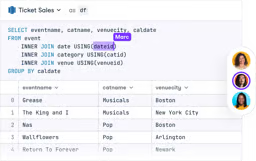
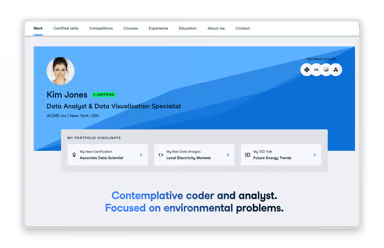
When searching for a job in the data field, your resume or CV will only tell employers so much. It’s one thing to claim to have strong communication skills, proficiency in multiple coding languages, and advanced knowledge of machine learning workflows. It’s quite another to demonstrate these qualities with a selected body of your work.
A data science portfolio is a powerful tool for showcasing your work and providing concrete evidence of your abilities. In this article, we will cover the types of projects you can use in your portfolio and advice on building one. In follow-up articles, we will go into greater detail about how to create two portfolio projects: an analytics project and a machine learning project.
What is a Data Science Portfolio?
A data science portfolio is a curated collection of one or more projects that you use to demonstrate your data skills. These projects can take various forms and are not limited to technical analyses. Below are some examples of projects you can consider including in your portfolio.
Portfolio project examples
- Analyze a sales dataset, providing insights on trends, sales figures, and popular products with a heavy emphasis on visualization.
- Perform an A/B test analysis to compare the effectiveness of an intervention in a business setting.
- Use online product reviews to perform natural language processing tasks like sentiment analysis or topic modeling.
- Use a dataset to create a data application, such as an interactive dashboard.
- Create a video tutorial on a new package or tool.
- Write an article on a trending topic in the data field.
- Use a machine learning algorithm to solve a particular problem, such as predicting customer churn or segmenting customers.
This is by no means an exhaustive list. As we will cover in the next section, you should choose projects tailored to your skills and the roles you are targeting.
Tip: To brush up on your knowledge, be sure to browse our catalog of DataCamp courses!
What Makes a Good Portfolio?
A portfolio should demonstrate your best qualities and be relevant to the roles you are applying for. Here is a list of 5 things to remember when creating your portfolio.
Cover a range of abilities
For most data-related jobs, you will do more than just crunch numbers. You will need to perform tasks such as visualizing results, communicating findings, and mentoring others. Ensure that your portfolio shows you are versatile and strong across the board. This does not mean every project has to contain every skill you possess. Your abilities can be distributed across your portfolio.
Keep your audience in mind
Who is going to be reviewing your portfolio? Your projects should be accessible to less technical audiences while also providing enough depth for those who do possess technical skills. Your projects should be easy to follow and provide a pleasant user experience. A clear introduction describing the purpose of the project and the methodologies used can be a great way to guide readers through your work.
Curate your portfolio
A portfolio is not a parking lot for every data project you have ever started. The projects in your portfolio should be strong examples of the professional output employers could expect from you. Each piece of work should be carefully reviewed and edited until you are satisfied that an employer would be impressed with your abilities. Aim for a fewer number of high quality projects.
Be memorable
It is easy to be lost in a sea of projects. Make sure your projects create a lasting impression on readers. Your projects should tell a compelling story, with a clear motivation and question/problem you are trying to solve. Ensure that your projects are aesthetically pleasing and show off a personal style. Finally, create content that is new and exciting. Another analysis of Titanic survivors is unlikely to spark someone’s curiosity.
Highlight relevant skills
Your portfolio should match what you include in your CV and align with the skills required for the roles and opportunities you are pursuing. If you are applying for a role that requires strong knowledge of SQL, at least one of your projects should contain evidence of this. If you claim to have excellent data visualization skills, take extra care that your visualizations are top-notch.
Want some more tips on how to develop a strong portfolio? Be sure to check out a previous blog entry which goes into even greater depth on how to make your work shine, including tips on storytelling and your personal brand.
Build your data portfolio
Showcase your skills and projects in minutes.
How to Use DataCamp Workspace to Create a Portfolio
DataCamp Workspace is a tool that has been developed with portfolios in mind. Here are some steps that you can use to leverage Workspace to create a portfolio that will get you hired.
Create a new workspace
You can create an empty workspace from the Workspace dashboard or use one of our curated datasets. Workspaces can be created in either Python or R, and both have the ability to connect to SQL databases. If you don’t have access to a SQL database, Workspace has several sample databases for you to start from now offers the ability to query DataFrames and CSVs.
Begin your project
Time to start your project! Be mindful that your project helps meet the criteria in the section above and reflects your skills, interests, and abilities. In a later article, we will go into greater depth on creating a portfolio project in Workspace, but here are some general tips to get the most out of Workspace.
- Where it makes sense, include text cells to guide readers through the project.
- Ensure your code is easy to read and contains code comments that explain your process if it’s not obvious.
- Spruce up your workspace by including images, such as a header at the top of the project.
- Make use of our no-code chart cells to effortlessly create visually-appealing interactive visualizations.
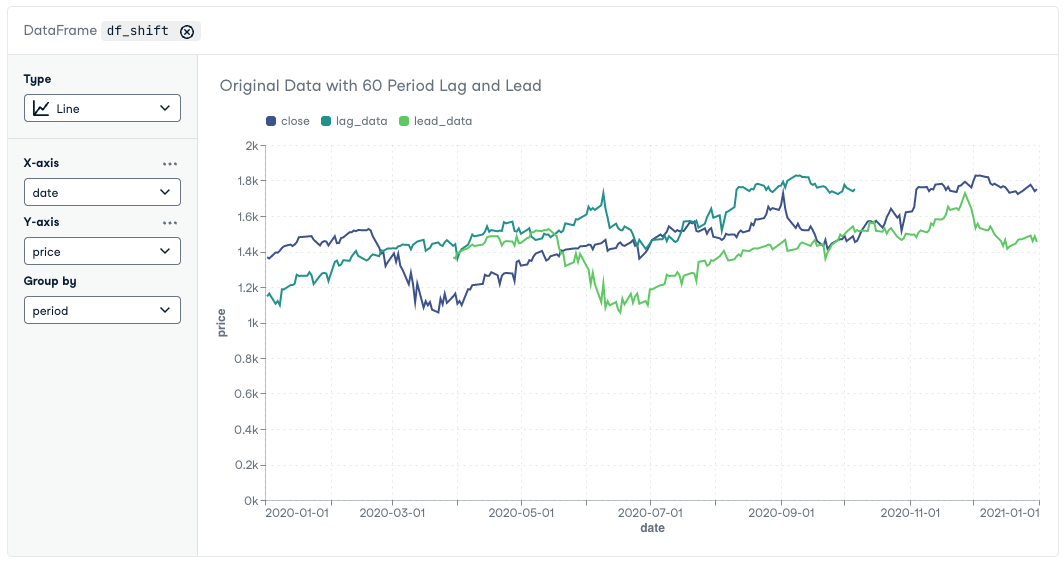
A chart rendered with a Workspace Chart Cell (link to image)
Tidy Up Your Workspace
Edit and proofread your work
Correct typos, ensure plots are clearly labeled, and ensure your workspace is aesthetically pleasing. You may want a friend or colleague to help you out. Another pair of eyes will often catch things that you miss.
Alternatively, you can take advantage of the AI features inside Workspace to proofread your written work. Below, we have used the “Generate” button on a text cell to catch all of the typos in the cell.
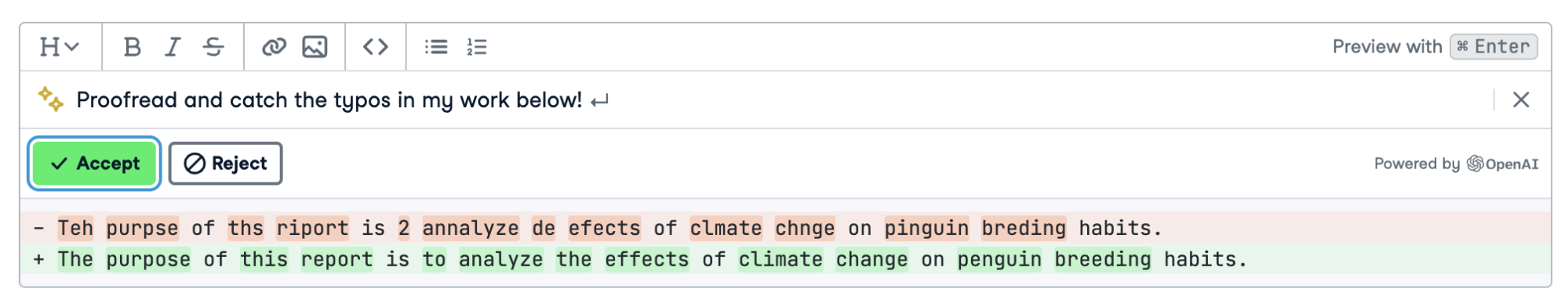
The generate text function in action! (link to image)
Format your written content
Workspace offers a wide range of text formatting tools, which allows you to do things such as add titles, headings, and lists. Headings will also generate a table of contents in your published report, allowing readers to navigate the project easily.
Hide code cells and output that aren’t integral to the report
In some cases, you may be targeting a non-technical audience. In this case, lengthy blocks of code may interrupt the flow of the report. Fortunately, with Workspace, you can use the “Hide code” and “Hide output” buttons to hide these sections in your final report. Hiding output can also be useful when you install additional packages.

Hide code and Hide output options on a Workspace code cell
Add the workspace to your DataCamp Portfolio
Once you're ready to show your work to the world, adding the workspace to your portfolio is easy.
In the editor, click on "Share" and enable the "Add to portfolio" toggle.
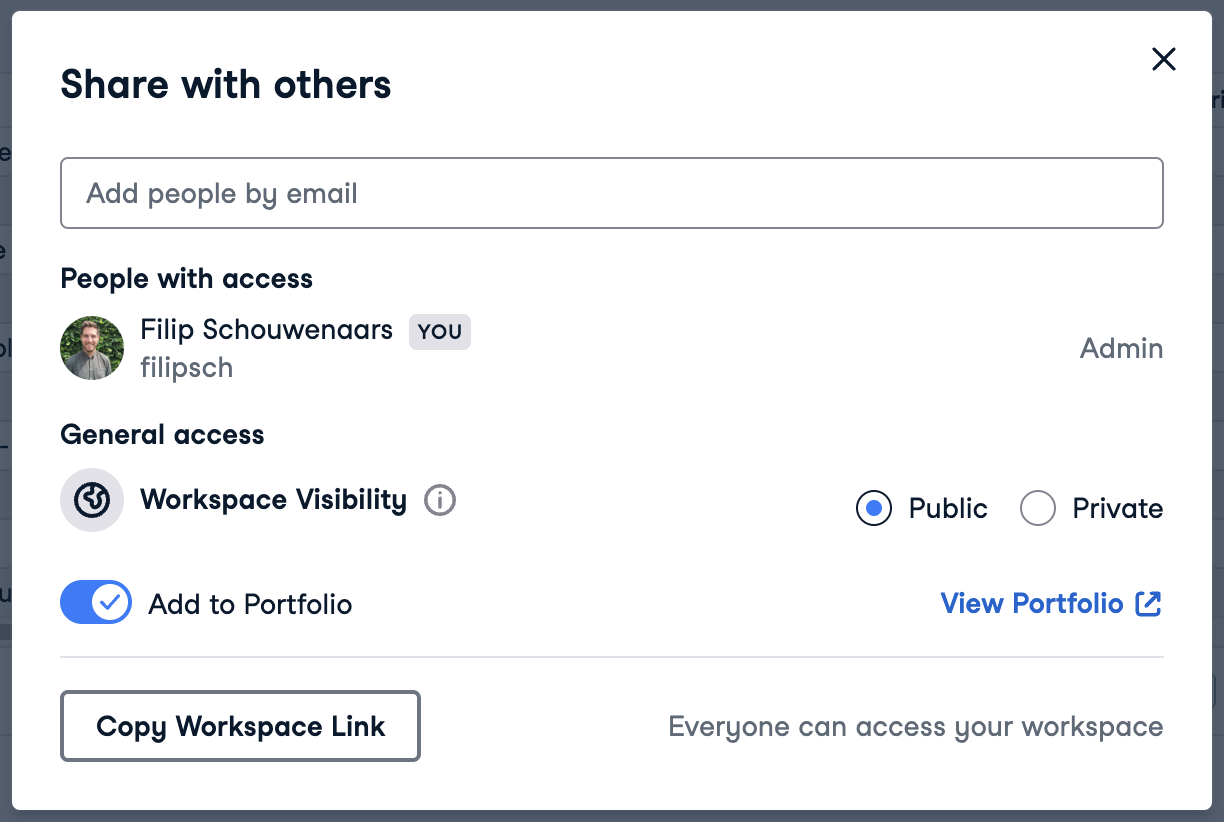
You can also add a workspace through the dropdown in your workspace overview.
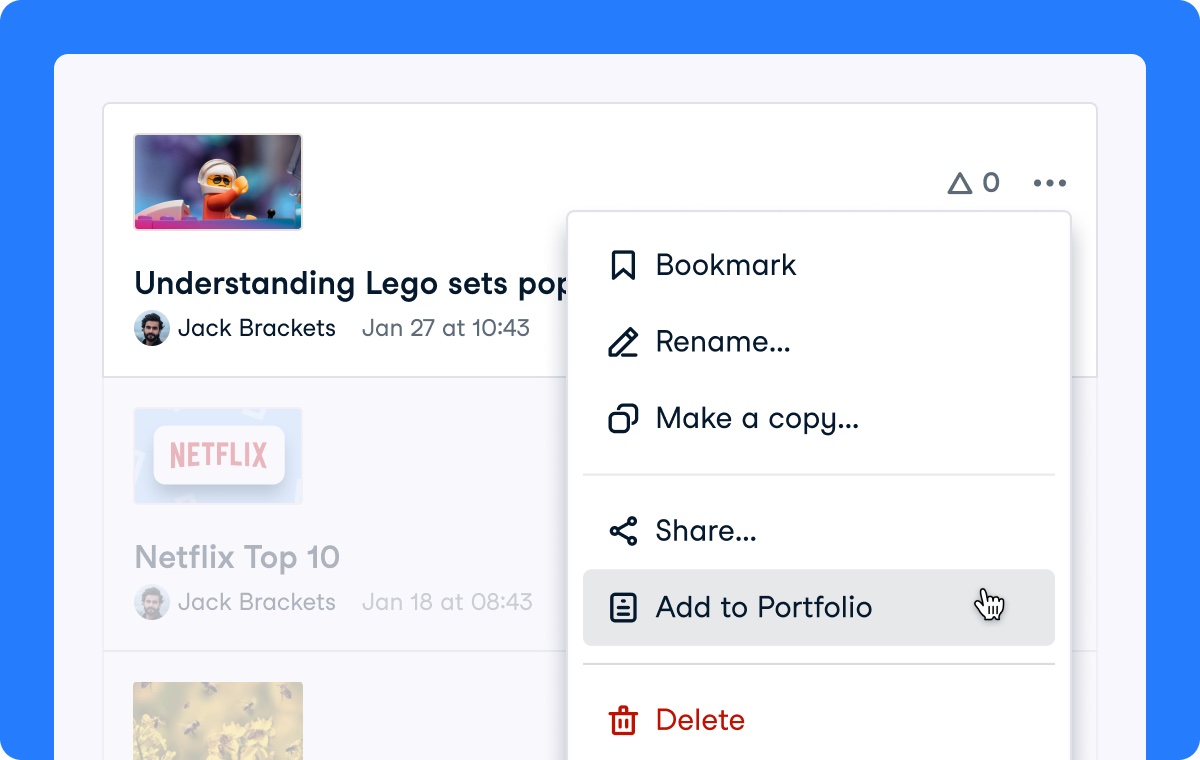
Your workspace is now available on your very own DataCamp portfolio, available for the world to see!
Next steps
In subsequent articles, we will go into greater depth. Find the second part in the series here! We cover topics such as constructing an analytics and machine learning portfolio project. In the meantime, we encourage you to explore DataCamp Competitions. Start by exploring past winning entries. There you can see how users have leveraged Workspace to build award-winning analyses that make for excellent portfolio projects.
After that, why not participate in a competition yourself? It's a great way to practice your data science skills on real-world problems, get feedback from other DataCamp learners, and start building out your own portfolio.
Additional Resources
Still want to know more about creating a great portfolio? Be sure to listen in to this DataFramed podcast where guest and author Nick Singh goes over the characteristics of a great data science portfolio.
You can also check out our recent webinar Tips for Buliding a Data Science Portfolio with DataCamp, including our own Head of DataCamp Workspace Filip Schouwenaars!
DataLab
Skip the installation process and experiment with data science code in your browser with DataLab, DataCamp's AI-powered notebook.