Course
You probably don’t think about month-end dates much, at least until you need to calculate them for your financial reports.
In this article, we’ll look at how EOMONTH() works, and why it’s so handy for building financial models, setting up schedules, or planning some other kind of report that depends on the last day of the month.
Understanding the Excel EOMONTH() Function
The EOMONTH() function returns the serial number for the last day of the month that is the indicated number of months before or after a specified date. This makes it easy to automate calculations involving month-end dates.
Here is the syntax for the EOMONTH() function:
=EOMONTH(start_date, months)-
start_date: The initial date from which to calculate. -
months: The number of months before (negative) or after (positive) the start date.
Excel EOMONTH() in Practice
To use the EOMONTH() function, follow these steps:
-
Enter your starting date in a cell (for example, A1).
-
In another cell, enter the
EOMONTH()formula referencing your start date and the number of months.
For example, to find the last day of the month three months after January 15, 2024:
=EOMONTH("2024-01-15", 3)This formula returns April 30, 2024.
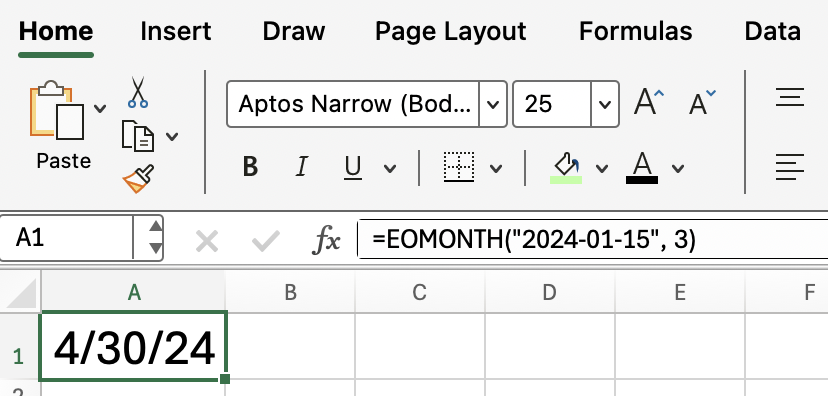
Remember that you have to format as a date, otherwise the output will look off.
Excel EOMONTH() Common Scenarios
The EOMONTH() function is commonly used in the following scenarios:
- Calculating due dates that fall on the last day of the month
- Determining reporting periods for financial statements
- Scheduling recurring monthly events
Excel EOMONTH() with Other Functions
You can (and in some cases you really should) combine EOMONTH() with other Excel functions to create more dynamic formulas. For example, to calculate the first day of the next month, add 1 to the result of EOMONTH():
=EOMONTH(A1, 0) + 1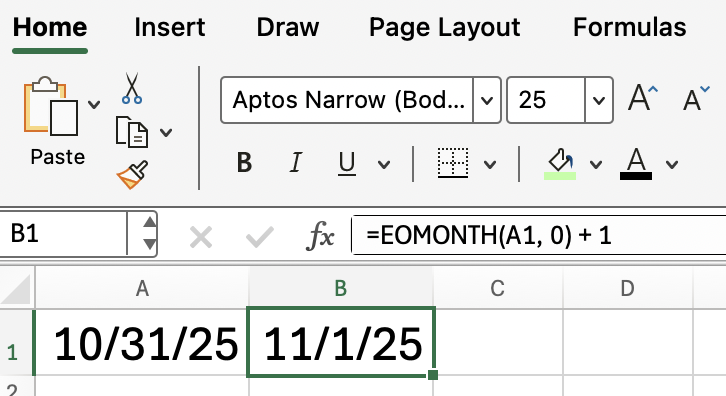
This formula returns the first day of the month following the date in cell A1.
Troubleshooting Excel EOMONTH() Errors
If you encounter errors with EOMONTH(), consider the following solutions:
- Ensure the start date is a valid Excel date.
- Check that the months argument is a whole number.
- Format the result cell as a date so that the output is something you, as a person, can easily read.
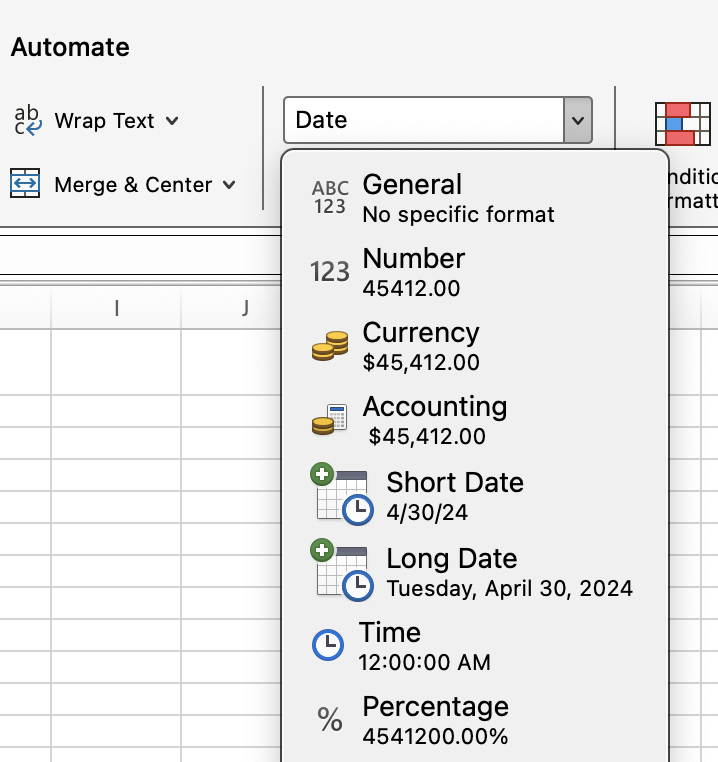
For this last point, which is a common issue, follow these steps:
- Select the cell with the formula.
- Go to the Home tab.
- Click on the Number Format dropdown and select Date.
Conclusion
If you find yourself working with dates in Excel, don't forget to study up on the EOMONTH() function, especially if you are someone working with dates in a financial and project management context.
Don't forget to take our Financial Modeling in Excel course to keep learning about things like cash flow, or else take our Advanced Excel Functions course to learn about new and interesting and helpful Excel functions.
Financial Modeling in Excel

I'm a data science writer and editor with contributions to research articles in scientific journals. I'm especially interested in linear algebra, statistics, R, and the like. I also play a fair amount of chess!
