Track
OpenAI has just released Deep Research, an AI agent powered by a version of the upcoming o3 model. It’s designed to browse the web, analyze multiple sources, and synthesize large amounts of information.
You might be wondering: Doesn’t ChatGPT already do this?
Unlike a regular ChatGPT session that generates quick responses, Deep Research can conduct multi-step investigations, reference multiple sources, and produce structured reports.
For instance, if you’ve ever researched the best car to buy—comparing reviews, weighing costs, etc.—you know that finding reliable information takes time and a lot of Internet browsing. Deep Research is built for exactly this kind of work.
I’ve tested Deep Research, and I’ve been both amazed and disappointed. It shows great potential, but it also produces incorrect facts and inferences. In this blog, I’ll be your human agent and summarize everything you need to know about Deep Research. I’ll walk you through practical examples, share prompting tips, and show you where Deep Research shines—and where you need to be extra careful.
What Is OpenAI’s Deep Research?
OpenAI’s Deep Research is an AI-powered agent designed to conduct in-depth, multi-step research on the Internet. Unlike standard ChatGPT browsing capabilities, which provide quick responses, Deep Research autonomously finds, analyzes, and synthesizes information from hundreds of online sources.
Deep Research is designed for anyone who needs comprehensive and reliable research, including:
- Professionals in finance, science, policy, and engineering who need well-cited, structured reports
- Business strategists conducting competitive analysis or trend forecasting
- Researchers and students gathering information from multiple sources
- Shoppers and consumers making high-stakes purchasing decisions (e.g., cars, appliances, real estate)
- Writers, journalists, and analysts who require fact-checked, multi-source insights
Essentially, if a task involves browsing multiple sources, cross-referencing data, and synthesizing information into a useful format, Deep Research is the tool for the job.
How Does Deep Research Work?
Powered by a version of the upcoming o3 model, Deep Research builds on OpenAI’s advancements in reasoning models but is specifically optimized for web browsing and real-world data analysis.
To achieve this, OpenAI trained Deep Research using reinforcement learning on real-world browsing and reasoning tasks. This allows the model to follow an iterative, step-by-step research process, improving its ability to synthesize complex topics into structured reports.
Deep Research Benchmarks
Humanity’s Last Exam
Humanity’s Last Exam is a newly released benchmark designed to test AI on expert-level multiple-choice and short-answer questions across over 100 subjects, from linguistics and rocket science to ecology and mathematics. This evaluation measures an AI’s ability to reason across disciplines and seek out specialized knowledge when needed—a critical skill for research-oriented models.
Deep Research achieved a record 26.6% accuracy, far surpassing previous models, including OpenAI’s own o1 (9.1%), DeepSeek-R1 (9.4%), and Claude 3.5 Sonnet (4.3%). Notably, the largest improvements over OpenAI’s o1 were seen in chemistry, humanities and social sciences, and mathematics, where Deep Research demonstrated its ability to break down complex questions and retrieve authoritative information.
|
Model |
Accuracy (%) |
|
GPT-4o |
3.3 |
|
Claude 3.5 Sonnet |
4.3 |
|
Gemini Thinking |
6.2 |
|
OpenAI o1 |
9.1 |
|
DeepSeek-R1* |
9.4 |
|
OpenAI o3-mini (high)* |
13.0 |
|
OpenAI Deep Research (with browsing + Python tools) |
26.6 |
* Models tested on the text-only subset of the exam because they are not multimodal. Source: OpenAI
GAIA
GAIA (General AI Agent benchmark) evaluates how well AI systems handle real-world questions, requiring a combination of reasoning, web browsing, multimodal fluency, and tool-use proficiency.
Deep Research set a new state-of-the-art (SOTA) record, leading the external GAIA leaderboard with strong performance across all difficulty levels. The model showed particularly high accuracy in Level 3 tasks, which require complex, multi-step research and synthesis.
|
GAIA Evaluation |
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 |
Average |
|
Previous SOTA |
67.92% |
67.44% |
42.31% |
63.64% |
|
Deep Research (pass@1) |
74.29% |
69.06% |
47.6% |
67.36% |
|
Deep Research (cons@64) |
78.66% |
73.21% |
58.03% |
72.57% |
Source: OpenAI
Deep Research’s high pass@1 score shows that even its first attempt at answering a GAIA question is more accurate than previous models. The cons@64 score (which measures performance with multiple response attempts) further highlights its ability to self-correct and refine its answers based on new information.
Internal evaluations
OpenAI also performed internal evaluations, in which Deep Research was rated by domain experts on expert-level tasks. I found the internal evaluations quite interesting!
The graph below shows that the model’s pass rate increases as it makes more tool calls. This highlights the importance of letting it browse and analyze information iteratively—giving it more time to think leads to better results.
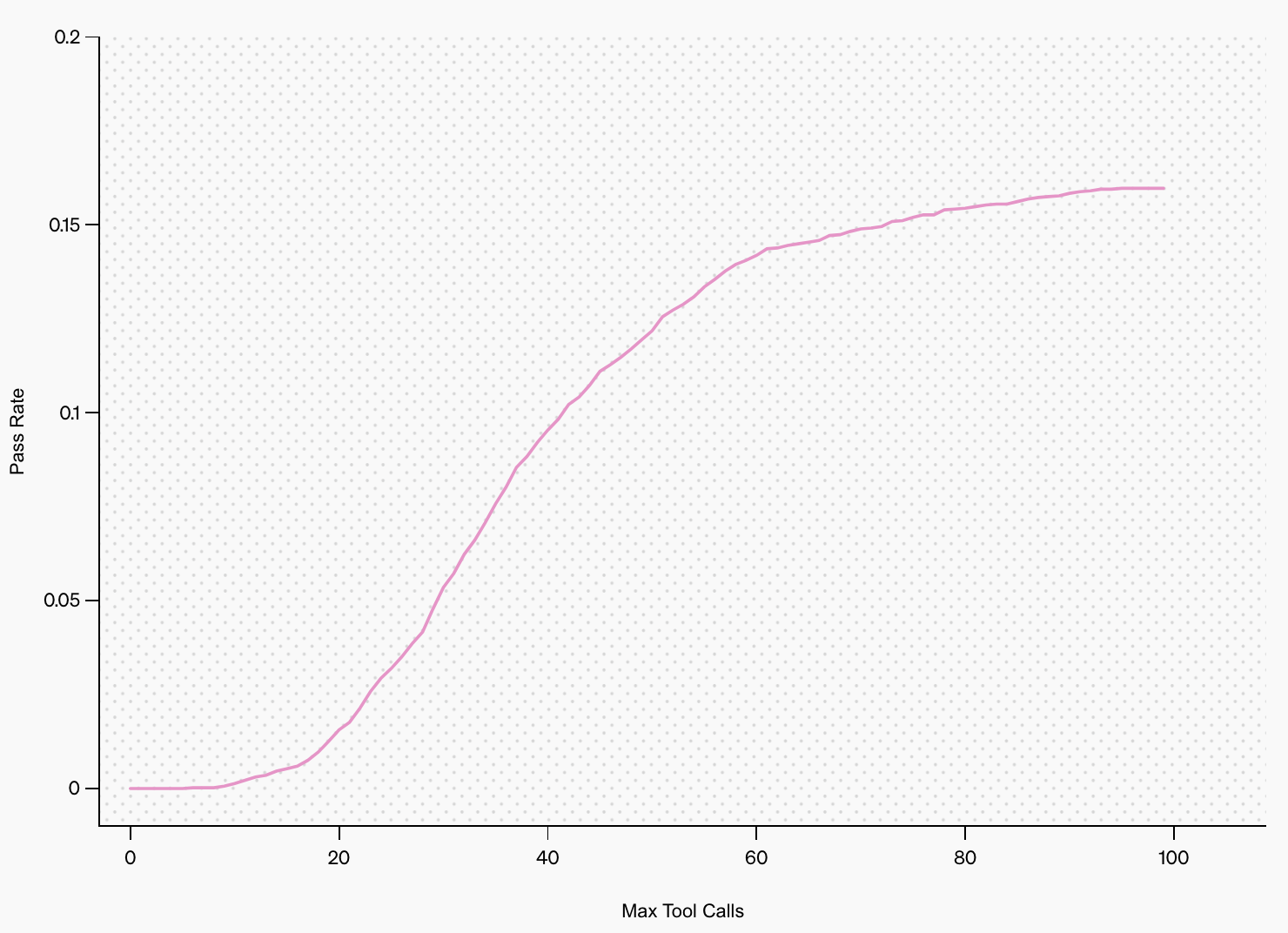
Source: OpenAI
Let’s take a look at another graph—see below. Deep Research performs best on tasks with lower estimated economic value, with accuracy dropping as the task’s potential financial impact increases. This suggests that more economically significant tasks tend to be more complex or rely on proprietary knowledge that isn’t widely accessible online.
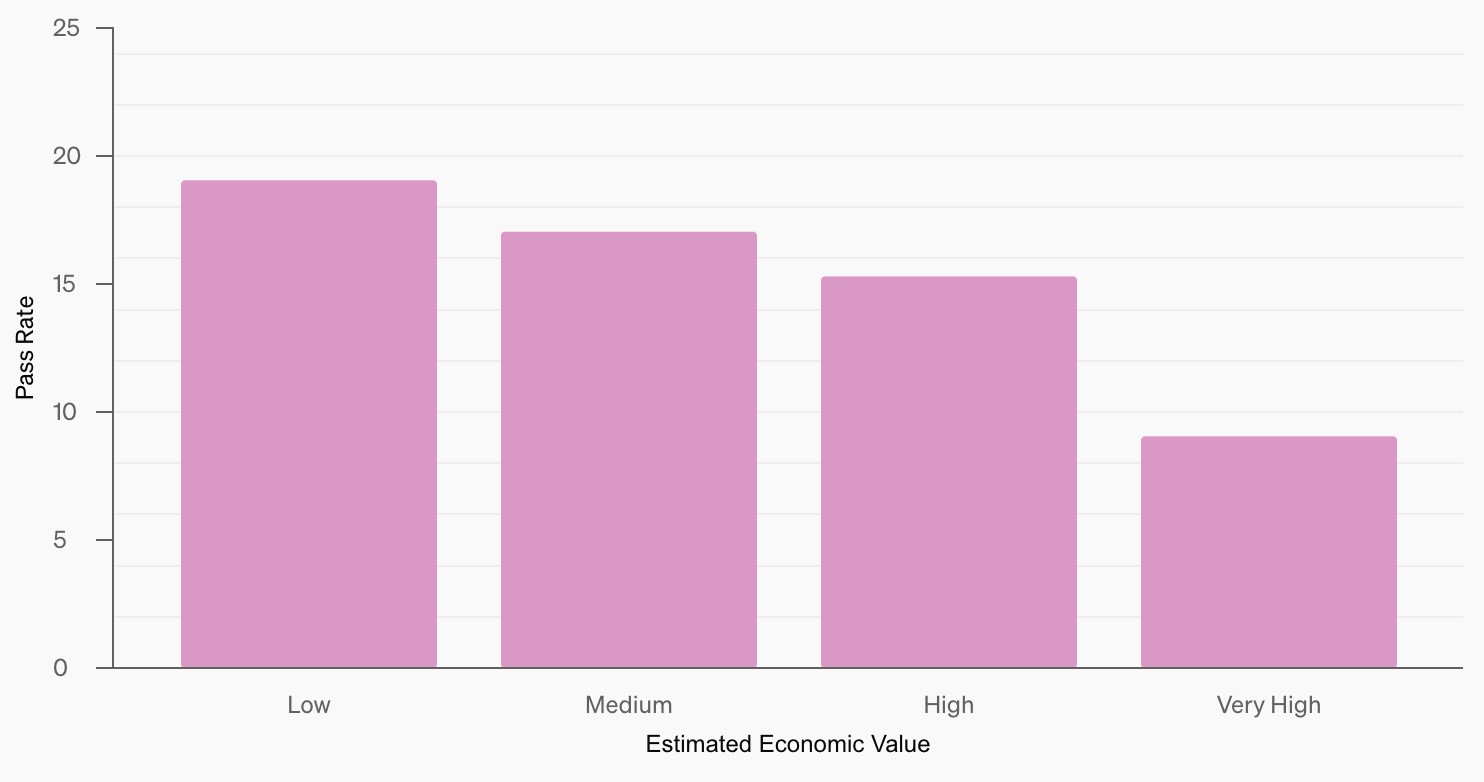
Source: OpenAI
The graph below contrasts pass rates with the estimated hours a human would take to complete each task. The model performs best on tasks that would take 1-3 hours for a person, but performance doesn’t decline consistently with time—indicating that what AI finds difficult doesn’t always align with what humans find time-consuming.
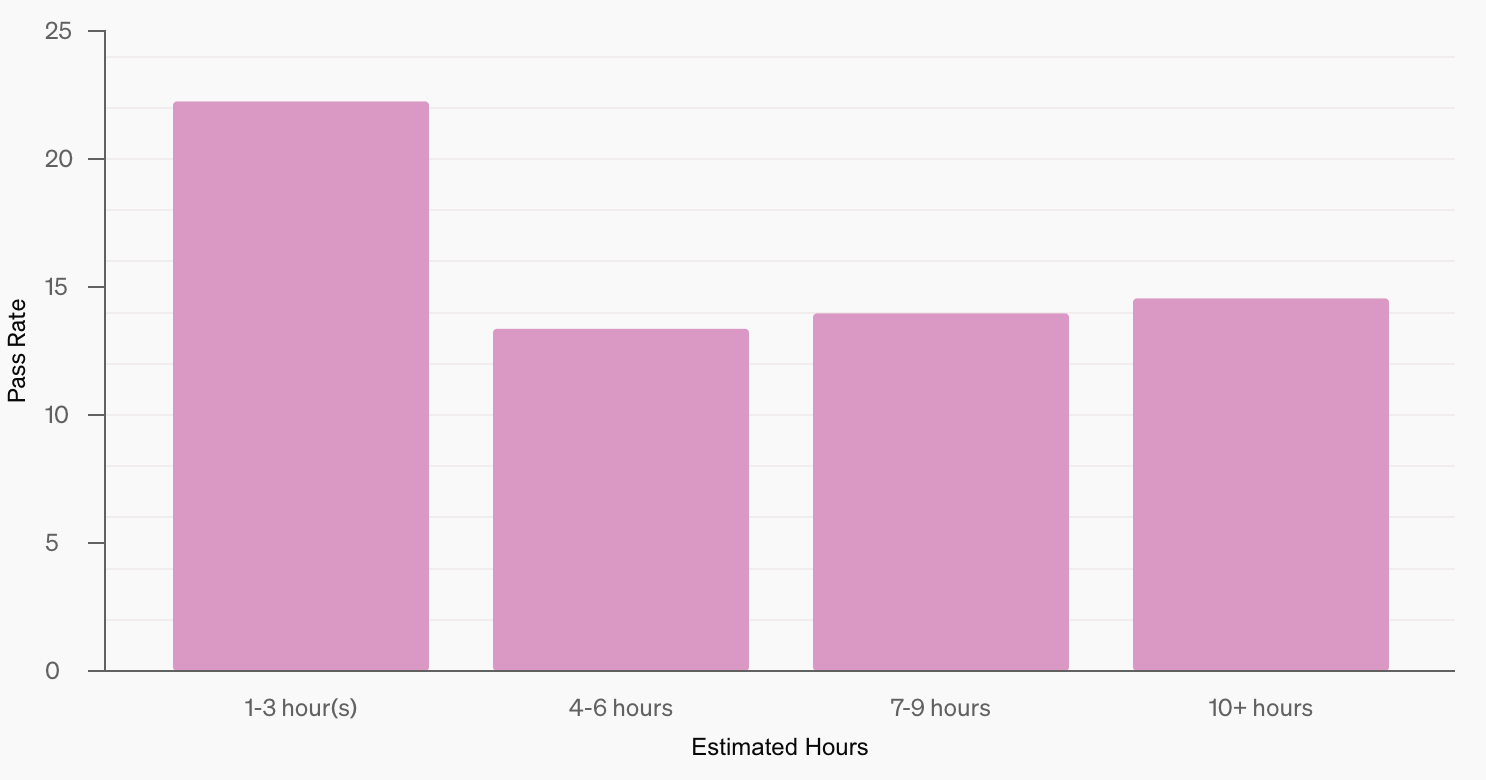
Source: OpenAI
How to Use Deep Research: Practical Examples
At the time of publishing this article, Deep Research is only available to Pro users, with a limit of 100 queries per month, but OpenAI plans to expand access to Plus, Team, and Enterprise users soon.
In my opinion, Deep Research is still in its early phase. While it shows great promise, the first example below highlights many of its problems. However, the second example demonstrates its immense potential.
Example 1: AI ecosystems
I constantly struggle to get a complete overview of the AI ecosystems of different companies. Take Google, for example—they have Gemini 2.0 Flash, Imagen 3, Veo 2, Project Mariner, Project Astra… what else am I missing? To finally get a clear overview, I prompted OpenAI’s Deep Research with this request.

Note that the model didn’t begin the research directly but instead asked for clarifications. In all my tests, no matter how specific my first prompt was, the model has always attempted to narrow down its research. This is useful, in my opinion, because I often think my prompt is clear and specific, but it usually benefits from some refinement.
I answered the model’s questions, and then the research began. A panel opened on the right side of the browser, showing the agent’s activity and sources in real time:
It took 11 minutes, and the model consulted 25 sources. Note that a source is a parent website, and the model can browse multiple pages from that website—for 25 sources and an average of four pages per source, you can expect the model to have browsed about 100 web pages.

Overall, I was disappointed with the result—you can read the Deep Research’s answer here. But let’s start with what I liked about it:
- Even though I didn’t specify a structure, the response was well-organized, with clear sections, proper use of bolding, font size, and bullet points.
- The sources are well-placed, appearing right after the information they refer to, and this system makes it easy to fact-check.
- The report struck a good balance between detail and length—it wasn’t shallow, but it also wasn’t a one-hour read. I can always ask for more details if I need to know more.
However, the answer had several issues, and I’ll focus on the major ones:
- Inaccuracies: It confused DeepSeek-V3 with DeepSeek-R1 (don’t forget that you can read the answer yourself here).
- Outdate information: Even though I specifically asked for an up-to-date report, Deep Research claimed Meta’s latest model was Llama 2 and Anthropic’s latest was Claude 2, mentioning rumors about something “codenamed” Sonnet and Haiku. I found this funny at first, but then I thought about how many people might take these answers at face value.
- Low prompt adherence: I explicitly told Deep Research to exclude GPT-4 and focus on the latest models, yet it didn’t follow that instruction.
- Incomplete answers: The OpenAI section failed to mention key models like o1, and in the Google section, it completely omitted Veo.
These issues make it hard to trust OpenAI’s Deep Research. I deliberately tested it on a subject I’m knowledgeable about, so I could fact-check the response—but what if I had to rely on Deep Research for a topic I know nothing about?
Example 2: Evergreen topic
Maybe the problem with Deep Research is that it’s not so good yet at identifying the most up-to-date information. So, I decided to test it on a more evergreen topic—one that doesn’t depend as much on recent developments.
I drive a car built in 2013 and occasionally think about replacing it. But I always get stuck on the same question: should I buy new or used? A new car depreciates quickly, but an old one could mean higher repair costs. I want to know what experts think about this, so this was an excellent opportunity to ask Deep Research to browse various studies and opinions and compile a report.
Before moving on, let me give you a tip: before you prompt Deep Research, optimize your prompt using your go-to LLM. Start with “You are a prompt engineer. Help me optimize this prompt: (your prompt here)”. Here’s the optimized prompt that I used for Deep Research:

Just as before, Deep Research asked for clarifications before starting and then completed the research in six minutes, consulting multiple web pages across 12 sources. You can read the full report here.
This time, the report was good—very good!
I’ve never imagined you could think about this problem from so many angles. The breadth of information was impressive, and by my estimate, Deep Research saved me 10+ hours of browsing and research. It pulled in academic studies, industry reports, market trend analyses, insurance cost comparisons, etc.
I’m not an expert in this field, so I can’t fully evaluate the accuracy of the report. However, from a consumer’s perspective, a lot of the information made logical sense and was genuinely helpful. I also fact-checked a few details against the cited sources and didn’t find any issues.
Just like in the first example, the depth was well-balanced, and the output structure was excellent. I particularly liked the table below—just look at those depreciation values, and you’ll understand why I’ll be holding on to my 12-year-old hybrid for a while.
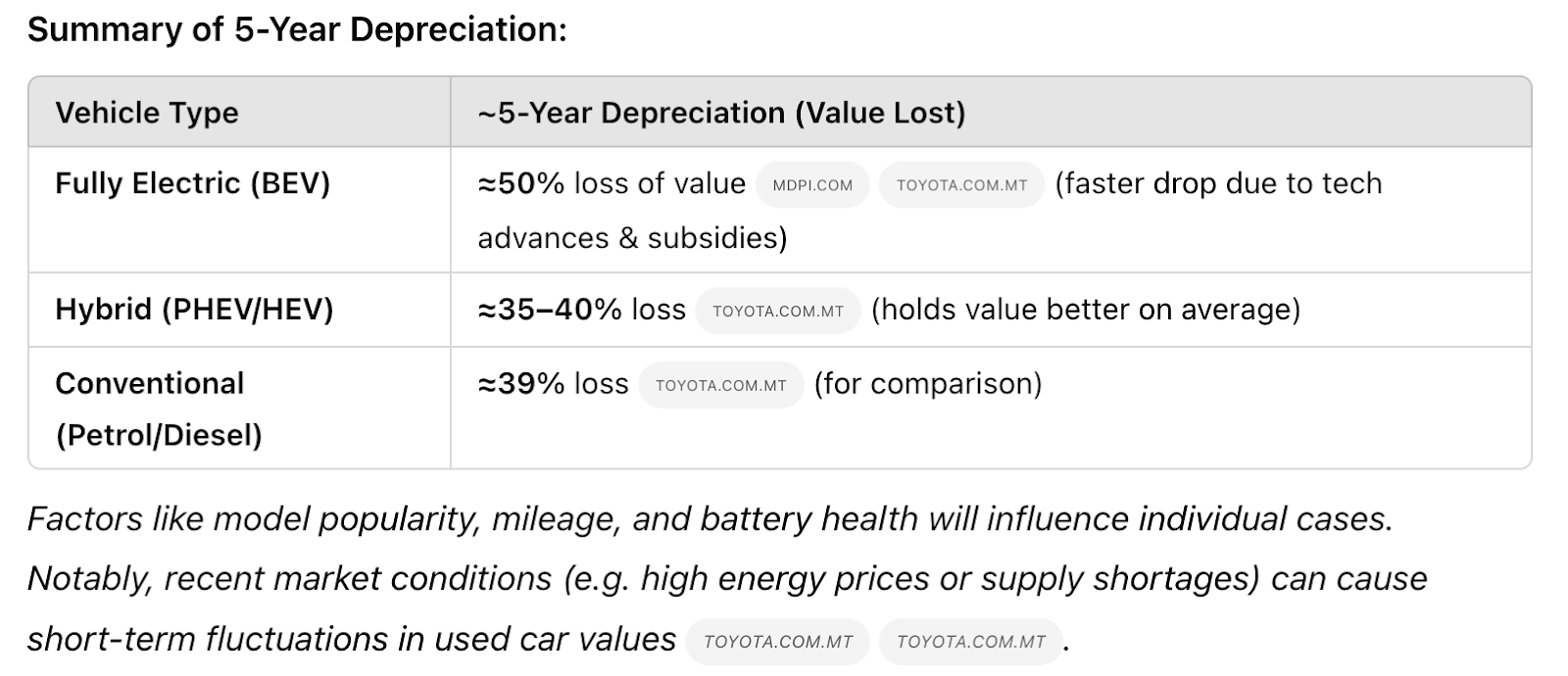
Conclusion
OpenAI’s Deep Research shows great promise and can save us a lot of research time. However, it’s still unreliable when it comes to up-to-date information, sometimes producing incorrect facts or flawed inferences.
I still think Deep Research is still in its early phase, and the OpenAI team openly acknowledges this in their announcement article.
Honestly, I’ll keep coming back to Deep Research, and I hope it gets better and better.
FAQs
Is Deep Research available on mobile devices?
Currently, Deep Research is only available in the desktop web version of ChatGPT, but OpenAI has announced mobile support within the month.
Can Deep Research work on highly technical or niche topics?
Yes, but its accuracy depends on the availability of reliable online sources. In niche fields with limited documentation, it may struggle to produce high-quality results.
How does Deep Research compare to ChatGPT’s standard browsing tool?
Unlike regular browsing, Deep Research conducts multi-step investigations, referencing multiple sources, analyzing information, and generating structured reports rather than quick answers.
Will Deep Research become available to free-tier users?
OpenAI has not announced plans to make Deep Research available to free-tier users. It is currently exclusive to Pro users, with plans to expand to Plus, Team, and Enterprise accounts.
What’s the difference between OpenAI’s Deep Research and Google’s Deep Research?
OpenAI’s Deep Research and Google’s Deep Research both conduct multi-step web investigations but differ in execution. OpenAI’s version, powered by an o3-based model, focuses on structured reports, reasoning, and Python-based data analysis, but has struggled with up-to-date accuracy. It takes 5–30 minutes per report and is currently limited to Pro users in ChatGPT. Google’s Deep Research, integrated into Gemini, uses Google Search for real-time information retrieval, completing research in 5–10 minutes. While OpenAI’s version excels in deeper analysis, Google’s may be better at finding the latest, authoritative sources.
I’m an editor and writer covering AI blogs, tutorials, and news, ensuring everything fits a strong content strategy and SEO best practices. I’ve written data science courses on Python, statistics, probability, and data visualization. I’ve also published an award-winning novel and spend my free time on screenwriting and film directing.




