Course
Everybody keeps saying that AI agents are the next big thing in AI, and they’re probably right. Large action models (LAMs) are important to this discussion because they can understand human intentions and translate them into actions within a given environment or system.
In this blog post, we’ll learn about large action models, how they work, and their immense potential for transforming industries and everyday life.
Project: Building RAG Chatbots for Technical Documentation
What Are Large Action Models (LAMs)?
Large action models (LAMs) are AI models designed to understand human intentions and translate them into actions within a given environment or system. Unlike their predecessors, which primarily focused on language processing and generation, LAMs are built to take concrete actions based on their understanding of human input and the context of their operating environment.
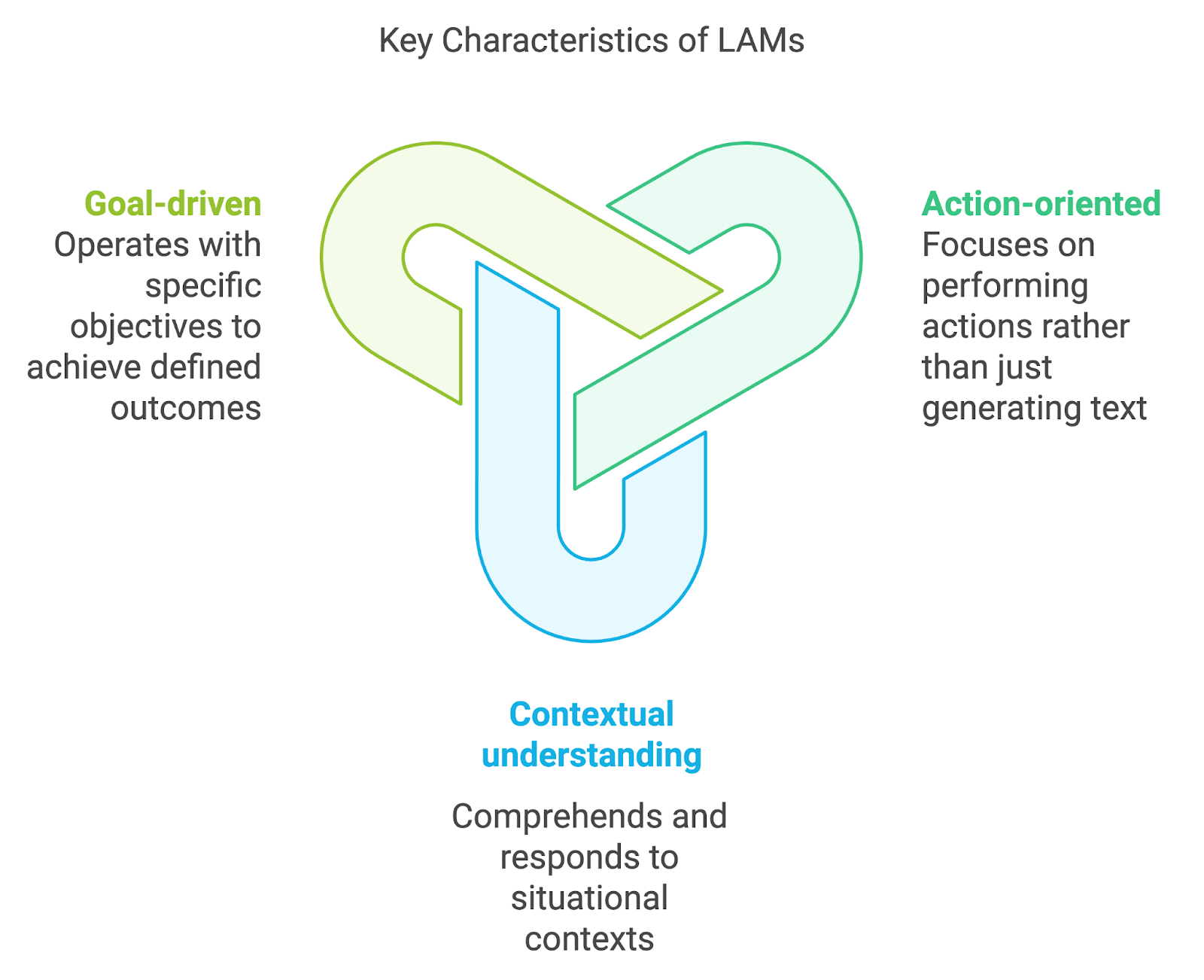
Several key characteristics set LAMs apart from other AI models:
- Action-oriented: The primary function of LAMs is to perform actions, not just generate text or provide information. This action-oriented design allows them to interact with and manipulate their environment in ways that traditional language models cannot.
- Contextual understanding: LAMs are equipped with the ability to comprehend the context of a situation. This deep understanding enables them to take appropriate actions that are relevant and meaningful within the given circumstances.
- Goal-driven: LAMs often operate with specific objectives or goals in mind. Whether it's completing a task, solving a problem, or optimizing a process, these models are designed to work towards defined outcomes.
This combination of characteristics enables LAMs to bridge the gap between understanding and action, making them powerful tools for various applications. But how exactly do these sophisticated AI agents work? Let's take a closer look under the hood.
How LAMs Work: A Look Under the Hood
To truly appreciate the potential of LAMs, it's essential to understand the underlying mechanisms that power these sophisticated AI systems.
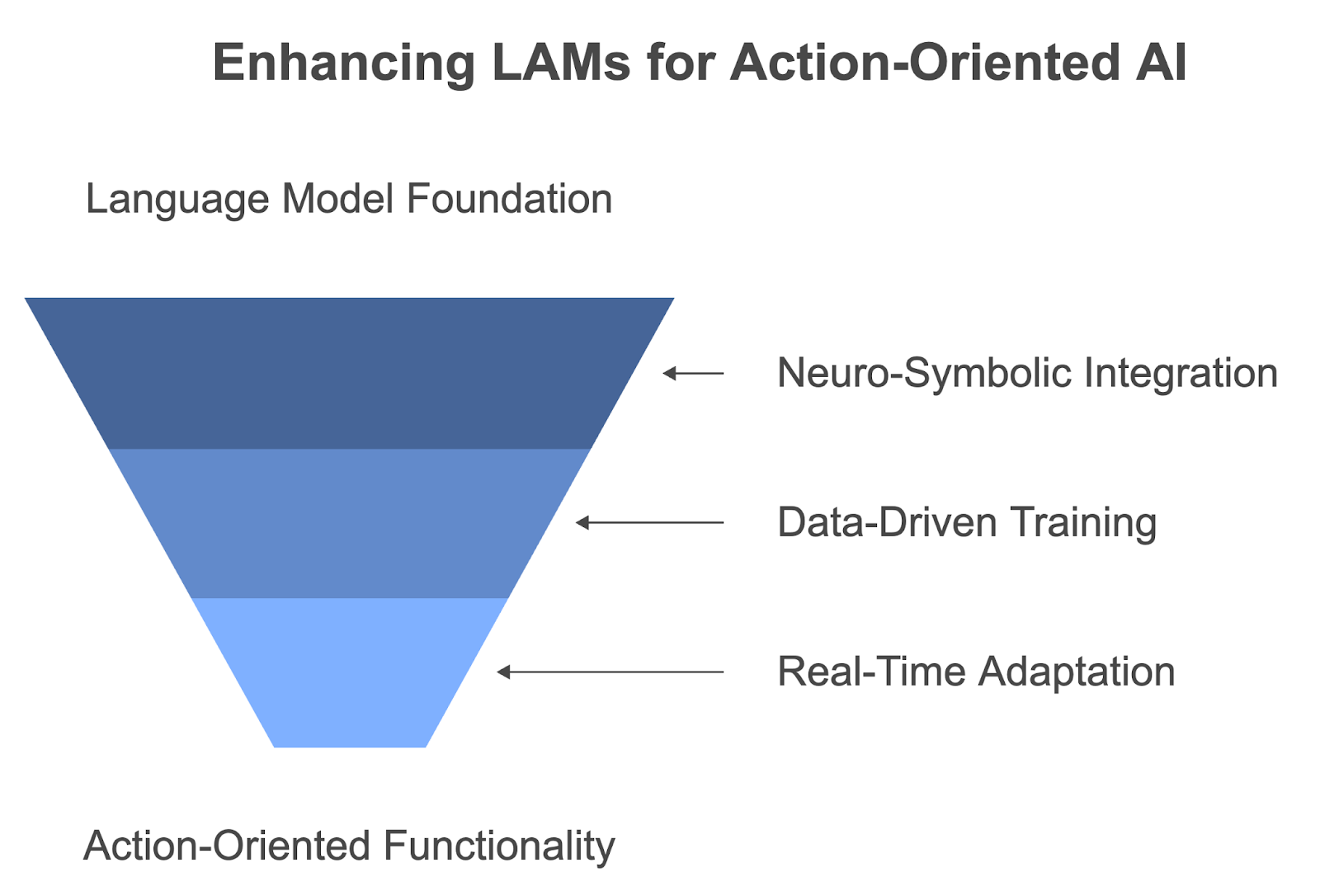
At their core, many LAMs build upon the foundation laid by large language models (LLMs). They leverage LLMs' advanced language understanding and generation capabilities, using this as a starting point for interpreting human intentions and formulating appropriate actions. However, LAMs go beyond mere language processing, incorporating additional layers of complexity to enable action-oriented functionalities.
One key aspect of LAMs is their incorporation of neuro-symbolic AI. This approach combines the strengths of neural networks with symbolic reasoning, creating a hybrid system that can handle both the nuanced understanding required for language processing and the logical decision-making needed for action planning. Neuro-symbolic AI allows LAMs to reason about abstract concepts, make inferences, and plan sequences of actions to achieve specific goals.
Training LAMs often involves exposing them to massive datasets of user action sequences. LAMs can learn to predict and generate optimal action sequences in response to different inputs and contexts by analyzing patterns in how humans interact with various systems and environments. This data-driven approach allows LAMs to capture the intricacies of human behavior and decision-making, enabling them to produce more natural and effective actions.
Another crucial feature of LAMs is their ability to operate in real-time, continuously taking action and adapting to changes in their environment. This real-time interaction capability is essential for applications that require dynamic responses, such as robotics or interactive gaming. LAMs can process incoming information, update their understanding of the situation, and adjust their actions accordingly, all in a matter of milliseconds.
With this understanding of how LAMs function, we can now explore the myriad ways in which they are poised to transform industries and everyday life.
Applications of LAMs: Transforming Industries and Everyday Life
The potential applications of LAMs are vast and varied, spanning multiple industries and aspects of daily life. By combining advanced language understanding with the ability to take concrete actions, LAMs are poised to transform how we interact with technology and automate complex tasks.
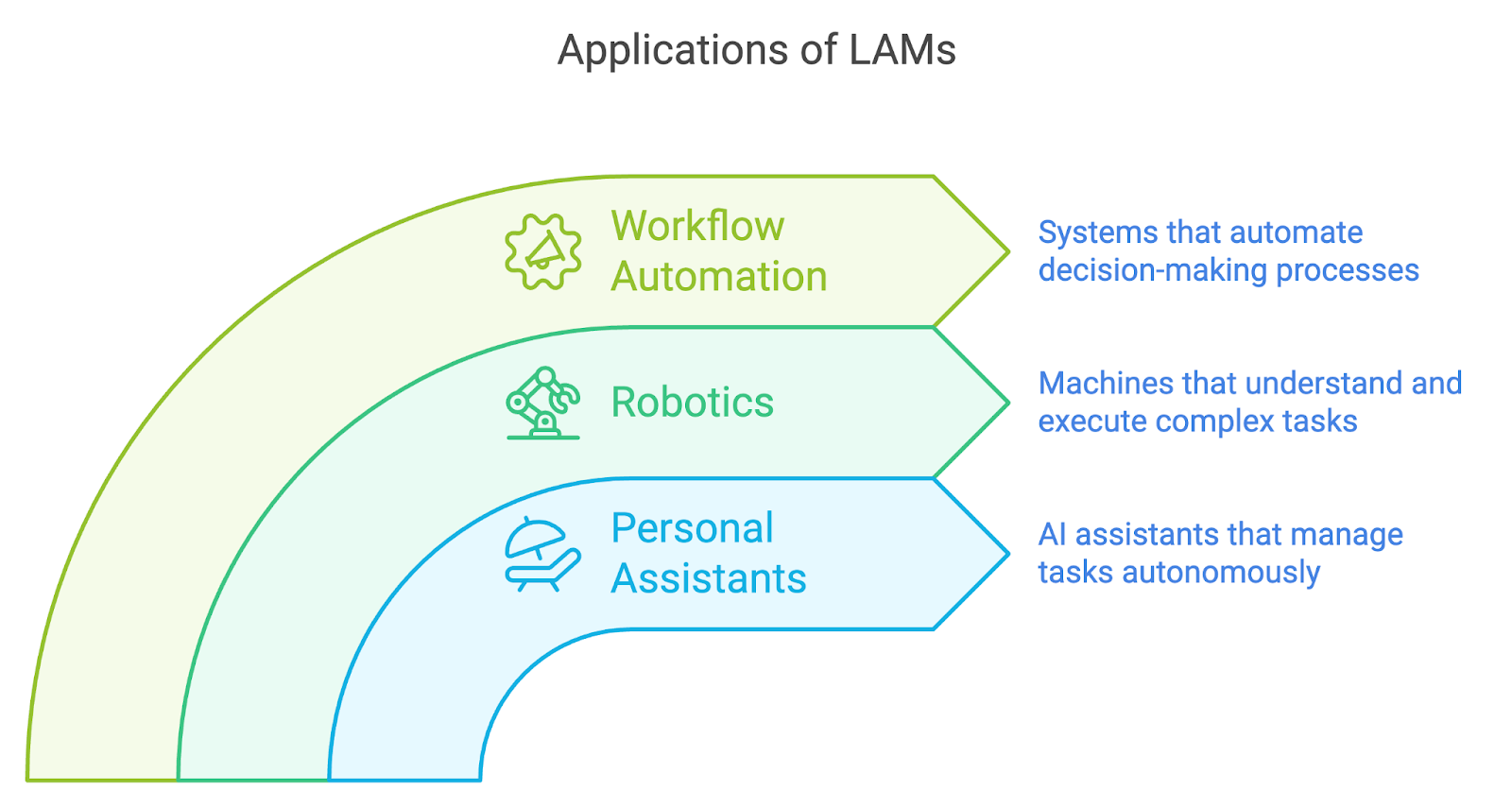
Automating tasks
One of the most promising areas for LAM applications is task automation. Here are some key examples:
- Personal assistants: LAMs can power next-generation personal assistants that go beyond simple voice commands. Imagine an AI assistant who can not only understand your request to "book a vacation" but can also research options, compare prices, make reservations, and even adjust your calendar—all based on your preferences and past behaviour.
- Robotics: In robotics, LAMs can enable machines to understand and respond to complex human instructions. This could revolutionize industries like manufacturing, where robots could be given high-level directives and figure out the specific actions needed to complete a task. In-home environments, LAM-powered robots could perform a wide range of household chores with minimal human input.
- Workflow automation: In business settings, LAMs can automate intricate workflows that require decision-making and adaptability. For example, in a customer service context, a LAM could handle complex customer inquiries, access relevant information, make decisions about how to resolve issues, and even execute actions like processing refunds or scheduling technician visits.
Enhancing decision-making
LAMs also have the potential to improve decision-making processes across various domains significantly:
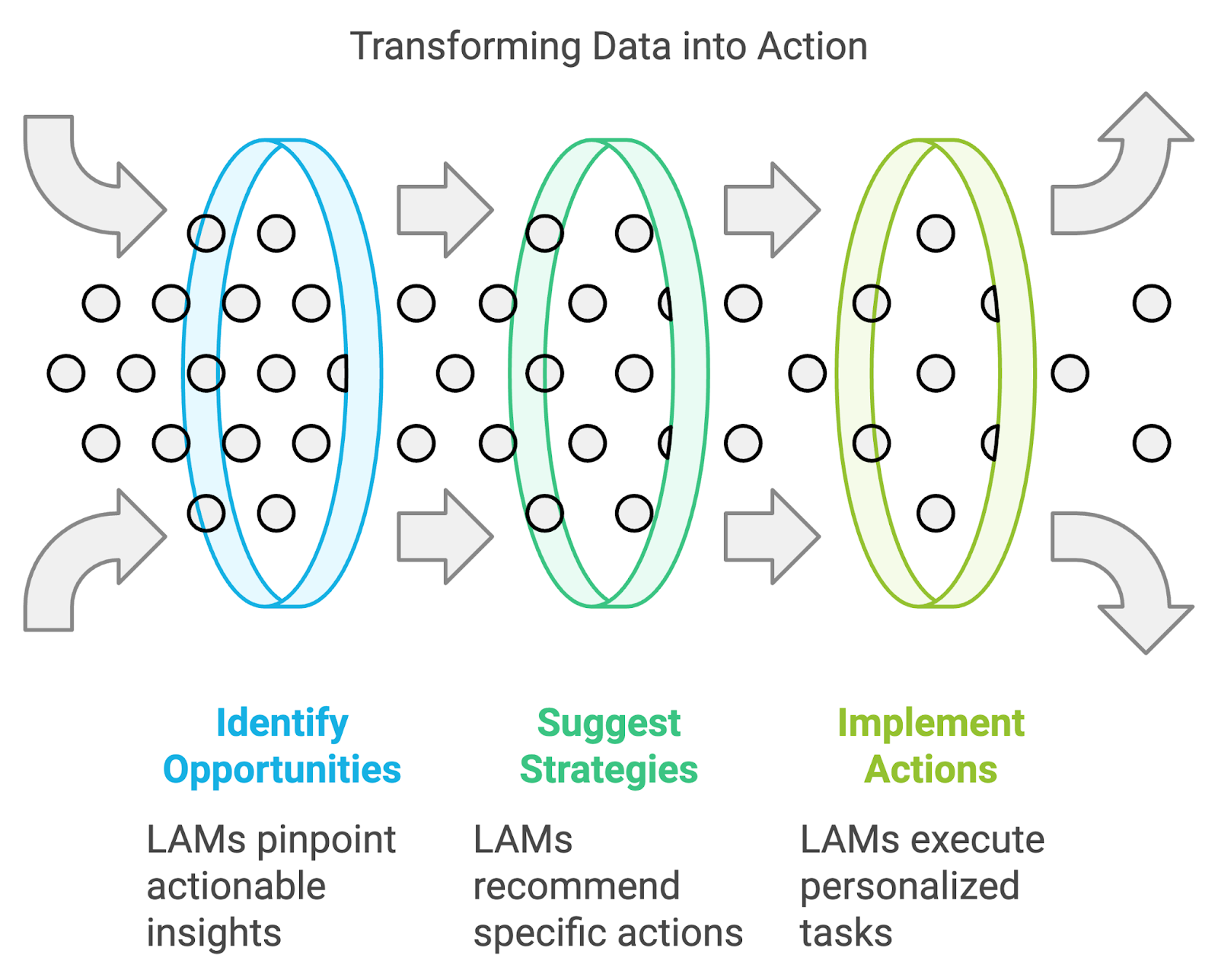
- Data analysis and insights: By combining their ability to process vast amounts of data with action-oriented outputs, LAMs can provide not just analysis but actionable insights. In fields like finance or marketing, a LAM could analyze market trends, customer behavior, and other relevant data to identify opportunities and suggest and potentially implement specific strategies.
- Personalized recommendations: LAMs can take personalization to the next level. Rather than simply recommending products or content, they could take actions to curate experiences. For instance, a streaming service powered by a LAM could not only suggest shows based on your preferences but also automatically create custom playlists, adjust playback settings, and even reach out to friends to arrange group viewing sessions.
Creating interactive experiences
The action-oriented nature of LAMs opens up new possibilities for creating more engaging and interactive experiences:
- Gaming and entertainment: In the gaming industry, LAMs could power non-player characters (NPCs) with unprecedented levels of intelligence and interactivity. These NPCs could engage in complex dialogues, adapt their behavior based on player actions, and even learn and evolve. Beyond gaming, LAMs could create interactive narratives for entertainment or educational purposes, where the story adapts in real time based on user input and preferences.
- Personalized learning: In education, LAMs could revolutionize personalized learning experiences. An AI tutor powered by a LAM could not only present information and ask questions but also adapt teaching methods in real-time, provide hands-on guidance for practical tasks, and even create custom learning materials on the fly based on a student's progress and learning style.
As exciting as these potential applications are, it's important to note that LAMs are not just theoretical concepts. Let's look at some real-world examples of LAMs in action.
Examples of LAMs in Action
While large action models are still an emerging technology, there are already some promising applications that showcase their potential:
- Rabbit: One notable example is a tool called Rabbit, which allows users to automate computer tasks using natural language instructions. Users can describe complex sequences of actions, and Rabbit will execute them, learning and adapting to the user's specific software environment and preferences over time.
- AI-powered game characters: Some cutting-edge video games are beginning to incorporate LAM-like technologies to create more realistic and adaptive non-player characters. These characters can engage in more natural dialogues, react to player actions in complex ways, and even learn from interactions to evolve their behavior over time.
- Intelligent process automation: In the business world, some companies are experimenting with LAM-like systems to automate complex business processes. These systems can handle multi-step workflows, make decisions based on various inputs, and even adapt processes in real-time based on changing conditions.
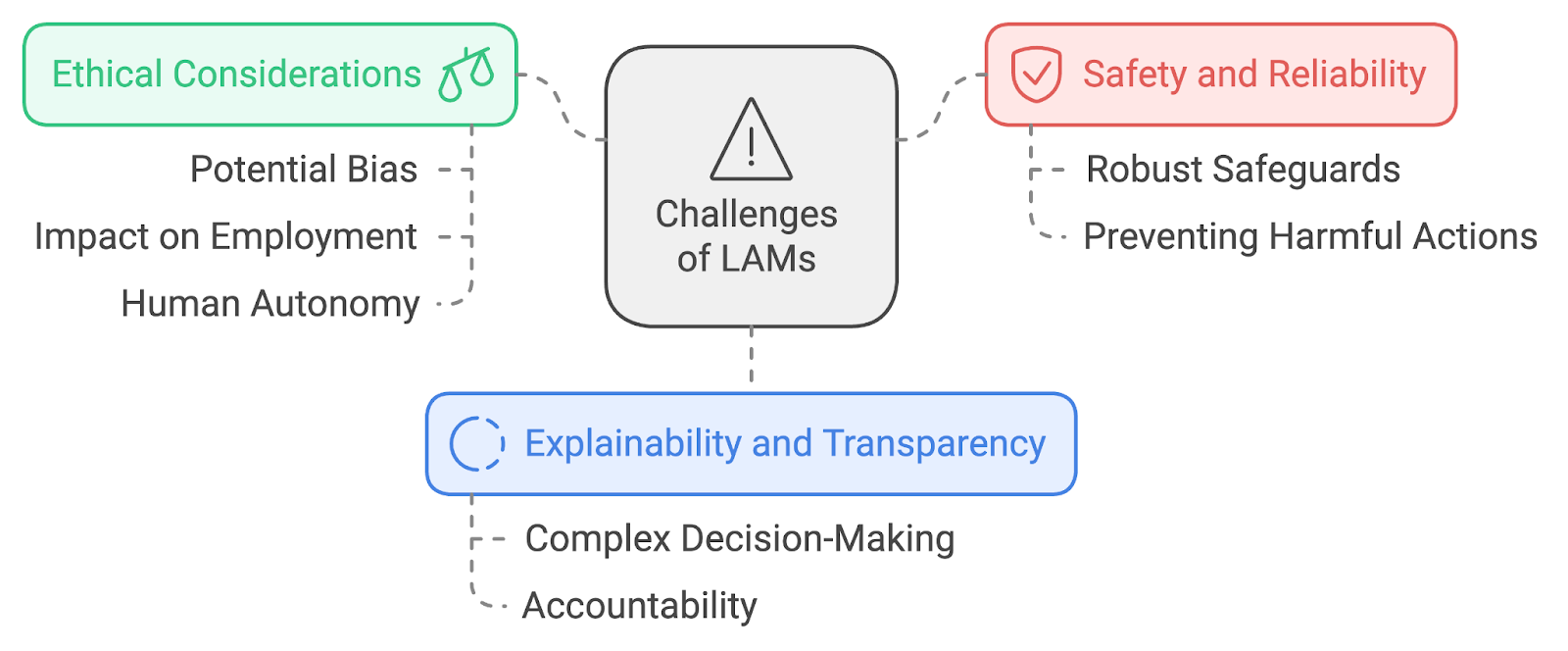
Challenges of LAMs
While the potential of LAMs is immense, their development and deployment also come with significant challenges that need to be addressed:
- Safety and reliability: As LAMs are designed to take action in the real world, ensuring their safety and reliability is paramount. Researchers and developers must implement robust safeguards to prevent LAMs from taking harmful or unintended actions, especially in critical applications like healthcare or financial systems.
- Explainability and transparency: The complex nature of LAMs, often involving deep neural networks and sophisticated decision-making processes, can make their actions difficult to interpret or explain. Improving the explainability of these models is crucial, particularly in scenarios where accountability is essential.
- Ethical considerations: The development and deployment of LAMs raise important ethical questions. Issues such as potential bias in decision-making, the impact on employment as more tasks become automated, and the broader implications for human autonomy and decision-making need careful consideration and ongoing dialogue.
Conclusion
Large action models hold significant potential to reshape numerous industries and facets of our daily lives. However, it is important to approach their development and implementation with a balanced perspective, acknowledging both their capabilities and the inherent challenges they present.
Develop AI Applications
Senior GenAI Engineer and Content Creator who has garnered 20 million views by sharing knowledge on GenAI and data science.


