Course
The rapid digitalization of our society and the increasing adoption of all types of electronic devices has resulted in an exponential growth of data. This tendency has presented no sign of slowing down in the coming future. Rather the opposite: the expected deployment of the Internet of Things and the 5G infrastructure, the rate of data generation is likely to increase even more.
Against this backdrop, companies have a huge demand for data professionals who can build solid and reliable data infrastructures and analyze huge amounts of data to support business decision-making.
Among the different data roles available, data analysts are extremely popular and well-paid. According to Forbes, the job market for data analysts is booming, and the horizon looks bright for these in-demand professionals.
So what does a data analyst do? Here, we explore the role and examine why they are rapidly becoming a must-have in every data department. In separate articles, we've outlined how to become a data analyst and how you can prepare for data analyst interview questions.
What is a Data Analyst?
Generally speaking, a data analyst is responsible for collecting, preparing, and analyzing data to extract meaningful insights.
A day in the life of a data analyst entails a wide array of duties, from developing systems for data collection and using programming languages to clean and analyze data to building reports and communicating insights to stakeholders.
Given their versatile nature, it is very common to use other job titles to describe data analyst, including:
- Business analyst
- Business intelligence analyst
- Market intelligence consultant
- Operations research analyst
- Competitive intelligence analyst
- Data strategist
Whatever the exact title is, corporations in nearly every industry can benefit from the work of data analysts, from healthcare and marketing to logistics and biology. This is one of the main reasons for the surging demand of data analysts.
Data Analysts vs Data Scientists
A common mix-up among aspiring data professionals is the differences between data analysts and data scientists. While there isn’t a clear line between the two roles – depending on the company, data analysts and data scientists may be involved in the same kind of tasks – there are also important differences regarding the nature of the work and the level of expertise in data usage.
As for the nature of the work, the data analyst has a rather exploratory and descriptive profile in contrast to the more experimental profile in the case of data scientist.
The data analyst form is more about finding patterns in big columns of (structured) data, building visualizations and reports, and communicating insights.
On the other hand, data scientists tend to deal with the unexpected through the use of techniques that fall in the realm of predictive analytics. This normally entails developing data models and machine learning algorithms to make predictions about the future.
As for the level of expertise required for the two roles, data scientists are sometimes considered a more technical version of a data analyst. Overall, data scientists should be more fluent in advanced programming and computing tools. Also, since data scientists are responsible for developing data models and machine learning algorithms, they need to have a solid background in math and statistics.
In the table below, you can find the main differences between data analysts and data scientists:
|
A Comparative Guide to the Skills |
||
|
Area of Skill |
Data Analyst |
Data Scientist |
|
Data Engineering |
Low |
Medium |
|
Data Exploration |
High |
High |
|
Data Visualization |
High |
Medium |
|
Tools and Programming Languages |
Medium |
High |
|
Data Modeling & Algorithms |
Low |
High |
|
Business Domain Knowledge |
High |
High |
|
Software Engineering |
Low |
Medium |
|
Communication & Presentation |
High |
High |
What Does a Data Analyst Do?
Despite the many job titles, some of the main responsibilities of a data analyst can generally be separated into tasks related to the different stages of the following project life cycle:
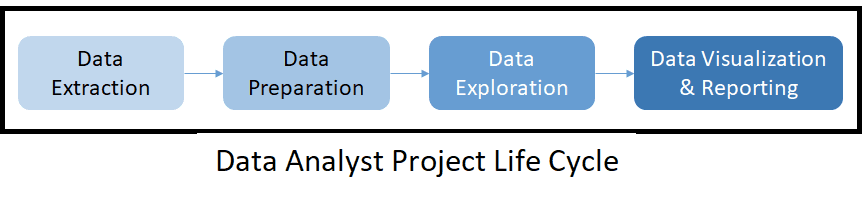
Source: DataCamp
Below, we’ve outlined in more detail what a data analyst does during this process:
Data extraction
Data analysts are often involved in data collection tasks. However, while data scientists deal with both structured and unstructured data, thereby increasing the number and complexity of the techniques needed for data collection, data analysts mostly work with structured data, normally stored in the company’s own relational databases.
Data preparation
Collected data often comes with duplicates, errors, extreme values, and other kinds of anomalies. To turn raw data into analysis-ready data, it has to pass through a cleaning process. Data analysts spend a considerable time preprocessing and summarizing data to find and address errors. You can learn more about the data preparation process with our online course.
Data exploration
Once data is clean, it’s time for exploration. During this stage, data analysts explore data looking for trends and patterns that can help them answer specific business questions. You can use all kinds of tools for this process, as our Exploratory Data Analysis in SQL course demonstrates.
Data visualization & reporting
Communicating the results of an analysis is a key part of the job of a data analyst. This can be done through the creation of data visualizations that are put together in dashboards and management reports, alongside comments that are shared with end stakeholders. Self-serving business intelligence tools, such as Tableau, and Power BI, are commonly used for this purpose.
What Skills do Data Analysts Need?
Data analysts are multifaceted and versatile professionals. Given the nature of their responsibilities, they require a balanced set of technical skills and leadership skills. You can read more about how to become a data analyst in our full article, but below, we've highlighted some of the knowledge you'll need.
Starting with the data analyst technical skills, we can highlight the following:
Programming
Data analysts often use programming languages in every step of the data analyst project life cycle. The two most common programming languages for data science are Python and R.
These highly popular languages allow data analysts to handle large datasets and perform all kinds of data techniques to find relevant patterns and trends.
If you want to get started in one of these languages, check out the Python and R courses.
Database management
Most of the datasets data analysts deal with are stored in relational databases. Structured Query Language (SQL) is the standard programming language in the industry to communicate and manipulate relational databases. Every aspiring data analyst should have SQL in their toolkit.
Data visualization
Presenting results in a compelling and insightful way is crucial to turn data into actionable decision-making. Data visualization is the art of embedding data in visual representations, such as graphs and charts.
There are many tools that allow data analysts to create beautiful visualizations, including Python’s libraries like matplotlib, R’s libraries like ggplot2, and Business Intelligence software, like Tableau and Power BI.
Statistics and math
Although data analysts don’t deal with complex machine learning algorithms, they still need a solid grasp of statistics and math. This knowledge is critical to understanding the different data techniques available, and determining the best tools and techniques to address a particular problem. Equally, this background can be critical when presenting data results to a technical audience.
As for the data analyst leadership skills, some essentials include:
Business acumen
Your work as a data analyst won’t be as impactful if you don’t understand the data you are dealing with. In addition to technical and coding skills, data analysts should have a certain degree of business domain expertise to understand what they are doing.
Developing business acumen in the industry or sector you are working in, whether it’s finance, healthcare, marketing, or otherwise, will help you make sense of data and conduct better analysis. This is also one of the reasons why everyone, no matter their background, is welcome in data science.
Communication
We already mentioned that communicating and presenting insights is an important part of what a data analyst does.
To have a bigger impact, your insights have to be well understood by the different departments and stakeholders in your company. That’s why having strong writing and speaking skills is an important asset for data analysts. This includes learning innovative approaches and frameworks for communication, such as data storytelling.
Problem-solving
Every data analysis starts with a question. Data analysts should be curious and inquisitive about data. Once the business questions are framed, data analysts need to be ingenious to find the most suitable data techniques to answer the questions. This makes data analysis a challenging task but also full of fun and reward.
Read our guide on the essential data analyst skills to cover this in more detail.
What Tools do Data Analysts Use?
Data analysts rely on various tools that make their work more accurate and efficient. The Data & Machine Learning Tools Landscape is rapidly evolving, with new tools popping up every day to deal with particular tasks.
It’s impossible to know all of them, but you should be open to learning new tools if required in your data analyst position.
Notwithstanding this, there are some tools that almost all data analysts use. Learning them is a great starting point if you are considering starting a data analyst career.
- Python or R. The go-to programming languages in data science.
- Jupyter Notebook. A popular Integrated Development Environment for code notebooks written in many different programming language, including Python and R
- SQL. The standard language for communicating with relational databases.
- Microsoft Excel. It’s the most popular spreadsheet and is widely used across departments.
- Tableau and Power BI. The two leading Business Intelligence tools. They allow data analysts to create interactive, ready-to-use dashboards and reports.
Data Analyst Salary Expectations
Data analysts are highly sought professionals. Higher competition between companies to hire data analysts has resulted in higher pay rates to attract talent.
As we explore in our data science salaries article, the salary average in the US is $70K, ranging from $46K to $106K, depending on various factors, including seniority and location.
Data Analyst Online Courses
Now that you know what a data analyst does, there are several ways to start a career in the industry. There is not a single route that is best in absolute terms. Everything will depend on your personal circumstances. You should ask yourself how much money and time you want to invest, and what type of education fits better in your lifestyle.
Among the different routes available to become a data analyst, online courses are a great, flexible, and affordable option to get started. DataCamp has plenty of data analysis related courses, from beginner to expert level, that can help you learn the foundations of data analysis in an accessible way. Below we present three different learning tracks to becoming a data analyst:
Data Analyst with Python (Course content: 62 hours)
This track starts with the basics of the Python programming language for data analysis. After covering the basics, you’ll dive deeper into data wrangling and data visualization techniques.
You’ll also learn to source data from different sources such as the web, databases, and JSON files. Finally, this track provides an overview of exploratory data analysis techniques and upskills the learner on concepts of relational databases and SQL.
Data Analyst with R (Course content: 77 hours)
This track focuses on the primary skills required by data analysts working with the R programming language. It offers comprehensive content covering the most commonly used R packages like tidyverse, ggplot, and dplyr.
Similar to the Python track, the course helps build an intermediate understanding of data analyst skills such as data sourcing, manipulation, and visualization.
Data Analyst with SQL (Course content: 41 hours)
This career track helps the learner develop an in-depth understanding of SQL Server, the concepts of relational databases, their design, and performance optimization.
Conclusion
So, what does a data analyst do? As we’ve seen, they are responsible for extracting, preparing, exploring, and visualizing data. Within these tasks, numerous skills are required, and companies from nearly all industries are looking for these data professionals who can harness their data to make better decisions.
If you are considering breaking into data science, the data analyst role is probably the most accessible one, as it doesn’t require a solid background in math and advanced computing, as is the case for data scientists. Sounds promising, right?
Now it’s time for you to go ahead and start your learning journey. When you're ready, prove your expertise with our Data Analyst Certification to stand out from the crowd to recruiters.
Get Certified as a Data Analyst
Start Your Journey Towards Becoming a Data Analyst and Get Certified!

I am a freelance data analyst, collaborating with companies and organisations worldwide in data science projects. I am also a data science instructor with 2+ experience. I regularly write data-science-related articles in English and Spanish, some of which have been published on established websites such as DataCamp, Towards Data Science and Analytics Vidhya As a data scientist with a background in political science and law, my goal is to work at the interplay of public policy, law and technology, leveraging the power of ideas to advance innovative solutions and narratives that can help us address urgent challenges, namely the climate crisis. I consider myself a self-taught person, a constant learner, and a firm supporter of multidisciplinary. It is never too late to learn new things.


