Future updates may include faster response times, web browsing, and file handling.
While we had been all waiting for GPT-5, OpenAI surprised everyone last summer with the release of the o1-preview model. Now, they have just announced that o1 is fully available and is no longer in preview mode.
Compared to the preview version, o1 can take multimodal inputs, has image understanding, and is much faster for simple queries. Previously, it took more than ten seconds just to respond to the prompt “Hi.”
OpenAI also introduced o1 pro mode, which is slightly more powerful and reliable than o1. While we briefly cover o1 pro mode in this article, we explore it in more detail in this separate article: What Is OpenAI’s O1 Pro Mode? Features, ChatGPT Pro & More.
OpenAI has reset the counter back to 1 and named it OpenAI o1, emphasizing its distinct focus on reasoning compared to the traditional GPT lineage. This marks the start of a new OpenAI o-series, similar to the GPT series we all know.
O1 models are not designed to replace GPT-4o in all cases. For applications requiring or consistently rapid response times, the GPT-4o and GPT-4o mini models remain the optimal choice.
Read on to find out more about the new O1 models!
Develop AI Applications
Learn to build AI applications using the OpenAI API.
How OpenAI o1 Works
The first thing you'll notice when interacting with o1 is that it takes noticeably longer to generate responses compared to GPT-4o. This deliberate pause reflects the model's emphasis on reasoning. O1 spends more time "thinking" before responding, allowing it to tackle complex tasks and solve harder problems in logic, math, coding, and science.
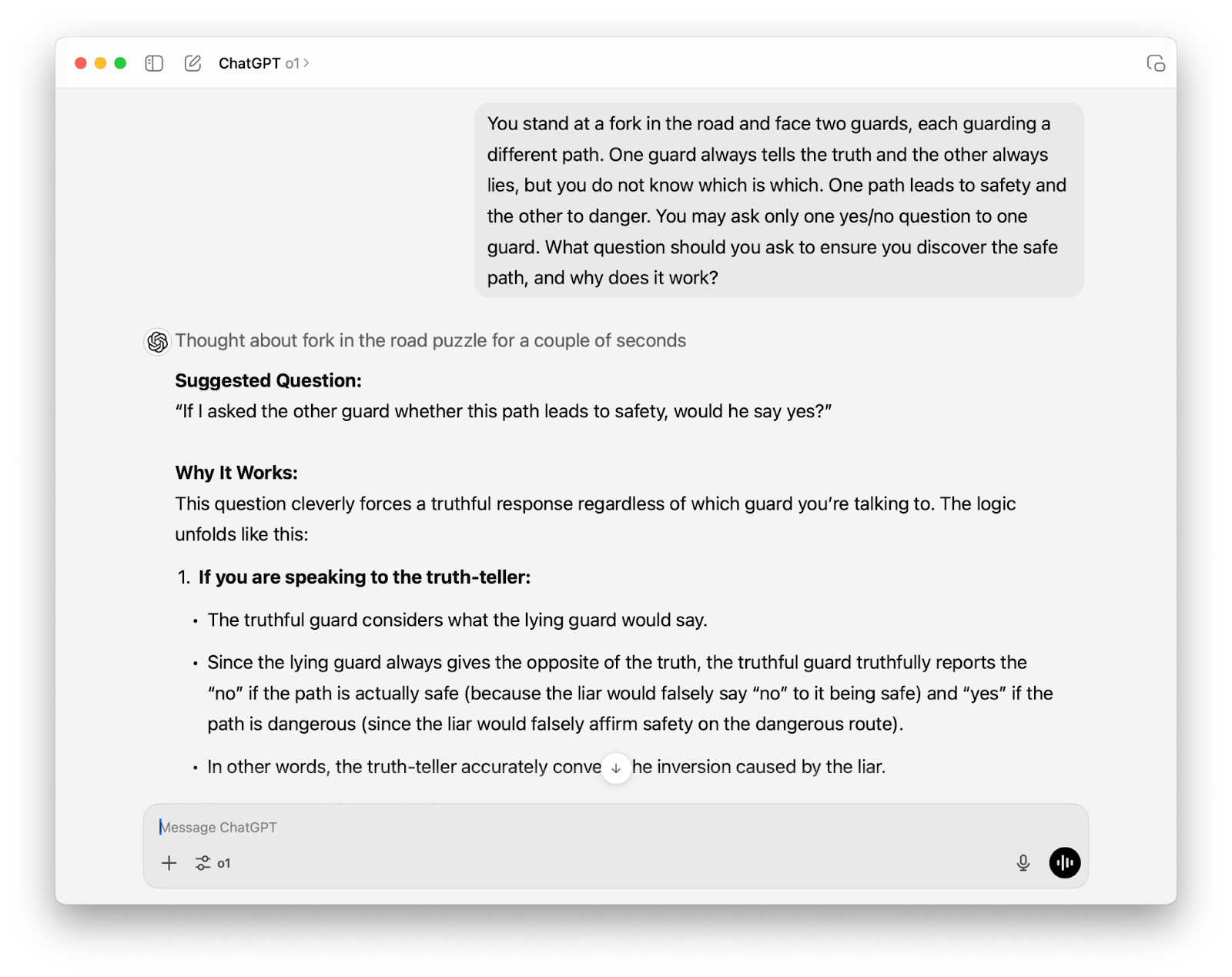
OpenAI o1-preview is tackling a logic problem
Reinforcement learning and chain-of-thought
O1's superior reasoning is achieved through a combination of reinforcement learning and chain-of-thought reasoning.
Through reinforcement learning, the model learns to refine its thinking process, exploring different strategies, recognizing mistakes, and adapting its approach to arrive at the most accurate and logical solution.
On the other side, chain-of-thought reasoning is a technique to break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable components. This approach allows o1 to 'think before it answers,' much like meticulously planning out the steps of a complex recipe before starting to cook.
By explicitly laying out its reasoning process, o1 can identify potential errors early on and increase the likelihood of arriving at the correct solution, just as we humans are less likely to make mistakes when we carefully outline our thought process.
The fact that OpenAI o1 uses chain-of-thought reasoning makes it especially effective in fields such as math, science, and coding, where getting a correct answer often requires multiple steps.
A new paradigm in compute allocation
A key differentiator of OpenAI o1 lies in its strategic reallocation of computational resources. While traditional LLMs have primarily focused on massive pretraining datasets, o1 shifts the emphasis toward the training and inference phases.
This shift shows that allocating more compute to these stages can yield significant gains in complex reasoning capabilities.

Source: OpenAI
The chart above shows the impact of increased computational resources on the performance of OpenAI's o1 model when tackling the challenging AIME (American Invitational Mathematics Examination. It features two graphs, each plotting the model's accuracy against the compute power dedicated to either training or testing (inference).
A clear positive correlation is evident in both graphs: as the computational resources increase, so does the model's accuracy in solving AIME problems on the first attempt. Notably, the relationship is more pronounced in the test-time graph, suggesting that giving the model more time to "think" during problem-solving leads to significantly improved performance.
This observation underscores the compute-intensive nature of o1, highlighting its reliance on substantial computational resources. However, the upward trends in both graphs also imply that further accuracy gains are possible with even more compute, offering promising avenues for future development in AI reasoning capabilities.
OpenAI O1 Benchmarks: Better at Reasoning-Heavy Tasks
To showcase o1's enhanced reasoning capabilities compared to GPT-4o, OpenAI evaluated the model on a variety of challenging math, coding, and science benchmarks.
Human exams
Human examination demonstrates that o1 consistently outperforms GPT-4o nad o1-preview.
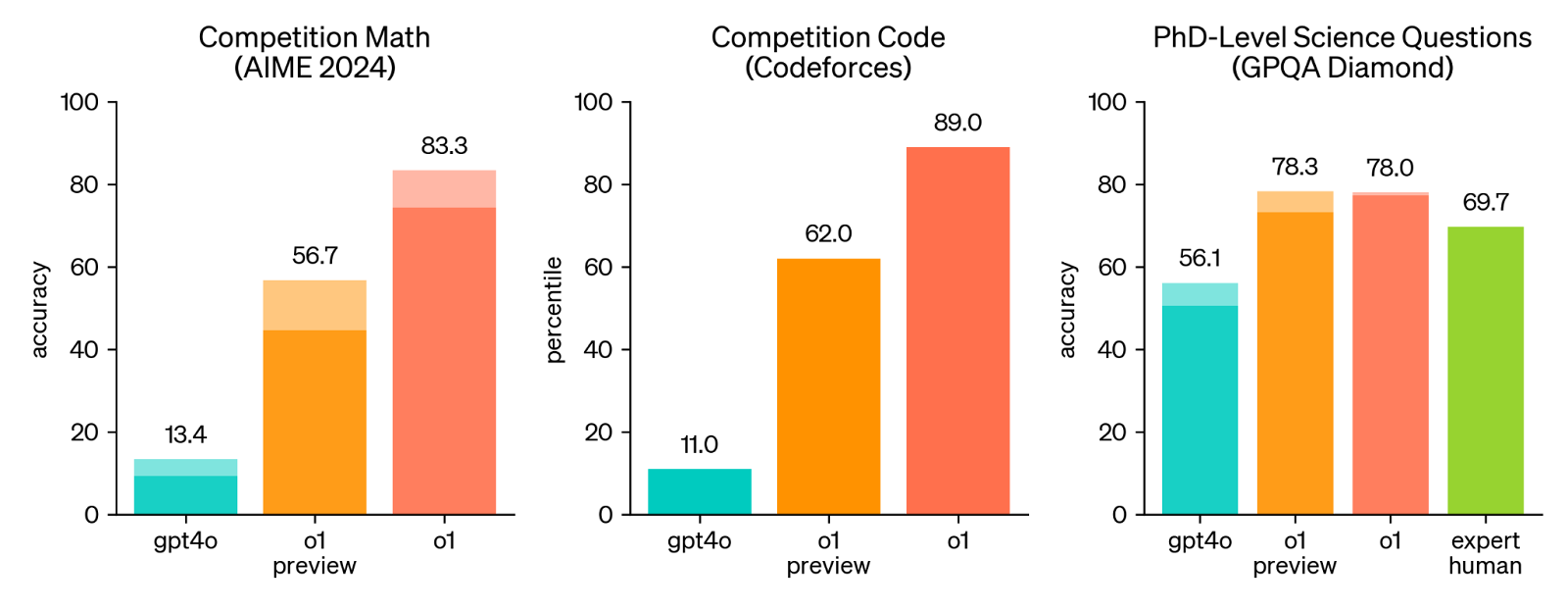
Solid bars show pass@1 accuracy and the shaded region shows the performance of majority vote (consensus) with 64 samples. Source: OpenAI
Perhaps the most striking observation is the giant leap in performance between GPT-4o and o1 (and even o-1 preview) on the math and coding benchmarks.
And while the improvement in the science domain is less pronounced, it's noteworthy that both o1-preview and the fully optimized o1 model outperform human experts on PhD-level science questions. This shows the potential of o1 to tackle intricate, real-world problems and even surpass human-level performance in certain domains.
OpenAI o1 has potential use cases in genetics.
ML benchmarks
Looking at the results on ML benchmarks, o1's advancements in reasoning are fairly obvious. On both MathVista (a mathematics benchmark) and MMLU, o1 showcases substantial gains in accuracy compared to GPT-4o.
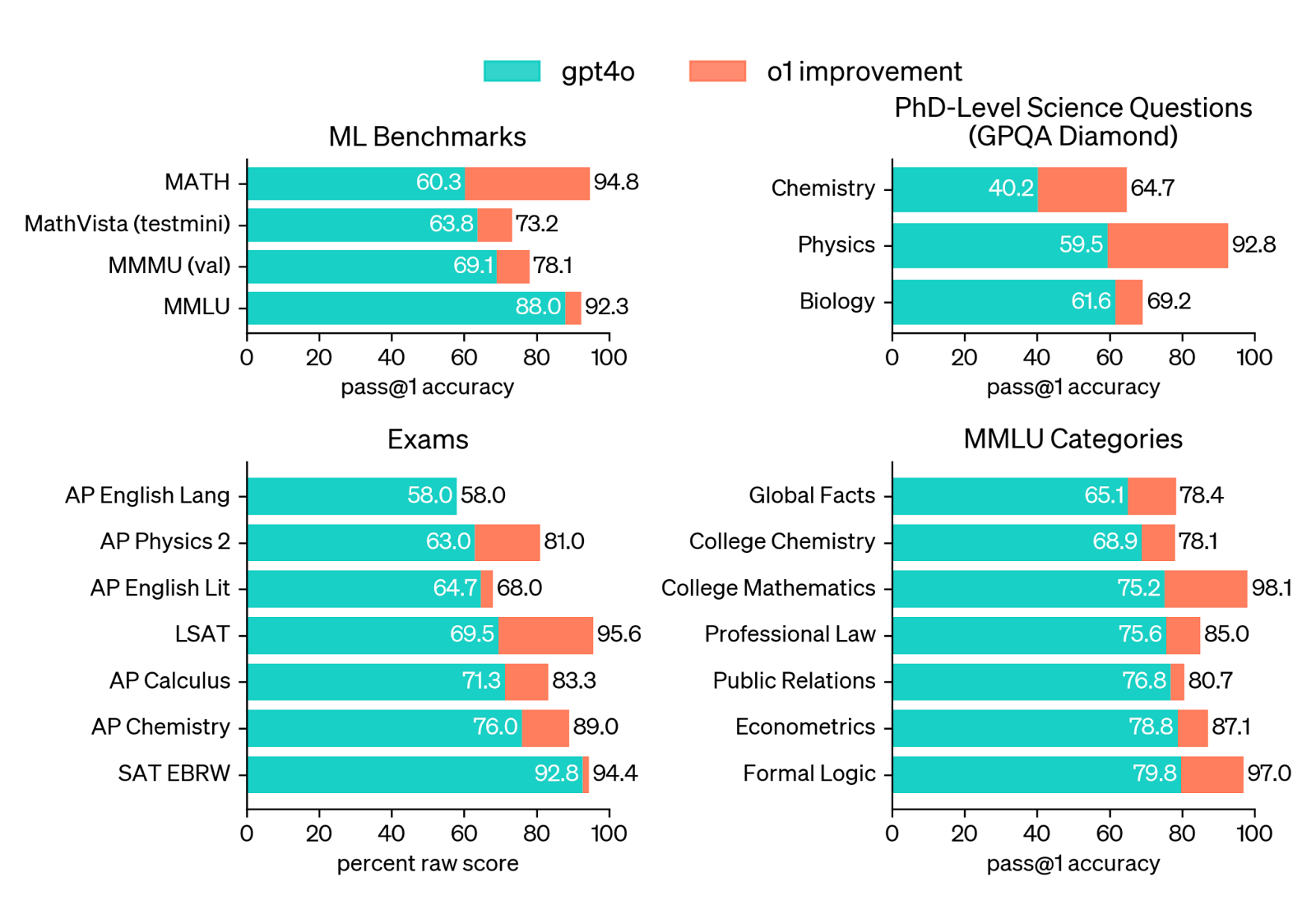
Source: OpenAI
A specialized version of o1, known as o1-ioi, demonstrated superior coding abilities by securing a 49th percentile ranking in the 2024 International Olympiad in Informatics, even under strict competition conditions.
In simulated contests (see chart below), o1-ioi's performance soared even higher, surpassing 93% of competitors.
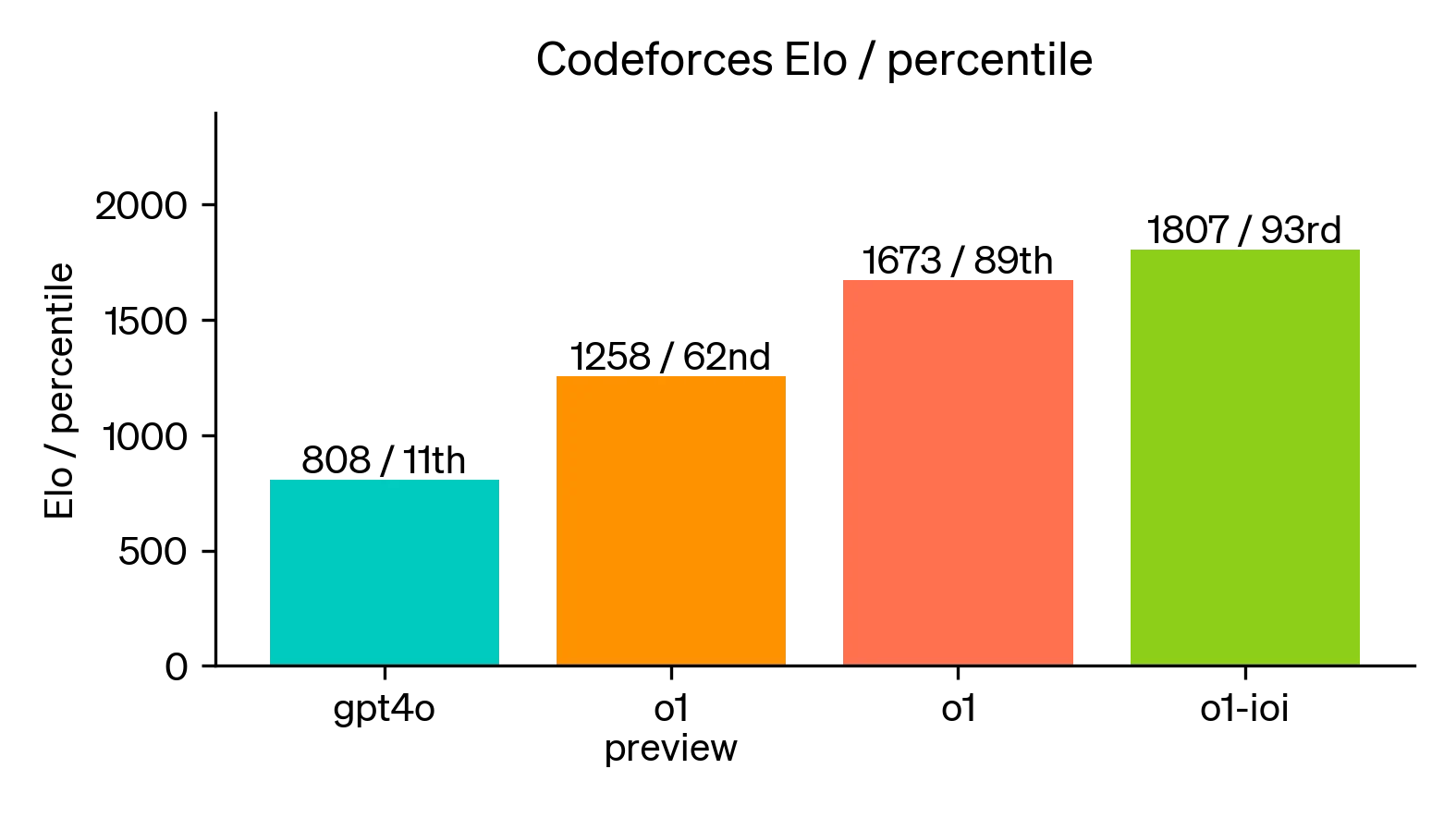
Source: OpenAI
OpenAI o1 Use Cases
OpenAI o1’s reasoning capabilities make it particularly well-suited for solving complex problems in science, coding, and mathematics.
Scientific Research
Healthcare researchers, for instance, could leverage o1 to annotate intricate cell sequencing data, while physicists might employ it to generate the sophisticated mathematical formulas required for quantum optics research.
Quantum physics and OpenAI o1
Coding
From suggesting code optimizations and generating test cases to automating code reviews and facilitating knowledge sharing, o1 has the potential to significantly enhance developer productivity and simplify workflows.
Additionally, o1’s ability to understand and generate code extends its utility beyond just coding. It can aid in project planning, requirement analysis, and software architecture design, helping developers craft more effective solutions.
Although o1’s full capabilities are still being developed, its current features are already promising. As OpenAI continues to refine the model, o1 is likely to become a valuable tool for developers, fostering innovation and influencing the future of software development.
As described in the benchmarks section, the o1 model shows great potential in the coding field.
HTML Snake with OpenAI o1
Mathematics
The field of mathematics could also see significant benefits from o1's advanced reasoning capabilities. Its strong performance on benchmarks like AIME suggests potential applications in solving complex equations, proving theorems, and exploring new mathematical concepts, benefiting both students and researchers alike.
Math with OpenAI o1
Reasoning-heavy use cases
Beyond specific domains, o1's focus on reasoning could make it a valuable asset for any task that requires critical thinking and logical deduction. From solving puzzles and riddles to analyzing complex arguments and facilitating informed decision-making, o1 could open up new ways for problem-solving.
Writing puzzles with OpenAI o1
How to Access OpenAI o1
If you have a ChatGPT Plus or ChatGPT Team subscription, you can access the o1 model directly within the ChatGPT interface. Select o1 from the model selector dropdown menu at the top of the page.
Keep in mind that with a ChatGPT Plus or Team account, you get 50 messages a week with OpenAI o1 and 50 messages a day with OpenAI o1-mini to start.
OpenAI o1 API
While o1 is accessible within ChatGPT for Plus and Team subscribers, developers and researchers needing greater flexibility and integration options will find the OpenAI o1 API more suitable for their needs.
Beta limitations
Even though the o1 model is out of preview in the chat interface, as of the time of writing this article (December 6th, 2024), the API offers access to only two variants of the o1 model:
- o1-preview: This is the early preview of the full o1 model, designed to tackle complex problems requiring broad general knowledge.
- o1-mini: A faster and more cost-effective version of o1, well-suited for tasks in coding, math, and science where extensive general knowledge might not be necessary.
Both o1-preview and o1-mini are accessible via the chat completions endpoint, making it easy to incorporate them into existing projects. The process involves selecting the desired model (e.g., model="o1-preview") when making API calls. To learn step-by-step how to use o1 via the API, read this tutorial: OpenAI O1 API Tutorial: How to Connect to OpenAI's API.
As o1 is currently in beta, certain API parameters and features are not yet supported. These include:
- Modalities: Currently, only text input and output are supported; image handling is not yet available.
- Message types: System messages are not supported; only user and assistant messages are allowed.
- Streaming: The streaming feature is not yet available for o1 models.
- Tools and function calling: These advanced capabilities are not currently supported.
- Logprobs: Log probabilities are not yet available.
- Other parameters: Parameters like
temperature,top_p, andnare fixed at 1, whilepresence_penaltyandfrequency_penaltyare fixed at 0. - Assistants and Batch API: o1 models are not yet integrated with the Assistants API or Batch API.
OpenAI plans to gradually add support for some of these parameters and features as o1 moves out of beta. More advanced functionalities like multimodality and tool usage are slated for inclusion in future iterations of the o1 series.
Understanding reasoning tokens
A key aspect of o1 models is the introduction of "reasoning tokens." These tokens represent the model's internal thought process as it breaks down the prompt, considers various approaches, and formulates a response. Although these reasoning tokens are not visible through the API, they do consume space in the model's context window and contribute to the overall token count, impacting billing.
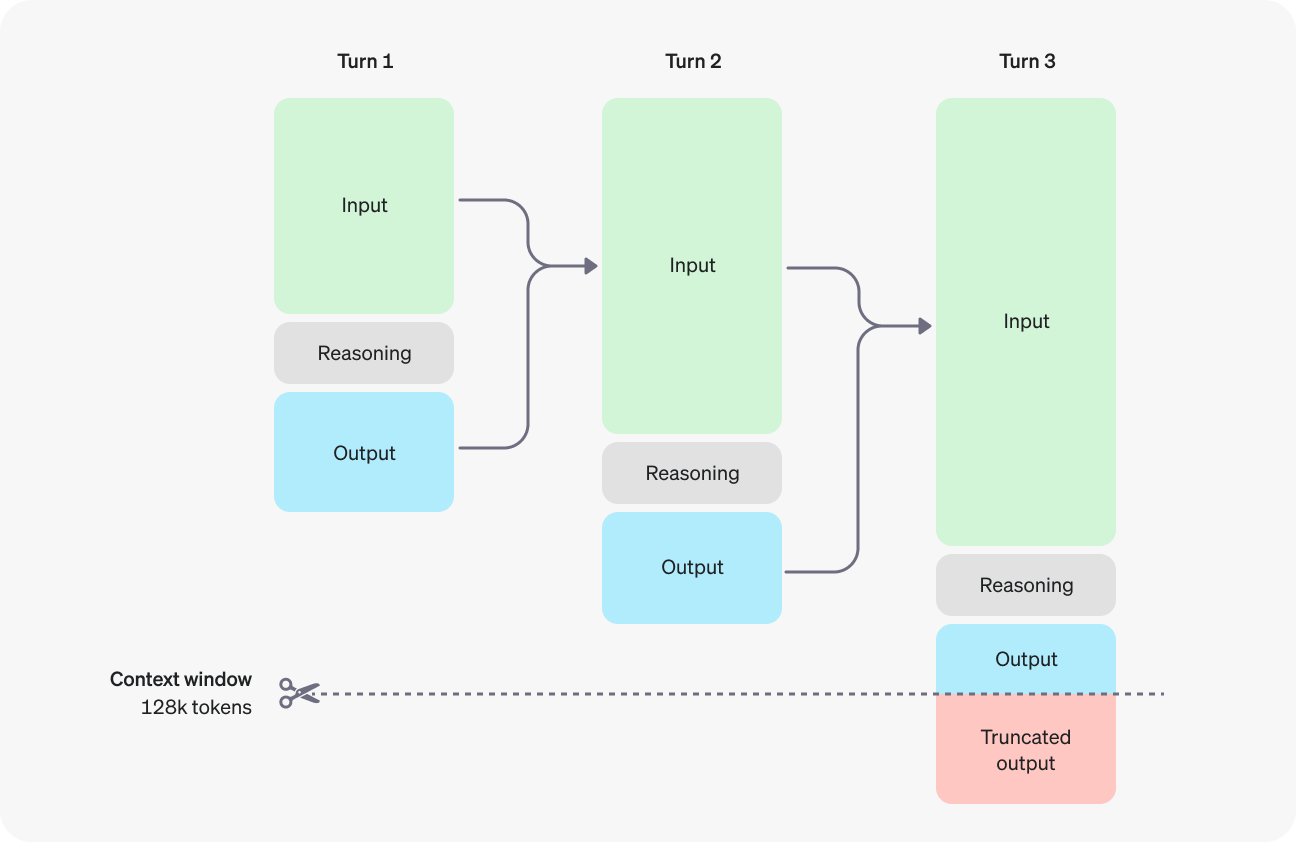
Source: OpenAI
Context window and costs
Both o1-preview and o1-mini offer a context window of 128,000 tokens. However, each completion has a maximum limit on the total number of output tokens generated, including both the invisible reasoning tokens and the visible completion tokens. To avoid unexpected costs and ensure the model has enough room to "think," it's crucial to manage the context window effectively and set appropriate limits using the max_completion_tokens parameter.
Prompting best practices
For optimal results with o1 models, keep your prompts simple and direct. Avoid techniques like few-shot prompting or explicitly instructing the model to "think step by step," as these may hinder rather than enhance performance. Utilize delimiters to clearly structure your input and, in retrieval-augmented generation scenarios, provide only the most relevant context to prevent the model from overcomplicating its response.
What Is OpenAI o1-mini?
Alongside the full-fledged o1-preview model, OpenAI has also released o1-mini, a smaller and faster variant designed to provide a more accessible entry point for developers and researchers exploring the capabilities of the o1 series.
While o1-mini may not possess the same depth of general knowledge as its larger counterpart, it excels in tasks that demand focused reasoning skills, particularly in the realms of coding, math, and science.
Its reduced size translates to faster response times and lower computational requirements, making it a practical choice for applications where speed and efficiency are important.
Although o1-mini is currently in beta and has certain limitations, it offers a glimpse into the potential of the o1 series and its focus on enhancing AI reasoning capabilities. As OpenAI continues to refine and develop the o1 models, we can expect o1-mini to evolve alongside its larger sibling, providing an increasingly powerful and versatile tool for a wide range of applications.
What Is O1 Pro Mode?
In addition to the standard o1 model, OpenAI has also introduced o1 pro mode. This model is designed for users who require even more advanced reasoning capabilities and are willing to sacrifice some speed for increased accuracy and the ability to handle highly complex tasks.
o1 pro mode leverages significantly more computing power than the standard o1 model. This allows it to "think longer" and "think harder" to generate more reliable responses, especially for challenging problems in fields like data science, programming, and case law analysis.
To access o1 pro mode, you'll need a subscription to ChatGPT Pro. This subscription grants you unlimited usage of o1 and o1 pro mode, as well as other advanced models and features.
We covered o1 pro mode in depth in a separate article: What Is OpenAI's O1 Pro Mode? Features, ChatGPT Pro & More.
Limitations of OpenAI o1
While OpenAI o1-preview offers impressive capabilities, there are a few limitations to be aware of. These constraints might affect its usefulness in certain contexts, so it’s worth being aware of the following things.
Hidden chain of thought
To ensure the potential for future monitoring and safety enhancements, the raw chain-of-thought reasoning process used by o1 is not directly visible to users. While this decision aims to enable more effective model oversight, it does limit transparency and could impact user understanding of the model's decision-making process.
Doesn’t yet browse the web
OpenAI o1-preview cannot browse the web, which means that the information it provides may not always be up-to-date. If you're looking for real-time or current event data, the model will not be able to retrieve it directly.
Longer response times
One of the most noticeable limitations is that the model takes a relatively long time to process complex queries. While this extra time allows it to produce more thoughtful responses, it may cause delays for users expecting faster answers.

Unsuitable for low-latency applications
Due to its slower response times, OpenAI o1 is not ideal for applications that require rapid interactions, such as real-time chatbots or translation services. In these use cases, the delay can result in a poor user experience, as waiting several seconds for a response can feel frustrating.
If the model is applied in situations where its strengths aren't aligned with the task, it can result in a negative user experience. This is especially true for scenarios requiring quick, on-the-fly responses, where the model's slower processing time may become a hindrance rather than a benefit.
OpenAI o1 Safety
The new o1 models feature a safety training approach that uses their reasoning abilities for better in-context safety.
A key safety measure is testing the model’s resistance to “jailbreaking” attempts, where users try to bypass safety rules. In a challenging jailbreaking test, GPT-4o scored 22 out of 100, whereas the newer o1-preview model achieved 84, indicating substantial improvement.
Safety efforts have been bolstered through rigorous testing, internal governance, and collaboration with the federal government. This includes using the Preparedness Framework, red teaming, and board-level reviews by their Safety & Security Committee.
Furthermore, partnerships with the U.S. and U.K. AI Safety Institutes have been formalized, granting them early access to research versions of the models.
However, it's crucial to approach these early results with cautious optimism.
The Future: OpenAI O-series
The introduction of OpenAI o1 marks not just a new model but the inception of a new series: the OpenAI O-series. This signals a deliberate shift in OpenAI’s strategic direction, emphasizing complex reasoning capabilities as a core focus for future AI development.
The impressive early results from o1 and o1 pro mode, particularly its strong performance on benchmarks requiring intricate problem-solving, suggest that this new series holds significant promise.
As OpenAI continues to refine and expand the capabilities of the o-series models, we can anticipate a future where AI plays an even more active role in scientific discovery, software development, and other fields requiring advanced cognitive skills.
However, the path to fully realizing the potential of the O-series is not without challenges. The compute-intensive nature of these models and the unique scaling constraints they present necessitate continued research and development.
Conclusion
While we eagerly anticipated the arrival of GPT-5 this year, OpenAI surprised us with the introduction of o1, a model that prioritizes complex reasoning capabilities.
The early successes of o1 across a variety of benchmarks demonstrate its potential to tackle challenging problems in fields like mathematics, coding, and scientific research.
Despite its promising capabilities, o1 is still in its early stages and faces challenges, including its compute-intensive nature and the need for ongoing research into safety and ethical deployment.
FAQs
What is OpenAI o1, and how is it different from other models?
OpenAI o1 is a new AI model focused on complex reasoning tasks like math, coding, and puzzles. It uses chain-of-thought reasoning to break down problems, improving accuracy compared to older models like GPT-4.
What tasks are OpenAI o1 models particularly good at?
OpenAI o1 excels at math problems, coding challenges, data analysis, and science tasks that require multi-step reasoning.
How can I access OpenAI o1?
You can access OpenAI o1 through ChatGPT, and developers can access it via OpenAI’s API.
What is the difference between OpenAI o1 and o1-mini?
o1-mini is a smaller version of o1, better suited for lighter tasks but with less power for complex reasoning.
What features are expected in future updates to OpenAI o1 models?
What is the pricing for using OpenAI o1 models?
The pricing for o1 models is usage-based and depends on the specific model and the number of tokens processed.
- For o1-preview, the cost is $15.00 per 1 million input tokens and $60.00 per 1 million output tokens.
- For o1-mini, the cost is $3.00 per 1 million input tokens and $12.00 per 1 million output tokens.
- It's important to remember that the total token count includes both visible completion tokens and invisible reasoning tokens, which contribute to the overall cost.

Author
Richie helps individuals and organizations get better at using data and AI. He's been a data scientist since before it was called data science, and has written two books and created many DataCamp courses on the subject. He is a host of the DataFramed podcast, and runs DataCamp's webinar program.
I’m an editor and writer covering AI blogs, tutorials, and news, ensuring everything fits a strong content strategy and SEO best practices. I’ve written data science courses on Python, statistics, probability, and data visualization. I’ve also published an award-winning novel and spend my free time on screenwriting and film directing.

Author
Josef Waples
I'm a data science writer and editor with contributions to research articles in scientific journals. I'm especially interested in linear algebra, statistics, R, and the like. I also play a fair amount of chess!