Course
Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) is often misunderstood.
Many people in tech assume that AutoML tools are only meant for business users or non-technical teams who do not understand how machine learning models are trained or deployed. This assumption is incorrect.
In practice, data scientists and machine learning engineers regularly use AutoML frameworks to reduce experimentation time, improve model performance, and automate repetitive stages of the machine learning lifecycle.
These AutoML tools support tasks such as feature engineering, model selection, hyperparameter tuning, and end-to-end pipeline automation, allowing teams to focus on higher-value work.
In this article, I’ll explore some of the top AutoML frameworks available today, designed for users at different levels of expertise. The tools are grouped into three clear categories:
- Open source frameworks
- No code and low code platforms
- Enterprise-grade AutoML solutions
For each framework, we highlight its key features and provide example code so you can start using it immediately.
What Are AutoML Frameworks?
AutoML refers to tools and systems that automate the entire machine learning model development process, from raw data to a trained, deployable model.
AutoML frameworks handle many of the repetitive and technical tasks involved in building machine learning models so that both expert practitioners and less technical users can work more efficiently.
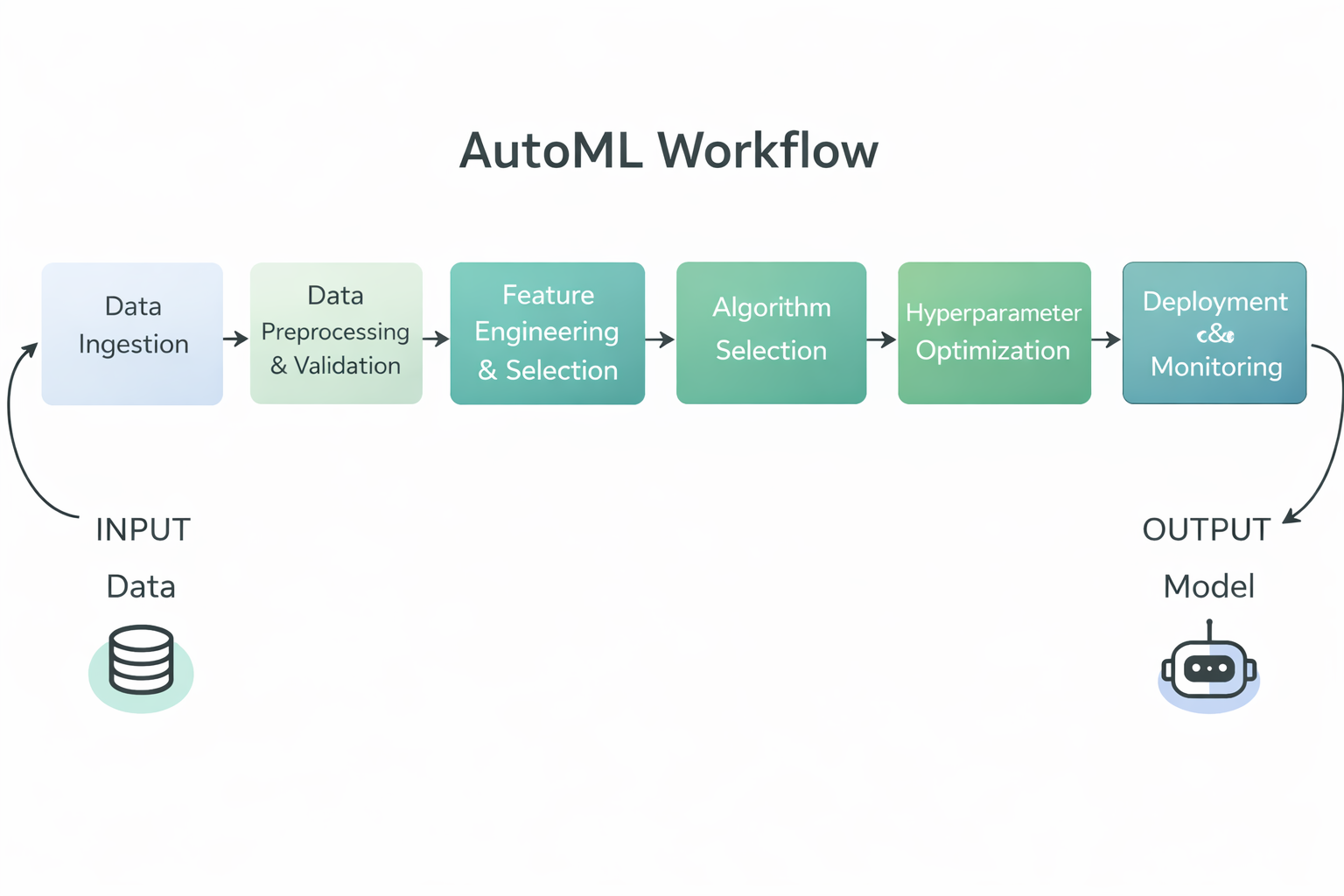
AutoML Workflow Diagram
Specifically, AutoML frameworks typically automate the following steps in the machine learning workflow:
- Data preprocessing and validation, including cleaning, normalization, and formatting of raw data for training.
- Feature engineering and selection, where meaningful input variables are created or selected automatically.
- Algorithm selection, which tests multiple model types to find the best fit for the problem.
- Hyperparameter optimization, tuning model parameters to improve performance without manual trial and error.
- Model evaluation and ranking, comparing trained models against key metrics to identify the best performer.
- Deployment and monitoring support in enterprise platforms, enabling teams to operationalize models at scale.
By automating these tasks, AutoML frameworks reduce manual effort, improve consistency and reproducibility, and make it possible for both technical and non-technical teams to build high-quality machine learning models more quickly.
Open Source AutoML Frameworks
Open source AutoML frameworks provide flexible, transparent, and developer-friendly tools that allow practitioners to automate model building while retaining full control over data, pipelines, and deployment workflows.
1. TPOT
TPOT is an open source Python AutoML framework that uses genetic programming to automatically discover and optimize complete machine learning pipelines.
It frames pipeline design as an evolutionary search problem, exploring combinations of preprocessing steps, models, and hyperparameters to identify high-performing solutions.
TPOT is especially effective for tabular data tasks where rapid experimentation and strong baselines are needed, while still allowing practitioners to inspect, export, and reuse the resulting pipelines within standard scikit-learn workflows.
Key Features:
- Genetic Programming Optimization: TPOT uses evolutionary algorithms to explore a large search space of machine learning pipelines and progressively improve them over time.
- Automated Pipeline Construction: It automatically combines preprocessing steps, feature selection methods, models, and hyperparameters into end-to-end pipelines.
- Scikit Learn Compatibility: TPOT leverages scikit-learn components, making it easy to understand, extend, and deploy the resulting pipelines.
- Customizable Search Space: Users can control which algorithms, transformations, and parameters TPOT is allowed to explore.
- Exportable Python Code: The best-performing pipeline can be exported as clean Python code for further inspection or production use.
Code Example:
This example demonstrates the minimal setup required to use TPOT. The dataset features and labels are loaded, a TPOTClassifier is initialized with default settings, and the fit method triggers the automated search process.
During training, TPOT evaluates multiple candidate pipelines using genetic programming and selects a high-performing model based on the specified evaluation metric.
import tpot
X, y = load_my_data()
est = tpot.TPOTClassifier()
est.fit(X, y)2. AutoGluon
AutoGluon is an open-source Python AutoML framework developed by AWS AI that automates machine learning tasks with a focus on high accuracy, minimal code, and support for tabular, text, and image data.
It builds a diverse set of models and uses automated model selection, hyperparameter tuning, and ensemble learning to deliver strong predictive performance across different data types.
Key Features:
- Multimodal Support: AutoGluon works with tabular data, text, images, and more, enabling versatile use cases in a single library.
- Automated Stacking and Ensembles: It combines multiple models using stack ensembling to boost accuracy beyond individual models.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: AutoGluon automatically optimizes model hyperparameters for better performance.
- Ease of Use: The high-level API lets users train powerful models with just a few lines of code.
- Robust Preprocessing: It automatically handles data preprocessing and recognizes different feature types to prepare data for model training.
Code Example:
This code loads the training and test datasets as AutoGluon tabular datasets. It then creates a TabularPredictor object specifying the target label and calls fit to train AutoGluon on the tabular training data. After training completes, it uses the trained model to generate predictions on the test set.
from autogluon.tabular import TabularDataset, TabularPredictor
label = "signature"
train_data = TabularDataset("train.csv")
predictor = TabularPredictor(label=label).fit(train_data)
test_data = TabularDataset("test.csv")
predictions = predictor.predict(test_data.drop(columns=[label]))3. FLAML
FLAML (Fast Lightweight AutoML) is an open source Python AutoML library developed by Microsoft Research that is designed to find high-quality machine learning models automatically and efficiently while minimizing computational cost and resource usage, making it ideal for environments where speed and efficiency matter most.
Key Features:
- Budget-Aware Optimization: FLAML uses cost-effective search strategies that prioritize cheaper configurations first and then explore more complex ones as needed, enabling strong performance with limited resources.
- Fast Hyperparameter Tuning: It automates hyperparameter tuning with a focus on speed and computational efficiency rather than exhaustive search.
- Support for Multiple Tasks: FLAML can handle common machine learning tasks such as classification, regression, time series forecasting, and more with minimal setup.
- Scikit-Learn Style Interface: It integrates with familiar interfaces like scikit-learn’s fit and predict, making it easy for practitioners to adopt.
- Customizable Search Space: Users can customize the estimators and search space to balance between accuracy and resource constraints.
Code Example:
This code example shows how to use FLAML’s AutoML class to perform an automated classification task on the Iris dataset, specifying a time budget and evaluation metric before training and then using the trained model to get prediction probabilities.
from flaml import AutoML
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
X_train, y_train = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
automl = AutoML()
automl_settings = {
"time_budget": 1,
"metric": "accuracy",
"task": "classification",
"log_file_name": "iris.log",
}
automl.fit(X_train=X_train, y_train=y_train, **automl_settings)
print(automl.predict_proba(X_train))4. AutoKeras
AutoKeras is an open-source AutoML library built on top of the Keras deep learning framework that automatically searches for and trains high-quality neural networks for a wide range of tasks, including structured data, images, and text, with minimal coding required.
It uses efficient neural architecture search to find suitable model architectures and hyperparameters, making deep learning more accessible to both beginners and experienced practitioners.
Key Features:
- Neural Architecture Search: AutoKeras performs automated architecture search to identify optimal neural network structures for your specific task.
- Multimodal Support: It supports structured tabular data, image data, and text data within a unified framework.
- Ease of Use: High-level APIs such as
StructuredDataClassifiersimplify training complex deep learning models with just a few lines of code. - Flexible Model Building: Users can customize search constraints and extend the search space for advanced use cases.
- Keras and TensorFlow Integration: Because AutoKeras is built on Keras and TensorFlow, it integrates seamlessly with these widely used deep learning ecosystems.
Code Example:
This code example imports necessary libraries and loads training and test datasets from provided URLs. It separates features and labels, then creates an ak.StructuredDataClassifier object that automatically searches for a strong deep learning model. The model is trained for a set number of trials and epochs, and the final evaluation result on the test set is printed.
import keras
import pandas as pd
import autokeras as ak
TRAIN_DATA_URL = "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf-datasets/titanic/train.csv"
TEST_DATA_URL = "https://storage.googleapis.com/tf-datasets/titanic/eval.csv"
train_file_path = keras.utils.get_file("train.csv", TRAIN_DATA_URL)
test_file_path = keras.utils.get_file("eval.csv", TEST_DATA_URL)
train_df = pd.read_csv(train_file_path)
test_df = pd.read_csv(test_file_path)
y_train = train_df["survived"].values
x_train = train_df.drop("survived", axis=1).values
y_test = test_df["survived"].values
x_test = test_df.drop("survived", axis=1).values
clf = ak.StructuredDataClassifier(overwrite=True, max_trials=3)
clf.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=10)
print(clf.evaluate(x_test, y_test))No-Code and Low-Code AutoML Platforms
No-code and low-code AutoML platforms simplify model development by abstracting complex workflows, enabling rapid experimentation and deployment for both technical teams and business users.
5. PyCaret
PyCaret is an open-source, low-code machine learning library in Python that automates the end-to-end machine learning workflow for tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, anomaly detection, and time series forecasting, enabling rapid prototyping with just a few lines of code while also supporting a graphical user interface for those who prefer low-code or click-through experiences.
Key Features:
- Low Code Automation: PyCaret significantly reduces the amount of code you need to write by automating the standard machine learning steps, such as data preprocessing, model training, evaluation, and selection.
- Multiple ML Task Support: It includes built-in support for a variety of machine learning tasks, including classification, regression, clustering, anomaly detection, natural language processing, and time series analysis.
- Integrated Preprocessing: PyCaret automatically performs common data preprocessing steps such as handling missing values, encoding categorical features, and scaling for models.
- Model Comparison and Selection: The
compare_modelsfunction trains and evaluates many models using cross-validation and provides a leaderboard of performance to help choose the best model. - Extensible and Integratable: It wraps established libraries (scikit-learn, XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost, etc.) and can integrate into BI tools such as Power BI, Tableau, and others.
Code Example:
This code snippet demonstrates loading a built-in dataset, initializing the PyCaret regression module with setup (which preprocesses the data and initializes the ML environment), and then using compare_models to automatically train, evaluate, and rank a variety of regression models, returning the best performing one.
from pycaret.datasets import get_data
from pycaret.regression import *
data = get_data("insurance")
s = setup(data, target="charges", session_id=123)
best_model = compare_models()6. MLJAR Studio
MLJAR Studio is a no-code and low-code AutoML environment that lets you train and compare machine learning models through a guided interface, while also offering an optional Python workflow through the open-source mljar-supervised engine.
Key Features:
- No code AutoML workflow: You can load a dataset, select features and a target, start training, and review results without writing code.
- Transparent modeling and reports: MLJAR emphasizes that it is not a black box and generates detailed reports explaining how models were built and how they perform.
- Automatic training and tuning: The AutoML engine handles preprocessing, model training, and hyperparameter tuning to find strong models.
- Model comparison with clear outputs: It trains multiple models and helps you compare them using generated summaries and performance views.
- Code optional through mljar-supervised: If you want more control, the same AutoML capabilities are available via the mljar-supervised Python package.
Code Example:
You do not need code to use MLJAR Studio because you can run AutoML through the GUI. However, the code below shows the optional programmatic approach using the mljar-supervised library. It loads a dataset, splits it into features and target, runs AutoML training, and then generates predictions using the trained model.
import pandas as pd
from supervised.automl import AutoML
df = pd.read_csv(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pplonski/datasets-for-start/master/adult/data.csv",
skipinitialspace=True,
)
X = df[df.columns[:-1]]
y = df["income"]
automl = AutoML(results_path="mljar_results")
automl.fit(X, y)
predictions = automl.predict(X)7. H2O AutoML
H2O AutoML is an open source AutoML capability within the H2O platform that provides scalable, automated machine learning with support for Python, R, and a no-code graphical interface called H2O Flow, enabling both technical and non-technical users to build, evaluate, and select models with minimal coding. Users can work through the web-based Flow interface to import data, run AutoML experiments, explore results, and export models without writing any code.
Key Features:
- Automated Model Training and Tuning: H2O AutoML automatically runs multiple algorithms, tunes hyperparameters, and generates a leaderboard of the best models without requiring manual model selection.
- No Code Web Interface: The H2O Flow graphical interface lets users interact with H2O via a browser based interface, perform machine learning tasks, and explore results without writing code.
- Support for Multiple Interfaces: In addition to the web UI, H2O AutoML can be accessed through Python and R APIs, giving flexibility for both low-code and no-code workflows.
- Automatic Preprocessing: H2O AutoML performs common preprocessing tasks such as handling missing values, encoding categorical variables, and scaling automatically.
- Model Explainability Tools: H2O offers explainability features that generate insights into model behavior and performance, helping users understand and trust model outputs.
Code Example:
This example shows how to use H2O AutoML through Python. It initializes the H2O environment, imports training and test datasets, specifies feature and target columns, starts an AutoML run with a limit on the number of models, and then displays a leaderboard ranking the best performing models.
Note: While this is the programmatic approach, the same tasks can be completed through the H2O Flow web interface without writing any code.
import h2o
from h2o.automl import H2OAutoML
h2o.init()
train = h2o.import_file(
"https://s3.amazonaws.com/h2o-public-test-data/smalldata/higgs/higgs_train_10k.csv"
)
test = h2o.import_file(
"https://s3.amazonaws.com/h2o-public-test-data/smalldata/higgs/higgs_test_5k.csv"
)
x = train.columns
y = "response"
x.remove(y)
train[y] = train[y].asfactor()
test[y] = test[y].asfactor()
aml = H2OAutoML(max_models=20, seed=1)
aml.train(x=x, y=y, training_frame=train)
aml.leaderboardEnterprise-Grade AutoML Solutions
Enterprise-grade AutoML solutions provide scalable, secure, and governed machine learning platforms designed for production deployment, compliance, and large-scale operational use.
8. DataRobot
DataRobot is an enterprise-grade no-code and low-code AutoML platform that enables business users, analysts, and data teams to build, deploy, and manage machine learning models without extensive programming.
The platform automates the full machine learning lifecycle, from data ingestion and feature engineering to model training, deployment, and monitoring, while providing strong governance, explainability, and operational controls required in regulated environments.
Key Features:
- No Code Model Development: Users can upload datasets, configure modeling tasks, train models, and generate predictions entirely through the graphical interface without writing code.
- Automated Machine Learning: DataRobot automatically explores algorithms, performs feature engineering, tunes hyperparameters, and ranks models based on performance and business metrics.
- Built-In Explainability: The platform provides global and local model explainability tools, including feature impact, prediction explanations, and compliance-ready reports.
- End-to-End MLOps: DataRobot supports model deployment, monitoring, drift detection, performance tracking, and retraining workflows within the same platform.
- Enterprise Governance and Security: The platform includes role-based access control, approval workflows, audit logs, and compliance reporting designed for regulated industries.
Code Example:
Although DataRobot is primarily used through its no-code interface, it also provides a Python API for programmatic control and automation. The example below shows how to authenticate with DataRobot, create a project from a dataset, and run AutoPilot to automatically train and evaluate models.
import datarobot as dr
dr.Client(config_path="./drconfig.yaml")
dataset = dr.Dataset.create_from_file("auto-mpg.csv")
project = dr.Project.create_from_dataset(
dataset.id,
project_name="Auto MPG Project"
)
from datarobot import AUTOPILOT_MODE
project.analyze_and_model(
target="mpg",
mode=AUTOPILOT_MODE.QUICK
)
project.wait_for_autopilot()9. Amazon SageMaker Autopilot
Amazon SageMaker Autopilot is a fully managed AutoML solution from AWS that enables users to automate the end-to-end machine learning workflow with no code or low code, especially through a web interface in Amazon SageMaker Canvas or SageMaker Studio.
Users can import data, configure the target variable, evaluate candidate models, and deploy models with a few clicks in the console, while the Python SDK and APIs remain available as an optional way to make experiments reproducible or to integrate with other systems.
Key Features:
- Web-Based No-Code Workflow: Most tasks, such as dataset upload, experiment setup, model training, evaluation, and deployment, can be done through the web interface in SageMaker Canvas or SageMaker Studio without writing code.
- Automated Data Analysis and Preprocessing: Autopilot examines the dataset for problem type, cleans and preprocesses it, and engineers features to prepare for model training.
- Model Selection and Optimization: Autopilot explores multiple machine learning algorithms and tunes hyperparameters to find high-performing models, then ranks them on a leaderboard.
- Explainability and Insights: The platform provides visibility into the models it generates, including how features influence predictions and comparative performance.
- Production Deployment: Users can deploy the selected model directly from the interface with minimal steps, generating endpoints for inference.
Code Example:
The code below shows how to run Amazon SageMaker Autopilot programmatically using the Python SDK. This approach is optional and can be used to reproduce results or integrate into automated pipelines.
from sagemaker import AutoML, AutoMLInput
automl = AutoML(
role=execution_role,
target_attribute_name=target_attribute_name,
sagemaker_session=pipeline_session,
total_job_runtime_in_seconds=3600,
mode="ENSEMBLING",
)
automl.fit(
inputs=[
AutoMLInput(
inputs=s3_train_val,
target_attribute_name=target_attribute_name,
channel_type="training",
)
]
)10. Google Cloud AutoML
Google Cloud AutoML is part of Vertex AI, Google Cloud’s unified machine learning platform that enables users to build, train, evaluate, and deploy high-quality models using fully managed infrastructure.
Vertex AI AutoML supports tabular data, natural language processing, computer vision, and video tasks, and is designed to be accessible through a no-code web interface in the Google Cloud Console.
All core steps, such as dataset creation, task selection, training, evaluation, and deployment, can be completed through the UI without writing any code.
Key Features:
- No Code Web Interface: Users can upload datasets, configure AutoML tasks, train models, review metrics, and deploy models entirely through the Vertex AI Console.
- Support for Multiple Data Modalities: AutoML supports tabular classification and regression, image classification and detection, text classification and extraction, and video analysis.
- Automated End-to-End Training: Vertex AI AutoML handles preprocessing, feature engineering, model architecture selection, and hyperparameter tuning automatically.
- Managed Infrastructure: All training and deployment runs on Google-managed infrastructure with built-in scaling and resource management.
- Production Ready Deployment: Trained models can be deployed directly from the UI as endpoints for online or batch predictions.
Code Example:
Although Vertex AI AutoML is primarily designed for no-code workflows, the Python SDK can be used to make experiments reproducible or integrate AutoML training into automated pipelines.
The following short snippet initializes a Vertex AI project, creates an image dataset from a CSV index stored in Cloud Storage, and launches an AutoML image training job.
from google.cloud import aiplatform
aiplatform.init(
project="YOUR_PROJECT_ID",
location="us-central1",
staging_bucket="gs://YOUR_BUCKET",
)
dataset = aiplatform.ImageDataset.create(
display_name="flowers",
gcs_source=["gs://cloud-samples-data/ai-platform/flowers/flowers.csv"],
import_schema_uri=aiplatform.schema.dataset.ioformat.image.single_label_classification,
)
training_job = aiplatform.AutoMLImageTrainingJob(
display_name="flowers_automl",
prediction_type="classification",
)
model = training_job.run(
dataset=dataset,
model_display_name="flowers_model",
budget_milli_node_hours=8000,
)AutoML Framework Comparison Table
This table compares popular AutoML frameworks based on their level of automation, interface style, and suitability for open source experimentation, low-code workflows, and enterprise-scale deployment.
|
Framework |
Category |
Code Level |
Interface Options |
Primary Use Case |
|
TPOT |
Open Source |
High |
Python API |
Automated pipeline discovery and optimization for tabular data |
|
AutoGluon |
Open Source |
Low |
Python API |
Fast, high-accuracy production-ready models across modalities |
|
FLAML |
Open Source |
Low |
Python API |
Cost-efficient and resource-aware model tuning |
|
AutoKeras |
Open Source |
Medium |
Python API |
Neural architecture search and deep learning automation |
|
PyCaret |
Low Code |
Very Low |
Python API, optional GUI tools |
Rapid experimentation and analytics-driven workflows |
|
MLJAR Studio |
No Code |
None |
Web UI, optional Python |
Business-friendly AutoML experimentation and model comparison |
|
H2O AutoML |
Hybrid |
Low |
Web UI (H2O Flow), Python, R |
Scalable AutoML for large datasets and enterprise deployment |
|
DataRobot |
Enterprise |
None to Low |
Web UI, Python API |
Enterprise ML with governance, explainability, and MLOps |
|
SageMaker Autopilot |
Enterprise |
None to Low |
AWS Console, Python SDK |
AWS native AutoML integrated with production pipelines |
|
Google Cloud AutoML |
Enterprise |
None |
Vertex AI Console, optional SDK |
Vision, NLP, and tabular AutoML on managed GCP infrastructure |
Final Thoughts
AutoML frameworks have matured into production-grade tools that support teams across the entire machine learning lifecycle. In practical settings, they are not limited to experimentation or prototyping.
I have used AutoML frameworks to participate in Kaggle competitions, to build complete end to end machine learning pipelines for real projects, and even to prepare for and succeed in technical interviews.
From a data scientist’s perspective, AutoML is a powerful way to establish a strong and unbiased baseline model with very little overhead.
By simply providing the data, these frameworks take care of feature engineering, model selection, hyperparameter tuning, and evaluation. This allows practitioners to focus on understanding the problem, validating assumptions, and improving results, rather than spending excessive time researching and testing models from scratch.
AutoML does not replace expertise. Instead, it accelerates the workflow by providing a reliable starting point that can be iteratively improved.
Building the model is only step one. Learn how to deploy and monitor your AutoML models in production with the MLOps Concepts course.
AutoML FAQs
Will AutoML replace data scientists?
No. AutoML automates repetitive tasks like model selection and hyperparameter tuning, but it cannot replace human judgment. Data scientists are still essential for defining the business problem, interpreting results, ensuring ethical AI practices, and handling complex feature engineering that requires deep domain knowledge.
Is AutoML only for non-technical users?
Not at all. While "no-code" platforms empower business analysts, many AutoML frameworks (like TPOT, AutoGluon, and FLAML) are code-first tools designed specifically for data scientists. Experts use them to rapidly establish baseline models, saving hours of manual trial-and-error so they can focus on higher-level optimization.
When should I choose traditional Machine Learning over AutoML?
Choose traditional (manual) machine learning when you need absolute control over the model architecture, when you are working with highly unstructured or unique data types that AutoML struggles to process, or when "explainability" is critical and you need to know exactly why a model makes a specific prediction (avoiding the "black box" problem).
Is AutoML expensive to run?
It depends. Enterprise platforms (like Vertex AI or DataRobot) often charge based on compute time or subscription tiers, which can get costly for large datasets. However, open-source libraries (like TPOT or H2O) are free to use, meaning you only pay for the infrastructure (laptop or cloud server) you run them on.
Can AutoML handle messy or raw data?
To an extent. Most AutoML tools can handle basic cleaning, such as imputing missing values or scaling features. However, they generally cannot fix fundamental data quality issues (like incorrect labels or biased sampling) or perform complex, domain-specific feature engineering. "Garbage in, garbage out" still applies.

As a certified data scientist, I am passionate about leveraging cutting-edge technology to create innovative machine learning applications. With a strong background in speech recognition, data analysis and reporting, MLOps, conversational AI, and NLP, I have honed my skills in developing intelligent systems that can make a real impact. In addition to my technical expertise, I am also a skilled communicator with a talent for distilling complex concepts into clear and concise language. As a result, I have become a sought-after blogger on data science, sharing my insights and experiences with a growing community of fellow data professionals. Currently, I am focusing on content creation and editing, working with large language models to develop powerful and engaging content that can help businesses and individuals alike make the most of their data.

