Track
AWS Lambda makes it possible to run code in the cloud without managing servers, unlocking a powerful, event-driven architecture ideal for scalable, cost-efficient applications. In this guide, we’ll walk through how AWS Lambda works and share best practices to help aspiring developers, IT professionals, and cloud engineers harness its full potential.
If you are new to AWS, be sure first to check out our Introduction to Amazon Web Services blog post and AWS Concepts Course.
What is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda is a popular serverless computing service from Amazon Web Services (AWS). It enables developers to run their code without managing or provisioning servers directly.
By automatically handling infrastructure tasks such as system updates, security patches, and scaling, AWS Lambda allows developers to concentrate solely on writing and deploying their code more quickly.
Before diving deeper, let’s briefly explore the core architecture and principles of AWS Lambda.
Core architectural principles
AWS Lambda uses a serverless model known as "Function as a Service" (FaaS). This approach means that AWS handles server provisioning, infrastructure management, and resource scaling transparently behind the scenes. Developers only supply the code, which gets executed automatically whenever needed.
Our AWS Cloud Technology and Services Concepts course goes into more detail about AWS serverless technologies.
Lambda functions run in response to specific events from different AWS services.
For instance, an Amazon S3 upload, an API Gateway request, or updates to an Amazon DynamoDB table can automatically trigger Lambda execution. This event-based design ensures applications respond dynamically to real-time demands.
Operational characteristics
AWS Lambda automatically scales your functions based on the number of triggering events. As more requests come in, the service will handle scaling seamlessly.
However, Lambda enforces account-level quotas and limitations on concurrency, which developers should be aware of and monitor proactively.
Memory allocation is adjustable in Lambda functions, with higher memory settings generally resulting in faster execution at a slightly higher cost. Developers can optimize performance and control costs by experimenting to find an efficient balance of memory and execution time.
Below are some best practices for optimizing AWS Lambda functions:
1. Right-size memory and timeout
- Experiment with memory settings using AWS Lambda Power Tuning to find the best performance/cost ratio.
- Set timeout values conservatively to avoid prolonged execution and unnecessary costs.
2. Minimize deployment package size
- Use only necessary dependencies and remove unused modules.
- For Python/Node.js, consider Lambda layers for shared libraries.
- Use compiled packages (like .zip) efficiently or container images for larger applications.
3. Keep functions stateless
- Avoid storing state in memory between invocations.
- Use external services like DynamoDB, S3, or ElastiCache for persistent state or shared data.
4. Optimize cold start times
- Use provisioned concurrency for latency-sensitive applications.
- Prefer smaller runtimes like Node.js or Go for lower cold start duration.
- Reduce the initialization code in the global scope.
5. Monitor and test performance
- Use Amazon CloudWatch for logs, metrics, and setting alerts on errors or duration.
- Integrate with AWS X-Ray for tracing and analyzing execution performance.
6. Control concurrency
- Set reserved concurrency to guarantee availability for critical functions.
- Use maximum concurrency limits to avoid exhausting downstream services.
7. Efficient I/O and networking
- Use asynchronous calls for parallel tasks (e.g., multiple API calls).
- Keep network requests efficient and retry-safe.
8. Clean error handling and retries
- Implement retries where appropriate.
- Use structured logging and meaningful error messages to simplify debugging.
How Does AWS Lambda Work?
AWS Lambda simplifies running code in the cloud significantly. Developers first upload code packaged into functions and select the runtime environment (Python, JavaScript, Java, C#, Go, Ruby, and others). The code remains idle until a predefined event invokes its execution, such as a web request, data upload, or scheduled event.
When triggered, Lambda allocates resources instantly, executes the function, and then terminates the resource after completion, billing you only for the exact computing resources and execution duration consumed.
Understanding how AWS Lambda works is critical in acing AWS interviews. The Top 20 AWS Lambda Interview Questions and Answers for 2025 blog post simplifies AWS Lambda interview preparation by providing a curated list of questions and answers.
What is AWS Lambda Used For?
AWS Lambda fits naturally into applications requiring scalability, flexibility, and rapid responsiveness. Some common use cases include:
- Building scalable APIs and backend environments with Amazon API Gateway.
- Processing and transforming data uploaded to storage services, such as Amazon S3 and DynamoDB.
- Automating workflows, scheduling tasks, sending notifications, and routine database maintenance.
- Real-time file processing, like generating image thumbnails or encoding video files.
For tasks such as video processing, Amazon Kinesis is a better choice. Explore the functions and uses of Amazon Kinesis, along with three crucial tips for cost optimization, by reading our What is Amazon Kinesis? blog.
Benefits and Limitations of AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda has clear advantages and limitations. Carefully evaluate the advantages and limitations when deciding to use AWS Lambda for your projects.
Benefits
- Reduced infrastructure overhead: Developers avoid managing servers or infrastructure, considerably reducing operational effort.
- Auto-scaling: Lambda scales dynamically with workload increases, helping applications handle unpredictable traffic spikes smoothly.
- Cost-efficiency: You only pay for actual usage, rather than fixed monthly server costs, ensuring efficient utilization of resources.
- Faster development cycles: Developers spend less time on infrastructure tasks, with more freedom to quickly experiment and iterate features.
- Easy integration: Lambda integrates closely with other AWS services, offering vast opportunities for extending functionality.
Limitations
- Cold-start latency: AWS Lambda incurs a brief initialization delay whenever a function runs after being idle for some time. For latency-sensitive applications, the delay may impact performance.
- Limited execution duration: Lambda functions have a maximum execution limit of 15 minutes, posing challenges when performing complex or long-running tasks.
- Security responsibility: AWS ensures service security, but developers must follow good practices, minimize permissions, validate inputs, and actively prevent vulnerabilities through careful code design.
To understand how to properly configure permissions for Lambda functions, take a look at our Streaming Data with AWS Kinesis and Lambda course.
Getting Started with AWS Lambda
Let’s now look at how you can get started with AWS Lambda.
Steps for getting started:
- Set up an AWS account: Create an AWS account at aws.amazon.com.
- Write your function: You can write your function code directly in the AWS Management Console or upload a .zip package or container image.
A simple hello world function looks like this:
def lambda_handler(event, context):
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': 'Hello, World!'
}- Create a Lambda function:
- Go to the AWS Lambda Console.
- Click Create function.
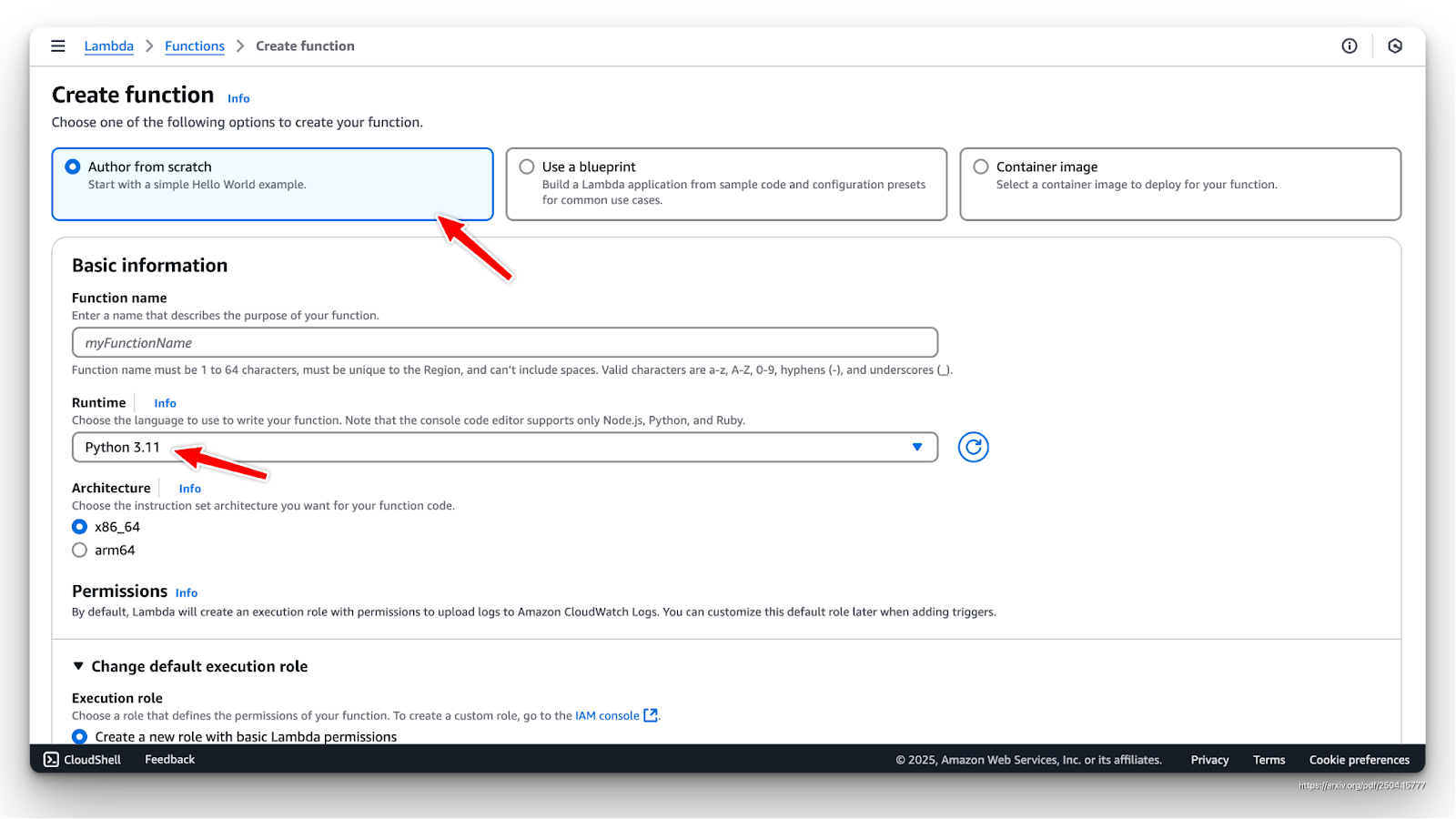
- Choose Author from scratch, use a Blueprint or Container.
- Configure basic settings like runtime, memory, and timeout.
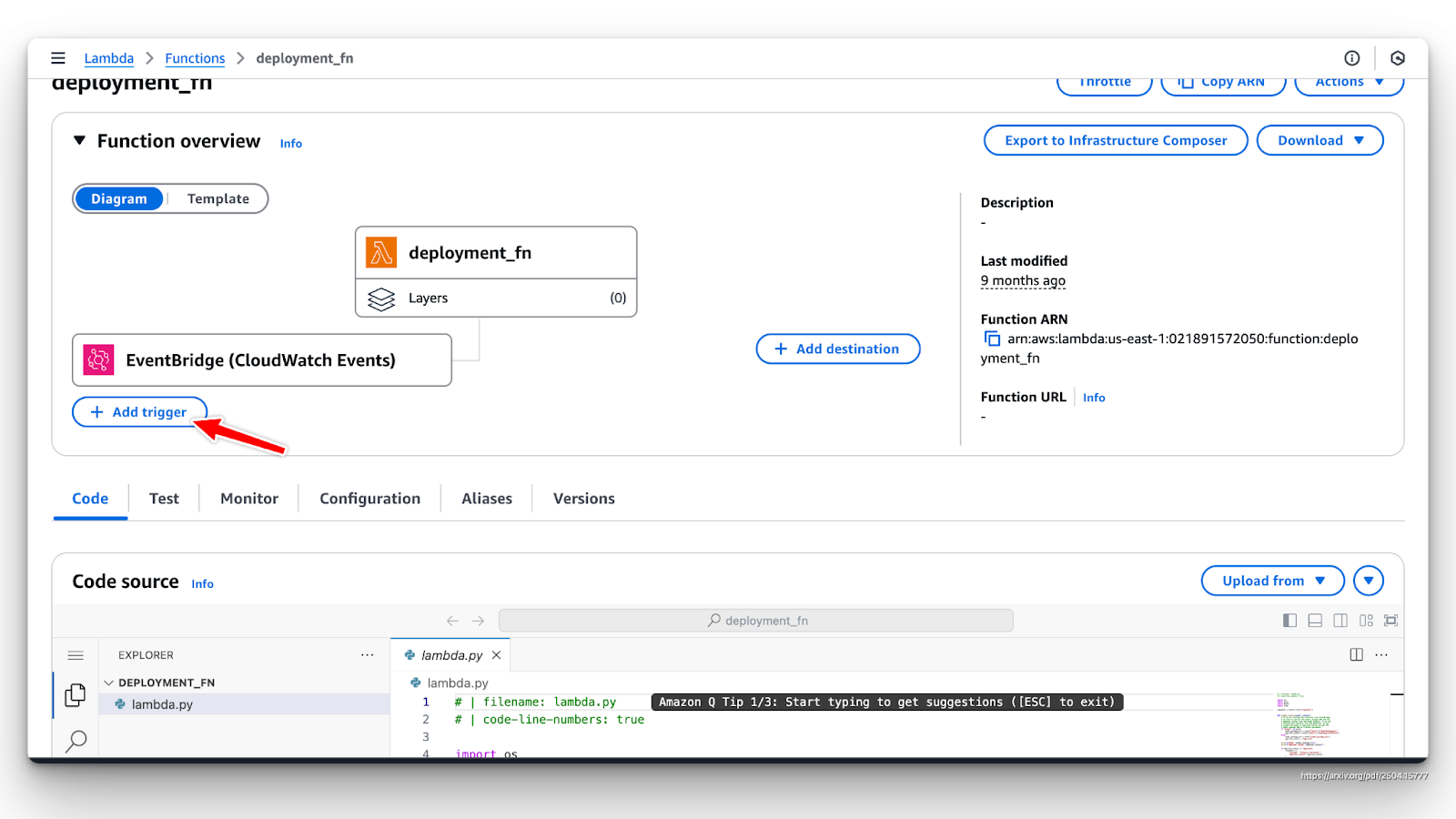
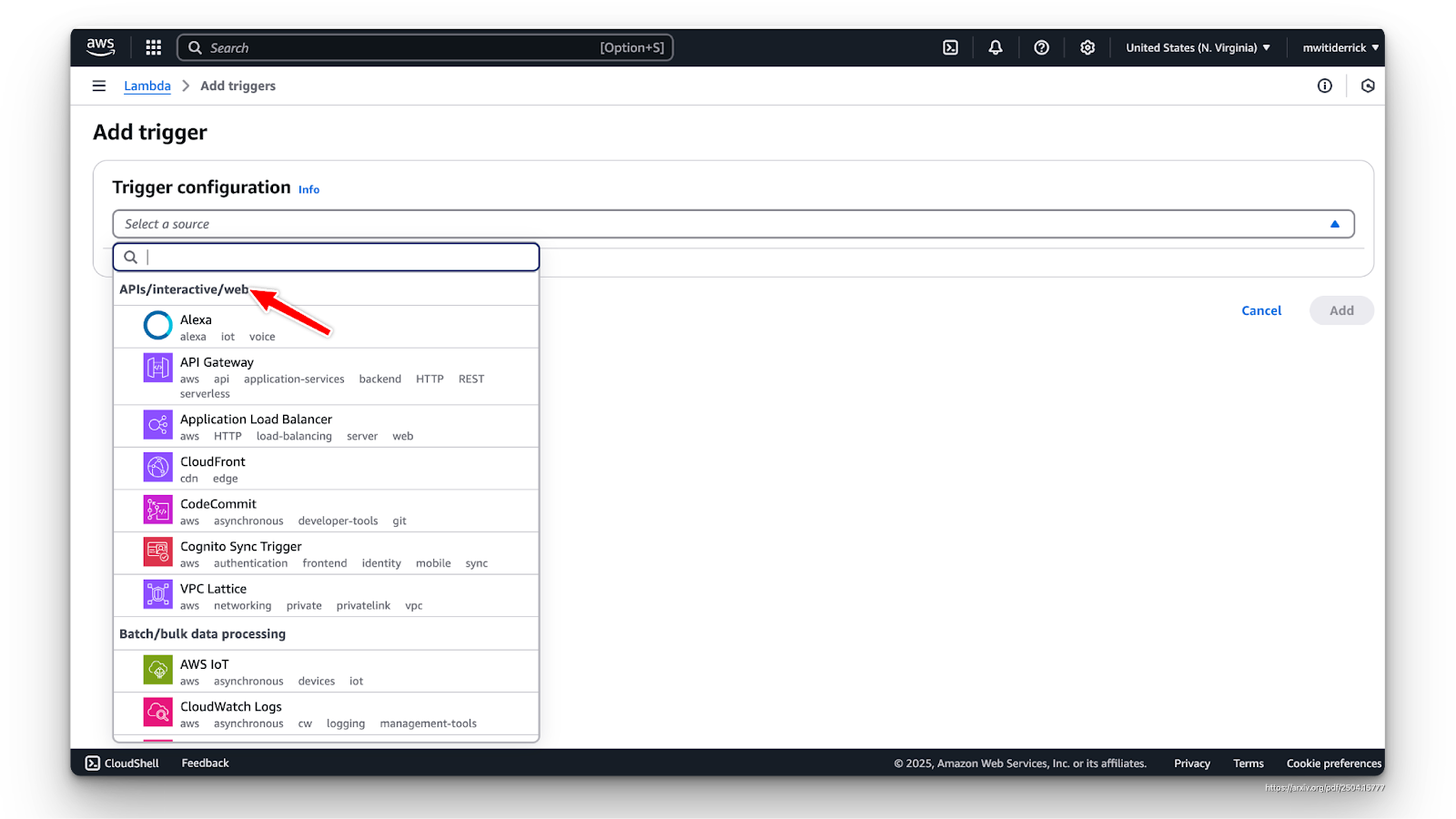
- Set a trigger: Lambda needs an event source to trigger your function (e.g., API Gateway, S3 uploads, DynamoDB streams, etc.).
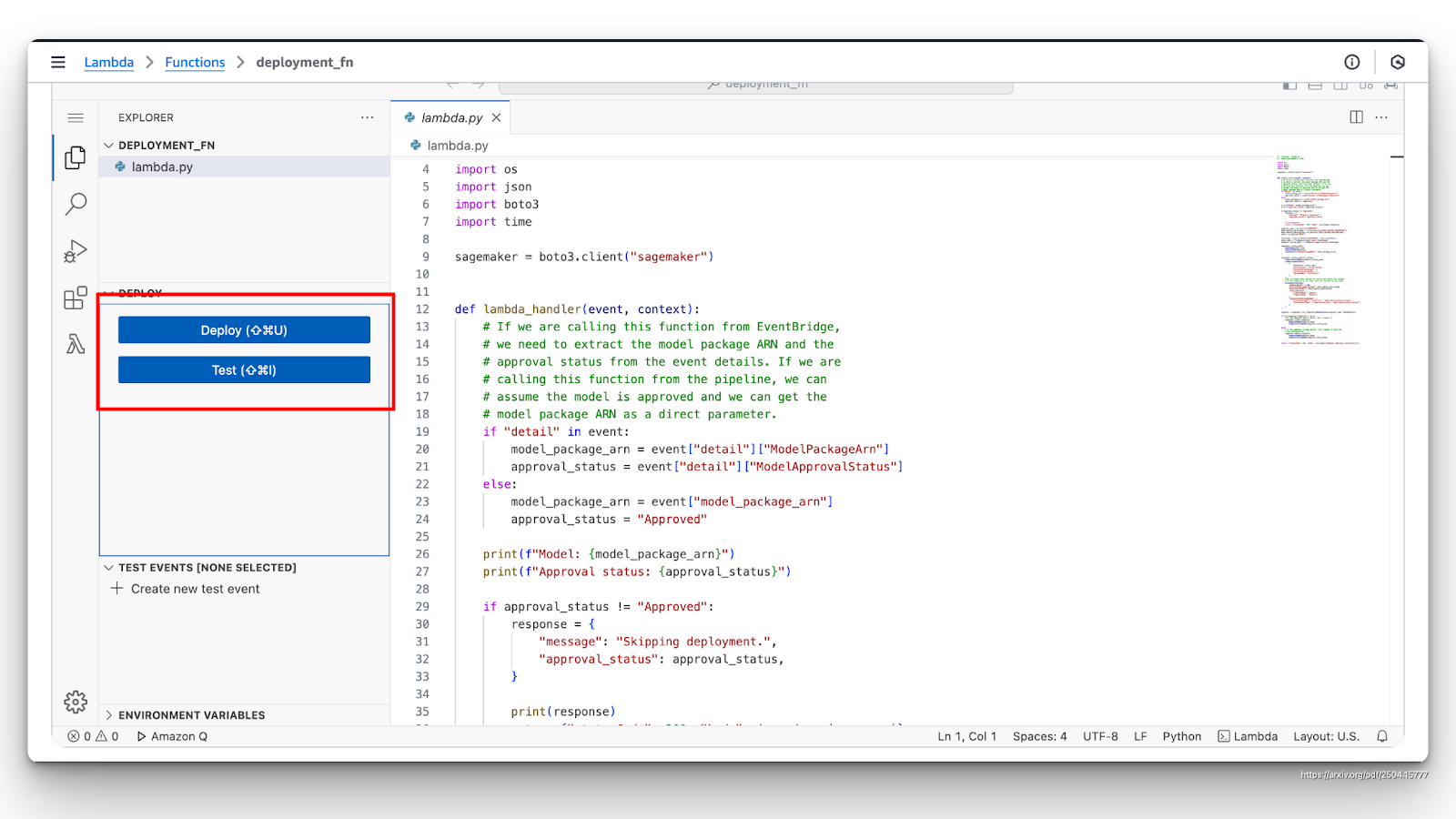
- Deploy and test: Deploy your function and test it using the console or by invoking it through the configured trigger.
- Monitor performance: Use Amazon CloudWatch to track logs and metrics and troubleshoot issues.
If you're interested in beginning your journey with AWS Lambda, our in-depth Step-by-Step Lambda tutorial will walk you through setting up and deploying your first function. We simplified the process, making it approachable even if you are new to AWS.
Advanced Features and Considerations
Once you're familiar with basic Lambda functionality, explore the following advanced features and considerations for enhancing your serverless architecture.
Performance optimization techniques
Here are some performance optimization techniques to keep in mind:
- Tune memory allocation settings to balance performance and cost.
- Minimize deployment package size to reduce cold-start times.
- Keep functions small, single-purpose, and lightweight to optimize execution speeds.
- Utilize provisioned concurrency to prewarm Lambda instances for consistent performance, particularly in latency-sensitive scenarios.
Security and compliance
Consider these security and compliance precautions:
- Follow the principle of least privilege when assigning IAM permissions to Lambda functions.
- Implement secure input validation practices diligently to prevent injection or security exploits.
- Pay attention to compliance requirements relevant to your industry; AWS Lambda is designed and managed in alignment with many security standards and regulations.
Conclusion
We've explored AWS Lambda as a robust serverless computing solution, highlighting its core architecture, practical use cases, benefits, limitations, and advanced considerations. By freeing teams from infrastructure provisioning, Lambda allows developers to spend more time writing quality code, building engaging functionalities, and improving their applications with outstanding cost efficiency.
As serverless technologies constantly evolve, AWS continues enhancing Lambda with stronger integrations, expanded language support, and even greater ease of use.
Getting certified is an important milestone for a cloud practitioner. Prepare for Amazon’s AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C02) by learning how to use and secure core AWS compute, database, and storage services from our AWS Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C02) course.
AWS Lambda FAQs
How does AWS Lambda charge users?
AWS Lambda charges based on the number of function invocations and the compute time your code consumes, making it a cost-efficient, pay-as-you-go solution.
What programming languages are supported by AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda supports multiple languages, including Python, JavaScript (Node.js), Java, C#, Go, and Ruby, among others.
What is a "cold start" in AWS Lambda?
A cold start refers to the slight delay that occurs when a Lambda function is invoked after a period of inactivity. AWS initializes the runtime, which may briefly increase latency.
How long can an AWS Lambda function run?
AWS Lambda functions have a maximum execution time of 15 minutes. Tasks requiring more time should consider alternative solutions such as AWS Step Functions or EC2.

