Cursus
Modern workflows increasingly handle unstructured data such as websites, PDFs, emails, and free‑text inputs. These require reasoning, summarization, and decision‑making. This is where Gumloop can be used for AI-powered automation for a new “cognitive layer” on top of traditional logic.
In this article, we’ll explore Gumloop, a visual IDE that was designed specifically for building AI-powered workflows and agents, and compare it to traditional iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) automation platforms like n8n and Zapier. We’ll also walk you through a step-by-step guide on building a simple AI agent on Gumloop.
Before we begin, I recommend opening a new tab, signing up for Gumloop, and following along to build your first agent in 15 minutes.
In my opinion, our Introduction to AI Agents course offers a great introduction to the topic of autonomous AI tools. Make sure to check it out.
What Is Gumloop?
Gumloop is an AI-native, no-code automation platform designed to help businesses build complex workflows and LLM agents without technical knowledge. While it visually resembles other drag-and-drop tools, its underlying abstraction is closer to an execution engine for AI logic than a simple integration layer.
Its main goal is to go beyond traditional automation by providing interpretation and reasoning. The core problem Gumloop solves is the gap between:
- Rigid IPaaS tools like Zapier, which excel at simple integrations but struggle with complex logic and unstructured data.
- Fully custom Python scripts that interact with LLMs (large language models), which are powerful but require engineering effort, infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance.
Gumloop sits in between. It allows users to visually compose workflows that mix traditional control flow (conditions, loops, transformations) with AI reasoning steps.
Gumloop key features
Gumloop’s key capabilities lie in its canvas-based interface, where workflows are built by connecting nodes.
Each node represents a discrete unit of work, such as fetching data, invoking a model, applying logic, or writing outputs. The visual layout helps to visualize a live mental model of how data and decisions flow through the system.
Key capabilities of Gumloop include:
- Drag-and-drop logic: Combine triggers, conditions, loops, and outputs visually, without writing glue code.
- AI reasoning nodes: Prompt large language models directly within the workflow to classify, extract, summarize, or decide.
- Browser automation engine: Interact with live websites using agents. Agents can load pages, scroll, click, and extract content dynamically.
- Native Python execution: Advanced users can drop in Python code when visual nodes are not enough.
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) support: Connect structured tools and resources to models in a standardized way.
- Gummie: A built-in AI assistant that helps generate nodes, explain errors, and accelerate development.
These features make Gumloop a powerful tool that goes beyond a basic workflow connector tool.
Target audience and fit
Gumloop is designed for users who need to move fast without sacrificing capability. In many organizations, automation initiatives stall because the people who understand the business problem cannot easily translate it into code.
Gumloop lowers that barrier by allowing logic, AI prompts, and integrations to be composed visually while still remaining expressive enough for complex workflows.
Therefore, some of its ideal users include:
- Operations leaders automating research-heavy internal workflows.
- Growth engineers building enrichment and qualification pipelines.
- Technical founders who want production-grade agents without a full platform build.
What makes Gumloop stand out is its ability to combine both browser automation (interaction with the real web) and LLM reasoning (interpretation and synthesis) in a single canvas. Unlike Gumloop, most platforms specialize in one or the other.
Common use cases for Gumloop include:
- Automated web scraping and research
- Outbound sales enrichment and lead qualification
- Intelligent document processing (contracts, invoices, reports)
- Internal ops workflows that require judgment rather than rules alone
Setting Up Gumloop
Getting started with Gumloop is straightforward, and the free tier is enough to follow along with this tutorial.
The onboarding experience is intentionally lightweight, so you should be able to sign up for a functioning workflow without configuring infrastructure or environments.
Account creation and onboarding
To begin:
- Sign up for a free Gumloop account, or log in using your Google or Microsoft account.
- Once logged in, you will land on the main dashboard.
- Create a new workspace and open a blank canvas.
The workspace acts as a container for your flows, credentials, and run history. For this tutorial, the default setup is sufficient.
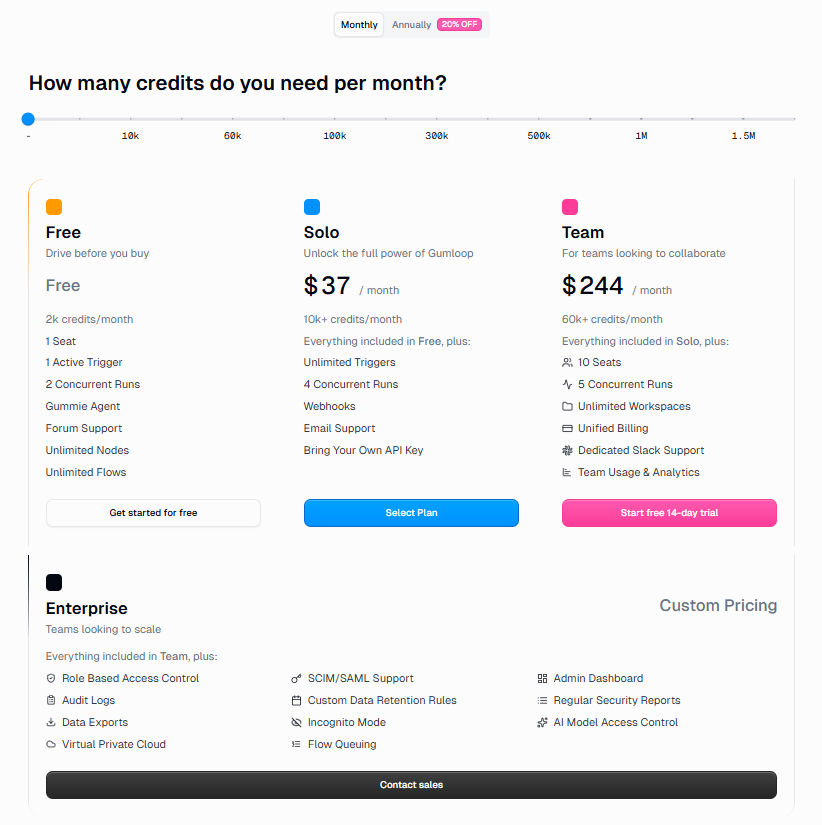
Credit-based pricing model
Gumloop uses a credit-based pricing system that maps closely to actual compute and execution costs. Rather than charging per integration or per task, the platform measures how much work your flow performs, especially when AI models or browser automation are involved. This makes it easier to reason about cost as workflows become more complex.
Key ideas to understand:
- Every action consumes credits, sometimes referred to as “fuel.”
- Simple operations like variable mapping or branching are cheap.
- Expensive operations involve compute-heavy tasks such as LLM calls or browser automation.
Gumloop classifies AI models into three distinct tiers based on capability and credit cost:
- Standard (2 credits/call, e.g., GPT-4.1 Mini, Claude 4.5 Haiku)
- Advanced (20 credits/call, e.g., GPT-4.1, Claude 3.7 Sonnet)
- Expert (30 credits/call, e.g., GPT-5, OpenAI o3)
While the newest models like OpenAI’s GPT-5.2, Google’s Gemini 3, or Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.6 are not yet available on the platform, the existing selection of Expert tier models provides sufficient reasoning power for virtually all complex automation use cases.
On the free tier:
- You receive a limited pool of 2000 credits per month.
- This is enough to build and test several small workflows, including the AI researcher in this article.
- AI calls use Gumloop’s shared API keys, and the credit cost includes both execution and model usage.
This model encourages experimentation while keeping costs predictable.
Bring your own key (BYOK)
For users who want more control, Gumloop supports a Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) pricing model. Gumloop allows you to input your personal credentials, such as API keys.
With BYOK:
- You connect your own OpenAI or Anthropic API key in the settings menu.
- Gumloop no longer applies AI markup to model calls.
- You only pay the base execution cost in Gumloop credits.
For this tutorial, BYOK is optional. However, if you already have model credits and plan to scale usage, it is worth enabling early.
Building an AI Research Agent Using Gumloop
Now we will build a simple end-to-end workflow that turns a company website into a structured research report. This example is intentionally practical.
Company research is a common task across sales, investing, partnerships, and hiring. In this example, we’ll showcase how Gumloop combines data collection, reasoning, and delivery in a single flow.
Step 1: Setting the trigger
Every Gumloop flow starts with a trigger. Triggers define how and when a workflow begins. In production systems, this could be a webhook, a scheduled job, or an external event. For learning purposes, a manual trigger keeps the flow simple and transparent.
Steps:
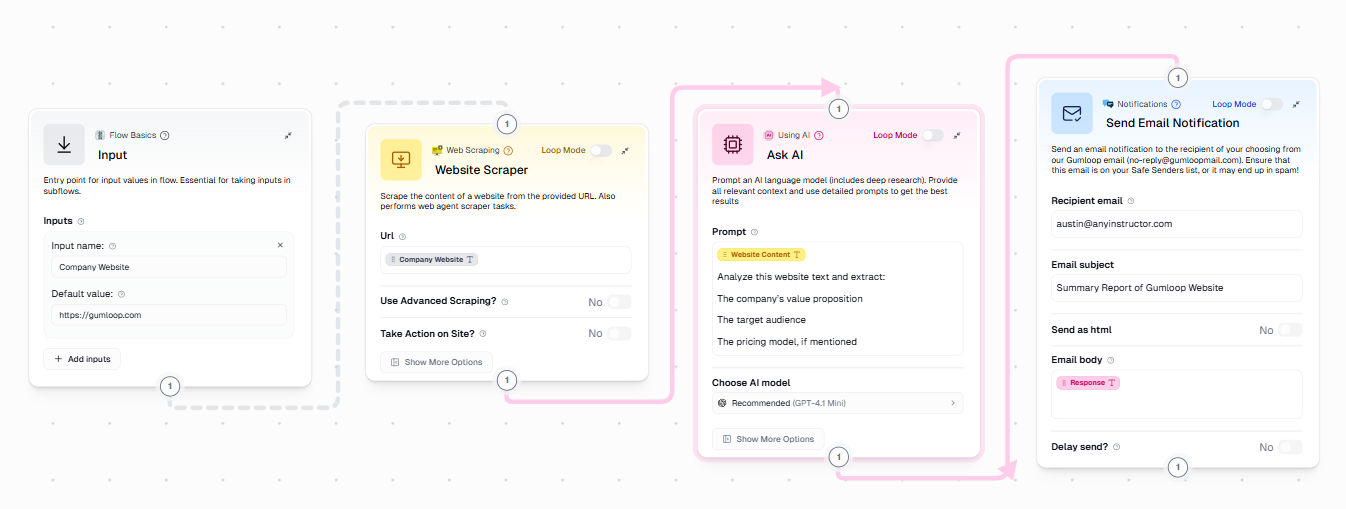
- Click on Build Your First Flow to open the main canvas.
- Click on the + sign on the left to add an Input node onto the canvas.
- Add a text input field named “Company Website”.
- Paste the URL “https://gumloop.com” into the Default value box.
- Save the node and click Run once to confirm the input field appears correctly.
Your input node should look like this:
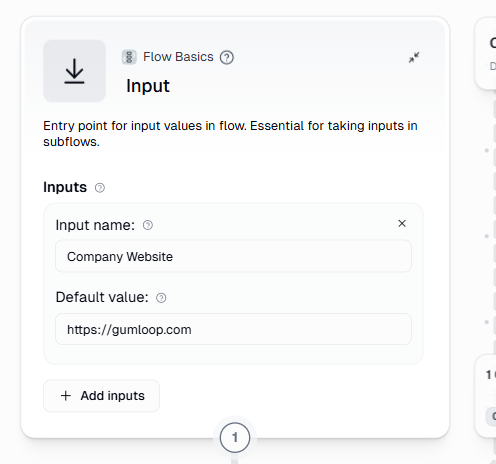
This trigger allows a user to manually supply the website URL each time the flow runs.
Step 2: Gathering intelligence
Next, we need to collect raw data for the AI to analyze. Unlike API-based integrations, website content is often messy, dynamic, and inconsistent. Gumloop’s browser automation abstracts away much of this complexity by handling page loading, rendering, and text extraction for you.
Steps:
- Click the + button on the left and then click on Core Nodes.
- Click on Web Scraping, and then Web Scraper.
- Connect it to the Input node.
- Drag the Company Website input into the scraper’s URL field.
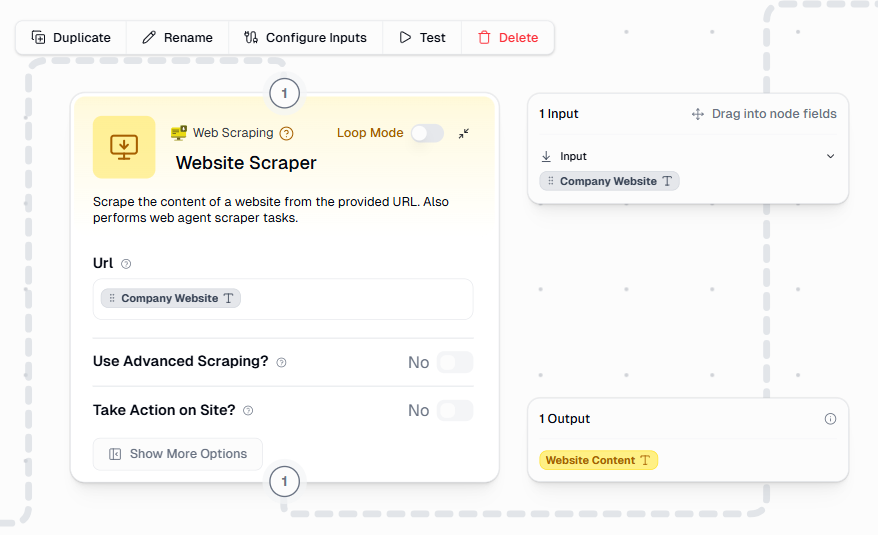
Step 3: Adding the brain for analysis
This is where the workflow becomes “intelligent.” Up to this point, the flow behaves like traditional automation. The AI node introduces interpretation and synthesis, allowing the workflow to answer questions that cannot be solved with rules alone.
Steps:
- Add an Ask AI node.
- Connect it to the output of the Website Scraper node.
- Drag and drop the website content field into the prompt box.
- Use a prompt such as:
“Analyze this website text and extract the company’s value proposition, their target audience, and their pricing model, if mentioned.”
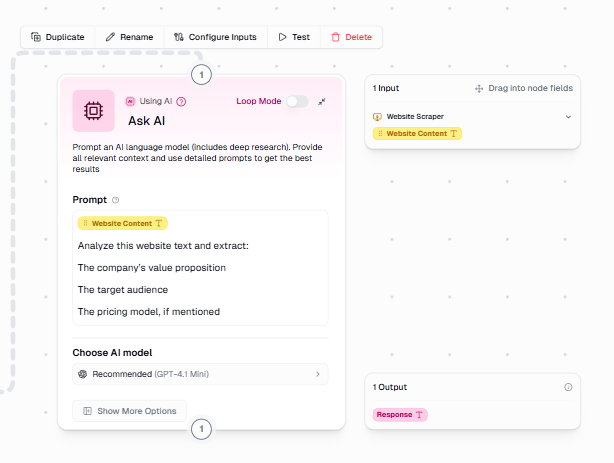
Within the node settings:
- Select a model appropriate for text analysis. I will go with OpenAI’s GPT-4.1 Mini.
- Different models can be chosen depending on cost, speed, or reasoning depth.
The key idea is that the AI node transforms unstructured text into structured insights.
Step 4: Delivering the report
Finally, we send the results to a useful destination. Outputs are where AI workflows bring in true operational value.
Options include:
- Send Email: Deliver the report directly to an inbox.
- Google Sheets: Append the results as a new row for tracking.
Steps:
- For this example, use the Send Email Notification node.
- Map the AI response into the email body by dragging and dropping the AI response into the email body field.
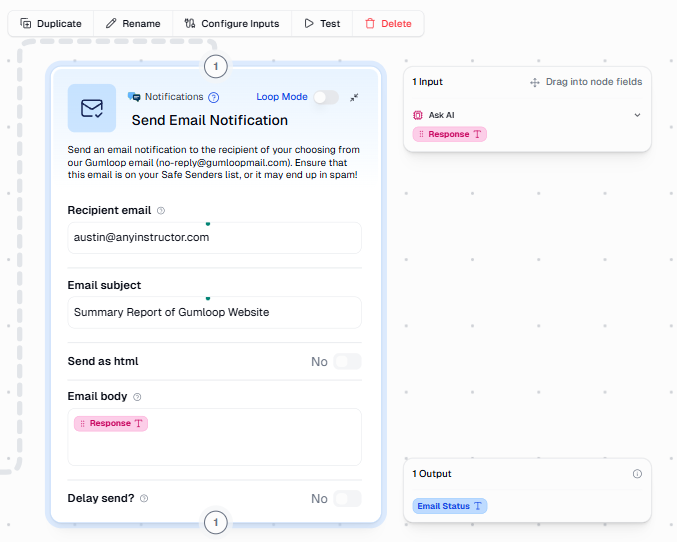
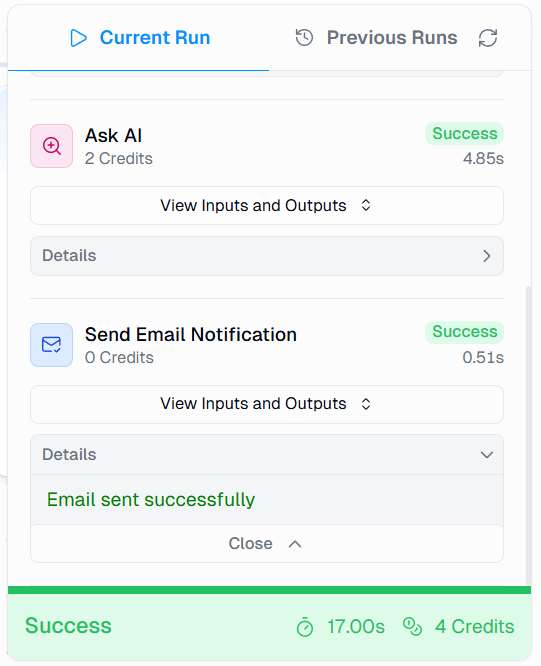
Once that is complete, click Run in the upper-right corner.
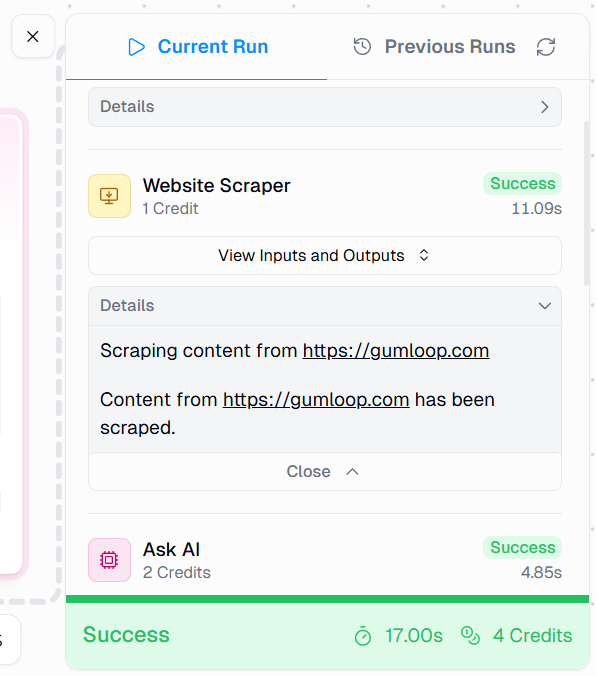
As the flow executes, you can watch live logs showing each step in action, from scraping to analysis to delivery. Once the run is complete, you’ll see the following screen:
Now go to your inbox to check if the flow has sent you an email with the relevant information. Here’s what my email notification looks like:
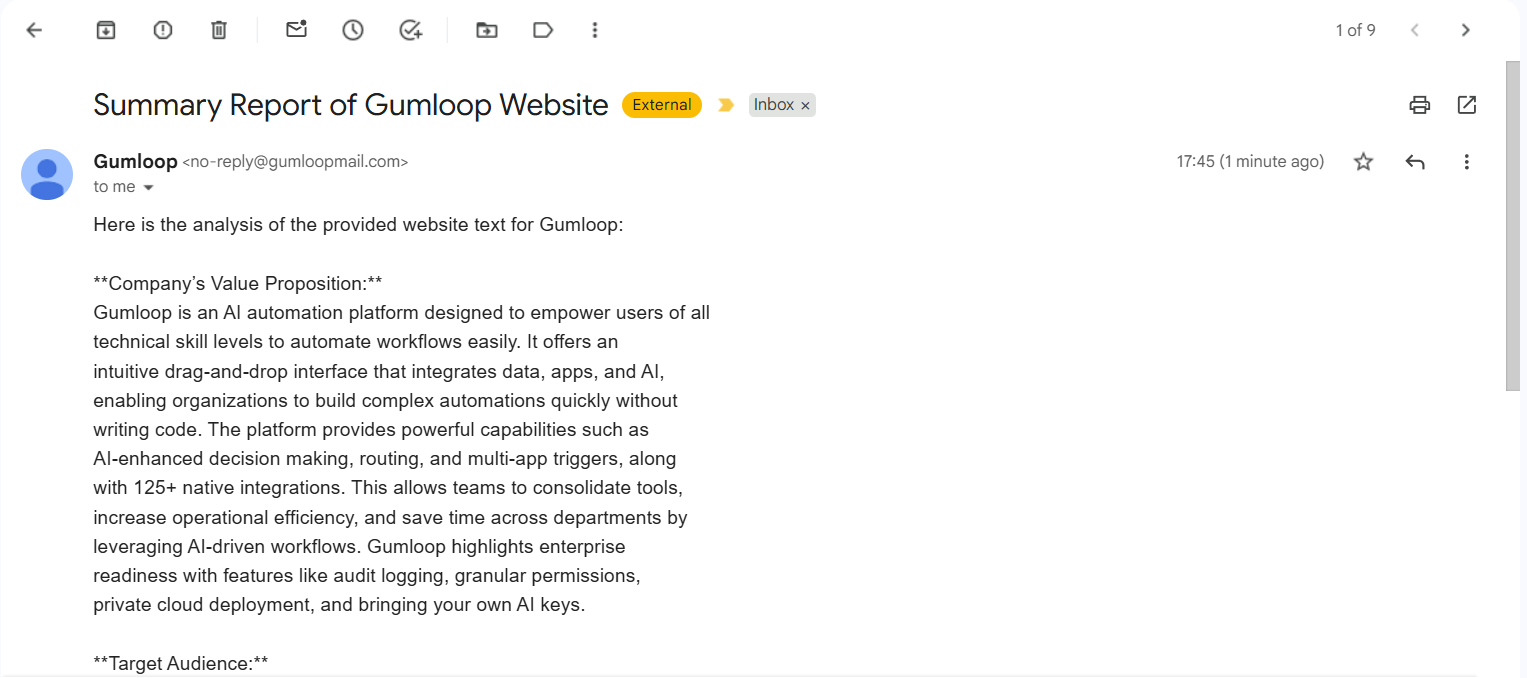
As you can see, the flow gave me the right output I wanted, right into my inbox.
Refining and Scaling Your Gumloop Flow
Once the basic workflow works, Gumloop provides tools to debug, extend, and scale it. This is where many no-code tools fall short, but Gumloop invests heavily in observability and iteration support.
Debugging with run history
The Previous Runs tab is essential for troubleshooting and refinement. Each execution is recorded with detailed intermediate outputs, making it possible to understand not just that something failed, but why it failed.
You can:
- Inspect the exact data passing through each wire.
- Verify whether the scraper was blocked or returned incomplete content.
- Replay a failed run without re-entering inputs.
This visibility is critical when dealing with external websites and AI outputs. This detailed run report is also available for viewing current runs.
Handling lists with loop mode
Real workflows rarely process a single input. As soon as a workflow proves useful, the next question is almost always how to scale it across many items without duplicating effort or logic.
Example scenario:
- Instead of one website, you want to analyze 50 company URLs.
Gumloop supports this with Loop Mode:
- Provide a list of websites as input.
- Enable Loop Mode (on the upper right corner) on relevant nodes.
- Each website in the list is processed automatically, often in parallel.
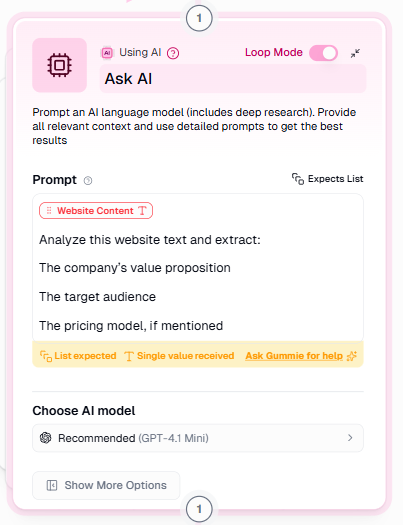
A visual indicator on the upper right side of the node shows when it is operating in batch mode, making the behavior easy to understand.
Optimizing with the AI assistant Gummie
Gummie is Gumloop’s built-in AI assistant, designed to reduce friction during both initial setup and later optimization. Rather than replacing the user, Gummie acts as a pair programmer who understands Gumloop’s primitives.
You can use Gummie to:
- Generate new steps by typing natural language instructions such as “Add a step that saves this to a CSV.”
- Explain cryptic error messages.
- Suggest optimizations or missing steps.
For non-engineers, Gummie significantly reduces friction when building more complex flows.
Gumloop vs Competitors
The AI automation tool ecosystem is expanding, and Gumloop isn’t the only tool in the market. Let’s look at some comparisons between tools.
Gumloop vs Zapier
Zapier is built around integrations and linear task execution.
Key differences:
- Zapier is integration-first, while Gumloop is AI-native.
- Zapier charges per task, which becomes expensive when looping over large datasets.
- Gumloop focuses on computing and reasoning, making it better suited to unstructured data such as text and PDFs.
Zapier remains excellent for simple, structured API-based automations. Gumloop excels when judgment and interpretation are required.
Gumloop vs n8n
n8n represents the opposite end of the spectrum.
Key contrasts:
- n8n is open-source and often self-hosted, appealing to engineers who want full control.
- Gumloop is fully hosted and managed, prioritizing speed and ease of use.
- Gumloop provides specialized AI nodes and MCP support, while n8n relies on more generic HTTP or framework-based integrations.
In practice, Gumloop offers a faster “time-to-agent” for operations teams, while n8n suits deeply technical, infrastructure-heavy setups.
|
Feature |
Gumloop |
Zapier |
n8n |
|
Core Philosophy |
AI-native; focuses on computing and reasoning. |
Integration-first; focuses on linear task execution. |
Open-source; focuses on full control and infrastructure. |
|
Ideal Use Case |
Operations requiring judgment, interpretation, and speed ("time-to-agent"). |
Simple, structured API-based automations. |
Deeply technical, infrastructure-heavy setups. |
|
Data Handling |
Excels with unstructured data (text, PDFs). |
Excellent for structured data. |
Handles complex technical flows (generic HTTP/frameworks). |
|
Hosting & Cost |
Fully hosted and managed. |
Charges per task (expensive for large datasets/looping). |
Often self-hosted; appeals to engineers wanting control. |
|
Key Differentiator |
Specialized AI nodes and MCP support. |
Massive ecosystem of pre-built integrations. |
Generic integrations allowing for custom engineering. |
For a comparison between the two Gumloop competitors, check out our comparison article of n8n versus Zapier.
Conclusion
Gumloop represents a shift in how automation is built. Instead of treating AI as an optional add-on, it embeds reasoning directly into the execution model, allowing workflows to adapt to messy, real-world data.
In this article, we’ve built a working AI company researcher from scratch using just Gumloop. This same pattern applies to further applications like hiring pipelines, sales research, compliance checks, and content creation.
To extend this workflow, I encourage you to experiment. You could, for instance, try:
- Adding a Google Search node before the scraper to discover companies automatically.
- Chaining multiple AI nodes for deeper analysis.
- Exploring the template library for advanced starting points.
If you want to see a different, more code-based approach in action, I highly recommend taking our Developing LLM Applications with LangChain course.
Gumloop FAQs
How does Gumloop compare to other AI automation tools like Zapier or n8n?
Gumloop is AI-native, meaning LLM reasoning and browser automation are core features rather than add-ons. Zapier excels at linear, integration-based workflows but struggles with unstructured data and loops, while n8n offers deep control for engineers through self-hosting but requires more setup.
What are some real-world examples of businesses using Gumloop successfully?
Teams use Gumloop for automated company research, sales lead enrichment, resume and candidate screening, document summarization, and internal ops reporting.
How does Gumloop handle data security and compliance?
Gumloop runs workflows in isolated environments and does not train models on customer data. Users can also enable Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) to keep AI requests within their own OpenAI or Anthropic accounts, reducing data exposure and improving compliance control.
Can Gumloop be integrated with any third-party apps or services?
Yes. Gumloop supports native integrations, browser automation for web apps without APIs, HTTP requests, Python execution, and Model Context Protocol (MCP), allowing it to connect to most third-party tools either directly or indirectly.
What are the main differences between Gumloop's free and paid plans?
The free plan includes limited execution credits and shared AI keys, which are sufficient for testing and small workflows. Paid plans (starting with Solo at $37/month) offer higher credit limits, better performance, advanced features, and support for BYOK, making them suitable for production and scaled use cases.

I'm Austin, a blogger and tech writer with years of experience both as a data scientist and a data analyst in healthcare. Starting my tech journey with a background in biology, I now help others make the same transition through my tech blog. My passion for technology has led me to my writing contributions to dozens of SaaS companies, inspiring others and sharing my experiences.
