Course
In today's data-driven world, organizations often struggle with the challenge of managing data spread across different teams and systems. Sales, finance, HR—each department might have its own tools and data sources, leading to silos that make it difficult to get a unified view.
To address these issues, data engineers often need to build and maintain an intricate web of data pipelines that copy, combine, and transform data to provide it to each department. As the number of teams and data sources grows, this intricate plumbing becomes increasingly burdensome to set up and maintain, which can lead to failures.
The data fabric concept was conceived as a holistic solution to these problems. Let’s explore this architectural solution for integrated data management.
If you want to learn more about data management, check out this article about data lineage.
What Is Data Fabric?
Data fabric is a broad data architecture system that allows for the seamless integration and management of data across a variety of environments. Think of it as a way to connect disparate data sources virtually without the need for redundant copies.
By knitting together these disparate data sources, a data fabric creates a unified framework where you can ensure consistent delivery, governance, and security of data, regardless of where it resides.
Unlike a traditional data pipeline, data fabric doesn’t copy data from different sources into a central repository. Instead, it leverages APIs and virtualization to allow data analysts and scientists to access data stored in different locations from one central catalog. This means less storage space is necessary because there is only one copy of the data.
Additionally, by creating a cohesive data infrastructure, the data fabric ensures that data is easily accessible, well-governed, and secure throughout its lifecycle.
Benefits of Data Fabric
The simplicity of a data fabric architecture offers numerous benefits for large organizations.
Eliminates data silos and improves access
By providing a unified data access layer, data fabric eliminates data silos, making it easier for data users, like analysts and accountants, to access and leverage data from across the organization. By putting all of your organization’s datasets into one central catalog, you can easily see and access all of the data.
Of course, this does not mean you must share all of your organization’s data with every employee. You still can—and should—implement role-based authentication measures to ensure security in your system.
Better consistency and quality management
Data fabric often improves data quality and consistency across your organization. By simplifying the backend of the automated data pipelines and standardizing governance frameworks, you can ensure that all your data remains clean, consistent, and accurate, which is crucial for making reliable business decisions.
Learn more about data quality in this Introduction to Data Quality course.
Improves governance compliance and security
Data fabric principles incorporate robust security measures and governance policies early in the data pipeline, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and protecting sensitive information. This comprehensive approach to data security reduces risk and enhances trust in the data being used. A simpler system is easier to secure.
Learn more about the subject in this Data Governance Concepts course.
Facilitates faster data-driven decisions
Most importantly, data fabric increases your organization’s agility in data-driven decision-making. By simplifying data management and providing real-time access to reliable data, data fabric enables organizations to be more responsive to changes in the data and make informed decisions quickly.
Data Fabric: Core Principles
The data fabric architecture style has three core principles: unified access, standardized governance, and automation.
A data fabric should include a logical data layer for unified data access. This layer abstracts the underlying data infrastructure, providing a seamless and unified interface for data access across diverse sources. Essentially, you want everyone who needs access to your organization’s data (analysts, scientists, ML ops, etc.) to have access to all the data they need in a unified manner.
Another principle of creating a data fabric is having standardized data governance and security. This ensures that all of your organization’s data assets adhere to uniform governance and security protocols. This standardization enhances reliability and regulatory compliance across your organization.
Data fabrics also use automated data pipelines on the backend for efficient data movement and transformation. This automation streamlines the process of moving, cleaning, and transforming data in the fabric's backend. It allows for real-time data processing, increasing efficiency and reducing manual effort.
Data Fabric: Key Components
There are several key components that make up a data fabric architecture. Let's discuss some of them.
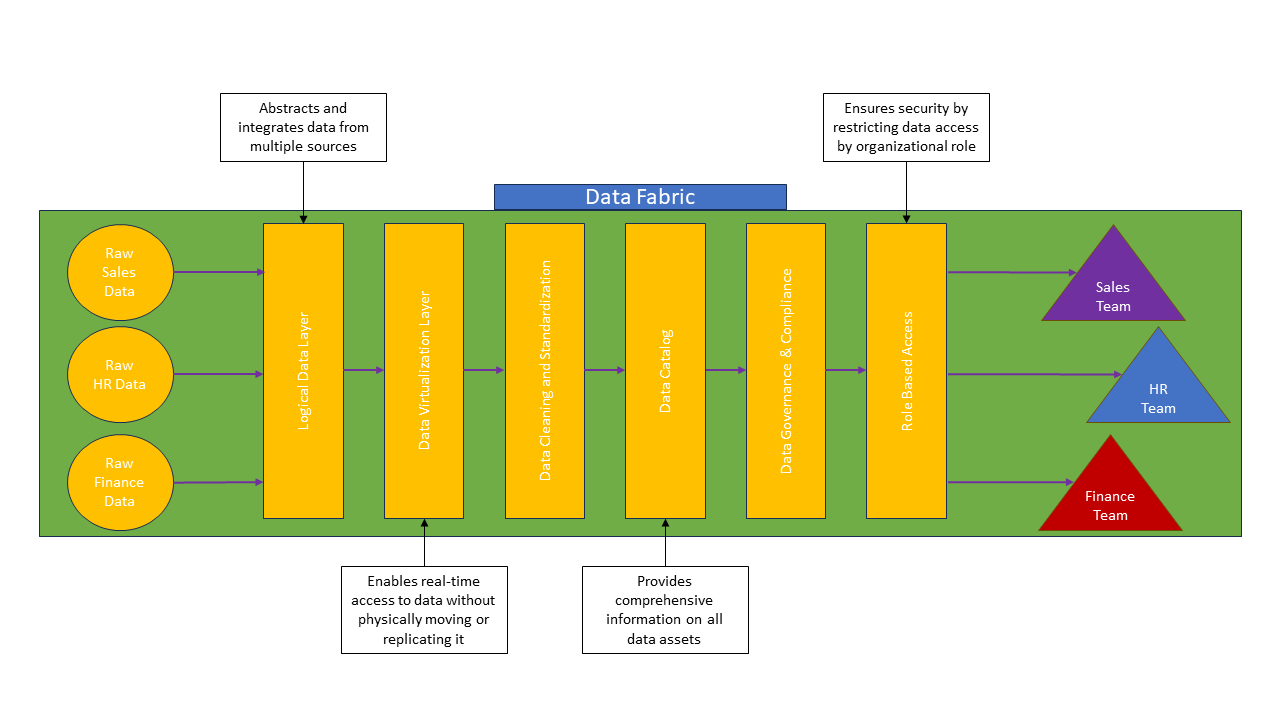
Data catalog
One of the most critical components of a data fabric is the data catalog. This is a central registry of all of your organization’s data assets. It provides metadata and lineage information to facilitate data discovery and management, ensuring users can easily find and understand the needed data.
Data integration tools
Data integration tools are another essential component. These enable the seamless movement of data between different systems and platforms. Data integration tools include ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) platforms, data integration frameworks, cloud-based integration services, and real-time data streaming solutions. These tools ensure that data is readily available wherever needed, enhancing overall data accessibility.
Transformation
Transformation services play a vital role in data fabrics, as they do in any pipeline solution. They clean, transform, and prepare data for analysis, performing tasks such as data cleansing, normalization, aggregation, and enrichment.
Data governance
The data governance framework is also crucial, as it ensures data quality, security, and compliance through policies and procedures that manage data throughout its lifecycle. Governance activities may include establishing data stewardship roles, implementing data quality checks, redacting sensitive information, enforcing role-based access controls, and ensuring regulatory compliance through regular audits.
One of the benefits of a data fabric framework is the ability to easily standardize these governance protocols across your entire data landscape. This helps maintain the integrity and reliability of your data.
In a data fabric architecture, each of these key components is woven together to create a unified experience. Data from disparate sources is integrated, transformed, and cataloged. Governance protocols are enforced throughout to ensure a safe, secure data environment.
Data Fabric vs. Traditional Data Management
Data management often unfolds organically in an organization as it grows and new data sources and teams develop. Each new data source requires a new pipeline to be built, and each new team may use its tools, naming conventions, and governance protocols.
This traditional data management approach has many limitations. Switching to a data fabric framework involves a complete rethinking of the way data gets from its sources to the users who need it throughout your organization.
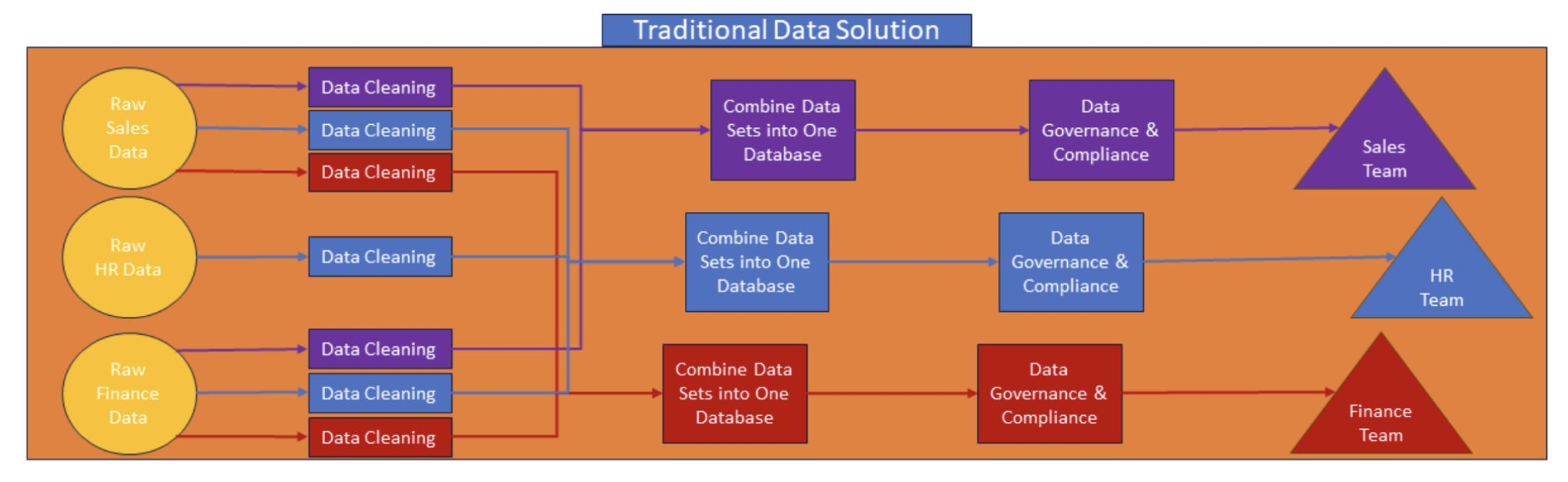
Limitations of traditional approaches
The traditional data management approach results in multiple siloed data systems where data is stored and managed in separate, isolated repositories. This method often involves point-to-point integrations between systems, leading to a complex web of connections and pipelines that are cumbersome to maintain.
In this design, each system might have its own database, transformations, and access controls. This makes it challenging to access all of the data at once to see a unified view of data across your organization.
This complexity is inefficient and opens the door to errors. Traditional systems also make it difficult to maintain data quality and consistency, leading to unreliable data and a decrease in trust in your organization’s data.
Traditional data management systems also have limited scalability, in part because many copies of the same data use up valuable storage space. They struggle to adapt to evolving data needs within the organization. Essentially, these legacy systems simply become too bulky, scattered, and redundant, making it difficult to keep up with the pace of business innovation.
Advantages of data fabric
A data fabric offers significant advantages over these traditional approaches. It provides a unified data platform for all data needs, consolidating data from various sources into a single, cohesive platform. This unification simplifies data management and improves organization.
Data fabric also enables better data governance and regulatory compliance. Because the data fabric framework consolidates all your data into one data catalog, standardizations can be applied across your entire data landscape. Standardized governance and security measures ensure all your data is in compliance with regulatory standards, such as HIPPA and FCRA, reducing risks and enhancing trust in your data.
|
Data Fabric |
Traditional Data Management |
|
|
Scalability |
Scales efficiently with growing data |
Limited scalability due to silos |
|
Governance |
Standardized governance and security |
Often lacks uniform governance |
|
Security |
Centralized security measures |
Security fragmented across systems |
|
Agility |
Enables quick, data-driven decisions |
Slower decision-making processes |
Data Fabric Use Cases
Data fabric enhances data capabilities across many organizational contexts. It can replace legacy data systems in large organizations where data management has become cumbersome.
Data fabrics can also be used at the beginning of an organization’s life to create a unified data program and prevent future data management issues.
One significant use case for data fabric is in Master Data Management (MDM). By creating a single source of truth for critical data, data fabrics ensure centralized management of master data. This centralization is essential for maintaining reliable and efficient business operations, ensuring consistency and accuracy in key data sets. You can read more about this model HERE.
For data analytics and business intelligence, data fabric provides fast access to trusted data, empowering organizations to make informed decisions quickly and effectively. Data fabric enhances the quality and speed of analytics processes by ensuring that data is readily available and reliable.
Data fabrics also ensure regulatory compliance. They enable standardized governance and protocols across the organization, simplifying adherence to data privacy regulations. This consistent data governance reduces the complexity of regulatory compliance, helping organizations protect their reputations and avoid costly penalties.
Data Fabric vs. Data Mesh
In the data world, there are many words and terms that sound alike. Let’s look at one that sounds very similar to data fabric: data mesh.
Data mesh
Data mesh is another approach to data management that has distinct characteristics. It focuses on the temporary integration of data from various sources for immediate analysis. This makes data mesh ideal for quick explorations and one-off reports, providing flexibility for simple and immediate data needs.
Unlike a data fabric, a data mesh encourages data decentralization and domain autonomy in governance. However, it has limitations, including data quality concerns and security considerations. It is not designed for long-term storage and comprehensive data management.
Data fabric
Data fabric offers a holistic approach to managing all data within an organization. It provides a comprehensive and integrated platform for data management. This includes data access, governance, security, and integration. Data fabric is suitable for long-term data management and continuous data-driven decision-making.
While data fabric implementation can be complex and requires careful selection of compatible tools and technologies, its benefits in terms of data unification, governance, and agility make it a powerful solution for many organizations' data management needs.
Implementing Data Fabric
So if you’ve decided that a data fabric architecture is useful for your organization, you may be wondering how to get started. Let’s go over a few initial steps.
Assessing your needs
Implementing data fabric in your organization begins with assessing your needs. Data fabrics are not a one-size-fits-all approach. Think of it more like a custom solution tailored to your organization’s data needs. This makes it essential that you evaluate your current data landscape and identify challenges before designing a data fabric.
The first steps in implementation are talking with stakeholders to understand the existing data infrastructure, identify pain points, and determine the specific challenges you aim to address with the data fabric.
Next, you need to define your business goals and desired outcomes from the data fabric. Are you trying to create a single source of truth? Reduce overhead costs? Replace old, failing infrastructure? Establishing clear objectives and outcomes that align with your organizational goals will help guide you and ensure that the data fabric you create meets your specific needs.
Choosing the right tools and technologies
Once you know the direction you want to take, you need to choose the tools you will use to get there. Choosing the right tools can seem a little overwhelming, but it is an important step.
One option is to use an all-in-one solution, like Microsoft’s Azure Service Fabric or IBM Cloud Pak. These provide every tool you need to incorporate a data fabric architecture into your organization. They do a lot of the heavy lifting for you and can simplify billing by only paying for one product. Check out this article on what Microsoft Fabric is for an in-depth look.
However, some organizations may need, or prefer, a more custom setup. You can create your own data fabric architecture by using a combination of off the shelf tools like:
- Apache Kafka for real-time data streaming and integration.
- Talend for comprehensive ETL processes.
- Informatica for data integration, data quality, and governance.
- Apache Spark for large-scale data processing and analytics.
- Databricks for collaborative data engineering and machine learning.
- Alation or Collibra for data cataloging and governance.
When choosing which technologies to use, consider their scalability, security, and compatibility with existing infrastructure in your organization. Ensure that the chosen solutions can scale with your needs, provide robust security, and integrate with your current systems.
It is also wise to consider their longevity. New technologies may be fleeting, and you may need to make major changes if your tool of choice becomes unsupported. Similarly, custom-built solutions may face challenges if there are changes in the team that developed them.
Data governance and change management
Implementing a data fabric into your organization will require robust data governance and change management strategies, especially if you used a different architecture for a long time and are now changing to a data fabric architecture. Careful planning will help you ensure a successful transition across your organization.
It’s important to establish clear data ownership, access control, and security policies. This involves defining who is responsible for data at each stage of its lifecycle, setting permissions for who can access and modify data, and implementing security measures to protect sensitive information. These policies will help you maintain data integrity, ensure compliance with regulations, and safeguard against data breaches.
You should also outline specific roles and responsibilities for data management. Depending on your situation, this might include designating data stewards who oversee data quality, data custodians who manage data storage and access, or committees to enforce data governance. Clearly defined roles will help to ensure accountability in data management processes.
It is crucial that you develop a plan for adoption and training on the new system throughout your organization. Introduce potential users to the new data fabric system through training sessions or workshops, and make sure you have adequate documentation people can reference.
It often takes people a while to adapt to new systems. Having some understanding and grace for your coworkers during this transition will help everything go smoother. You will likely need to provide ongoing support to address any issues or questions that arise during the transition and the period right after.
The Future of Data Fabric
As with most current technologies, the future of data fabric is set to be transformed by advancements in automation and machine learning. Automated intelligence will likely enhance data integration through context-aware workflows and self-healing pipelines that detect and optimize performance in real-time. AI-driven insights could offer predictive analytics and intelligent data catalogs, making data management more proactive and efficient.
Blockchain technology may be integrated to provide immutable data provenance and automate governance tasks via smart contracts.
As edge computing grows, data fabrics might manage decentralized data processing across edge devices and cloud services.
Advancements in quantum computing may introduce quantum-safe encryption and accelerate complex data transformations.
As these technologies continue to evolve, data fabric may become a critical asset, providing the foundation for intelligent, data-driven operations across industries.
Conclusion
Data fabric represents a transformative approach to data management. It’s an architectural structure that seeks to address the challenges of data siloing, quality, and governance. By breaking down barriers to data access and fostering a unified data environment, data fabrics can support data-driven decision-making in large organizations.
Learn more about Responsible AI Data Management and Making Data Governance Fun with DataCamp. Or dive deeper into data storage and management with DataCamp’s Introduction to Data Warehousing course.

I am a PhD with 13 years of experience working with data in a biological research environment. I create software in several programming languages including Python, MATLAB, and R. I am passionate about sharing my love of learning with the world.

