Track
Excel can help you manage and visualize project schedules without needing additional software, especially through the use of a Gantt chart; a simple yet powerful way to track tasks, deadlines, and dependencies over time. These charts provide a structured approach to project management, helping teams and individuals stay organized.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through how to build a Gantt chart in Excel, customize it to fit your needs, and even automate task dependencies to make scheduling easier. Whether you're working solo or managing a team, a good Gantt chart can make a huge difference.
What is a Gantt Chart?
A Gantt chart is a visual timeline that helps in tracking project tasks over time. It consists of horizontal bars that represent different tasks, with their positions indicating the start and end dates. This format makes it easier to see dependencies, track deadlines, and identify potential delays.
These charts are commonly used in project management, task scheduling, and workflow planning. For example, a marketing team might use a Gantt chart to track campaign launches, a construction company can use it to plan building phases, and a student can organize assignments leading up to an exam.
Creating a Simple Gantt Chart in Excel
Let’s take a look at the process for creating a Gantt chart in Excel. If you’re looking for other methods, check out our guides on creating Gantt charts in matplotlib and how to make a Power BI Gantt chart.
Step 1: Setting up the data
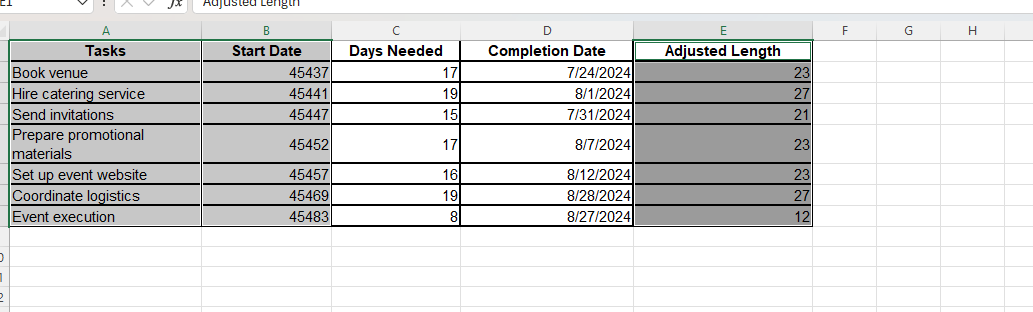
We need a structured dataset before creating the chart. For our example, the table should include columns for Task Name, Start Date, Duration, and End Date. The End Date is usually calculated by adding the Duration to the Start Date using a simple formula in Excel.
For instance, if your data is in Excel with:
- Start Date in column B
- Duration (in days) in column C
- End Date in column D
Then in D2, the formula would be:
=B2 + C2For example:
|
Tasks |
Start Date |
Days Needed |
Completion Date |
Adjusted Length |
|
Book venue |
5/25/2024 |
17 |
7/24/2024 |
23 |
|
Hire catering service |
5/29/2024 |
19 |
8/1/2024 |
27 |
|
Send invitations |
6/4/2024 |
15 |
7/31/2024 |
21 |
|
Prepare promotional materials |
6/9/2024 |
17 |
8/7/2024 |
23 |
|
Set up event website |
6/14/2024 |
16 |
8/12/2024 |
23 |
|
Coordinate logistics |
6/26/2024 |
19 |
8/28/2024 |
27 |
|
Event execution |
7/10/2024 |
8 |
8/27/2024 |
12 |
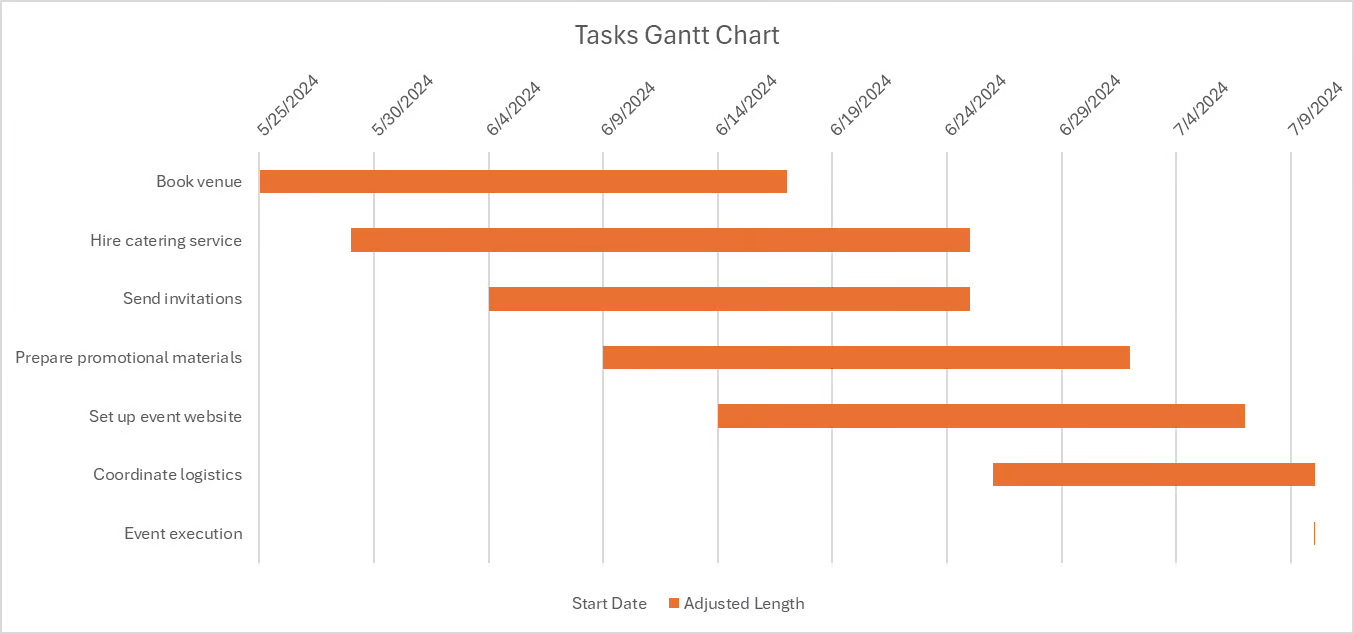
Step 2: Creating a stacked bar chart
Once the data is ready, use a stacked bar chart to display it as a Gantt chart. To do this:
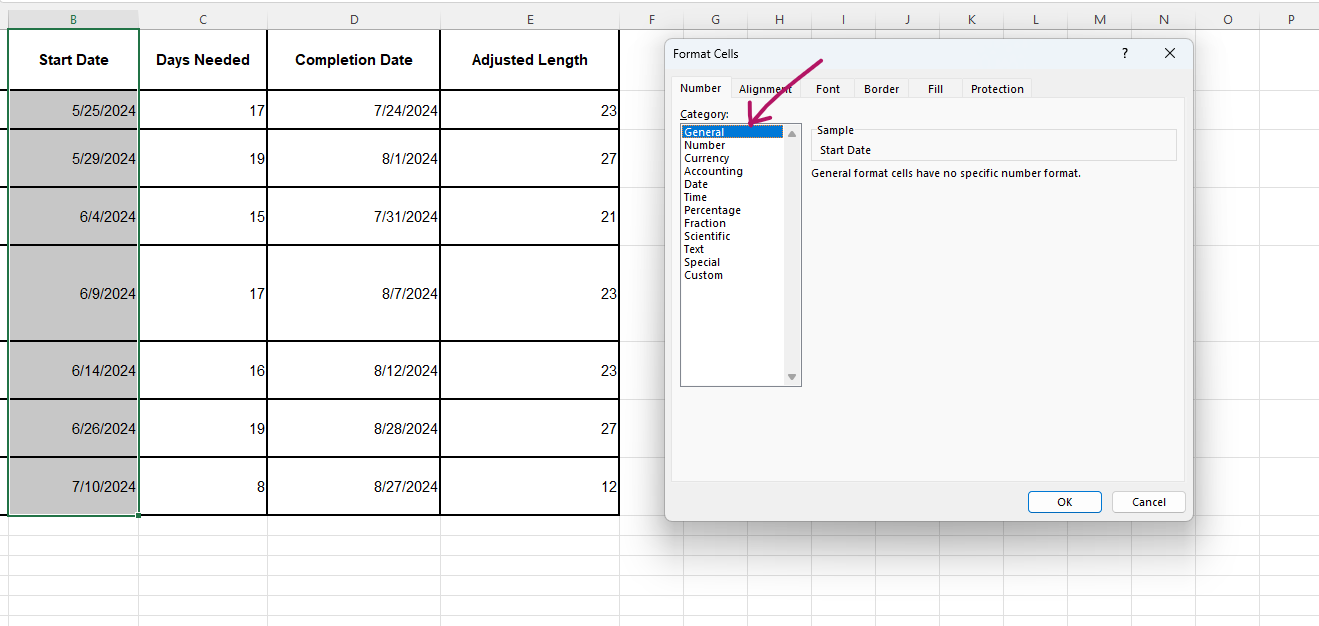
- Select all the dates in the start date column and change the format from "Date" to "General." Press CRT + 1 to access the menu.
- Select the Tasks, Start Date, and Adjusted Length columns by pressing CTR or CMD.
- Go to Insert > Recommended Charts > All Charts > Bar > Stacked Bar.
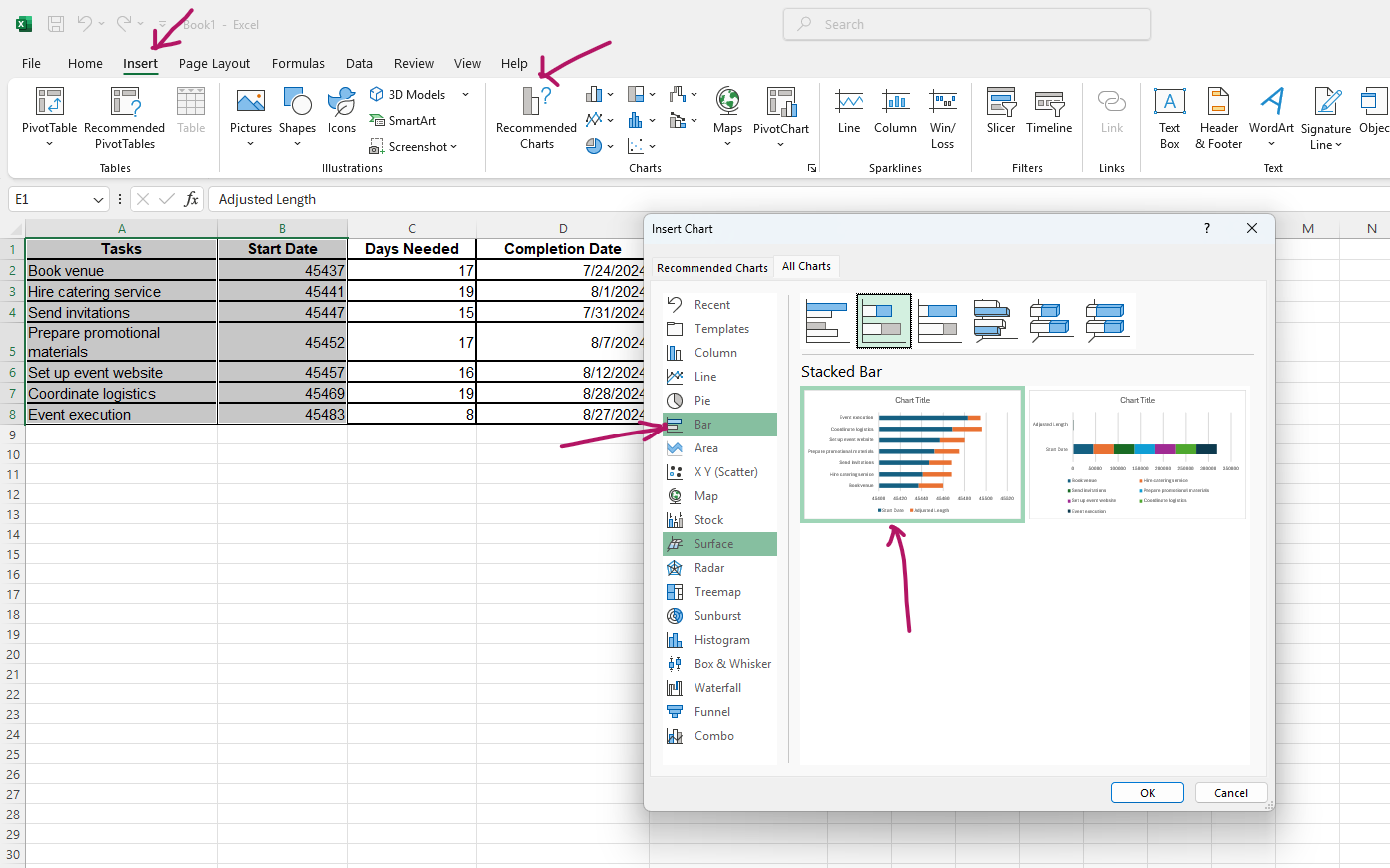
- Select the dates on the chart and change the format back to "Date".
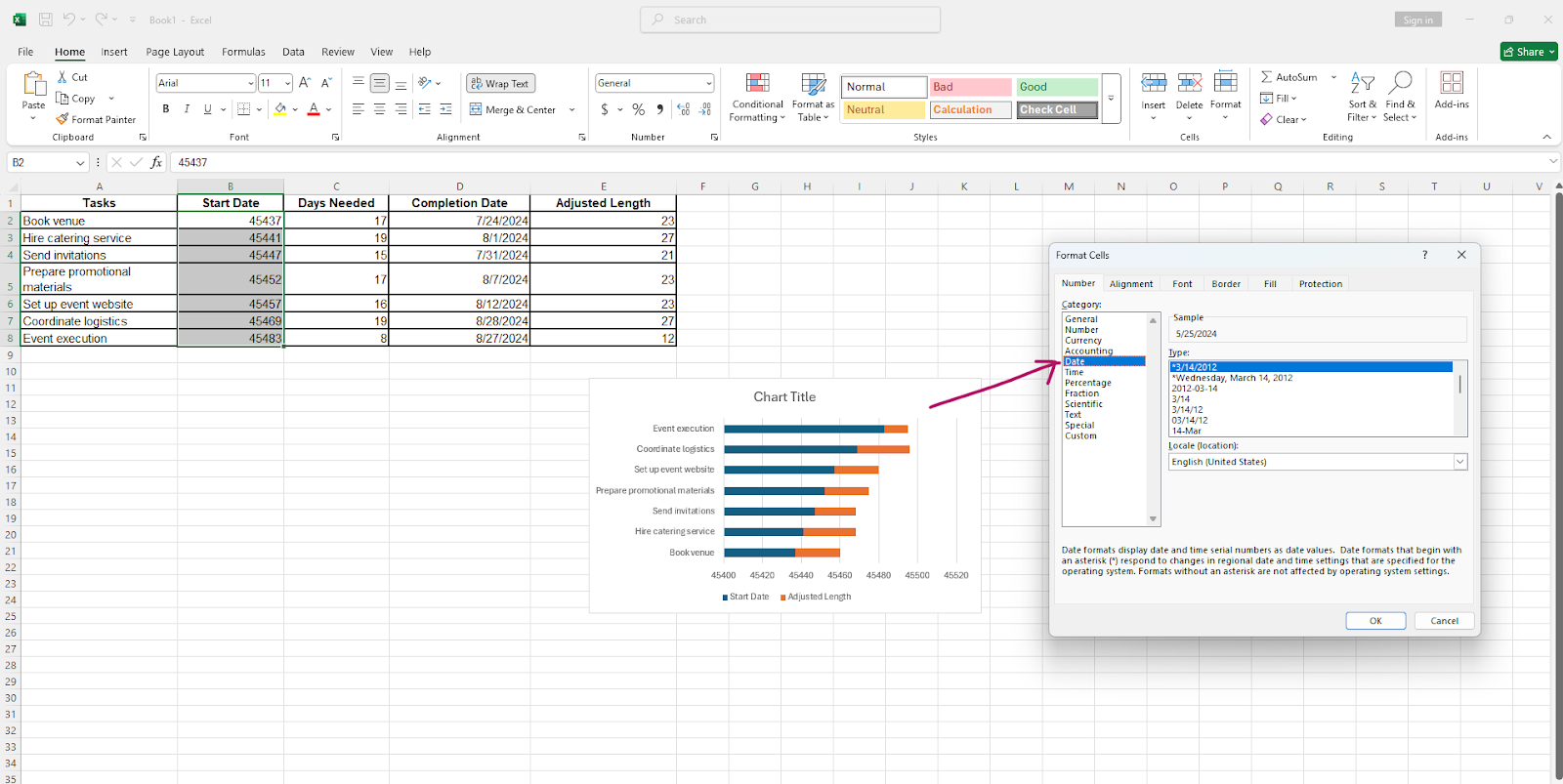
- Click on the blue series in the chart; in the format data series pane, select "No Fill".
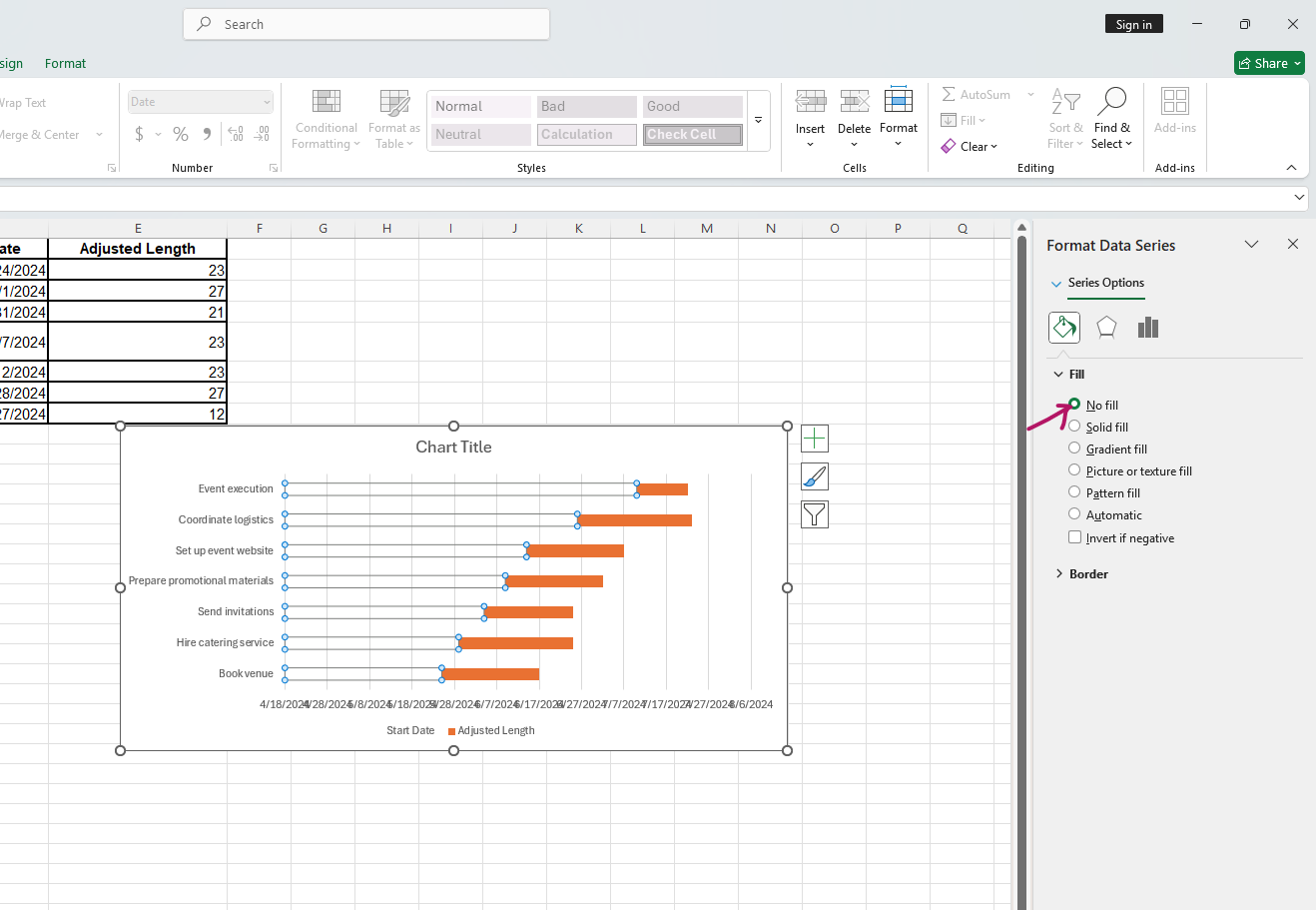
- Double-click on the task list. In the format axis pane, check "Categories in reverse order."
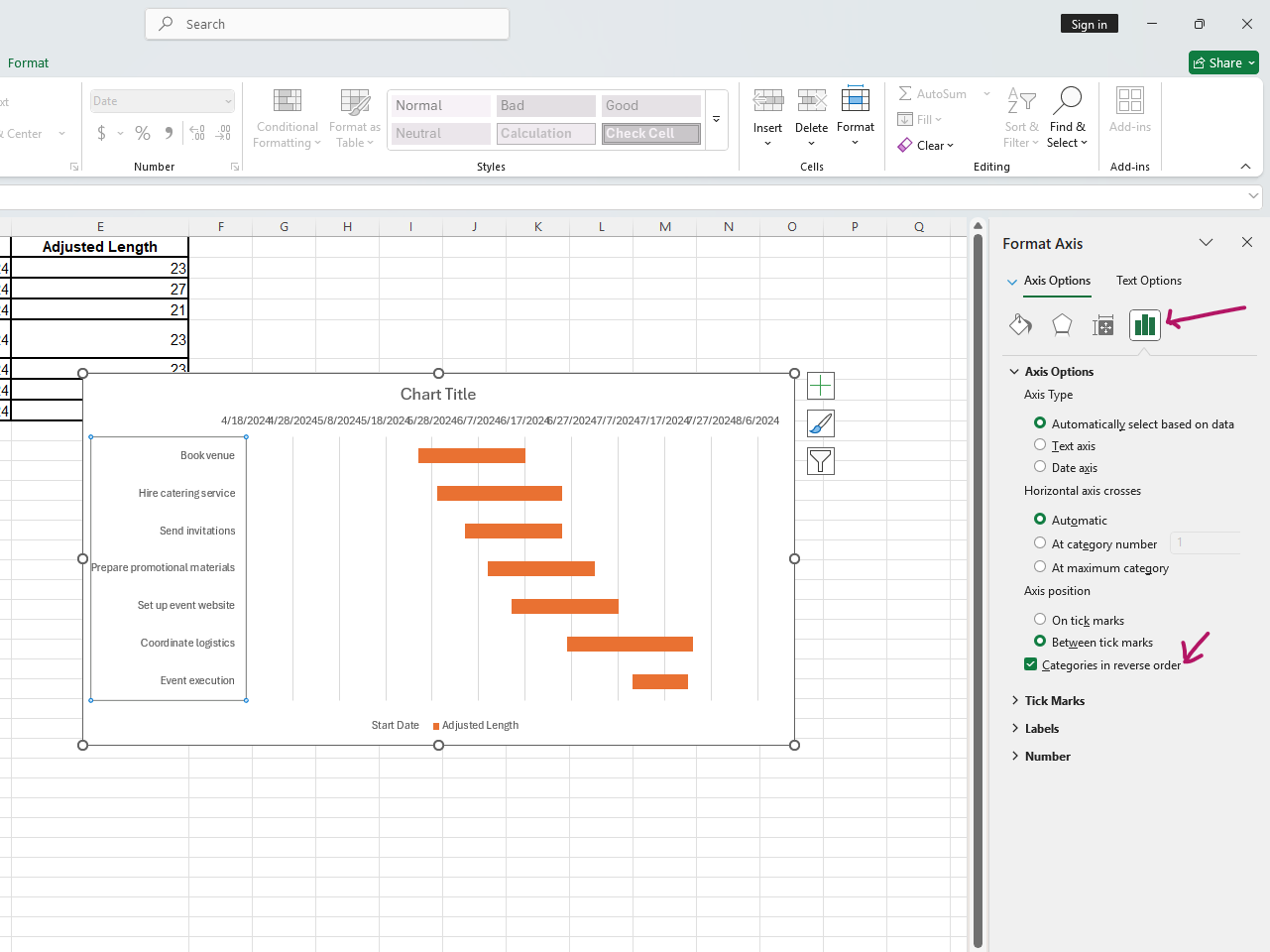
- Double-click on the dates in the format axis pane and adjust the minimum and maximum bounds to fit your project timeline.
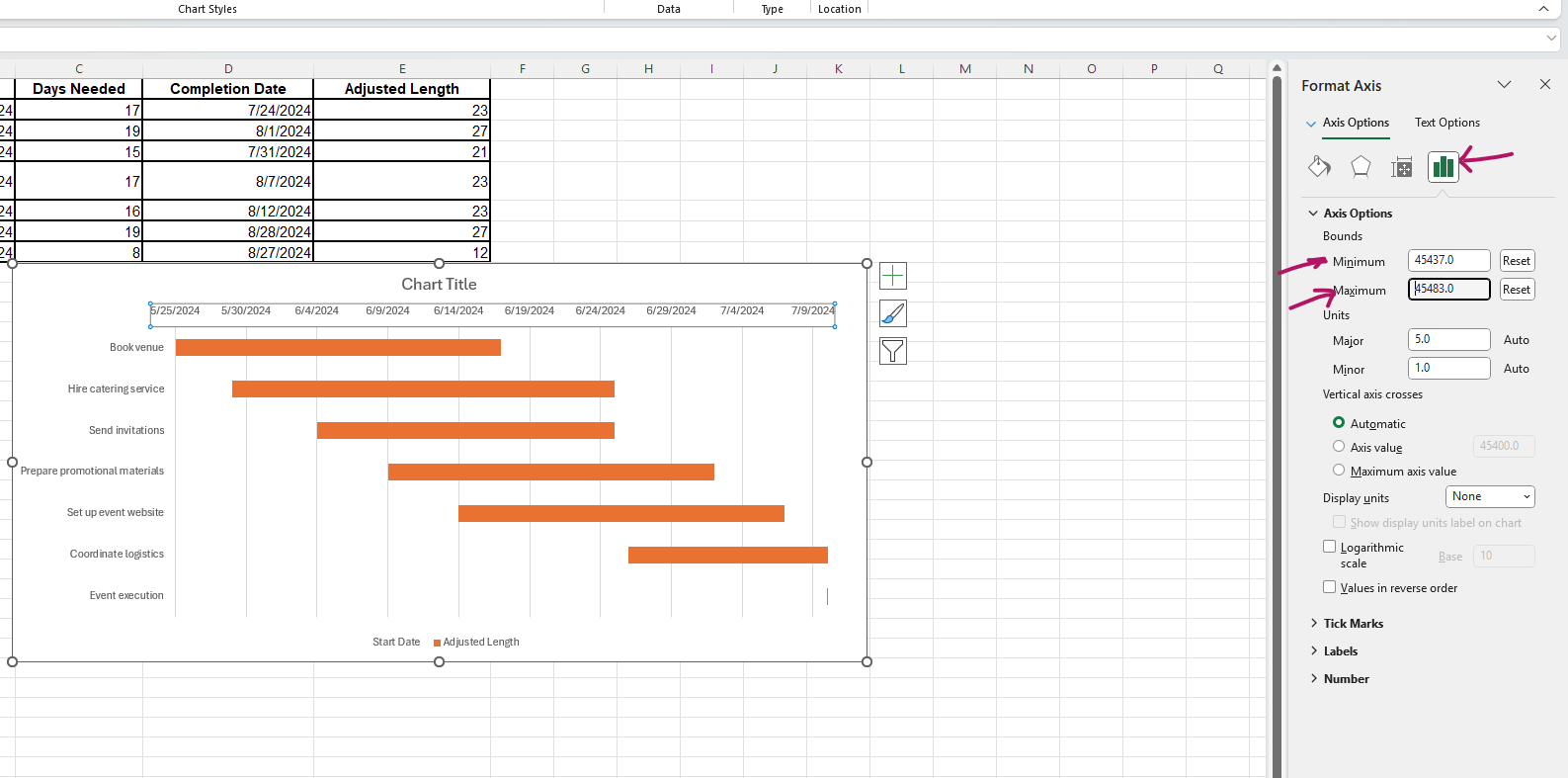
- Click on the title to give the Gantt chart an appropriate title.
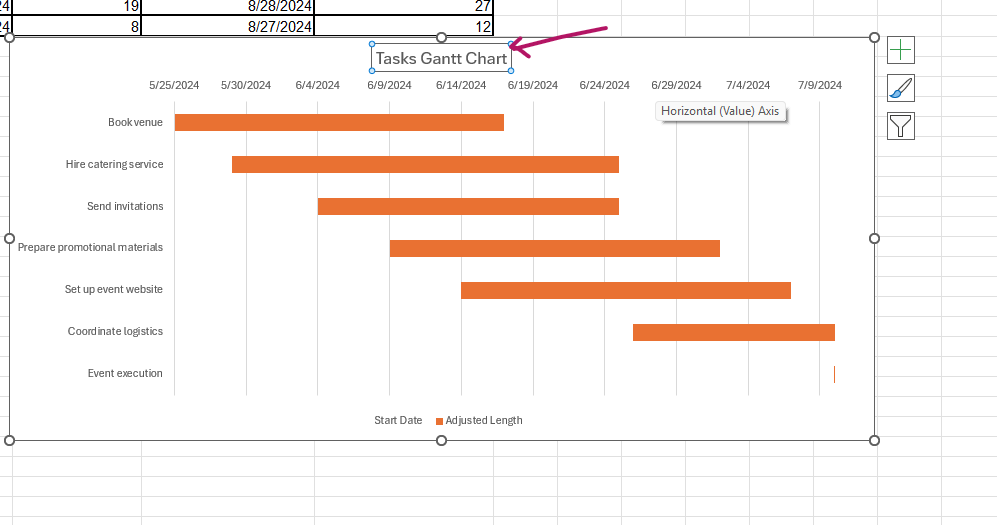
- Click the date, then Home, and tilt them to make them more visible.
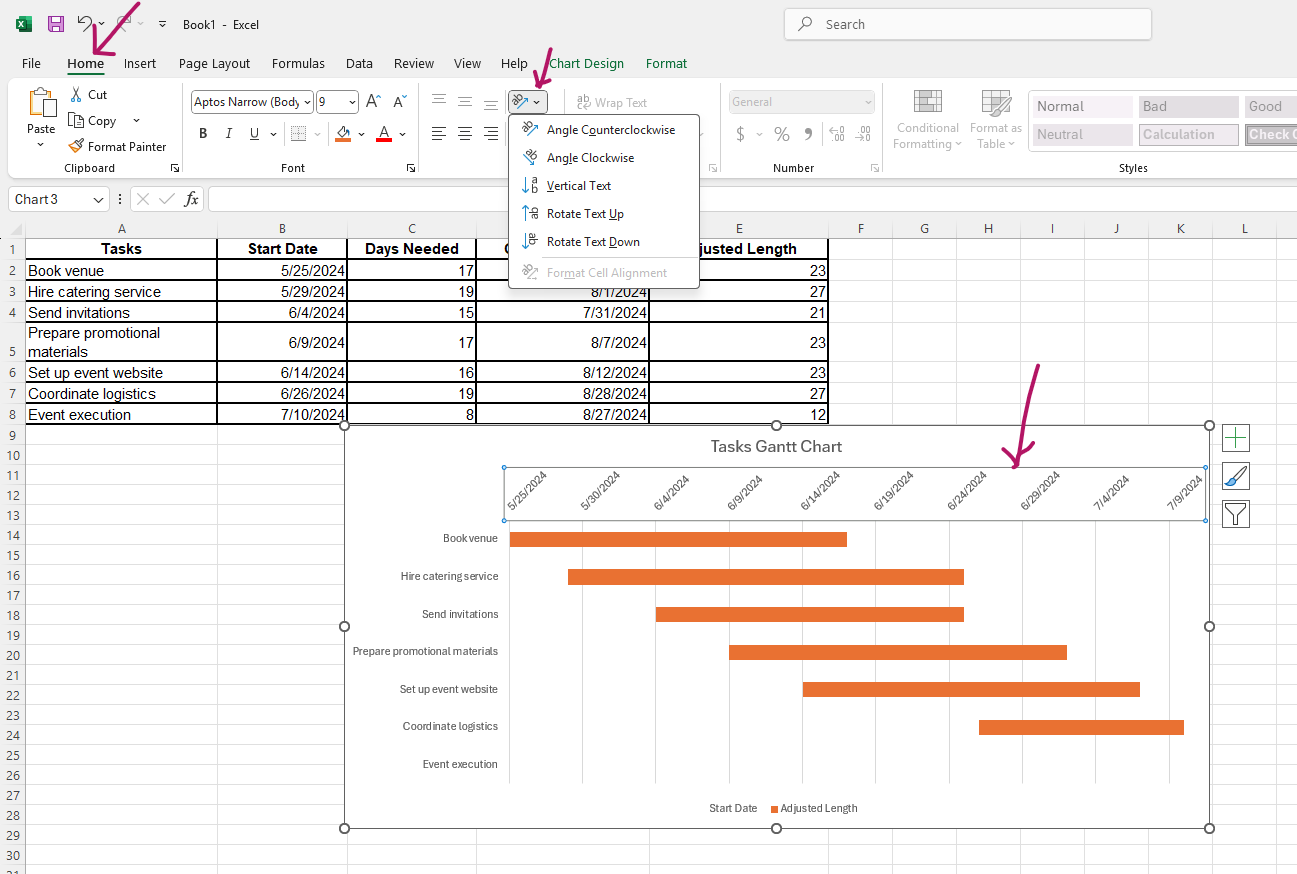
Step 3: Formatting the Gantt chart
You can make the chart easier to read by making the following adjustments:
- Modify the axis labels so that dates appear correctly.
- Change the colors of the bars for better distinction between tasks.
- Remove unnecessary elements like gridlines to keep the chart clean.
Making a Gantt Chart with Dependencies in Excel
Now that we have a basic Gantt chart set up, the next step is to incorporate task dependencies. This helps ensure that tasks start in the correct order and adjust dynamically as the project evolves.
Step 1: Adding a dependency column
Dependencies indicate that a task cannot start until another is completed. For example, writing a report might depend on completing research. A new column can be added to track which tasks depend on others.
To make it easier, you can use Gantt templates that already include the dependencies functionality.
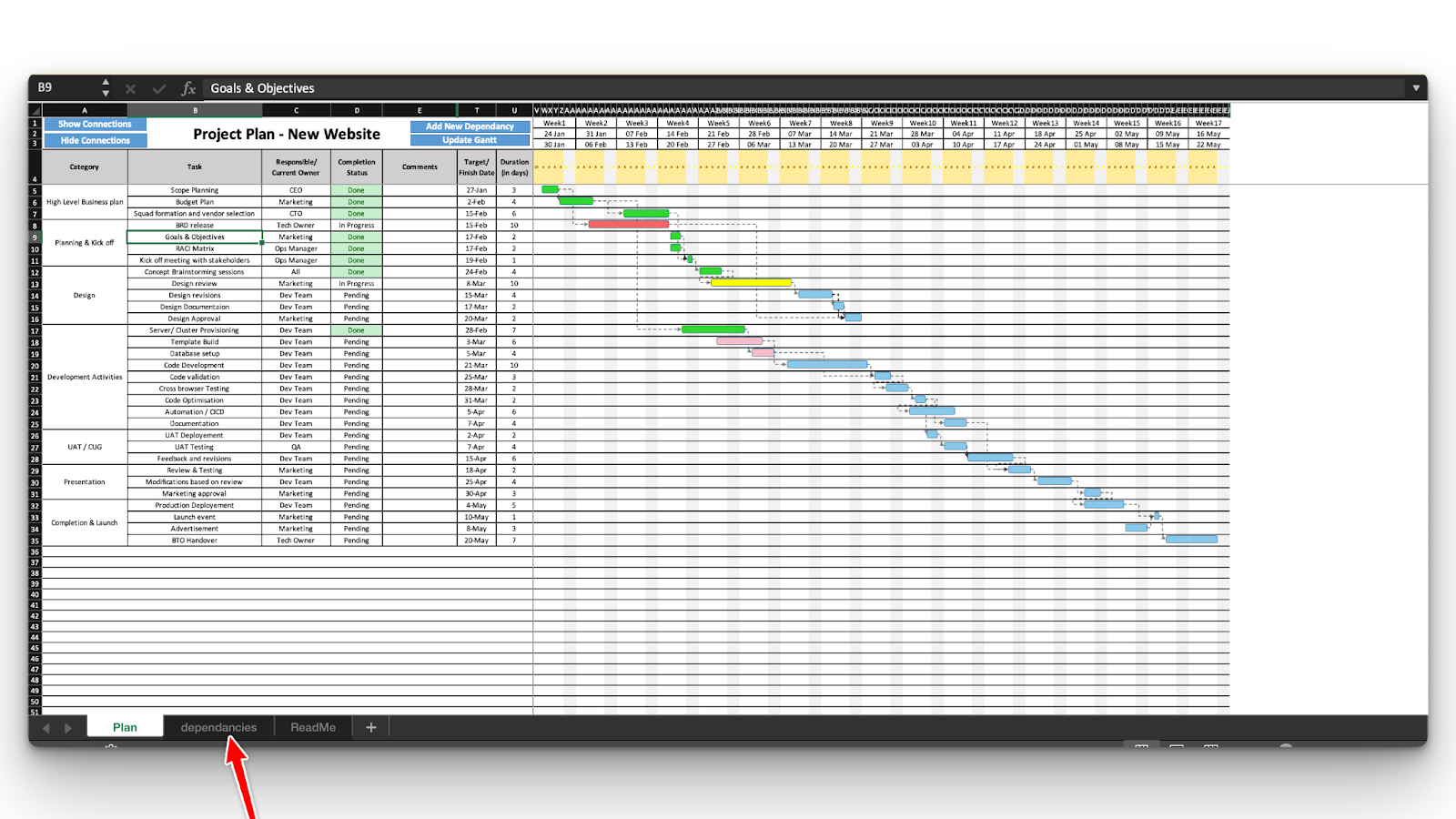
Step 2: Automating start dates using formulas
By using Excel formulas, you can adjust dates automatically based on dependencies. Use the WORKDAY Excel function to skip weekends, ensuring a more realistic schedule. For example:
=WORKDAY(B2, C2)This feature ensures that the next task starts only after the previous one is completed, making the chart dynamic.
Using a Simple Gantt Chart Template in Excel
If building a Gantt chart from scratch feels overwhelming, templates can be a great alternative. Many free templates are available online that allow quick customization. These templates come with preformatted bars and formulas, making setup faster.
While templates save time, they may not always fit specific needs. Customizing a chart from scratch gives more flexibility, but a template can serve as a starting point.
You can get the template on the internet, for example, from Microsoft’s website. Download the template to use it in Excel.
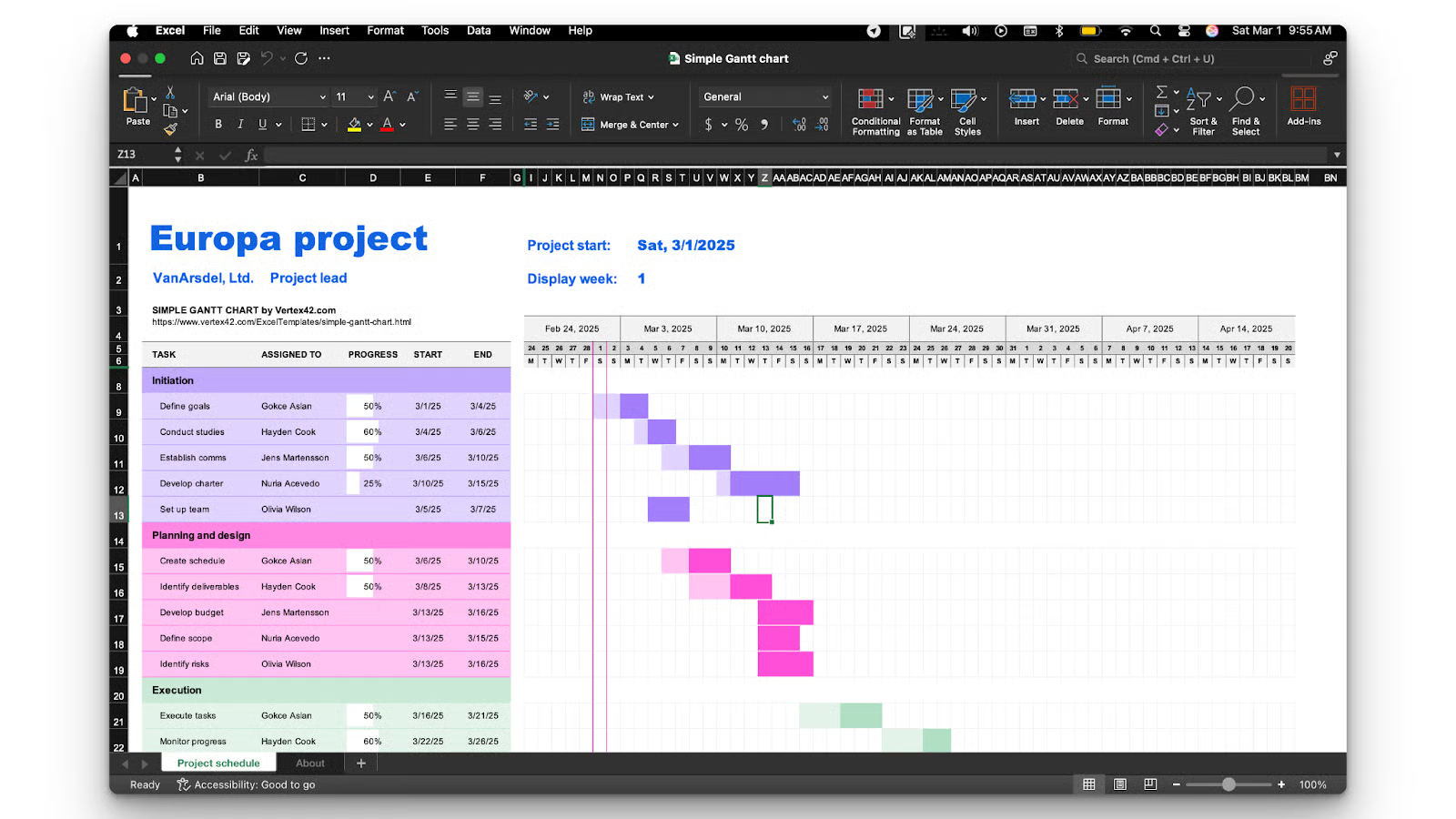
Gantt Chart Example in Excel: A Real-World Use Case
Gantt charts are a powerful tool for visualizing project timelines and tracking progress. Consider a construction project to see how a Gantt chart works in practice.
For example, a construction company planning a new office building might break the project down into key phases: design, permitting, site preparation, foundation work, framing, electrical installation, and final inspections. Each of these phases depends on the completion of previous tasks, making a Gantt chart an effective way to manage dependencies and avoid delays.
With the project tasks and their timelines laid out, team members can adjust deadlines as needed, ensuring efficient coordination between subcontractors and suppliers.
Once the structured dataset is ready, you can create a Gantt chart using the same steps as before.
How to Make a Gantt Chart in Excel
Regular updates help in tracking progress, adjusting deadlines, and ensuring everything stays on schedule. A well-maintained Gantt chart keeps projects running smoothly, avoiding last-minute surprises.
Conclusion
Throughout this guide, we have explored how to create and customize a Gantt chart in Excel. By working through practical steps, we learned how to structure project timelines, visualize tasks, and manage dependencies efficiently.
From setting up a basic Gantt chart to incorporating task dependencies, Excel provides the flexibility needed to handle various project management needs. Following best practices, such as maintaining clear data organization, updating schedules regularly, and using formulas for automation, ensures that Gantt charts remain useful and easy to manage.
Understanding how to use Gantt charts in Excel helps improve task tracking and deadline management, whether planning a small project or overseeing a complex workflow. Apply these skills today to enhance your project planning process and keep everything on track. Refer to our Excel Fundamentals track to dive deeper into the essential Excel skills.
Excel Gantt Chart FAQs
What is a Gantt chart used for?
A Gantt chart is a project management tool to visualize tasks over time. It helps track deadlines, dependencies, and progress, making managing projects easier and ensuring tasks are completed on schedule.
How do I create a Gantt chart in Excel?
To create a Gantt chart in Excel, set up a table with task names, start dates, and durations. Use a stacked bar chart to represent the timeline, then format the bars to resemble a Gantt chart by hiding the start date series and adjusting the colors.
Can I make a Gantt chart in Excel with task dependencies?
Yes, you can include dependencies by adding a column for predecessor tasks and using formulas like WORKDAY or IF to automate start dates based on previous task completion.
What are the benefits of using a Gantt chart in Excel instead of specialized project management software?
Excel is widely accessible, easy to use, and does not require additional software purchases. While it lacks advanced features like automatic scheduling and collaboration tools, it provides a flexible and cost-effective way to track project tasks.