and Responsibilities
To help you get a better idea of what each job entails, let's have a look at their roles and responsibilities:
Data analyst role
Data analysts are known to work with large data sets to identify patterns and trends, which can be used to inform business decisions. They use statistical tools, techniques, and programming languages like SQL and Python to collect, clean, transform, and analyze data.
Some common responsibilities of a data analyst include:
- Collecting data from various sources
- Cleaning and organizing large dataset
- Manipulating data for Exploratory Data Analysis
- Performing statistical analysis and data mining
- Creating visualizations and reports to present findings
- Identifying patterns and trends in datasets
With our Data Analyst with Python career track, you can learn more about these roles and responsibilities and begin your journey toward entering the profession.
Business Analyst Role
Business analysts focus on understanding business objectives, gathering requirements, and providing strategic recommendations for improving processes, products, or services. They use analytical skills to interpret data and provide insights that inform decision-making.
Some common responsibilities of a business analyst include:
- Identifying and defining business needs
- Gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data
- Evaluating current processes and identifying areas for improvement
- Developing solutions to business problems
- Creating reports and visualizations to communicate insight
Want to explore a career as a business analyst? Our webinar on How to Become a Business Analyst provides a good overview of the role. You can also explore our full guide on what business analytics actually is.
Similarities Between Data Analysts and Business Analysts
While their primary focus may be different, there is an overlap in some of the skills both roles require.
Both data analysts and business analysts need to have strong analytical skills, be proficient in SQL and other programming languages, and be able to interpret data and provide insights.
Additionally, both roles also require excellent communication skills as they need to communicate their findings to stakeholders who may not have a background in data analysis. They also need to be able to work with cross-functional teams and collaborate effectively
Here are a few examples of tasks or projects where data analysts and business analysts may collaborate:
- Customer segmentation analysis:
- A data analyst might work on segmenting customer data based on purchasing patterns, demographic details, or engagement metrics using statistical and machine learning tools.
- A business analyst would then interpret the segmented data to develop strategies for personalized marketing campaigns or to identify high-value customer groups.
- Sales forecasting:
- A data analyst uses historical sales data to build predictive models, analyzing seasonal trends and market dynamics.
- A business analyst collaborates by assessing how these forecasts align with organizational goals, recommending adjustments to sales strategies or inventory management.
- Process optimization:
- A data analyst gathers and analyzes operational metrics to pinpoint inefficiencies, such as delays in production workflows or underperforming systems.
- A business analyst uses this data to propose actionable solutions, such as implementing new tools or revising standard operating procedures.
This synergy highlights the complementary nature of these roles. While data analysts provide the "how" through quantitative insights, business analysts offer the "why" and "what next" by connecting these insights to strategic business needs.
Our course on Data Communication Concepts covers the soft skills needed for both roles, as does our SQL Fundamentals skill track.
Key Skills for Data Analysts and Business Analysts
Now that we've covered the roles and responsibilities let's take a look at some key skills needed for both data analysts and business analysts, including some resources to help you get started:
Key skills for data analysts
As data analysts tend to be more technical, some of their key skills will be more on data analytics tools or visualization software.
- Proficiency in SQL for querying databases - Data Analyst in SQL career track
- Python, or other programming languages for cleaning data - Python Fundamentals skill track
- Data mining and statistical analysis - Statistics Fundamentals with Python skill track
- Data visualization and reporting using business intelligence (BI) tools
- Problem-solving skills
Key skills for business analysts
- Strong communication skills - Data Communication Concepts course
- SQL querying of company databases - SQL Fundamentals skill track
- Ability to interpret data and provide insights
- Critical thinking and problem-solving skills
- Process improvement and project management skills
- Business acumen and understanding of industry trends
Salary Comparison: Data Analysts vs Business Analysts
Next, let's have a look at a commonly asked question: how much does a data analyst or business analyst make? We’ve got full guides on data analyst salaries and business analyst salaries, but you can find the top-line info below:
According to Glassdoor, the average salary for a data analyst in the US is around $82,000 per year, while the average salary for a business analyst is around $93,043 per year.
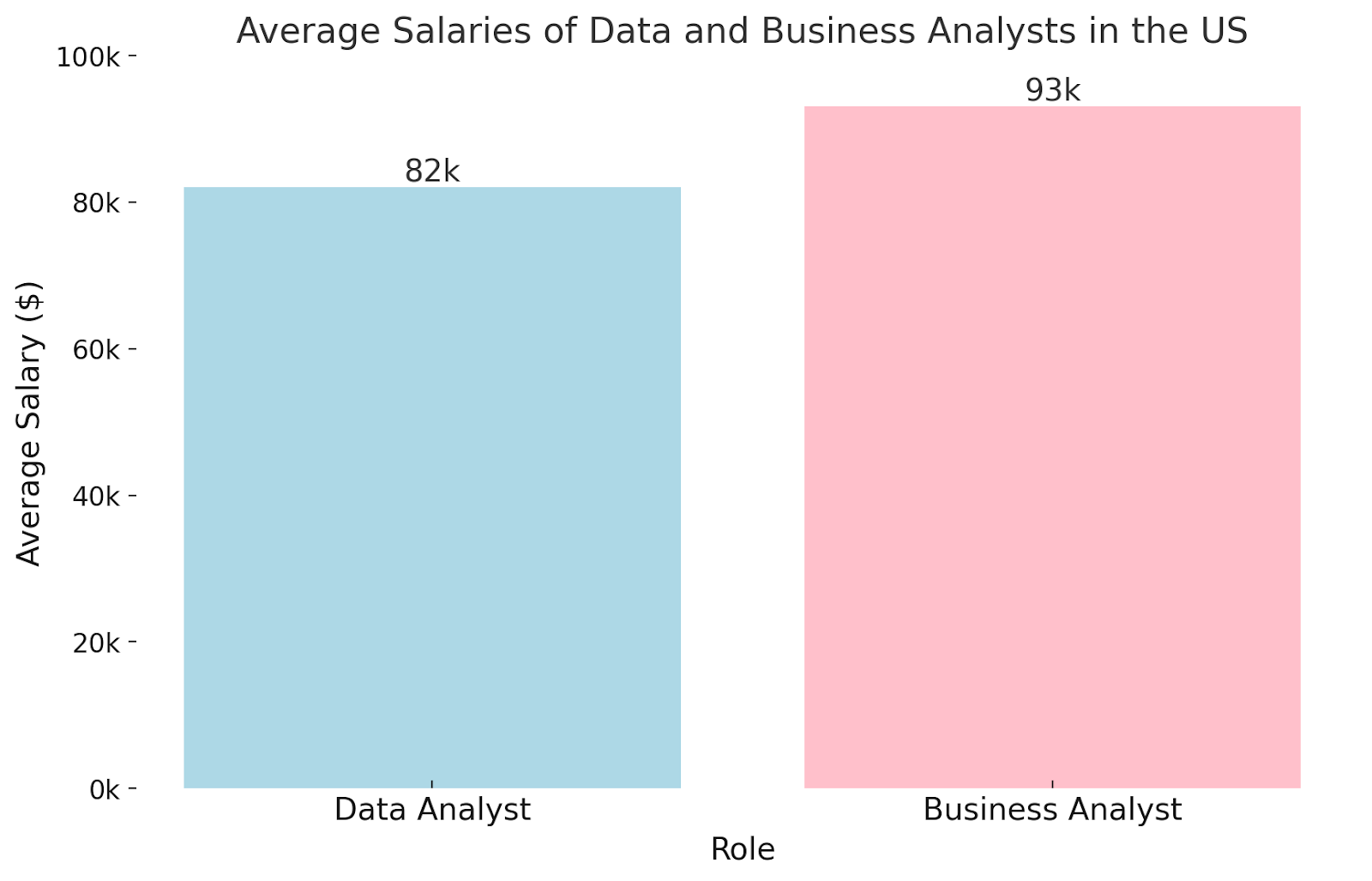
However, these numbers can vary depending on experience level, industry, and location. Data analysts and business analysts with more experience and specialized skills may earn higher salaries.
Entry-level data analysts earn an average salary of around $57,880 per year, while entry-level business analysts earn around $74,000 per year.
Do take note that the job title naming convention is less likely to change for a business analyst than a data analyst.
For example, data analysts typically have either a tier-based system (Data Analyst I, Data Analyst II, and so on) or a Junior/Senior system. Business Analysts tend to just keep their job title unchanged.
Career Progression for Data Analysts and Business Analysts
Both data analysts and business analysts have plenty of room to grow in their careers, with opportunities to specialize or step into leadership roles. Here’s a look at how these career paths typically unfold:
Data analyst career path
Below is an example of how you might progress in your career as a data analyst:
Getting started
As a Junior Data Analyst, you’ll focus on the basics—cleaning data, creating reports, and learning tools like SQL, Python, or Tableau. This is where you’ll build your technical foundation. After some experience, you’ll step up to a Data Analyst role, handling larger datasets and digging deeper into patterns and trends that can help guide business decisions.
Mid-level roles
Once you’ve honed your skills, you might become a Senior Data Analyst, leading projects, mentoring junior analysts, and diving into more complex tasks like predictive modeling or advanced visualizations. If you’re interested in a niche, you could specialize in areas like machine learning, geospatial analytics, or data engineering.
Stepping into leadership
Ready for the big leagues? You could move into roles like Analytics Manager, where you’ll guide a team of analysts, prioritize projects, and align analytics with company goals. Or, if you prefer a technical route, you could aim for Data Scientist or even work as a Data Consultant, solving tough problems for multiple organizations.
Reaching the top
At the highest levels, you might become a Director of Data Analytics, overseeing the entire analytics function, or even a Chief Data Officer (CDO), shaping how your company uses data to drive decisions.
Business analyst career path
Here's a comparison of how a business analyst's career might shape up:
Starting out
As a Junior Business Analyst, your focus will be on smaller projects, like gathering requirements or putting together basic reports. It’s all about learning how businesses work and how to communicate with different teams. A step up to a Business Analyst role means more responsibility—working closely with stakeholders, understanding their needs, and recommending solutions that make a real impact.
Growing your expertise
With experience, you could become a Senior Business Analyst, managing complex projects and offering advice on big-picture decisions. You might also choose to specialize in a field like systems analysis or process improvement.
Leading teams
If leadership excites you, you could move into a Business Analytics Manager role, where you’ll lead a team, set priorities, and ensure everything aligns with company strategy. Or, if you love working on the big picture, transitioning to Product Manager or Strategy Consultant could be a great fit.
Shaping strategy
At the top of the ladder, roles like Director of Business Analytics or even Chief Operations Officer (COO) let you guide the business at a strategic level, drawing on all your experience in analytics and decision-making.
Overview of Data Analytics vs Business Analytics
Since both of the roles sit within two different parallel fields within data, we'll also share with you some differences between these two categories: data analytics and business analytics.
Data analytics
Data analytics focuses solely on analyzing data to identify patterns and trends, using tools and techniques such as statistical analysis, data mining, and machine learning. The goal is to gather insights from the data that can inform decision-making.
Business analytics
Business analytics is more focused on using data analysis to drive business decisions and improve processes or products. It involves gathering and analyzing data to identify opportunities for business growth, cost reduction, or process optimization
Our course on Business Process Analytics in R is a good place to start.
Roles and responsibilities comparison
Below, we've compared the two roles in a table for easy reference:
| Role | Data Analyst | Business Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Analyzing complex datasets to identify patterns and trends | Understanding business needs and providing strategic recommendations |
| Data Collection | Collecting data from various sources | Gathering and analyzing business data |
| Data Cleaning | Cleaning and organizing large datasets | Evaluating current processes for data-driven improvements |
| Analysis Methods | Performing statistical analysis and data mining | Interpreting data to inform business decisions |
| Reporting | Creating visualizations and reports to present findings | Creating reports and visualizations to communicate insights |
| Solution Development | Identifying patterns and trends in datasets | Developing solutions to business problems |
| Tools Used | Statistical tools, SQL, Python, BI tools | SQL, process improvement tools, project management tools |
Which Career Path is For You?
Before deciding which career path to pursue, you should try to find out your strengths to see which matches you better.
If you enjoy working with large datasets, have a strong analytical mindset, and are interested in identifying patterns and trends, then becoming a data analyst may be the right fit for you.
On the other hand, if you're more inclined towards understanding business needs through managing business stakeholders and providing strategic recommendations, then a career as a business analyst may be the better fit.
How to Start a Career in Both Roles
You're now probably wondering—how can I get started?
Here are some action steps you can take to start a career in both these fields:
1. Develop your data cleaning skills
For both roles, it's essential to have a strong foundation in technical data analysis skills like:
- SQL
- Excel
- Statistical analysis
To get started, you can consider our Skills Tracks like SQL Fundamentals, Excel Fundamentals, and Statistics Fundamentals with R.
These are a great way to start without worrying about any technical set-up, as all the coding environments have been set up for you in the DataCamp learning environment in your browser.
Advance Your Career with Excel
Gain the skills to maximize Excel—no experience required.
2. Learn programming languages
Next, you can progress to learning a programming language for more flexibility in your data analysis work. Some popular options include:
- Python
- R
Python is one of the most popular languages used in data analytics. Learning it will give you an advantage in the job market.

Our Cheat Sheet on using Python for Data Science using Pandas
Looking for somewhere to start learning Python? Our Introduction to Python course is a great place to start.
The R programming language is popular among scientific research and healthcare data analysis communities and is well-suited for statistical analysis.
Become a ML Scientist
3. Gain experience with data visualization
Familiarize yourself with popular tools such as:
- Tableau
- Power BI
- Amazon QuickSight
- Google Looker Studio
Learning these tools will help you analyze and visualize data. DataCamp also offers interactive courses for Tableau Fundamentals and Power BI Fundamentals to get you started without having to download any of their desktop apps.
Become a Tableau Data Analyst
4. Build your communication and presentation skills
As mentioned earlier, both roles require effective communication to present findings and collaborate with stakeholders. You'll need to master how to present well using a range of different tools and to a variety of professionals throughout an organization.
To learn how to do this well, try practicing a presentation about data insights from a data project you've done and sharing it with someone who can provide feedback.
5. Pursue a certification
While not always necessary, obtaining certifications can help you with a structured approach.
Learning without guidance or direction can be overwhelming, so it is always a good idea to start with the resources that experts have created.

Our Professional Data Analyst Certification
Some of the commonly pursued certifications in data analytics and business analytics are:
- DataCamp Data Analyst Certification (Associate/Professional)
- Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP)
- Microsoft Certified: Power BI Data Analyst Associate
- Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate
You can also explore our separate guide on business analyst certifications to find a relevant qualification.
Get certified in your dream Data Analyst role
Our certification programs help you stand out and prove your skills are job-ready to potential employers.
6. Network and gain experience
To really stand out in the job market, it's essential to gain practical experience through internships or part-time work. You should also work on data analytics projects to start building a portfolio of work you can show to prospective employers.
You can also network and attend data analytics conferences or events (virtual ones included) to learn from industry experts and make valuable connections.
You might also want to check out common business analyst interview questions to make sure you have all the basics down.
Final Thoughts
The two roles of data analyst and business analyst are closely related but have distinct differences in their focuses.
Here's a summary of what we covered:
- Data analysts use technical skills to analyze data and draw insights
- Business analysts focus on understanding business needs and providing strategic recommendations
- To start a career in either role, you'll need to develop both technical and soft skills, gain practical experience, and pursue certifications.
To get started in either of these fields, it's important to have the right guidance and resources. If you're interested in a career as a data analyst, DataCamp offers an Associate Data Analyst Certification that covers all the basic tools and skills used on the job.
For a career as a business analyst, check out our SQL for Business Analysts career track, as well as our Data Analysis in Excel course.

I'm Austin, a blogger and tech writer with years of experience both as a data scientist and a data analyst in healthcare. Starting my tech journey with a background in biology, I now help others make the same transition through my tech blog. My passion for technology has led me to my writing contributions to dozens of SaaS companies, inspiring others and sharing my experiences.

