Track
Amazon S3 is one of those tools that you’ll encounter again and again when working in the cloud. S3 is used in most AWS projects, whether it is for storing static files or building a scalable architecture, which explains why it is such a popular interview topic. What interviewers will assess is not just how many S3 facts you know, but if you can use this service effectively to solve real-world problems, optimize performance and ensure your systems remain secure and scalable.
In this article, I’ve put together a list of 25 AWS S3 interview questions that reflect real-world scenarios. I’ve grouped them into categories – Basic, Intermediate, Advanced, and a special section for Cloud/DevOps Engineers – so no matter where you are in your career, there’s something here for you!
And before you start: If you are completely new to cloud computing, I recommend taking our Introduction to Cloud Computing course first. This course breaks down cloud basics, explains key terms like scalability and latency, and covers the advantages of cloud tools from providers like AWS.
Basic AWS S3 Interview Questions
These questions focus on what S3 is and how it works. You will most likely encounter these questions if you have never worked with S3 before, or if the interviewer isn’t certain of your skill level and wants to start with the basics.
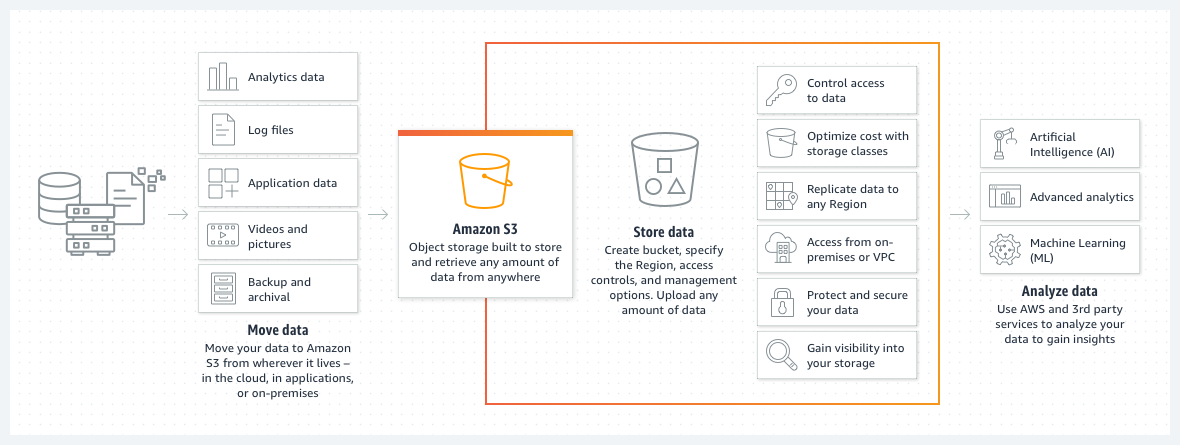
What is Amazon S3, and what are its main features?
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is an object storage service that allows you to store, retrieve, and manage data at any scale.
Source: AWS
Main Features:
- Unlimited storage: Store any amount of data without capacity planning.
- Scalability: Automatically scales to meet data access and storage needs.
- High durability: 99.999999999% durability ensures data reliability.
- Flexibility: Supports a wide range of data formats and integrates with other AWS services.
- Security: Offers encryption, IAM policies, and bucket policies for access control.
- Lifecycle management: Automates transitioning or deleting objects based on rules you set.
What is an S3 bucket?
An S3 bucket is a container for storing objects in Amazon S3. Each bucket has a globally unique name and serves as the root directory where you can upload files (objects). Buckets are used to organize data and manage access permissions.
What are the different types of storage classes in S3?
Amazon S3 offers multiple storage classes tailored to different use cases:
- S3 Standard: For frequently accessed data with low latency.
- S3 Intelligent-Tiering: Automatically moves data between tiers based on access patterns.
- S3 Standard-IA (Infrequent Access): For infrequently accessed data requiring quick access.
- S3 One Zone-IA: Similar to Standard-IA but stores data in a single availability zone, offering lower cost.
- S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval: For archived data needing quick access.
- S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval: For archival storage with options for expedited or bulk retrieval.
- S3 Glacier Deep Archive: The lowest-cost option for long-term storage with retrieval times of hours.

S3 Storage Class Types. Image by Author
How does S3 ensure data durability and availability?
Durability measures the likelihood that your data will remain intact and not be lost due to hardware failures, corruption, or other unexpected events. S3 ensures 99.999999999% durability by automatically replicating data across multiple devices in multiple Availability Zones (AZs). In practical terms, this means that if you store 10 million objects in S3, on average, you could expect to lose one object every 10,000 years due to a storage failure.
Availability refers to how often you can access your data when you need it. For example, S3 Standard has 99.99% availability, meaning that in a given year, there might be up to 53 minutes of downtime where S3 is temporarily inaccessible. The service is designed to handle disruptions without impacting users.
How is data secured in S3?
There are multiple mechanisms that can help keep data secure in S3:
- Encryption: S3 supports server-side encryption (SSE) with S3-managed keys, AWS Key Management Service (KMS), or customer-provided keys, as well as client-side encryption.
- Access control: Permissions are managed using IAM policies, bucket policies, and Access Control Lists (ACLs).
- Block public access: A global setting to prevent accidental public exposure of bucket contents.
- Logging and monitoring: Use AWS CloudTrail and S3 access logs to monitor access patterns and detect unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA delete adds an extra layer of security for delete operations.
What are the key differences between S3 and other AWS storage services like EBS or EFS?
S3 (Simple Storage Service): Object storage for unstructured data. Ideal for storing files, backups, and static assets. Accessed via HTTP/HTTPS.
- EBS (Elastic Block Store): Block storage for use with EC2 instances. Best for running databases or applications requiring low-latency, high-performance storage. Data is tied to a specific instance or AZ.
- EFS (Elastic File System): File storage that can be accessed simultaneously by multiple EC2 instances. Best for shared file systems or content management systems.
If you’re interested in reading more on this topic, have a look at this hands-on tutorial on S3 and EFS.
Intermediate AWS S3 Interview Questions
The intermediate-level questions focus on practical features and strategies, like managing costs, setting up replication, and integrating S3 with other AWS services. These are the kinds of concepts you’ll encounter when optimizing or scaling an application using S3.
What is a lifecycle policy in S3, and how can it be used?
A lifecycle policy in S3 is a set of rules that automatically manage the lifecycle of objects stored in a bucket. You can use it to transition objects between storage classes or delete them after a specified period. This can simplify data management and drastically reduce costs.
What strategies can you use to reduce S3 costs in a project?
- Use the right storage class: Store frequently accessed data in S3 Standard and archive data in Glacier or Deep Archive.
- Set up lifecycle policies: Automate transitions and deletions to avoid storing unnecessary data.
- Delete unused objects: Regularly audit and clean up unused or outdated files.
- Optimize file size: Compress files and bundle smaller objects to reduce request costs.
- Monitor usage: Use AWS Cost Explorer and S3 Storage Lens to analyze and optimize usage patterns.
- Leverage intelligent-tiering: Automatically optimize costs for unpredictable access patterns.
Can you explain S3 replication (cross-region and same-region)?
S3 replication is used to copy objects from one bucket to another automatically.
- Cross-Region Replication (CRR): Replicates data to a bucket in a different AWS region for compliance, disaster recovery, or low-latency access.
- Same-Region Replication (SRR): Replicates data within the same region for additional redundancy or to separate workloads.
Replication requires enabling versioning on both the source and destination buckets and is commonly used for backup and compliance needs.
How does AWS S3 integrate with other AWS services like Lambda and CloudFront?
S3 + Lambda: Trigger Lambda functions using S3 Event Notifications for serverless workflows like image processing, data transformation, or log analysis.
S3 + CloudFront: Use CloudFront as a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to distribute content stored in S3 with low latency and high performance. CloudFront can cache S3 objects at edge locations for faster delivery to users worldwide.
What is versioning in S3, and why is it useful?
Versioning is a feature in S3 that allows you to maintain multiple versions of an object within a bucket and is useful for:
- Data recovery: Retrieve previous versions of objects in case of accidental deletions or overwrites.
- Conflict resolution: Avoid overwriting changes in collaborative environments.
- Compliance: Retain historical versions of data for audit purposes.
Can you describe S3 Event Notifications and their use cases?
S3 Event Notifications let you configure S3 to send notifications when specific events occur, such as object creation, deletion, or updates. Notifications can be sent to services like Amazon SQS to queue of events, AWS Lambda to process events in real time or Amazon SNS to broadcast events to multiple subscribers.
What are pre-signed URLs in S3, and how are they used?
A pre-signed URL provides temporary, time-limited access to a specific object in S3.They allow users to download private files without changing bucket permissions and enable uploads to a specific bucket without granting full access, so they’re great for file sharing.
Advanced AWS S3 Interview Questions
The advanced section dives into more complex scenarios, where you’ll need to demonstrate your understanding of S3 at scale, how to troubleshoot issues, and how to secure and optimize your storage solutions. These questions are designed to evaluate how well you can apply S3 in a production environment with security, performance, and cost considerations in mind.
How do you implement security policies for S3 buckets?
Security policies for S3 buckets can be implemented using IAM (Identity and Access Management) policies and bucket policies.
IAM policies: Define permissions for AWS users or groups, specifying which actions can be performed on which S3 resources. For example, an IAM policy might allow an application to read objects from an S3 bucket but not delete them.
Bucket policies: Define permissions directly on S3 buckets. They can allow or deny access based on conditions like IP address, user agent, or the presence of multi-factor authentication (MFA). Bucket policies are more granular than IAM policies and can be used to control access at the bucket level.
There are some best practices to follow, like using least privilege principles, enabling bucket encryption and logging to monitor access and using MFA delete for added protection on delete operations.
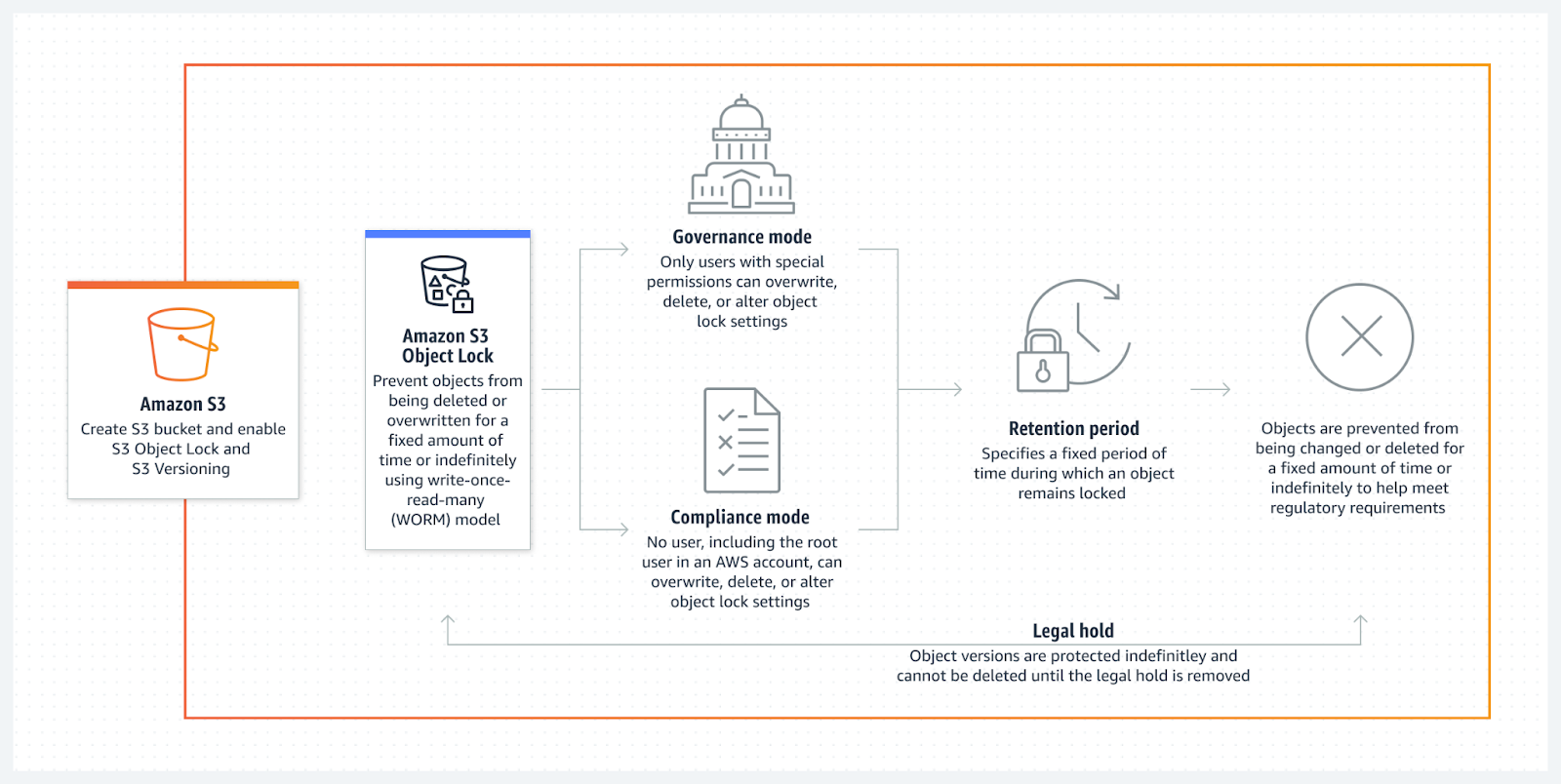
Can you explain the concept of S3 Object Lock and its use cases?
S3 Object Lock enables you to prevent objects from being deleted or overwritten for a specified retention period.
Source: AWS
This is really helpful in the following scenarios:
- Compliance: For organizations that need to comply with regulations like SEC Rule 17a-4(f), which requires data to be immutable for a certain period.
- Data protection: To protect critical data from accidental or malicious deletion during the retention period.
Depending on your needs, Object Lock works in two modes:
- Governance mode: Users with the right permissions can overwrite or delete locked objects.
- Compliance mode: Prevents anyone from overwriting or deleting locked objects, ensuring compliance with retention policies.
How would you troubleshoot S3 performance issues?
- Check network latency: Latency can be affected by the distance between users and S3 buckets. If there is a high latency, you could use Amazon CloudFront as a CDN to improve access times.
- Optimize object sizes: Large objects can result in higher latency. Consider splitting large files into smaller ones for better upload/download performance.
- Request distribution: If a high number of requests is concentrated in a single S3 prefix (e.g., s3://mybucket/data/), performance may degrade. You could use randomized object keys to distribute requests evenly across partitions.
- Monitor with CloudWatch: Use Amazon CloudWatch metrics to track request latencies, throughput, and error rates.
- Check for throttling: Ensure you are not exceeding the request rate limits, especially for highly concurrent operations.
- Investigate data transfer costs: If you're transferring large amounts of data, check if you could be using S3 Transfer Acceleration or AWS Direct Connect to improve speed.
How would you handle and optimize large file uploads to S3?
To optimize large file uploads to S3, you can use:
- Multipart upload: Break large files into smaller parts (up to 5GB per part) and upload them in parallel. This improves upload efficiency and allows for easy retries if an upload fails.
- S3 Transfer Acceleration: For geographically distributed users, this speeds up uploads by routing them to the nearest AWS edge location.
- Optimize the network: Ensure you’re using high-speed internet connections and that there are no bandwidth bottlenecks.
- Use AWS SDKs: AWS SDKs (e.g., for Python, JavaScript) provide built-in functionality for handling multipart uploads and managing retries automatically.
- Use AWS Snowball: If you need to transfer massive amounts of data (terabytes or petabytes), AWS Snowball provides physical devices that help with bulk data transfers.
How does S3 Select optimize data querying and reduce costs?
S3 Select allows you to retrieve a subset of data from an object (like a CSV or JSON file) without needing to download the entire object. This can significantly reduce both data transfer costs and the time it takes to process large datasets like large log files or analytics datasets.You define a SQL query to filter or retrieve specific columns or rows from an object. Only the data returned by the query is transmitted, so you avoid transferring large objects in their entirety.
AWS S3 Interview Questions for Cloud Engineers/DevOps Engineers
These are the questions that evaluate not just technical knowledge but also how you apply S3 in solving business problems, maintaining system reliability, and integrating with broader workflows like CI/CD pipelines.
There is no “right” answer here, as you’ll be asked to talk about your experience and what you might do in specific scenarios, but I’ve compiled a list of the type of questions you might get, what the interviewer is looking to assess and what elements a good answer would include.
Describe a scenario where you used S3 to solve a business problem.
What interviewers are looking for:
This question is about understanding your ability to identify business challenges and how you leveraged S3 to address those challenges effectively. The interviewer is looking for your problem-solving skills, how you applied S3 features, and how the solution you implemented benefited the business.
What to include in your answer:
- The business problem you were trying to solve (e.g., high data storage costs, slow file access times).
- The solution you implemented using S3 (e.g., specific features like lifecycle policies, Cross-Region Replication).
- The results or impact on the business (e.g., cost savings, improved user experience, or performance).
Example answer:
"In a previous project, we were working with a media company that needed to store and deliver large video files to users worldwide. The challenge was high latency and storage costs. We used S3 to store the videos and integrated CloudFront for fast global delivery. Additionally, we implemented S3 Intelligent-Tiering to automatically move infrequently accessed videos to cheaper storage classes. This reduced our storage costs by 30% and improved the delivery speed by 50%, resulting in higher customer satisfaction."
How have you optimized S3 costs for a project?
What interviewers are looking for:
Interviewers are testing your understanding of AWS pricing and how you can make informed decisions about storage strategies. They want to know if you can balance cost-efficiency with performance.
What to include in your answer:
- Specific strategies you used to optimize costs (e.g., storage classes, lifecycle policies, data deletion).
- The rationale behind those choices (e.g., balancing cost with access frequency).
- The results you achieved in terms of cost reduction.
Example answer:
"In a project, we had a large dataset that was frequently accessed in the early stages and rarely accessed after a month. To optimize costs, I set up S3 Lifecycle policies to transition older data to S3 Glacier after 30 days. Additionally, I used S3 Intelligent-Tiering for data that had unpredictable access patterns. As a result, our storage costs decreased by 40%, and we were able to allocate more budget to other parts of the infrastructure."
What are some considerations when designing a multi-region S3 architecture?
What interviewers are looking for:
For this question, interviewers want to assess your knowledge of designing for availability, resilience, and cost efficiency in a global architecture. They want to see if you understand the trade-offs of a multi-region setup, such as latency, replication, and costs.
What to include in your answer:
- The importance of cross-region replication and how it impacts data availability and fault tolerance.
- The trade-offs between latency and cost when designing for multi-region use.
- Specific tools or configurations, such as CloudFront or IAM, to handle data in a multi-region setup.
Example answer:
"In a previous project, I was tasked with designing an S3 architecture to serve customers across multiple continents. To achieve high availability and fault tolerance, I set up Cross-Region Replication (CRR) between S3 buckets in two regions: one in the US and another in Europe. This ensured that data was available even if one region failed. To minimize latency, I also integrated CloudFront as a CDN to cache data closer to users, reducing access times. While CRR added some additional cost, it was justified by the need for resilience in our global user base."
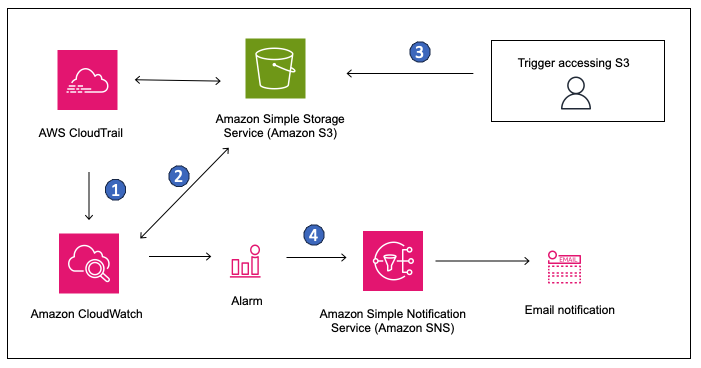
How do you approach monitoring and alerting for S3 buckets?
What interviewers are looking for:
Interviewers want to see that you understand how to proactively monitor and detect potential issues in your S3 infrastructure. They want to see your ability to use AWS tools for monitoring and how you can set up alerts for effective incident management.
What to include in your answer:
- The tools you use for monitoring (e.g., CloudWatch, CloudTrail, a third party observability solution).
- How you configure tools like CloudWatch metrics for monitoring and CloudWatch alarms for notifications (or whatever tool you used).
- The importance of tracking activities and setting up logs for auditing purposes.
Example answer:
"For monitoring S3 buckets, I primarily use CloudWatch to track metrics such as request count, storage usage, and error rates. I set up alarms for unusual spikes in request rates or storage usage, which can indicate potential issues. Additionally, I enable CloudTrail to log S3 API calls, ensuring I can trace and audit all interactions with the buckets. This helped me quickly identify issues with unexpected changes to bucket policies and prevent unauthorized access."
Source: AWS
Can you discuss your experience with S3 and its integration into CI/CD pipelines?
What interviewers are looking for:
Interviewers want to understand how well you can integrate S3 into modern development workflows like CI/CD. They’re assessing your experience with automating storage operations as part of a broader DevOps pipeline.
What to include in your answer:
- How you’ve used S3 to store build artifacts, logs, or static assets.
- How you’ve automated the process of pushing artifacts to S3 as part of CI/CD.
- How S3 integration improved the speed or reliability of the CI/CD pipeline.
Example answer:
"In one of my recent projects, we integrated S3 into our CI/CD pipeline to manage build artifacts. After a successful build, the pipeline automatically uploaded the artifacts to a dedicated S3 bucket. We then used S3 Event Notifications to trigger AWS Lambda, which initiated the deployment process. This streamlined the deployment pipeline and allowed us to manage artifacts centrally. It significantly reduced deployment times and allowed for better versioning of build artifacts."
How can you implement high availability and fault tolerance for an application using S3?
What interviewers are looking for:
The interviewer wants to know if you can design for redundancy and resilience, and make sure your application remains operational even in the face of failures. They are looking for specific strategies and tools you have used to build fault tolerance into S3-based applications.
What to include in your answer:
- How you use Cross-Region Replication and versioning for data redundancy.
- Your approach to failover strategies and how to handle disaster recovery.
- Any tools you use to monitor and respond to failures.
Example answer:
"To ensure high availability and fault tolerance for an application that relied heavily on S3, I used Cross-Region Replication (CRR) to replicate data between regions. This setup guaranteed that even if one region went down, the application could still access data from another region. I also enabled versioning on S3 to avoid data loss from accidental deletions or overwrites. Additionally, I set up CloudWatch alarms to monitor the health of replication processes and notify us in case of failure, allowing us to take corrective action quickly."
How do you enforce compliance with S3 bucket configurations across your organization?
What interviewers are looking for:
This question tests your understanding of compliance and governance in AWS environments. The interviewer is looking for your experience in maintaining security standards, auditing, and ensuring that all configurations comply with organizational policies.
What to include in your answer:
- Tools you use for compliance checks (e.g., AWS Config, IAM policies).
- How you enforce bucket policies and manage public access.
- How you handle auditing and logging for compliance.
Example answer:
"To enforce compliance with S3 bucket configurations, I used AWS Config to track whether buckets met our internal policies, such as ensuring that public access was blocked and encryption was enabled. I also implemented IAM policies to restrict who could access or modify S3 buckets, ensuring only authorized users could make changes. We used CloudTrail to log all S3 activity for auditing purposes, making it easier to track access patterns and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements."
Conclusion
If you have made it this far, you’re all set for your AWS S3 interview!
That said, S3 is only a small part of AWS, and you will probably be asked questions about other services. If you want to be prepared, or just reduce the gaps in your knowledge, I’d recommend taking our Introduction to AWS course, or, if you prefer hands-on learning, our AWS Cloud Technologies and Services course.
You can also take your studies further and add an official AWS certification to your CV or LinkedIn profile to showcase your skills to prospective employers. AWS offers a few different certifications depending on your level and role, so there is something for everyone!
I wish you the best of luck with your interview!
AWS Cloud Practitioner

I am a product-minded tech lead who specialises in growing early-stage startups from first prototype to product-market fit and beyond. I am endlessly curious about how people use technology, and I love working closely with founders and cross-functional teams to bring bold ideas to life. When I’m not building products, I’m chasing inspiration in new corners of the world or blowing off steam at the yoga studio.
FAQs
How deep should my knowledge of AWS S3 be for a cloud engineering interview?
It depends on the role. For junior positions, understanding basic features and storage classes may be enough. For senior roles, expect questions on cost optimization, security, performance tuning, and integrating S3 with other AWS services.
How can I prepare for hands-on AWS S3 interview tasks?
Practice setting up and securing an S3 bucket, configuring lifecycle policies, using pre-signed URLs, and testing cross-region replication. Hands-on experience with the AWS CLI and SDKs can be a huge advantage.
How does S3 compare to other cloud storage solutions like Google Cloud Storage or Azure Blob Storage?
S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Azure Blob Storage offer similar features but differ in pricing, performance, and integrations. While AWS S3 is often the default choice for companies already using AWS, Google Cloud and Azure offer competitive pricing, unique features, and sometimes better regional performance depending on the workload. The best choice depends on factors like existing cloud infrastructure, data access patterns, compliance needs, and cost.
What’s the best way to answer scenario-based S3 interview questions?
Use the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result). Describe the problem, your role in solving it, the specific steps you took, and the outcome. Interviewers want to see both technical knowledge and problem-solving ability.
