Course
Google Antigravity is an agent-driven IDE that pairs powerful models like Gemini 3 with an agent-first workflow. Instead of manually configuring tools, terminals, and browser sessions, you collaborate with an AI agent that can plan work as tasks, run commands, edit code, and even interact with your browser to test and document your app.
In this tutorial, I’ll walk you through how to build a working Personal Finance Risk Dashboard using Google Antigravity. You’ll see how to:
- Install and configure Antigravity with agent-assisted development
- Prompt the agent to set up a Next.js, Tailwind, and shadcn/ui application
- Review and refine the autogenerated implementation plan
- Let the agent test your app in the browser using the Antigravity extension
- Iterate on features like dark/light mode and debugging with computer use
By the end, you’ll have a multi-page dashboard that visualizes risk levels for Savings, Bonds, Index Funds, and Crypto, complete with interactive controls and a modern fintech UI, built through a single prompt. I also recommend checking out our guide to the Gemini 3 API and Gemini 3 Flash tutorial.
Disclaimer: This tutorial is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice; always conduct your own research or consult a qualified financial professional before making investment decisions.
What is Google Antigravity?
Google Antigravity is an agent-first development platform that turns your IDE into a mission control for AI agents. At its core, it gives agents synchronized control over your editor, terminal, and browser, so they can plan work, change code, run commands, and verify behavior end-to-end from a single place.
Instead of manually wiring together scripts and tools, you describe the outcome you want and let Antigravity’s agents handle the heavy lifting. They can:
- Turn a high-level request into a task-level plan or implementation checklist
- Run terminal commands to create projects, install dependencies, and start dev servers
- Edit code across your workspace, from layout files to shared components
- Use a browser extension to open your app, click through flows, and capture screenshots or walkthrough recordings as Artifacts.
Antigravity is built around Google’s Gemini 3 models, but also supports other providers like Claude Sonnet 4.5 and GPT-OSS. It comes with two main surfaces, i.e., an Editor view that feels like an IDE (if you ever used Cursor or VS Code), and an Agent Manager view that acts as mission control for longer-running, multi-workspace tasks. Together, they make it easier to work at a task-oriented level while the agents handle the implementation details.
Google Antigravity Demo: Building a Finance Risk Dashboard
In this section, we’ll build a personal finance risk dashboard with Google Antigravity. The agent will turn a single natural-language prompt into a Next.js project that models different investment products and their risk profiles.
By the end, you’ll have:
- A multi-page dashboard for Savings, Bonds, Index Funds, and Crypto
- Interactive sliders for time horizon
- A polished dark/light mode UI
- Knowledge of how Antigravity agents plan, implement, test, and iterate on a full feature
Step 1: Installing Google Antigravity
Let's start by downloading Google Antigravity from the official website and selecting the installer according to your machine specifications.
Click Download for MacOS (or your OS), and it will take you to a platform selection screen to choose the appropriate binary for your machine and complete the installation.
For this tutorial, I ran it on a Mac with Apple Silicon, but the interface won’t be any different for any machine.
Once downloaded, set up Google Antigravity just as you would any other application and launch it.
Step 2: First-time setup
On first launch, Antigravity walks you through an onboarding wizard.
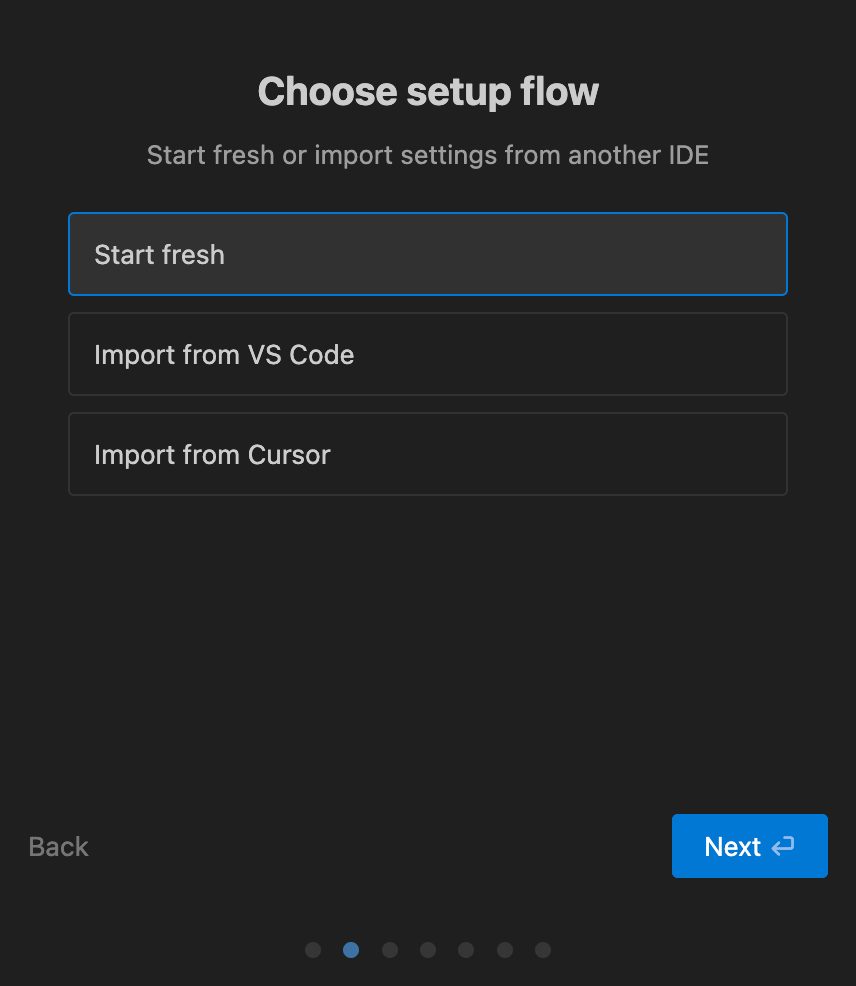
Step 2.1: Choose setup flow
If you are a power user of Cursor or VS Code and would like to use its settings for setting up Antigravity, then choose the options accordingly. However, I like to start fresh, so select Start fresh and click Next.
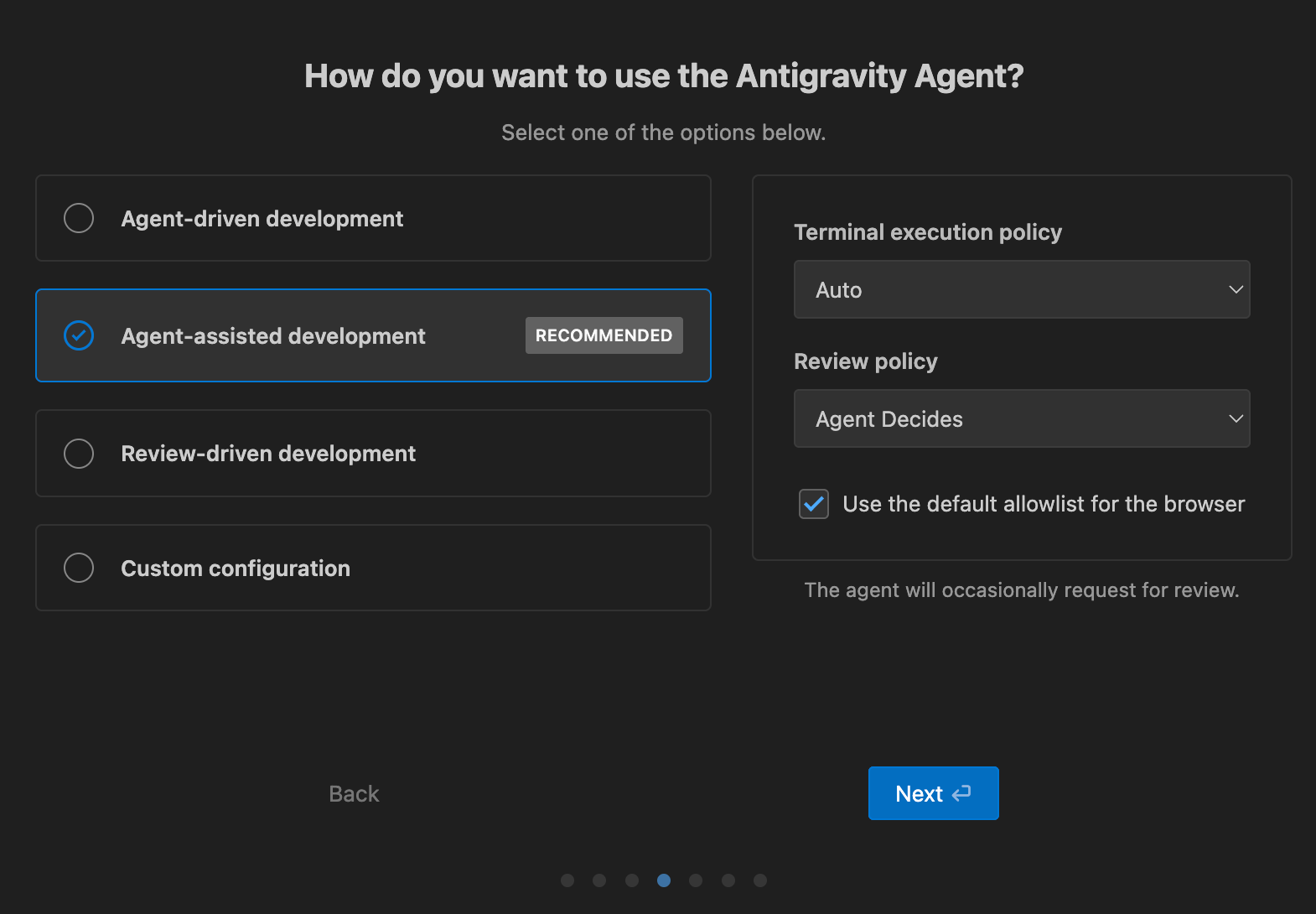
Step 2.2: Set up Antigravity Agent
Next, you’ll see a screen about Agent usage. For this tutorial, choose:
- Agent-assisted development (recommended): This option lets the agent do most of the work but keeps a human in the loop so you can review plans and changes as it goes.
- Terminal execution (Auto): This allows the agent to run safe, routine terminal commands automatically without asking every single time.
- Review policy (Agent decides): Let the agent choose when it needs a human’s explicit review vs. when it can proceed on its own.
- Use the default allowlist for the browser: It limits the agent’s browser access to a pre-approved set of safe domains and actions for added security.
Click Next to finish setup.
Once setup is complete, the next step is to create a workspace for our experiment.
Step 3: Creating a new workspace
Once setup completes, you’ll land on the Antigravity home screen. To proceed further, click Open Folder and create/select a new directory for this project. eg: ~/Antigravity/personal-finance-dashboard. This folder will become your Next.js app.
On the right side, you should see the Agent panel where you can select a model and send prompts.
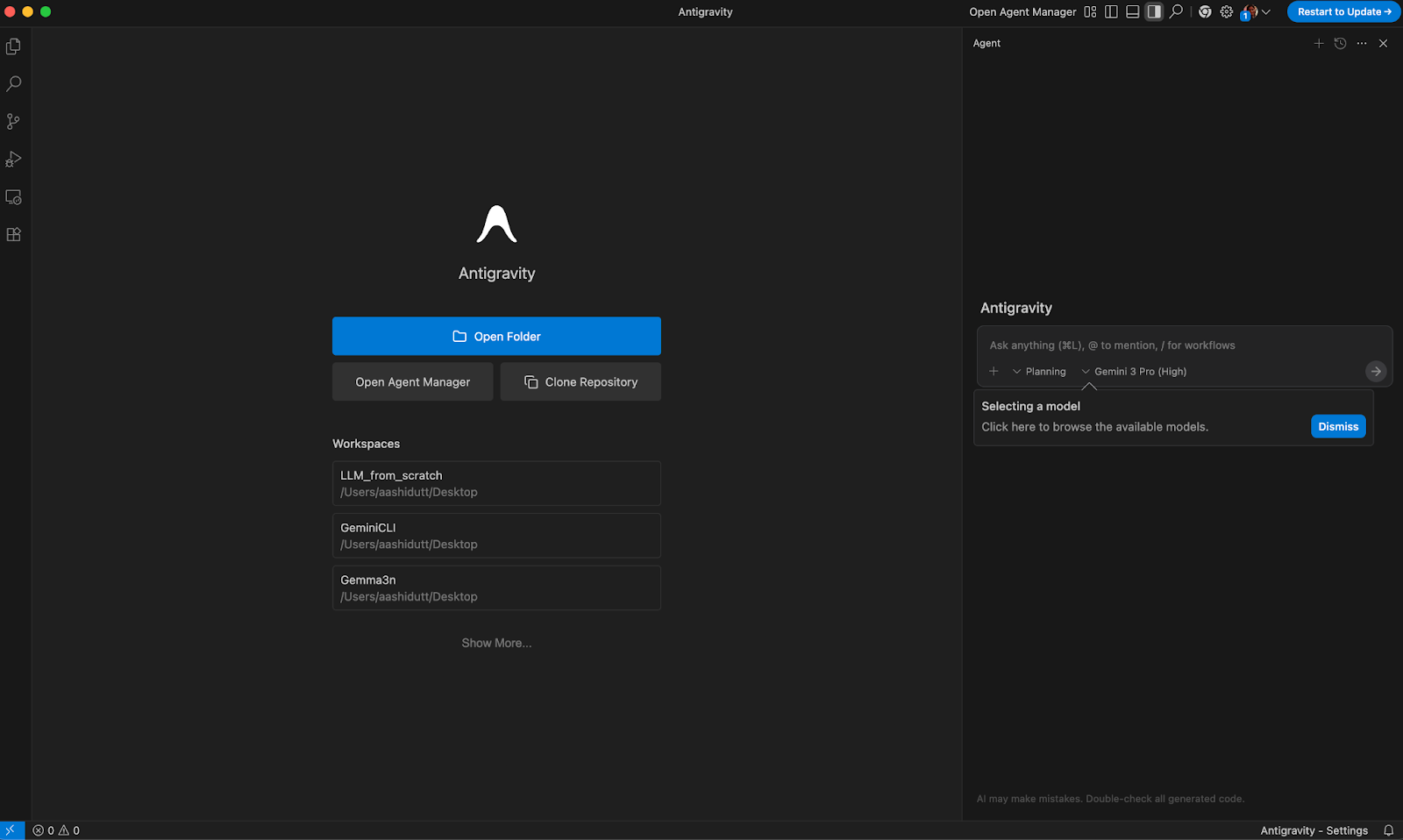
Step 4: Build the app
With your workspace open, pick a model (for example, Gemini 3 Pro or Claude Sonnet 4.5, or GPT OSS 120B) in the Agent panel. Then, paste the following prompt:
Build me a Next.js app called “Personal Finance Risk Dashboard” that shows different risk profiles for Savings, Bonds, Index Funds, and Crypto, each on its own page.
For every product, display risk level, volatility, and projected returns (with a slider for time horizon),
and use Tailwind plus shadcn/ui to make the UI look like a polished, responsive fintech dashboardNote: At the time of writing this tutorial, I tried with the Gemini 3 Pro(low) model, but it ran into some errors. However, feel free to try out the model as per your use case.
You’ll see the agent respond with something like:
Immediately after, Antigravity will propose a terminal command to scaffold the project. Just click Accept to let the agent run the command and run a couple of background steps to make a complete checklist for the app.
Below is a screenshot of the background steps running in the side terminal, starting with dependency installation.
You can leave it running while you watch the logs.
Step 5: Reviewing the Task checklist artifact
Once scaffolding is done, the agent generates a Task checklist artifact for the whole project.
Each section contains checkboxes such as:
- Initialize Next.js project with TypeScript and Tailwind CSS
- Set up shadcn/ui component library
- Savings/Bonds/Index Funds/Crypto page with risk profile
- Implement dark mode, animations, and a responsive layout
- Test navigation and slider functionality
Once this list is ready, the agent then begins to cover each task one by one. At this point, you can now open the Explorer sidebar to see what the agent created:
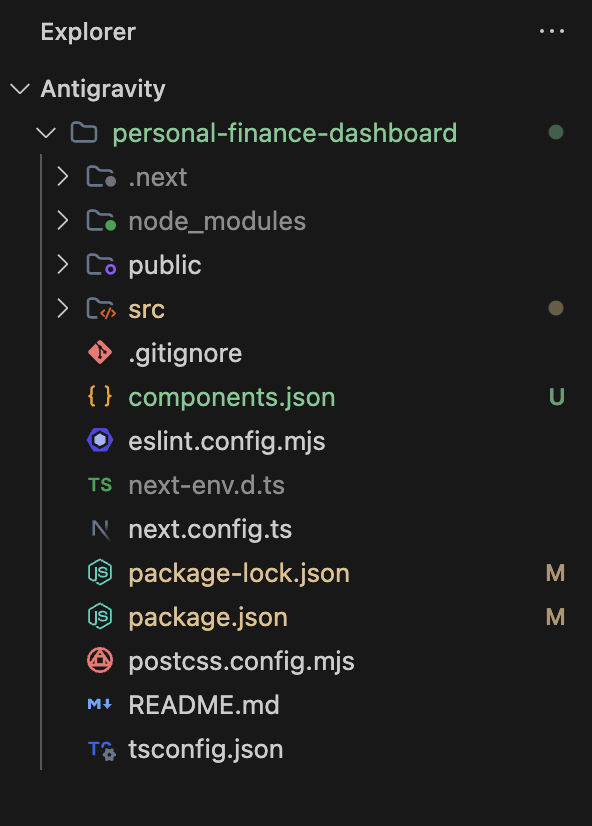
Now you have a standard Next.js, Tailwind, and a shadcn/ui file ready to be customized for this application.
Step 6: Reviewing the implementation plan
Alongside the checklist, Antigravity generates a more detailed Implementation Plan artifact:
The User Review Required section typically includes:
- Design approach: It includes dark mode, gradients, animations, and responsive design information of the application.
- Data model: This parameter contains all the risk metrics, like savings, bonds, index funds, and crypto, for our financial risk application.
- Core application structure: This describes how the main layout files will be modified to set up the global styles, typography, metadata, homepage, and dark-mode theme.
- Product pages: This lists the dedicated Next.js pages like
/savings,/bonds,/index-funds,/crypto, and the specific risk, volatility, and return information each one will display. - Shared components: This section defines reusable UI components like navigation bar, risk profile cards, returns calculator, and product overview cards that are used across the homepage and product pages.
- Utilities and types: This covers the TypeScript utilities in
lib/financial-data.tsthat hold product data, risk profiles, projected returns calculations, and helper functions for formatting money and percentages. - Verification plan: This outlines how the app will be tested, including starting the dev server, manually checking each page and slider, validating dark mode and responsiveness, and using the browser agent to record a full walkthrough with screenshots.
We can adjust risk numbers if we want more realistic data or add extra requirements. Finally, add comments in the Task/Implementation Plan artifacts if you want the agent to adjust the course.
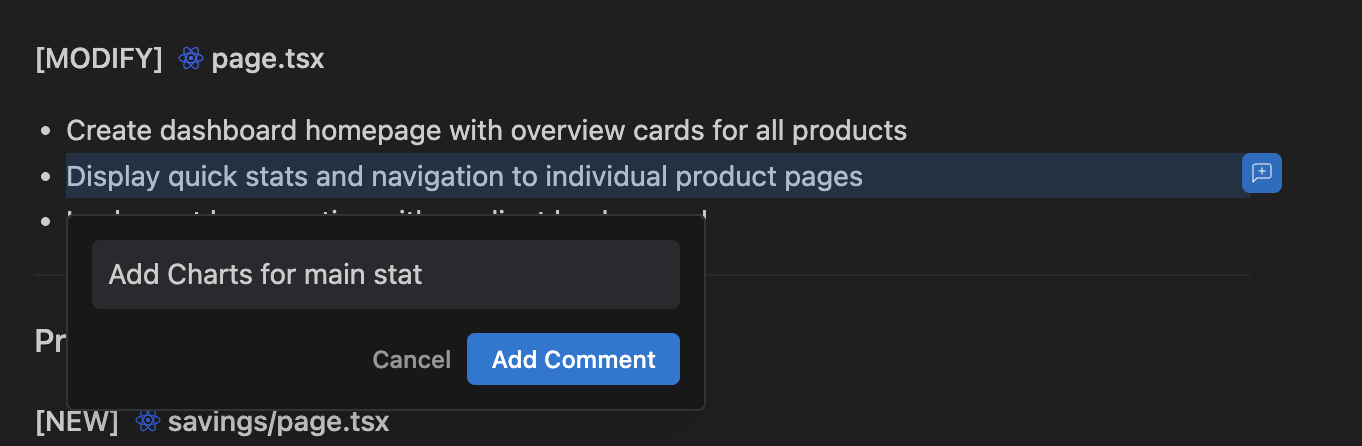
Once the plan looks good, click Proceed in the Implementation Plan tab. When you do this, the agent will start modifying and creating source files under the src/ directory. It will build individual pages for Savings, Bonds, Index Funds, and Crypto.
Along the way, it will create reusable components for cards, sliders, and charts, apply Tailwind and shadcn/ui styling across the app.
Finally, you’ll see new Background Steps and Progress Updates for each code change.
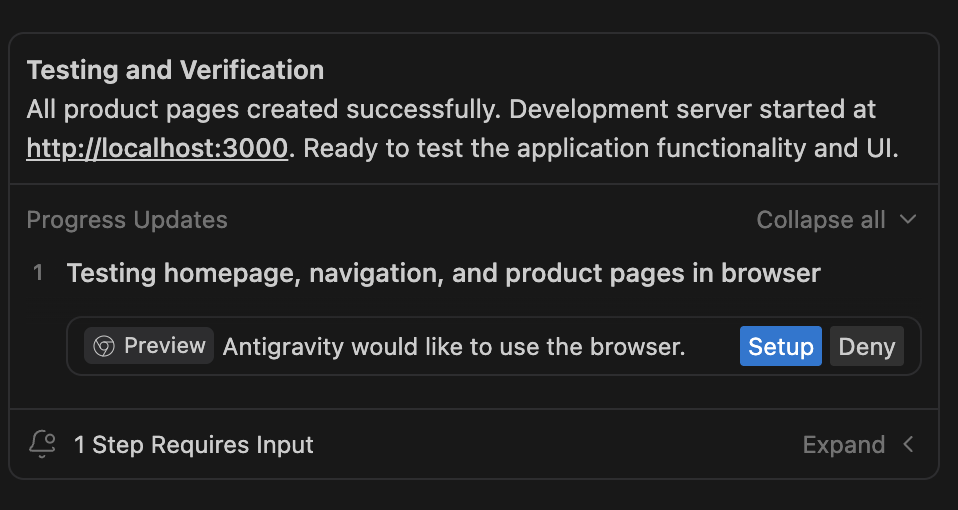
Step 7: Testing and verification
Once implementation is complete, Antigravity moves into Testing and Verification. You’ll see a new progress item where Antigravity will ask to use the browser via the Setup or Deny button. Simply click Setup to proceed.
Before the agent can interact with the browser, you need the official extension.
Visit the Chrome Web Store listing and click on Add to Chrome.
After installation, when the agent is controlling the browser, you’ll notice a glow around the screen as shown below:
This glow indicates that the Antigravity Agent is actively using the browser, i.e, clicking, scrolling, and testing the app as part of the verification step.
Step 8: Reviewing the walkthrough artifact
When testing completes, you’ll see a final Progress Updates summary as follows:

The Walkthrough artifact typically includes:
- Screenshots of each page
- A recorded browser session of the agent clicking through the app
- A narrative description of what it tested (example: “Verified Savings page slider updates projected returns in real time”)
If everything looks good, click Accept all to apply the changes.
Here is our final app:
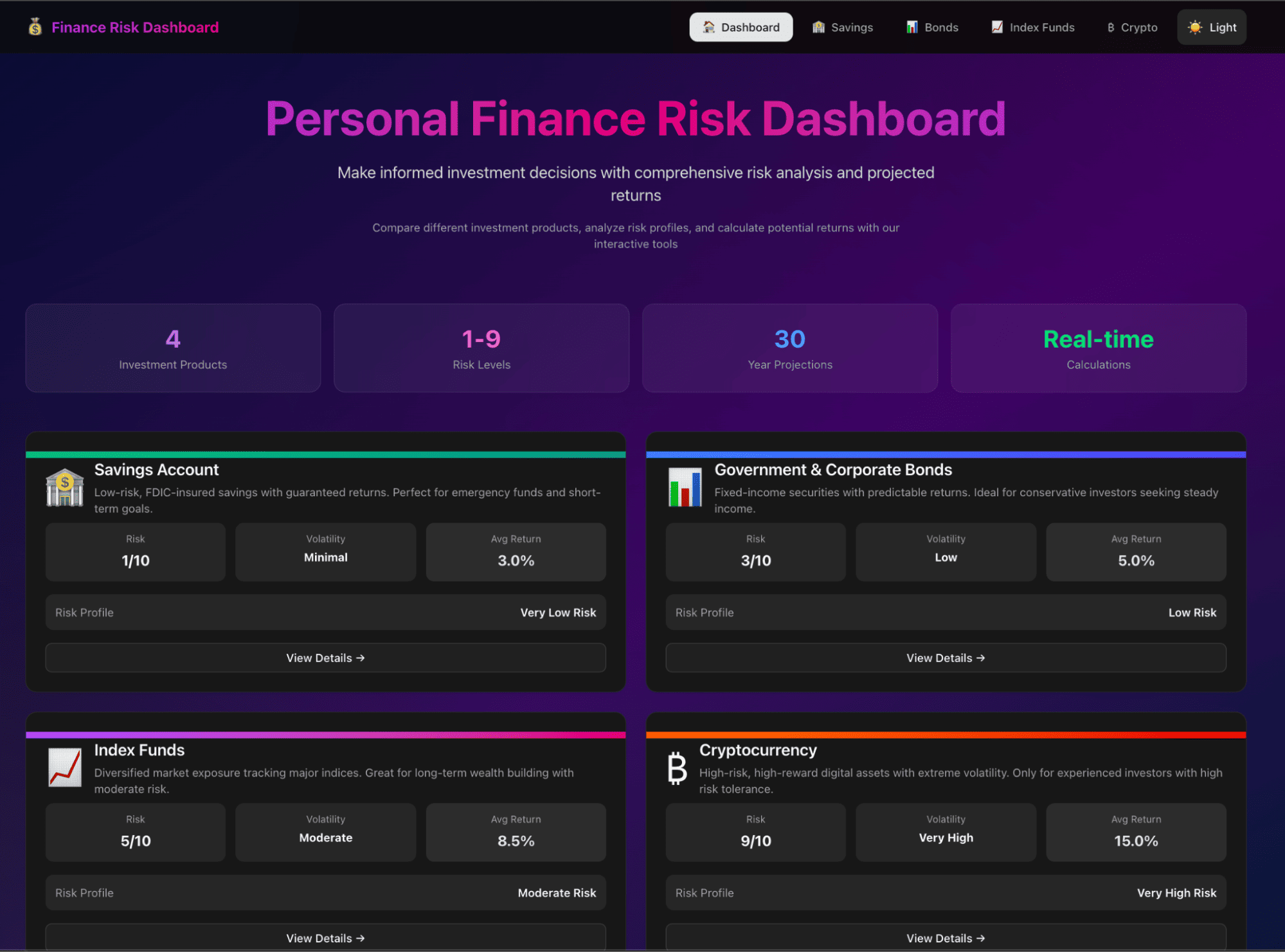
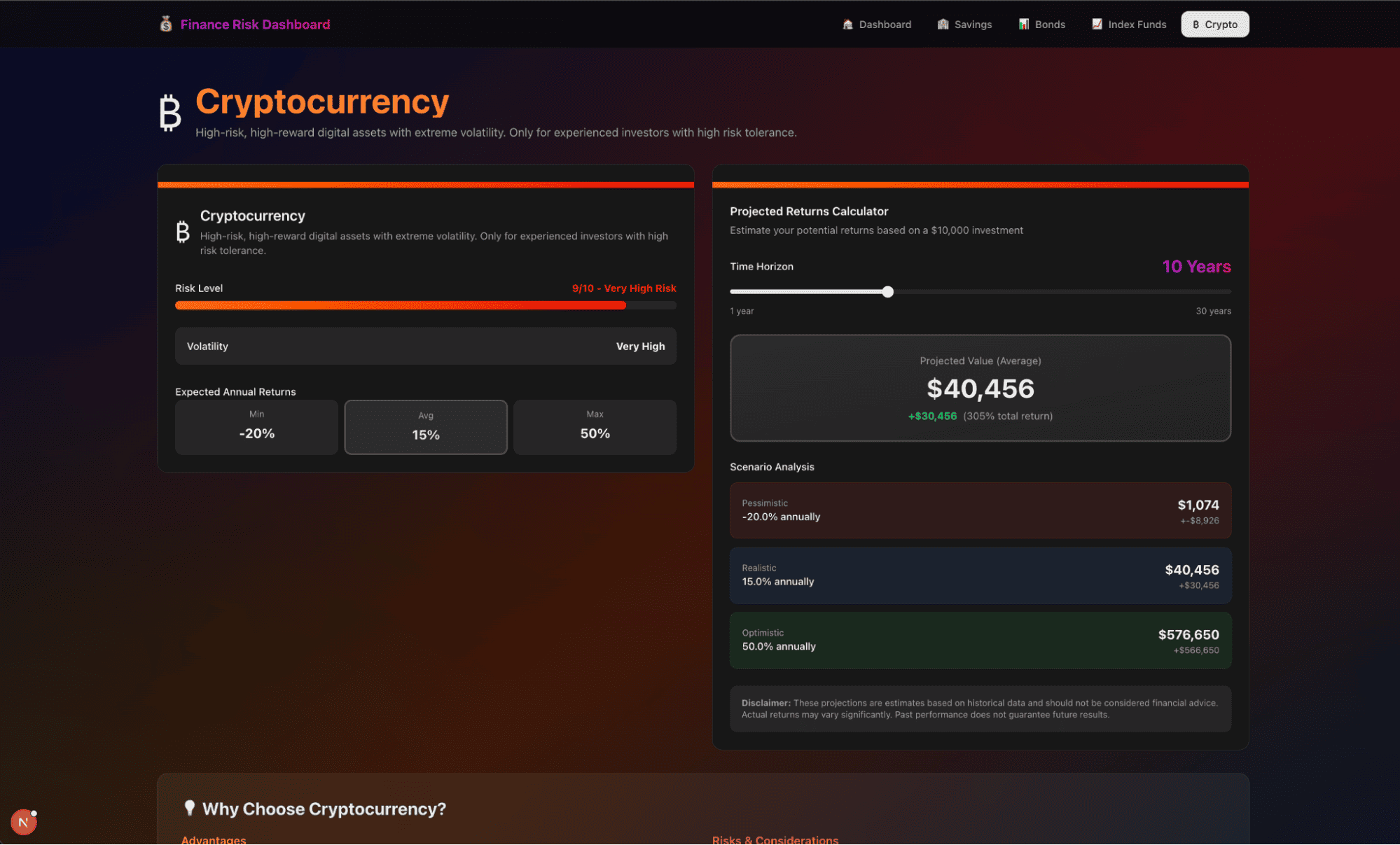
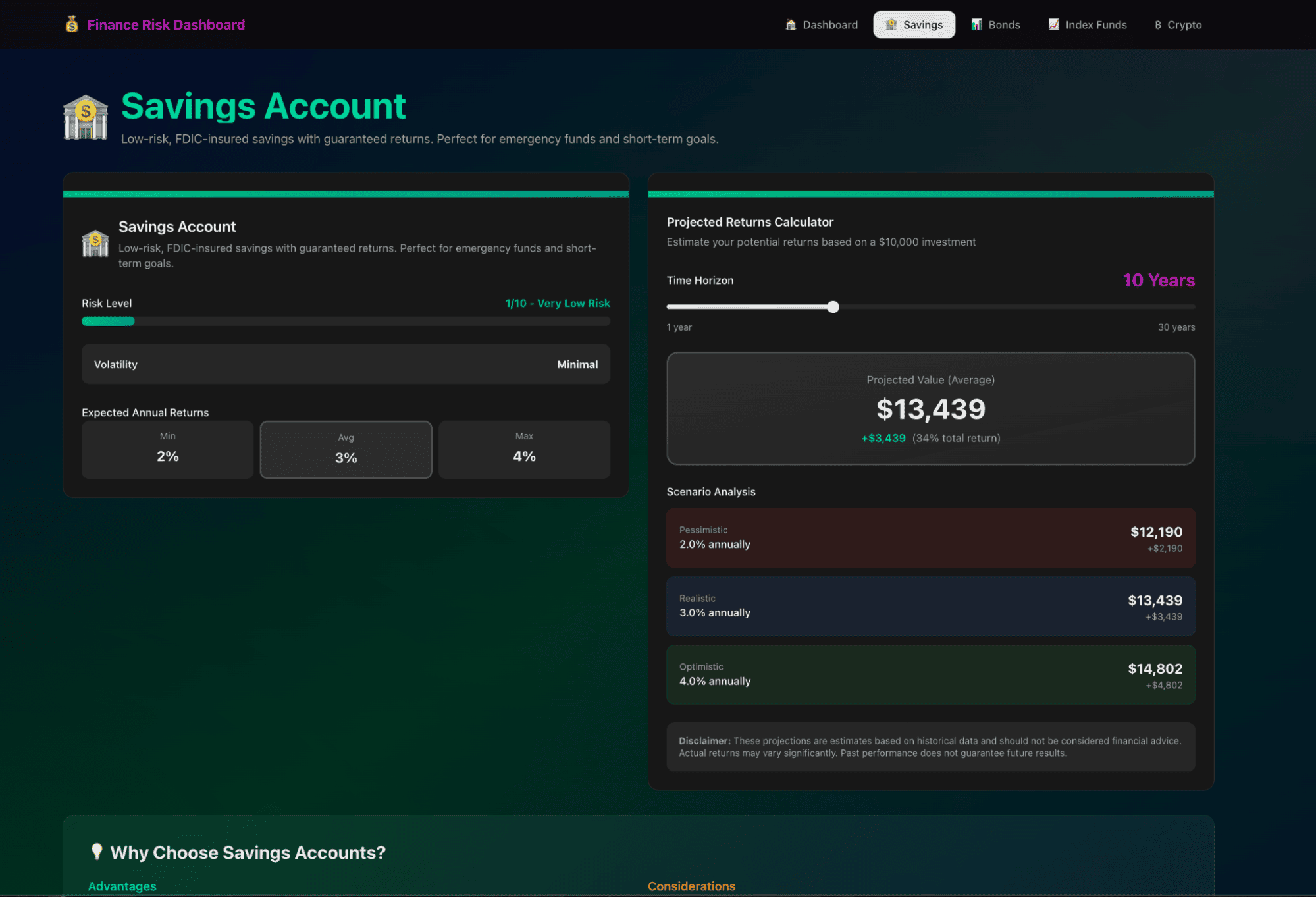
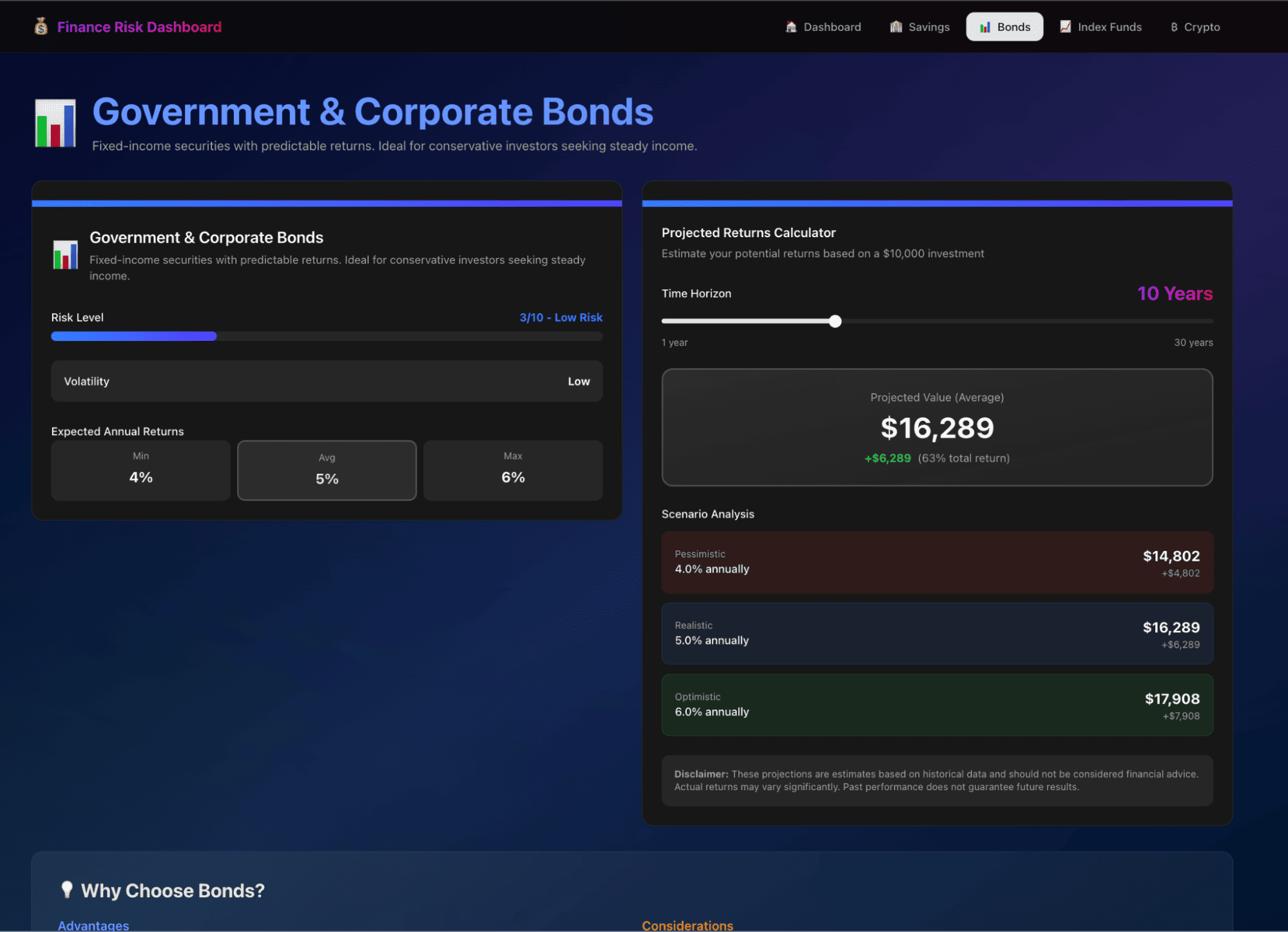
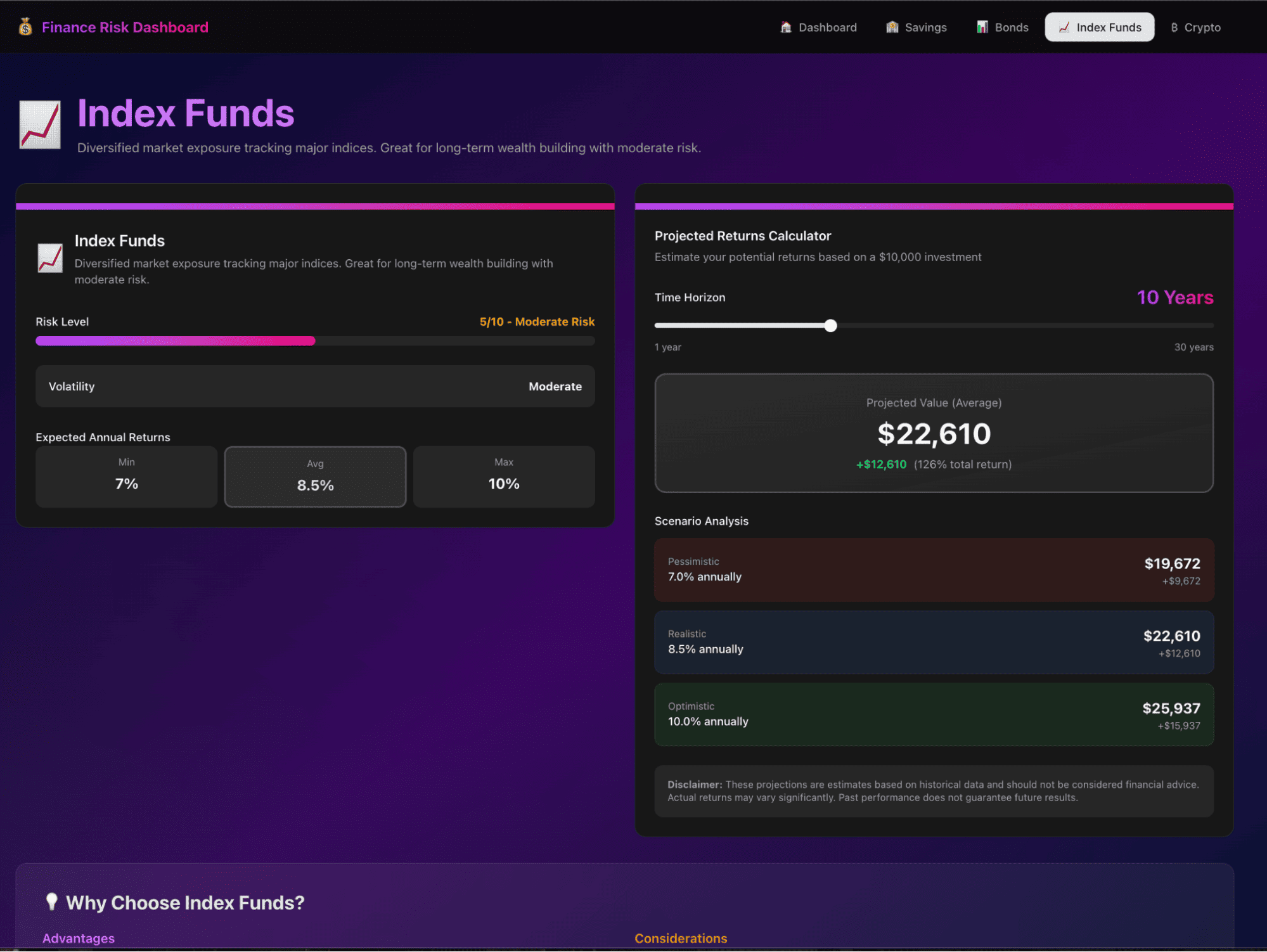
Step 9: Editing the dashboard
Now let’s iterate on the UI. Suppose you want a dark/light mode toggle in the dashboard header and add a few charts for each page. In the Task or Implementation Plan, or directly in the Agent panel, you can ask:
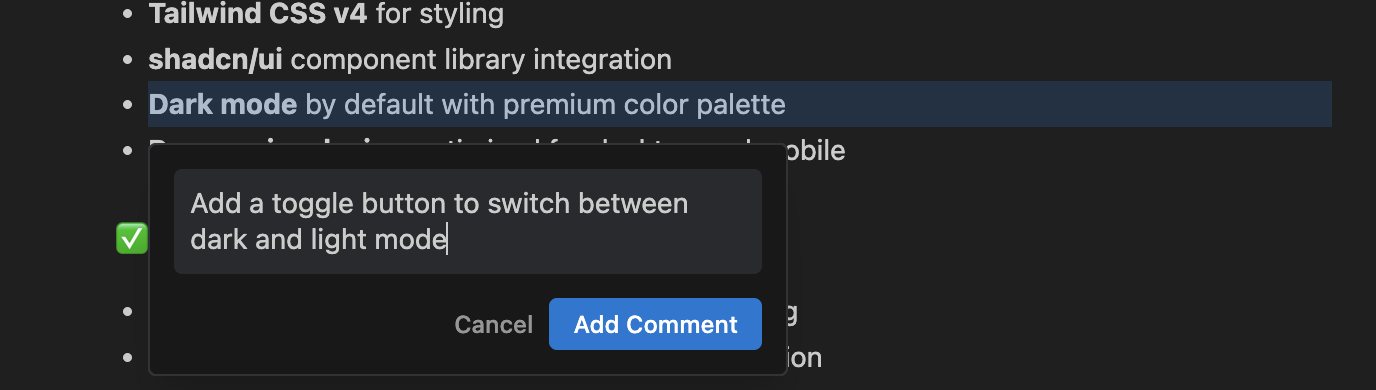
Antigravity will:
- Update the layout components to include a theme toggle (likely using shadcn/ui’s theme utilities)
- Add, replace, or remove chart components
- Re-run the app and test the toggle in the browser
Now click on Submit, and both our earlier comment and this comment will be implemented.
Step 10: Review errors and debugging
In practice, you may notice that reviews often lead to a lot of errors, maybe due to the model, but Antigravity still keeps working on it with Computer Use.
Even when the agent encounters errors, it can:
- Read the error message in the terminal
- Open the app in the browser and reproduce the issue
- Take screenshots and playback recordings of the broken state
- Use those visual cues and logs to fix the bug
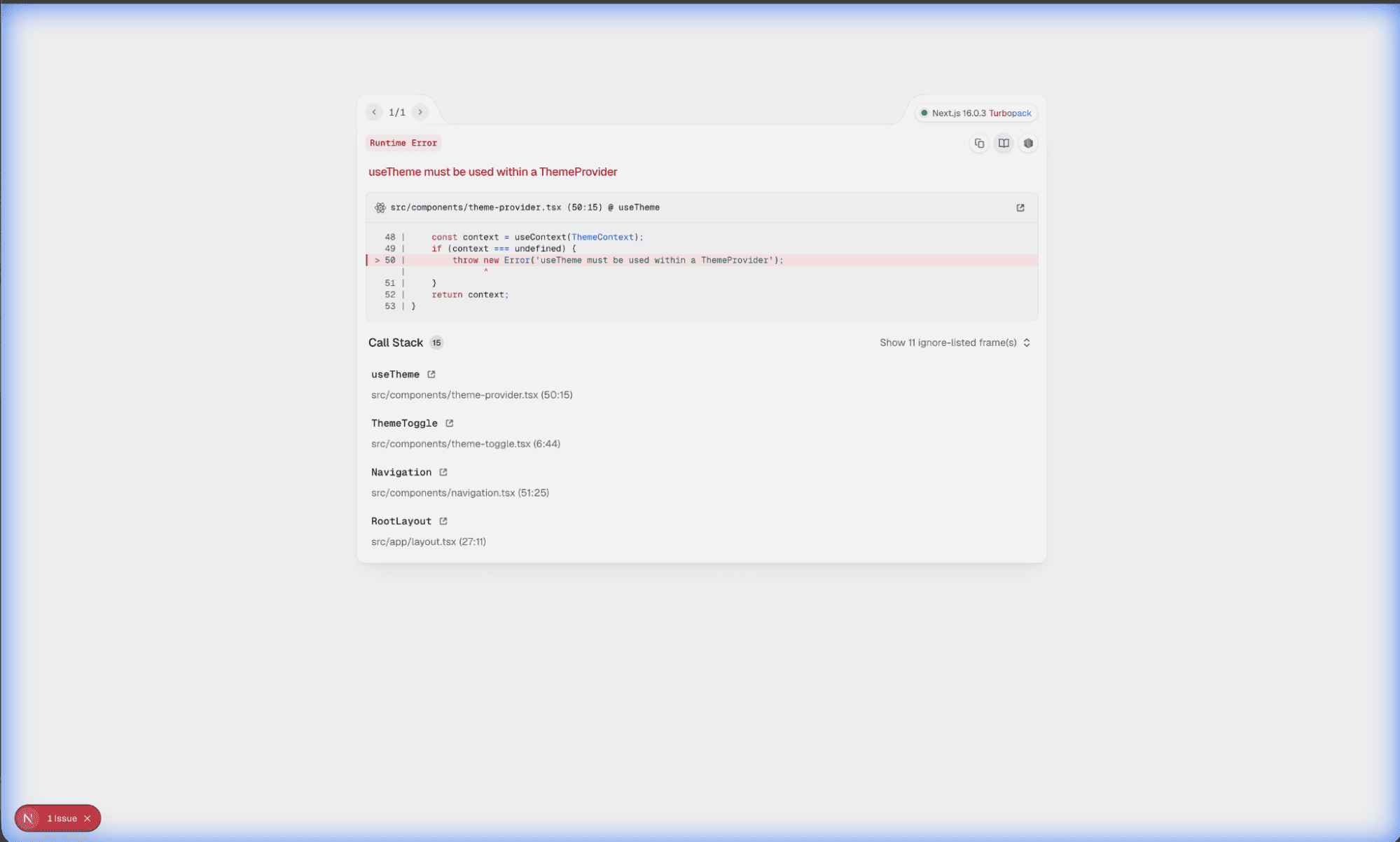
You can follow along by opening the Walkthrough or checking the new Progress Updates for debugging steps.
At this point, you’ve:
- Prompted an agent to scaffold a full Next.js + Tailwind + shadcn/ui app
- Reviewed and edited a structured Implementation Plan
- Let Antigravity handle setup, coding, testing, and browser verification
- Iterated on the UI with comments and additional prompts
- Watched the agent debug issues via computer use and screenshots
Now our final app is ready for review.
Step 11: Final result
After iterating on the toggle and layout, you’ll end up with a final application where the charts are removed, and the light/dark mode toggle works across the entire dashboard.
Dark mode:

Light mode:
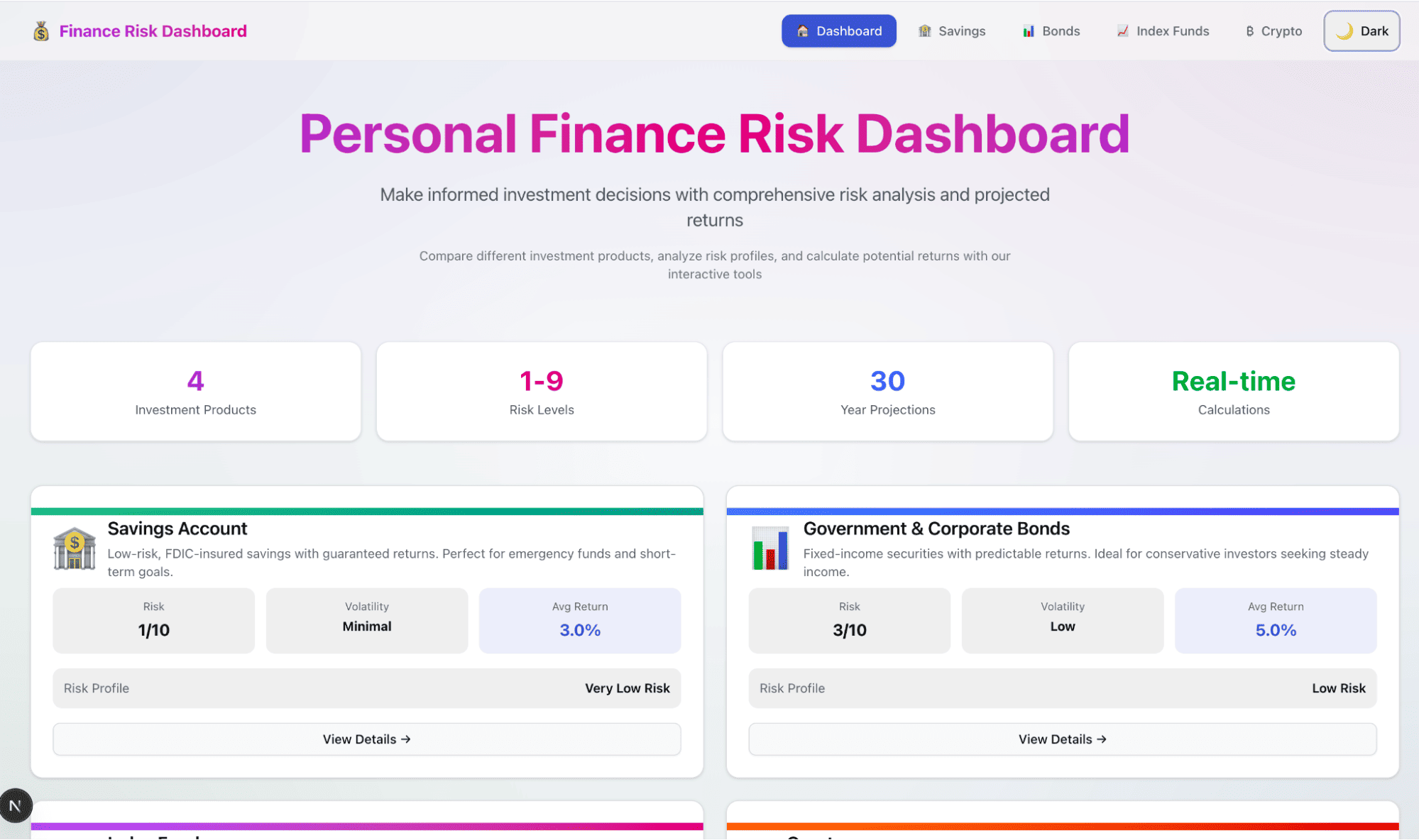
You can see our dashboard in action in the video below:
Final Thoughts
Google Antigravity shifts development from manual coding in an editor to collaborating with an agent that can plan, implement, and verify full features.
In one workflow, we saw:
- Planning: It includes a Task checklist and an Implementation plan artifact
- Execution: Most of the executions were Agent-made via terminal commands, file edits, and UI building
- Verification: For this, we required browser automation, walkthrough recordings, and test summaries
- Iteration: These were mostly comment-driven refinements (dark/light mode, layout tweaks), where the agent worked on user-provided comments.
- Debugging: Finally, an automated investigation of errors through computer use made debugging easy
You can now reuse the same pattern for other demo apps:
- A workout intensity dashboard
- A city noise explorer
- A feature-complete food delivery UI
If you’re looking to learn more about creating AI Agents, I recommend taking the Building AI Agents with Google ADK course.
Google Antigravity FAQs
Does Google Antigravity support programming languages besides JavaScript and Next.js?
Yes. While much of Antigravity’s early focus is on web frameworks like JavaScript, TypeScript, React, and Next.js, it’s designed to support multi-language workflows. The platform’s AI agents can plan and execute commands across different project types, so broader language support is expected to expand over time.
What are the current rate limits or pricing model for Google Antigravity?
Google Antigravity is currently in public preview and free to use. It provides generous rate limits for tasks powered by Gemini 3 Pro and other supported models. These limits reset periodically, and pricing details for future paid tiers have not yet been announced.
How does Antigravity ensure that an AI agent’s work is correct and auditable?
Antigravity automatically generates “Artifacts” that document each stage of an agent’s work, including task lists, implementation plans, terminal logs, screenshots, and recorded browser walkthroughs. This audit trail helps developers verify and review every step of what the agent has done.
Can multiple agents run in parallel within Antigravity?
Yes. Antigravity allows users to create and manage multiple AI agents simultaneously. Each agent can focus on different tasks or workspaces (for example, one handling code implementation while another tests features or updates documentation), enabling true parallel agent workflows.
What hardware or operating system requirements does Antigravity have?
Antigravity is available for macOS, Windows, and Linux. It runs best on modern systems with sufficient RAM and processing power for AI-assisted tasks. For macOS, versions Monterey or newer are recommended, and for Windows, a 64-bit installation is required.

I am a Google Developers Expert in ML(Gen AI), a Kaggle 3x Expert, and a Women Techmakers Ambassador with 3+ years of experience in tech. I co-founded a health-tech startup in 2020 and am pursuing a master's in computer science at Georgia Tech, specializing in machine learning.
